Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm A
Uploaded by
PremOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm A
Uploaded by
PremCopyright:
Available Formats
I
I
T
-
J
E
E
O
b
j
e
c
t
i
v
e
M
a
t
h
e
m
a
t
i
c
s
E
r
.
L
.
K
.
S
h
a
r
m
a
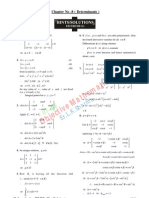
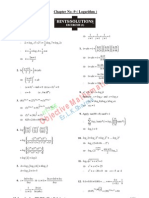
[93] Mathematics for I I T-J EE (Hints/Solutions)
1.
{ }
2 3
( ) 2, ( 2) 1, 2 f x min x x = + +
from graph of ( ) , f x locations of non-differentiability
are : 1 x= and 3
Required no. of points =2.
2. ( ) | | |cos | tan ( 1, 2)
4
f x x x x x
| |
= + + + e
|
\ .
( ) f x is discontinuous at
4
x
= and hence non-
differentiable.
New , locations of non-differentiability are :
0, ,
4 2
x
=
3.
cos .sin sin( ) sin( )
sin .cos sin( ) sin( )
x y x y x y
x y x y x y
+ +
=
+ +
( )
1
2( ) sin( ) '(0)
2
f x y x y f
| |
+ = + =
|
\ .
( ) sin
2
x
f x
| |
=
|
\ .
Now ,
1
"( ) sin
4 2
x
f x
| |
=
|
\ .
4 "( ) ( ) 0 f x f x + =
4. { } ( ) sin , cos , 0 f x max x x =
from graph of ( ) f x , locations of non-differentiability
in (0, 2 ) are :
3
, ,
4 2
x
=
Required no. of points =3n.
5.
( ) f x is non-differentiable for { } 0, 2 x ln e
6.
2
0
(1 ) 1
lim
( 3)
h
f h
h h
+
(Apply L'Hospital's Rule)
2
0
'(1 ) '(1)
lim
3 3 3
h
f h f
h
= =
+
( )
9 7 5 2
1
1
30 56 30 63 6
3
x
x x x x x
=
= + +
53
3
=
7.
( ) ; 0
( )
( ) ; 0
f x x
g x
f x x
>
=
<
3
( ) ( ) g x f x x x x R = = + e
( ) g x is continous x R e
8. For continuity at 1 x=
4 2 2 0 a b a b + = + + = ...(i)
for differentiability at 1 x=
(2 3) 5 b b + = =
3 a =
( 3 ) 18 a b + =
9. ( ) f x will have exactly three points of non-
differentiability if
2
0 x ax b + + = have one positive
root and another root as zero.
(0) 0 0 f b = =
2
0 0; x ax x a + = =
Chapter No -12 ( Continuity and Differentiability )
I
I
T
-
J
E
E
O
b
j
e
c
t
i
v
e
M
a
t
h
e
m
a
t
i
c
s
E
r
.
L
.
K
.
S
h
a
r
m
a
[94] Mathematics for I I T-J EE (Hints/Solutions)
Now , ( ) 0 0 a a > <
0 b = and a R
e is required condition
10.
3
( ) 2 5 f x x
(
=
(1) 3 f = and (2) 11 f =
( ) f x is discontinous when it becomes the integer. .
Required no. of points =13
11.
( )
cosec
0
lim(cos sin ) 1 form
x
x
x x
0
(cos sin 1)
lim
sin x
x x
exp
x
=
`
)
0
sin cos
lim
cos x
x x
exp
x
=
`
)
1
. . L H L
e
=
1 2 3
2 3
2 3 2 3
0
lim lim
y y y
x x x
y y
y x
x x
e e e e e e
ae be
ae be
+
+ + + +
=
` `
+
)
+
)
lim
y
e
=
( )
3
2
1
y
y y
e e
e
+ +
( )
3
1
y
y
b
ae b
=
+
1
. . RH L
b
=
Now , for continuity of ( ) f x at
0 x=
1 1
a
e b
= =
1
and a b e
e
= =
1
( ) a b e
e
| |
+ = +
|
\ .
