Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FCE Exercises
Uploaded by
Berter Muñoz BarríaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FCE Exercises
Uploaded by
Berter Muñoz BarríaCopyright:
Available Formats
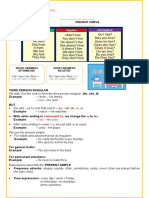
FCE (First Certificate) Phrasal Verbs with 'Up'
It's hard to predict what phrasal verbs you might see in the FCE exam, but here are some you should try to learn. Look at the phrasal verbs and their definitions for 1 minute and try to remember as many as possible. Then click to hide the information and try to answer the questions.
Note: sb means somebody and sth means something.
PhrasalVerb Don't worry, I'll back you up The bully beat up the other children. Terrorists tried blow up the station. Why did he break up with me? You mustn't bring up his divorce. His divorce might come up. We always end up eating fast food. I usually get up early. I tried to give up eating chocolate. Children grow up quickly nowadays. I can't keep up. If you don't understand, look it up. You should take up a new sport. Don't turn up late on a first date. Please don't throw up on the sofa.
Meaning help/support sb hit/kick sb repeatedly Explode end a relationship mentionsth a topic is mentioned finally do this thing Leave my bed stop a habit Become older/an adult do sth fast enough look for a piece of info Start doing a hobby Arrive be sick
Click here to show/hide this information
FCE Part 1: Multiple Choice Cloze
Choose the best word to complete the following sentences.
1. I _______ up football when I was 12 years old, and I loved it.
came
took
brought
turned
2. I _______ up football after I broke my leg, because I didn't enjoy it. gave took kept turned
3. I couldn't ______ up with the work my teacher gave me - it was too difficult. back end bring keep
4. "Tell your boss you want more money. I'll _____ you up. bring back look put
5. She's sensitive about her weight, so only talk about it if she _____ it up. makes gets brings comes
FCE part 2: Open Cloze
The missing word could be the verb (e.g. bring/brought/bringing), the pronoun (e.g. it) or the particle (e.g. up). 1. I woke up at 6 am, but I didn't up until I heard the phone ring. it up on the Internet. up. up. three times this morning. up when you like.
2. If you don't know the answer, you could 3. I love films with explosions and things being
4. Did Tom tell you about his new job? No, it never 5. I'm not coming to work today. I've thrown 6. You don't need an appointment - just 7. He's depressed because he's 8. I promise I'll back
up with his girlfriend.
up if you need my help. up
9. Simon was attacked on the way home last night. The robbers beat badly. 10. It's bad manners to up the topic of religion at the dinner table. up fighting with my best friend. up but it was impossible.
11. The party started well, but I 12. He ran so fast. I tried to
13. I
up in a small town in Scotland. up.
14. Biting your fingernails is disgusting. You should really give 15. I'd never up skiing. It looks really dangerous to me.
Adjective + preposition (easy)
Many common adjectives are always used with a preposition. For example: I'm frightened of spiders.
It's a good idea to learn these if you can. There are some common examples in the tables below. Note: sb = somebody, and sth = something.
frightened of sth scared of sth OF afraid of sth tired of sth good at sth bad at sth FOR IN TO Famous for sth interested in sth kind to sb rude to sb worried about sth/sb excited about sth
AT
ABOUT
Many adjectives can use two prepositions. For example:
angry annoyed furious
I'm
With him
About the washing up.
The teacher is very bad at dancing.
Prepositions of Time
For and since are both used to say how long something was. However, we use them with different time words.
FOR
We use for when we say the number of hours, days, months, etc. We also use it in expressions like "for ages" and "for a long time". I'm going to live in France for 2 years. I sat down for 5 minutes. I've worked here for 3 months.
SINCE
We use since when we say when something started (e.g. Tuesday, 2008, midnight). We only use since with perfect tenses - you can read more about them in my grammar pages. I've lived here since October. I'd known Sam since 1999.