12. ( ) (2 ) ( ) ( ) f x f a x f a x f a x = + =
0
( ) ( )
'( ) lim
h
f a h f a
f a
h
( ( ) f x is odd function)
0
( ) ( )
'( ) lim
h
f a h f a
f a
h
+ +
=
0
( ) ( )
'( ) lim
h
f a h f a
f a
h
=
( ) ( ) ( ) f a x f a x + =
Now , ( )
'( ) ' f a f a
=
( )
'( ) 0 '( ) 0 f a f a
= =
13.
2
0
( ) sin cos
2
x
x
tf t dt x x x =
}
( ) cos cos sin xf x x x x x x = +
( ) sin 1 f x x =
1
6 2
f
| |
=
|
\ .
14. | | | | ( ) sin sin2 f x x x = +
Points of discontinuity exist at :
5 3 9 5
, , , , , 2 , , , 3
4 2 4 2 4 2
x
=
Total no. of points of non-differentiability
in (0 , 10)
9 =
15.
2
2
; 0
2
( ) 1 ; 0
; 0
2
x
x
x x
f x x
x
x
x x
<
= =
>
+
1
; 0
2 1
( ) 1 ; 0
; 0
2
x
x
f x x
x
x
x x
<
= =
>
+
LHL at
0 x=
is 1 (0) f =
( ) f x is discontinuous at 0 x=
16.
2
3 | |; 2 | | x t t y t t t = = +
for
2 2
0; 3 and 2 t x t t y t t > = = +
2
for 0; 2 and 3 x x t y t > = =
2
2
3
3
2 4
x x
y y
| |
= =
|
\ .
.... (i)
for
2
0; 4 and t x t y t < = =
2
for 0,
16
x
x y < = .... (ii)
from (i) and (ii)
2
2
3
; 0
4
( )
; 0
16
x
x
f x
x
x
>
<
Now , ( ) f x is continuous and differentiable at x =0
I
I
T
-
J
E
E
O
b
j
e
c
t
i
v
e
M
a
t
h
e
m
a
t
i
c
s
E
r
.
L
.
K
.
S
h
a
r
m
a
[95] Mathematics for I I T-J EE (Hints/Solutions)
17. | |
2
2
( ) f x x x
(
=
Let ; x k k I = e
( ) 0 f k =
2 2
lim ( ) ( 1) ( 1)
x k
f x k k
=
2 2 2( 1) k k = + =
2 2
lim ( ) ( ) ( )
x k
f x k k
+
=
=0
Now , L.H.L. =R.H.L. ( ) f k =
2( 1) 0 0 k = =
0 0 0 at 1 k = = =
( ) f x is continous at 1 x=
18.
1
( ) 1 [0, )
x
f x e x
s e
(1) 1 1 f s
(1) 0 (1) 0 f f s =
Now ,
1
( ) (1) 1
x
f x f e
s
1
( ) (1) 1
1 1
x
f x f e
x x
s
Apply limit 1 x
'(1) 1 f s
1 1
( 1) .... 1.
n n
na n a a
+ + + s
19.
1/
0
0
1
'(0 ) lim
h
h
h
e
f
h
+
+
=
1/ 1
0
'(0 ) lim(1 ) 0
h
h
f e
+
= + =
1/
0
0
1
'(0 ) lim
h
h
h
e
f
h
+
=
( )
1
1/
0
'(0 ) lim1 1
h
h
f e
= + =
'(0 ) 0; '(0 ) 1 f f
+
= =
20. ( ) ( ) ( ) f x y f x f y xy + = +
( ) ( ) ( )
( 0)
f x y f x f y
x y
y y
+
= + =
Now ,
0 0
( ) ( ) ( )
lim lim
y y
f x y f x f y
x
y y
+
= +
2
'( ) 3 ( ) 3
2
x
f x x f x x c = + = + +
for 0 x y = =
(0) (0) (0) 0 f f f = + +
(0) 0 f =
2
( ) 3
2
x
f x x = +
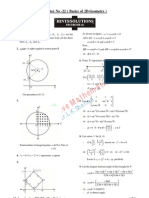
21.
2
4 y x = represents part of the circle
2 2
4 x y + =
Similarly
2
1 y x = +
represents part of the conjugate
hyperbola
2 2
1 x y + =
from graph of ( ) f x , options (a) and (c) are true.
22.
2 ( ) ( )
3 3
x y f x f y
f
+ + + | |
=
|
\ .
for 0 x y = =
2 2 (0)
(0) (0) 2
3
f
f f
+
= =
0 (0) ( ) ( )
3 3
x y f f x f y
f
+ + + + | |
=
|
\ .
( ) 2 f x kx = +
( ) 2 2 f x x = + ( ) '(0) 2 f =
| | | | ( )
1 2 2
1 1 1
3
2 2 and (1) 4
2
x dx f x dx f dx
+ = = =
} } }
options (a) , (b) and (d) are correct.
23.
1
( ) sin (sin ) f x x x R
= e
from graph , ( ) f x is non-differentiable
2
n
x
=
I
I
T
-
J
E
E
O
b
j
e
c
t
i
v
e
M
a
t
h
e
m
a
t
i
c
s
E
r
.
L
.
K
.
S
h
a
r
m
a
[96] Mathematics for I I T-J EE (Hints/Solutions)
3
2
y log x
= meet ( ) f x at five locations.
| | ( )
1
0 1
( ) 0 1 0 2 . f x dx dx
= + + =
} }
( )
1 ;
( )
0 ;
x n
y sgn f x
x n
=
= =
=
options (a) , (b) and (c) are correct.
24.
sin [ ]
4
( )
[ ]
x
f x
x
=
2
sin
1 4
lim ( )
1 2
x
f x
| |
|
\ .
= =
2
sin
1 2
lim ( )
2 2 x
f x
| |
|
\ .
= =
( ) f x is discontinuous at 2 x=
Similarly , ( ) f x is continous at 1.5 x= .
25.
0 0
lim ( ) lim ( ) (0)
x x
f x f x f
+
= =
1
1
sin (for continuity at 0)
2 2 2
c a
b x
| |
= = =
|
\ .
1
1 and 2sin
2
a c
b
| |
= =
|
\ .
for differentiability , '(0 ) '(0 ) f f
+
=
( )
/2
0
1 1
2
'(0 ) lim 1
h
h
e
h
f a
h
+
= =
/ 2
2
0
2 2
'(0 ) lim
2
h
h
e h
f
h
+
=
2 2
2
0
1 1
2 1 .... 2
2 2! 2 3! 2
lim
2
h
h h h
h
h
| |
| | | |
+ + + |
| |
|
\ . \ .
\ .
=
1
'(0 )
8
f
+
=
1
0
1
sin
2 2
'(0 ) lim
h
c h
b
f
h
| |
|
\ .
=
2 2
1
2
4
1
4
b
b
c c
| |
|
\ .
= =
Now ,
2
1
'(0 ) '(0 )
8
4
b
f f
c
+
= =
2 2
64 4 b c + =
options (b) and (c) are correct.
26. Statement (2) is true , but statement (1) is not always
true.
If limiting value of ( ) g x at x a is approaching to
from same side , then
( )
( )
lim ( ) lim ( )
x a x a
f g x f g x
=
for example :
sin
Let ( ) ( 1) and ( )
x
f x sgn x g x
x
= =
Now
0
sin
lim 1
x
x
x
| |
=
|
\ .
( )
0 0
sin
lim ( ) lim 1
x x
x
f g x sgn
x
| |
=
|
\ .