DURING
We use during with nouns (e.g. the holiday, my party, the night). Sometimes it means for all the time, and sometimes it means for just a part of the time. My grandmother worked in the USA during the war. I heard a strange noise during the night.
The teacher has been making this website since 2010.
Verb + preposition (easy)
Many common verbs are always used with a preposition. For example: I waited for 10 minutes, then I went home. It's a good idea to learn these if you can. Note: sb = somebody, and sth = something.
Thank sb for sth wait for sth prepare for sth For ask for sth apply for sth pay for sth apologise for sth Of In About To From At take care of sb/sth believe in sth Think about sth Belong to sb Prevent sb from doing sth laugh at sb/sth
Many verbs can use two prepositions. Forexample:
wrote I talked spoke I talked spoke
to him about the washing up.
with him about the washing up.
argued fought agreed
Most people agree that talk/speak to and talk/speak with can be used in the same way.
The teacher is thinking about her next holiday.
Prepositions of Time (in, on, at)
IN
We use in with years, seasons and months. I got married in 2007. I got married in December. I got married in the winter.
On
We use on with days and dates. I got married on 31st December. I got married on New Year's Eve
AT
We use at with times and well-known holiday periods. I got married at 3.30. I got married at New Year.
Here are some other examples you should learn:
In + the morning, the afternoon, the evening, but at night. At + mealtimes (at breakfast, at dinner ...). At + the weekend. At the moment, at present, at that moment. In the past, in the future.
Remember: we don't use in/on/at when we say "this / last / next". I'll see you next week. The teacher doesn't like working in the afternoon. Sheprefers sleeping.
wake up get up Put something on Takes omething off Go out set off get in wash up tidy up drop off Turn something on Turn something off
to stop sleeping To leave your bed To get dressed To remove clothes to leave the house (not for work) to leave (possibly for work) To return home to wash the plates and cups to put things into the right places to fall asleep (usually for a short time) e.g. a light, a shower (to start) e.g. a light, a shower (to stop
Phrasal Verbs - Relationships
Look at these phrasal verbs and definitions. When you think you can remember them, click 'hide words and test me' to practise using them.
Ask someone out
to say "would you like to go to the cinema/a restaurant...?"
Go out (with someone) to go on a date (to the cinema/a restaurant...) with someone 1 Go out (with someone) - 2 to be someone's boyfriend/girlfriend Get on (with someone) Fall out (with someone) to like someone and talk easily to argue and stop being friends
break up (withsomeone) to stop being boyfriend/girlfriend make up (withsomeone) chat someone up to be friends again after falling out to flirt with someone (talk to someone like you are attracted to them)
Phrasal Verbs for Sleep
Look at these examples for 1-2 minutes and try to remember as many as possible. Then click to hide the information and try to answer the questions.
PhrasalVerb My alarm clock goes off at 7am. I usually wake up at 7am. I get up at 7.30. Sometimes I drop off at work. Exercise can wear you out. You should lie down and rest. You'll sleep in if you forget to set your alarm. I like to lie in at the weekend. Can I sleep over at your house? Ring
Meaning
stop sleeping leavemybed gotosleep makeyoutired restonyour back sleeplongerthanwanted stay in bed after waking up sleep at a friend's house
Some phrasal verbs can also be adjectives: I feel really worn out. = tired Other phrasal verbs can become nouns. For example, lie in means to stay in bed in the morning. The noun is a lie-in. And sleep over means to sleep at a friend's house - the noun (usually a kind of party) is a sleepover. Note: to oversleep means to sleep for longer than you planned. I have a lie-in every Saturday. I had a sleepover for my 12th birthday party. I overslept this morning.
Phrasal Verbs for Speaking
Look at these examples for 1-2 minutes and try to remember as many as possible. Then click to hide the information and try to answer the questions.