0
sin
lim 1 1
x
x
sgn
x
| |
= =
|
\ .
27.
2
( ) [ 3 4] g x x x x R = + e
output of ( ) g x is integral
2
sin( ( ))
( ) 0
1 [ ]
g x
f x x R
x
= = e
+
( ) f x is continous x R e
Statement (1) is false and satement (2) is true
28. Statement (2) is false. Let
| | 1 ; 0
( )
1 ; 0
x x
g x
x
=
=
=
( ) y g x = is discontinuous at
0 x=
but | ( ) | y g x = is
continous at 0 x= .
29. Statement (2) is false because ( ) f x is having a unique
vertical tangent at 2 x=
30. ( ) sin [0, ) g x x x = e
from graph ( ) f x is continuous and differentiable for
all [0, ) xe but the continuity of function doesn't
ensure the differentiability.
Statement (1) and (2) are true but the reasoning is not
appropriate.
I
I
T
-
J
E
E
O
b
j
e
c
t
i
v
e
M
a
t
h
e
m
a
t
i
c
s
E
r
.
L
.
K
.
S
h
a
r
m
a
[97] Mathematics for I I T-J EE (Hints/Solutions)
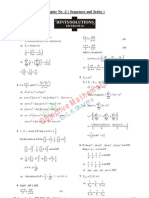
1.
( ) h x is non-diff. at
1 2
0, , , 1
3 3
x=
Required no. to tocations =4.
2. ( ) ( ) 0; 1 f x g x x = =
0 1 0 + = + =
3. For four distinct real roots :
4 1
, 1
9 2
| |
e
` |
) \ .
1
2
=
4.
( ) y x = is non-differentiable for { } 2, 3, 5, 6 xe
5. '(3 ) '(2 ) '(6 )
+ + +
+
( )
2
2
1 (4 ) 4
x
d
x x
dx
=
= +
1 4 4 9 = + + =
6.
5
5 5
2
3 3 3
( )
2
x
x dx xdx = =
} }
=8
7. ( ) f x is discontinous at
1 x=
and hence non-
differentiable.
( ) f x is continuous at
0 x=
, 1 but there exist sharp
change in graph of ( ) f x and hence non-differentiable
at 0 x= and 1. x=
Now Domain of '( ) f x is { } 1, 0, 1 R
Required no. of locations =3.
8. ( )
( )
4
lim ( ) 2 ( 2)
x
f g x f b
+
+
=
( )
( )
4
lim ( ) 2 (2 )
x
f g x f a
= = +
(2) ( 2)
4
f g f b
| | | |
= =
| |
\ . \ .
Now ,
2 2 2 b a b = + =
4 b a =
( ) 2 8 b a =
9. For continuity of ( ) f x at 0 x=
1
0
0( ) (1) lim
2 1
x
x
x
x e
a b
x
+
| |
+
+ =
|
|
+
\ .
0
1
lim 1
2 1
x
x
x e
b exp
x x
+
| | | |
+
= | |
| |
+
\ . \ .
0
1
lim
(2 1)
x
x
e x
b exp
x x
+
| |
=
|
|
+
\ .
1/4
b e =
'(1)
2
f a f a
| |
= =
|
\ .
Let
1
2 1
x
x
x e
y
x
| |
+
=
|
|
+
\ .
I
I
T
-
J
E
E
O
b
j
e
c
t
i
v
e
M
a
t
h
e
m
a
t
i
c
s
E
r
.
L
.
K
.
S
h
a
r
m
a
[98] Mathematics for I I T-J EE (Hints/Solutions)
( )
1
( ) ( ) (2 1)
x
ln y ln x e ln x
x
= + +
2
1 1 1 2 1
.
2 1 2 1
x x
x
dy e x e
ln
y dx x x x x e x
| |
+ +
=
| ` `
|
+ + + ) \ . )
1
1 1 2 1
3 1 3 3
x
dy e e e
ln
dx e
=
+ + + | | | |
=
`
| |
+
\ . \ . )
1 1 1
'(1)
3 3 3
e e
f ln
+ + | | | |
=
`
| |
\ . \ . )
1 1 1
3 3 3
e e
a ln
+ + | | | |
=
`
| |
\ . \ . )
[ ] 1 a =
1/ 4
[ ] [ ] 1 1 1 0 a b e
(
+ = + = + =
.
10.
( ) ( )
( ) ,
f x f y
f xy x y R
y x
+
= + e
Apply partial differentiation w.r.t. y
2
( ) 1
'( ). . '( )
f x
f xy x f y
x y
= +
Now put ( ) 1 (1) 0 and '(1) 1 y f f = = =
( ) 1
'( ). '(1)
1
f x
f x x f
x
= +
2
1 1 dy
y
dx x x
+ = {Apply integrating factor}
( ) ( ) (1) 0 y x lnx c f = + =
lnx
y
x
=
( )
2
1
( ) '( ) 1
lnx
f x f x lnx
x x
= =
x e = is location of local maxima
Now , | |
1
and 3 3 M M
e
= + =
11. (a)
{ }
3 2
( ) , f x min x x =
( ) , , a p r s
(b) { } ( ) | |, | 1| , | 1| f x min x x x = +
( ) , b p r
(c) ( ) 2 4 2 2 f x x x = +
( ) , , c p q s
(d) ( ) sin cos f x x x = +
( ) , d p r
12. Let ( )
2
( ) (0) 0 f x ax bx f = + =
2
Now, ( ) 2
2 4
x x
f x f f x
| | | |
+ =
| |
\ . \ .
2 2
2 2
2
4 2 16 4
ax bx ax bx
ax bx x
| |
+ + + + =
|
|
\ .
2 2
2 16 4
a a b
a x x b b x
| | | |
+ + + =
| |
\ . \ .
on comparision ,
16
; 0
9
a b = =
2
16
( )
9
x
f x =
I
I
T
-
J
E
E
O
b
j
e
c
t
i
v
e
M
a
t
h
e
m
a
t
i
c
s
E
r
.
L
.
K
.
S
h
a
r
m
a
[99] Mathematics for I I T-J EE (Hints/Solutions)
(a)
32 9
'( ) ' 4
9 8
x
f x f
| |
= =
|
\ .
(b)
from graph , points of non-differentibility =6
(c) ( ) f x is increasing in [0 , 4]
( ) 0 [0, 4] g x x = e
'(3) 0 g =
(d) | ( ) | y f x =
( ) ( ) 0 y f x f x x R = > e
2
16
9
x
y =
| ( ) | y f x = is differentiable
You might also like
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument6 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument10 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument9 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Differentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDifferentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Limit ContinuiTY Differential ASSIGNMENT FOR IIT-JEEDocument17 pagesLimit ContinuiTY Differential ASSIGNMENT FOR IIT-JEEApex Institute100% (2)
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)From EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)No ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument8 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- JC2 Prelim H2 Math Solution Paper 1Document10 pagesJC2 Prelim H2 Math Solution Paper 1Huixin LimNo ratings yet
- Functions Ex.2 (B)Document20 pagesFunctions Ex.2 (B)Gokul NathNo ratings yet
- Section G: Integer Answer Type: X FX F XDocument10 pagesSection G: Integer Answer Type: X FX F XsatwiksmNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument10 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Maths FormulaDocument4 pagesMaths Formulamickey_disney93No ratings yet
- Functions, Limits & Continuity DifferentiationDocument5 pagesFunctions, Limits & Continuity DifferentiationSharath Aefdsffdf FdNo ratings yet
- Control 3 Calculo2Document9 pagesControl 3 Calculo2camilo_akuNo ratings yet
- AJC H2 Math 2013 Prelim P1 SolutionsDocument15 pagesAJC H2 Math 2013 Prelim P1 Solutionsnej200695No ratings yet
- Continuity and Differentiation: Points To RememberDocument8 pagesContinuity and Differentiation: Points To RememberAakash ChanNo ratings yet
- MA2211 NotesDocument145 pagesMA2211 NotesBala SubramanianNo ratings yet
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document10 pagesNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Formula RioDocument6 pagesFormula RioJorge Laura GutierrezNo ratings yet
- BT2 Revision Package Solutions (2008 Prelims)Document111 pagesBT2 Revision Package Solutions (2008 Prelims)gerwynngNo ratings yet
- NJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument10 pagesNJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument5 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Hints/Solutions For M1204: (Continuity & Differentiability)Document5 pagesHints/Solutions For M1204: (Continuity & Differentiability)Sivakumar NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Fourier SeriesDocument26 pagesFourier SeriesPurushothamanNo ratings yet
- IIT 2012 12 13 p1 p2 Mat UN4 SADocument66 pagesIIT 2012 12 13 p1 p2 Mat UN4 SAAnkit RaiNo ratings yet
- Info Booklet, Revised 2011Document27 pagesInfo Booklet, Revised 2011ordinanceNo ratings yet
- 2012 ACJC Prelim H2 Math SolnDocument15 pages2012 ACJC Prelim H2 Math Solnckhowh_23284524667% (3)
- Exercise 1 (C) : DX DyDocument7 pagesExercise 1 (C) : DX DyGokul NathNo ratings yet
- AIEEE 2011 Mathematics Question PaperDocument12 pagesAIEEE 2011 Mathematics Question Papermohit24031986No ratings yet
- Answers Are You Ready For CalculusDocument6 pagesAnswers Are You Ready For CalculusKevin HsiehNo ratings yet
- MAM2085F 2013 Exam SolutionsDocument8 pagesMAM2085F 2013 Exam Solutionsmoro1992No ratings yet
- 2014 2 SARAWAK SMKStJoseph Kuching MATHS QADocument11 pages2014 2 SARAWAK SMKStJoseph Kuching MATHS QASK100% (3)
- Ajc h2 Math p1 SolutionsDocument15 pagesAjc h2 Math p1 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Misrimal Navajee Munoth Jain Engineering College, Chennai - 97Document26 pagesMisrimal Navajee Munoth Jain Engineering College, Chennai - 97bhagyagr8No ratings yet
- 07-Limit ContDocument15 pages07-Limit ContAnonymous BnbPSoovbNNo ratings yet
- Function: X Is Chosen at Random From The First 1000 Natural Numbers. If (.) Denotes TheDocument4 pagesFunction: X Is Chosen at Random From The First 1000 Natural Numbers. If (.) Denotes TheShrey PandeyNo ratings yet
- Nyjc h2 Math p1 SolutionDocument10 pagesNyjc h2 Math p1 SolutionjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- GRAFICASDocument8 pagesGRAFICASPercyes_CivilunhNo ratings yet
- Mathes 3 NotesDocument127 pagesMathes 3 NotesShashi Bhushan PatelNo ratings yet
- Recitation 5: Sections 12.1-12.3Document40 pagesRecitation 5: Sections 12.1-12.3Oğuzhan ÖzdemirNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Home Practice Test-5/Mathematics: Differential Calculus - 2 HWT - 1Document12 pagesSolutions To Home Practice Test-5/Mathematics: Differential Calculus - 2 HWT - 1varunkohliinNo ratings yet
- AJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document12 pagesAJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Inequation & Equation Solutions FinalDocument67 pagesInequation & Equation Solutions FinalAkshay PatelNo ratings yet
- Answers Paper AIEEEDocument17 pagesAnswers Paper AIEEESuyash ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 2013 JC2 H2 Maths Rev G Solutions Pure Maths IDocument34 pages2013 JC2 H2 Maths Rev G Solutions Pure Maths IAnnabel SeahNo ratings yet
- Advanced Engineering Mathematics Solutions (2-4 2-7&2-10)Document26 pagesAdvanced Engineering Mathematics Solutions (2-4 2-7&2-10)Fa VelizNo ratings yet
- Additional Calculus Problems 2-Integration and Applications SolutionsDocument5 pagesAdditional Calculus Problems 2-Integration and Applications SolutionsNicholas TehNo ratings yet
- MA1521 Solution3Document5 pagesMA1521 Solution3Ray TanNo ratings yet
- Edexcel C3 June 2005 To June 2011 All Questions Mark SchemeDocument44 pagesEdexcel C3 June 2005 To June 2011 All Questions Mark SchemeOrhan AtestemurNo ratings yet
- Answers 2009-10Document19 pagesAnswers 2009-10Yoga RasiahNo ratings yet
- Rvhs h2 Math p1 SolutionsDocument13 pagesRvhs h2 Math p1 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- EGM6341 Sol HW 01Document22 pagesEGM6341 Sol HW 01Redmond R. ShamshiriNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Set ADocument17 pagesFinal Exam Set AAtikah J100% (1)