PhrasalVerb He pointed out that she was late. He talked her into getting a job. He talked her out of buying that coat. He brought up my divorce. He owned up to the crime. He chatted me up in the bar. He went on about it for ages. He told her off for fighting. He went into all the details. He needs to speak up.
Meaning tell/inform sb about sth persuade sb to do sth persuade sb not to do sth mentionsth Admit flirt withsb talk for a long time speak angrily, because sb did sth wrong talk in detail about sth talk more loudly
Note: sb = somebody and sth = something
You might also like
- Learning English Grammar OnlineDocument6 pagesLearning English Grammar OnlineNoranita ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Word Formation Ful LessDocument5 pagesWord Formation Ful LessElfo SindarNo ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument16 pagesEnglish GrammarLyssia dfghjklNo ratings yet
- Simple English: Phrasal Verbs: 100s of examples + MP3sFrom EverandSimple English: Phrasal Verbs: 100s of examples + MP3sRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- NP C8 CD8.1 ScriptDocument5 pagesNP C8 CD8.1 ScriptGinko KuinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5a Tenses LessonDocument86 pagesLesson 5a Tenses LessonWane DavisNo ratings yet
- Grammar - Beginner To Pre-IntermediateDocument13 pagesGrammar - Beginner To Pre-IntermediateReza VahdatparastNo ratings yet
- Learning EnglishDocument17 pagesLearning EnglishHasan ShNo ratings yet
- Non - Finite VerbsDocument4 pagesNon - Finite Verbsmohitguptabtech100% (1)
- Unit 9: It Depends How You Look at It: GrammarDocument5 pagesUnit 9: It Depends How You Look at It: GrammarCristina Rodriguez PardoNo ratings yet
- Trabajo de InglesDocument18 pagesTrabajo de InglesLuisAntonioMagallanesMartinezNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Level 7Document13 pagesUnit 1 - Level 7Diana SierraNo ratings yet
- 150 autres phrases anglaises vraiment utiles: 150 phrases anglaises vraiment utilesFrom Everand150 autres phrases anglaises vraiment utiles: 150 phrases anglaises vraiment utilesNo ratings yet
- Related Links: Grammar Exercises Grammar LessonsDocument4 pagesRelated Links: Grammar Exercises Grammar LessonsyeswanthNo ratings yet
- Basic 05 Unit 9 & Unit 10Document26 pagesBasic 05 Unit 9 & Unit 10Franco Huamán BrittoNo ratings yet
- Unidad II Ing-: CUAM "Cuestión de Excelencia"Document27 pagesUnidad II Ing-: CUAM "Cuestión de Excelencia"Miguel PerezNo ratings yet
- Present Simple ContinuousDocument8 pagesPresent Simple ContinuousJosmaツNo ratings yet
- 12 English TensesDocument113 pages12 English Tensescharles izquierdoNo ratings yet
- TENSE Consolidation Simp. Pres. Vs Pres. Cont.Document21 pagesTENSE Consolidation Simp. Pres. Vs Pres. Cont.tatianypertelNo ratings yet
- IngleseDocument9 pagesIngleseFrancesca Di GiamberardinoNo ratings yet
- Another 150 Really Useful English Phrases.: 150 Really Useful English Phrases, #2From EverandAnother 150 Really Useful English Phrases.: 150 Really Useful English Phrases, #2Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (7)
- Common Mistakes of Turkish LearnerDocument24 pagesCommon Mistakes of Turkish LearnerSuhail AzizNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Unit 6Document5 pagesUnit 1 - Unit 6Laura RosarioNo ratings yet