- ACJC 2014 H2 Maths Supp Exam (Solution For Students)Document9 pagesACJC 2014 H2 Maths Supp Exam (Solution For Students)RaymondZhangNo ratings yet
- Basic (1) MathDocument2 pagesBasic (1) MathIan KrebsNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument5 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- 2007 YJC Paper 1solDocument12 pages2007 YJC Paper 1solYudi KhoNo ratings yet
- 22Document4 pages22PremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument5 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument10 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument12 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument11 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- 31Document8 pages31PremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument9 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument8 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument8 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument7 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument6 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument7 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm AAnupam PathiNo ratings yet
- Megalite PDFDocument9 pagesMegalite PDFAnup SharmaNo ratings yet
- DocDocument1 pageDocPremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument10 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry EquationsDocument6 pagesTrigonometry EquationsPremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument5 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument10 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Books For AIEEEDocument2 pagesBooks For AIEEEbanur2No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Newton's Laws of MotionDocument13 pagesChapter 5 Newton's Laws of MotionPremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument10 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Books List PDFDocument4 pagesBooks List PDFRohit Kumar100% (2)
- PLCDocument936 pagesPLCjulio cidNo ratings yet
- Dorma Automatic DoorDocument4 pagesDorma Automatic DoorClef GonadanNo ratings yet
- BELLTPO CHARTS WORKSPACE VIDEOLINKS Troubleshooting InstuctionsDocument3 pagesBELLTPO CHARTS WORKSPACE VIDEOLINKS Troubleshooting InstuctionsRameishYedllaNo ratings yet
- Generic Classes and Methods: A Deeper Look: Java How To Program, 11/eDocument35 pagesGeneric Classes and Methods: A Deeper Look: Java How To Program, 11/eWilburNo ratings yet
- Ahb7816t ElDocument3 pagesAhb7816t ElcjtrybiecNo ratings yet
- BTM380 F12Document7 pagesBTM380 F12Kevin GuérinNo ratings yet
- Guppa - Se Ultra300x Servicemanual PDFDocument560 pagesGuppa - Se Ultra300x Servicemanual PDFPatrik Benjaro100% (1)
- MRT Pro HDD Repair & Data Recovery Tool Suite Product Description PDFDocument37 pagesMRT Pro HDD Repair & Data Recovery Tool Suite Product Description PDFSree Loo33% (3)
- Chapters 1 - 6: - Chapter 6Document51 pagesChapters 1 - 6: - Chapter 6Delasdriana WiharjaNo ratings yet
- 2 2 4 A Designtoollogicconverter (Finished)Document6 pages2 2 4 A Designtoollogicconverter (Finished)api-283923425No ratings yet
- Digital DocumentationDocument5 pagesDigital DocumentationTushar DeshwalNo ratings yet
- Beginner's Guide To Using Slack: How To Download and SetupDocument10 pagesBeginner's Guide To Using Slack: How To Download and Setupapi-438333796No ratings yet
- How Make .2875 BTC A Day in The Deep Web (Step by Step) EasilyDocument7 pagesHow Make .2875 BTC A Day in The Deep Web (Step by Step) EasilyLocal Agency God100% (1)
- Amesim English s01Document20 pagesAmesim English s01Chetan P BhatNo ratings yet
- Transfer Order 6.10.23Document1 pageTransfer Order 6.10.23ShivajiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 2017Document3 pagesSyllabus 2017sandman21No ratings yet
- HettichDocument74 pagesHettichomkarniranjanNo ratings yet
- Objective of MRP and MRP2 in Computer StudyDocument14 pagesObjective of MRP and MRP2 in Computer StudyMostafa FawzyNo ratings yet
- Project ManagementDocument10 pagesProject ManagementVanessa NacarNo ratings yet
- Setting Up An MVC4 Multi-Tenant Site v1.1Document61 pagesSetting Up An MVC4 Multi-Tenant Site v1.1Anon Coder100% (1)
- SAPDocument19 pagesSAPdzulfatuhNo ratings yet
- 300G Im 20121214Document4 pages300G Im 20121214Josue Vieira OliveiraNo ratings yet
- PMO PresentationDocument30 pagesPMO PresentationHitesh TutejaNo ratings yet
- Punching Report - Unikl MsiDocument9 pagesPunching Report - Unikl MsiRudyee FaiezahNo ratings yet
- Ray Tracing - Technical ReportDocument8 pagesRay Tracing - Technical ReportCong-Son TranNo ratings yet
- Low-Cost Dual-Band E-Shaped Patch Antenna For Energy Harvesting Applications Using Grey Wolf OptimizerDocument5 pagesLow-Cost Dual-Band E-Shaped Patch Antenna For Energy Harvesting Applications Using Grey Wolf Optimizermubeen khanNo ratings yet
- .Game Development With Blender and Godot - SampleDocument6 pages.Game Development With Blender and Godot - Sampleсупер лимонNo ratings yet
- Hatch Mott Proposal - FINAL REVISEDDocument82 pagesHatch Mott Proposal - FINAL REVISEDbubbles82No ratings yet
- Manned Maneuvering Unit Design and Performance SpecificationDocument82 pagesManned Maneuvering Unit Design and Performance SpecificationBob Andrepont100% (1)
- Dynamics 365 Enterprise Edition Licensing GuideDocument52 pagesDynamics 365 Enterprise Edition Licensing Guidefran.obando1332No ratings yet
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingFrom EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- ParaPro Assessment Preparation 2023-2024: Study Guide with 300 Practice Questions and Answers for the ETS Praxis Test (Paraprofessional Exam Prep)From EverandParaPro Assessment Preparation 2023-2024: Study Guide with 300 Practice Questions and Answers for the ETS Praxis Test (Paraprofessional Exam Prep)No ratings yet
- Images of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryFrom EverandImages of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryNo ratings yet
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- How Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsFrom EverandHow Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (9)
- Magic Multiplication: Discover the Ultimate Formula for Fast MultiplicationFrom EverandMagic Multiplication: Discover the Ultimate Formula for Fast MultiplicationNo ratings yet
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorFrom EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldFrom EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (80)
- Applied Predictive Modeling: An Overview of Applied Predictive ModelingFrom EverandApplied Predictive Modeling: An Overview of Applied Predictive ModelingNo ratings yet
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)From EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)No ratings yet
- A Guide to Success with Math: An Interactive Approach to Understanding and Teaching Orton Gillingham MathFrom EverandA Guide to Success with Math: An Interactive Approach to Understanding and Teaching Orton Gillingham MathRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Who Tells the Truth?: Collection of Logical Puzzles to Make You ThinkFrom EverandWho Tells the Truth?: Collection of Logical Puzzles to Make You ThinkRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)