- The Present Simple Tense: Zion LanguagesDocument23 pagesThe Present Simple Tense: Zion LanguagesZion Languages100% (1)
- Tenses Part - 1 Simple Present TenseDocument5 pagesTenses Part - 1 Simple Present Tensesiva kumar100% (1)
- Simple Present: Do You Speak English?Document27 pagesSimple Present: Do You Speak English?Andreea GîleaNo ratings yet
- Final ÇalışmaDocument8 pagesFinal ÇalışmatesayisteNo ratings yet
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Gerund or Infinitive ExplanationDocument8 pagesGerund or Infinitive ExplanationMarisa MendesNo ratings yet
- GerundDocument18 pagesGerundBecik Uswatun HasanahNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument10 pagesGerunds and InfinitivesNguyễn BìnhNo ratings yet
- Leaf StudyDocument5 pagesLeaf StudyNatália DiasNo ratings yet
- USE 1 Completed Action in The Past: Did You Have Dinner Last Night?Document25 pagesUSE 1 Completed Action in The Past: Did You Have Dinner Last Night?Dashrathsinh RathodNo ratings yet
- Grammar B2Document29 pagesGrammar B2Inma MuñozNo ratings yet
- Rewiew GrammarDocument37 pagesRewiew GrammarFabricio Alberti Cervantes FalenNo ratings yet
- The Present Simple and Present Continuous TensesDocument34 pagesThe Present Simple and Present Continuous TensesOorrmm Jubujubu100% (1)
- Common Mistakes of Turkish LearnerDocument24 pagesCommon Mistakes of Turkish LearnerHidemi OrimotoNo ratings yet
- 000 - Substitution and EllipsisDocument6 pages000 - Substitution and EllipsisLingvo CasaNo ratings yet
- Grammar TestDocument21 pagesGrammar TestAlina MaksimenkoNo ratings yet
- Present Simple PracticeDocument10 pagesPresent Simple PracticeAdy GamerNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument12 pagesTensesRitaLucasNo ratings yet
- Using The Present ContiDocument10 pagesUsing The Present ContiLi CastilloNo ratings yet
- Pronunciation Practice BookDocument56 pagesPronunciation Practice BookJisleny Giraldo Hurtado100% (2)
- The Grammar GameshowDocument29 pagesThe Grammar GameshowOkan Taşin100% (1)
- Grammar British CouncilDocument89 pagesGrammar British CouncilAlfredo HernandezNo ratings yet
- En A1-B1 2016Document221 pagesEn A1-B1 2016Marius Alexandru Ion100% (1)
- Past Perfect Progressive/Continuous: How Long Something Had Been Happening Before Something Else HappenedDocument15 pagesPast Perfect Progressive/Continuous: How Long Something Had Been Happening Before Something Else HappenedStefanDaniel97No ratings yet
- E-Learning English, Grammar Review, Level 1, A-Z: SubjectDocument35 pagesE-Learning English, Grammar Review, Level 1, A-Z: SubjectJuan Caubet FernándezNo ratings yet
- Business EnglishDocument21 pagesBusiness EnglishŞtefania FcSbNo ratings yet
- Simple Present USE 1 Repeated ActionsDocument16 pagesSimple Present USE 1 Repeated ActionsGaram Esther GohNo ratings yet
- Full Tenses PDFDocument40 pagesFull Tenses PDFsarief100% (2)
- Present Tense SimpleDocument35 pagesPresent Tense SimpleLara PopNo ratings yet
- Antonius Chiky Betricia Yuniaringtyas Clara Cleodora YuvitaDocument25 pagesAntonius Chiky Betricia Yuniaringtyas Clara Cleodora YuvitaClara Cleodora100% (1)
- Guide 2 Daily RoutinesDocument4 pagesGuide 2 Daily RoutinesLaura Liceth RAMIREZ DIAZNo ratings yet
- Dosier AlvaroDocument22 pagesDosier AlvaroFernando Muñoz MontesinosNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Tense and ExercisesDocument9 pagesSimple Present Tense and ExercisesPapa Martelo MarteloNo ratings yet
- Unidad 13Document40 pagesUnidad 13Juan HermidaNo ratings yet
- SBH ScenerioV1Document7 pagesSBH ScenerioV1silenceindigoNo ratings yet
- Motivation in The Hospitality IndustryDocument11 pagesMotivation in The Hospitality Industryabhijeet_katteNo ratings yet
- Classification of HotelsDocument8 pagesClassification of HotelsAnies YulindaNo ratings yet
- Devoir de Synthèse N°1 - Anglais - 7ème (2011-2012) Mme SAWSEN ABIDDocument2 pagesDevoir de Synthèse N°1 - Anglais - 7ème (2011-2012) Mme SAWSEN ABIDMesmed NacNo ratings yet
- GRAMMAR 12 - PAST PERFECT CONT - W KeyDocument11 pagesGRAMMAR 12 - PAST PERFECT CONT - W KeyTú BíNo ratings yet
- Kunci Jawaban SMK Kls XiDocument21 pagesKunci Jawaban SMK Kls XiAsshiyyatul Fitryy Awaq88% (8)
- Tips For Making The Best Fried RiceDocument5 pagesTips For Making The Best Fried RiceDavin HimawanNo ratings yet
- MENUDocument9 pagesMENUrianNo ratings yet
- Origins of First 'Restaurant' Challenged After 200 YearsDocument15 pagesOrigins of First 'Restaurant' Challenged After 200 YearsNiharika KotwalNo ratings yet
- EIC1 Workbook AKDocument15 pagesEIC1 Workbook AKAuxiliar De coordinación BLSNo ratings yet
- Becerrino Spelling Bee Contest 2023Document2 pagesBecerrino Spelling Bee Contest 2023daieron123 guzmanNo ratings yet
- Indian Food Code (25-06-2012)Document60 pagesIndian Food Code (25-06-2012)harry_bccNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument114 pagesEnglishClaudia HenriquesNo ratings yet
- Adverbios de FrecuenciaDocument11 pagesAdverbios de FrecuenciaChurrasca RumanaNo ratings yet
- Jimbo's StandDocument118 pagesJimbo's StandJasonNo ratings yet
- Barista Training Resource Manual - TTM - 2Document46 pagesBarista Training Resource Manual - TTM - 2norumulatt100% (1)
- Coriolis - Schematic of Coriolis StationDocument1 pageCoriolis - Schematic of Coriolis StationSquamataNo ratings yet
- Tests A Answer Key: Diagnostic TestDocument8 pagesTests A Answer Key: Diagnostic TestYONo ratings yet
- School Newsletter - 24.08.12Document2 pagesSchool Newsletter - 24.08.12salfordprimaryNo ratings yet
- TESISDocument4 pagesTESISSylvia MahumasNo ratings yet
- Channel Your English Beginners - Test Booklet Final Exam A. Listen To Four Short Conversations and Answer The Questions. Circle A, B or C. (8 Marks)Document4 pagesChannel Your English Beginners - Test Booklet Final Exam A. Listen To Four Short Conversations and Answer The Questions. Circle A, B or C. (8 Marks)John DoeNo ratings yet
- Conversation Activator Video ScriptDocument8 pagesConversation Activator Video ScriptHugo A FENo ratings yet
- Tuscan EstateDocument18 pagesTuscan EstatePravin KumarNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management PaperDocument54 pagesStrategic Management PaperCianne Alcantara76% (21)
- Vegan Recipes For Kids 6to10pgDocument5 pagesVegan Recipes For Kids 6to10pgnandsantosNo ratings yet
- The Beginners Guide To MacrosDocument120 pagesThe Beginners Guide To Macrosmichaelchris2pher88% (17)
- AaronDocument2 pagesAaronAbbiesalonNo ratings yet
- Priprema Za Pismeni Viii RazredDocument3 pagesPriprema Za Pismeni Viii RazredOljaTejicNo ratings yet
- Starbucks SWOT AnalysisDocument2 pagesStarbucks SWOT AnalysisRubayath Namibur RazzakNo ratings yet
- Menu LunchDocument4 pagesMenu LuncheatlocalmenusNo ratings yet