Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm A
Uploaded by
PremOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm A
Uploaded by
PremCopyright:
Available Formats
I
I
T
-
J
E
E
O
b
j
e
c
t
i
v
e
M
a
t
h
e
m
a
t
i
c
s
E
r
.
L
.
K
.
S
h
a
r
m
a
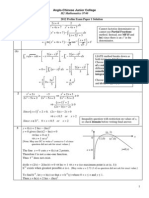
[176] Mathematics for I I T-J EE (Hints/Solutions)
1. Reflection of vertex point A about the perpendicular
bisector of AB represents the vertex B
and B C vertex points are (2 , 1) and (2 , 1)
Now
2 2 1
1
2 1 1
2
2 1 1
ABC
A =
Apply
2 2 3
R R R +
( )
1
2( 1 4)
2
A = +
3 A = Square units
2. Points A and B are (3 , 0) and (0 , 2) respectively
similarly , ( , 0) and (0, ) P a Q b
Now , locus of orthocentre of
ARB A
is same as that of
locus of R.
( ) BP AQ
As AB subtend on angle of 90 at R , locus of R circle
with AB as diameter
from figure , locus of 'R' is ( 3) ( 2) 0 x x y y + =
2 2
3 2 0 x y x y + =
3.
PQR A is equilateral and PS QR
1 4
cos30
15 5
l l = =
4. Minimum distance between lines 2 5 =
PQ is perpendicular to the given parallel lines
line PQ is
7 1
4 2
y
x
1
( 7) ( 4) 0
2
y x =
1
2
k = .
5. | | PA PB AB s
| | PA PB is maximum if A , P and B are
collinear
Let point 'P' be
1 2
,
3
| |
|
\ .
Slope of AB= slope of AP
1 2
0
2 0
3
0 2 2
+
+
=
7 =
is (7, 5) P
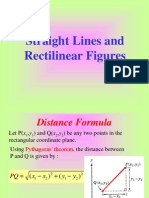
Chapter No -23 ( Straight Lines )
I
I
T
-
J
E
E
O
b
j
e
c
t
i
v
e
M
a
t
h
e
m
a
t
i
c
s
E
r
.
L
.
K
.
S
h
a
r
m
a
[177] Mathematics for I I T-J EE (Hints/Solutions)
6.
Let angle of inclination of variable line be
1 1
is ( cos , sin ) A r r
If A lies on
1 1
10, then ( sin ) ( cos ) 10 y x r r = + = +
1
10
(sin cos )
r
=
Similarly
2
20
(sin cos )
r
=
Let be , where cos and sin OP r r h r k = =
Now ,
2 1 1
OP OA OB
= +
1 2
2 1 1
r r r
= +
2 sin cos sin cos
10 20 r
= +
40 3 (sin ) 3 (cos ) r r =
3 3 40 k h =
Locus of P is 3y 3x =40
7. ( 2 ) ( 3 ) 0 p q x p q y p q + + + =
( 1) (2 3 1) 0 p x y q x y + + + =
( 1) (2 3 1) 0 x y x y + + + =
fixed point is
2 3
,
5 5
| |
|
\ .
8.
from figure , A , B , C and D are concylic points
( )( ) ( )( ) OA OC OB OD =
1 2
1 2
1 2
( )( )
C C
C C
m m
| || |
=
| |
\ .\ .
1 2
1 mm =
9.
from figure ,
2 2
( ) 6
r
OA r =
6 sum =
( 1)(2 1)
.
6
n n n + +
3 2
(2 3 ) n n n = + +
10.
2 2
(4 ) 0and (2 ) 0 a a a a > <
2 2
(4 )(2 ) 0 a a a a <
2
(4 )(2 ) 0 ( 4)( 2) 0 a a a a a < <
2 4 a < <
(2, 4) a e
11. Given lines are 1, 1
(1 ) (1 )
y x y x
p p q q
= =
+ +
and
0. y=
I
I
T
-
J
E
E
O
b
j
e
c
t
i
v
e
M
a
t
h
e
m
a
t
i
c
s
E
r
.
L
.
K
.
S
h
a
r
m
a
[178] Mathematics for I I T-J EE (Hints/Solutions)
Let the or thocentre be (h , k)
12.
for , ABC A maximumarea
1
( )
2 2
AC
AC
| |
=
|
\ .
max
1 5
(5)
2 2
| |
A =
|
\ .
=6.25 Square units.
If
6 ABC A =
Square units then four locations are
possible for point B. (As shown in figure)
13.
2 2; 4 2 AB BC = =
: 1: 2 AD DC =
5 14
point ,
3 3
D
| |
|
\ .
Equation of BD is
14
2
2 8
3
5
1
1
2
y
x
= =
+
+
8
1 =
3 y x = +
14.
from figure ,
1
tan
2
=
Let slope of line through (2 , 3) be m
1 2
2 1 2
m
m
+
=
|2 1| |2 4| m m = + ...(i)
2 1 2 4 m m =
3
4 3
4
m m = =
In equation (i) , if m then also it is satisfied
3
or
4
m =
3 1
2
y
x k
| |
=
|
\ .
4
or
3
k O =
15. Let slope of side BC be 'm' BC is equally inclined with
AB and AC
1 7
1 1 7
m m
m m
+
=
+
( 3)(3 1) 0 m m + =
1
3or
3
m =
Side BC can be given by :
10 1
3or
1 3
y
x
+
=
3 7 0or 3 31 0 y x y x + + = + =
I
I
T
-
J
E
E
O
b
j
e
c
t
i
v
e
M
a
t
h
e
m
a
t
i
c
s
E
r
.
L
.
K
.
S
h
a
r
m
a
[179] Mathematics for I I T-J EE (Hints/Solutions)
16. Let angle of inclination of L =0 be ' '
from figure ,
6 6
1 cos , 2 sin
3 3
Q
| |
+ +
|
|
\ .
As Q lies on the line x +y =4
( )
6
3 cos sin 4
3
+ + =
3
cos sin
6
+ =
3
sin
4 2
| |
+ =
|
\ .
15 or 75 =
17. 5 2 9 and 3 x y kx y + = + =
point of intersection
3 15 9
,
5 2 5 2
k
P
k k
| |
|
\ .
3
5 2k
=
If , 5 2 1or 3 I k e =
2, 3, 1, 4 k =
18. Lines (1) and (3) are parallel , hence k e
19.
2 2 2 2
( 4 ) ( 3 ) 0 x x y y + =
2 2
4 0 and 3 0 x x y y = =
0; 4 and 0, 3 x y = =
Vertices of rectangle ABCD can be given by :
(0, 0) , (0, 3) , (4, 0) and (4, 3)
Let line by
2
x
y C = +
( ) 2 , 0 and (6 2 , 3) Q C P C
Now area (AQPD)
1
(6 2 2 )(3)
2
C C =
3 1
(6 4 ) 6
2 2
C C = =
Required lineis 2 1 y x = +
20.
2 and 1
PQ
PQ m = =
Now , by parametric form of straight line ,
3 2
2
cos(105 ) sin(105 )
= =
2cos(105 ) 3 ; 2sin(105 ) 2 = + = +
1 3 3 1
3 ; 2
2 2 2 2
| | | |
= = + +
| |
| |
\ . \ .
7 3 5 3
2 2 16 3
2 2
| | | |
+
= = +
| |
| |
\ . \ .
21.
1 2 2 3 3 1
0 L L L L L L + + = ... (i)
(a) 0; 0 = =
1 2 3 1 1 2 3
0 ( ) 0 L L L L L L L + = + =
equation represent pair of lines.
(b) 0; 0 = =
Pair of lines
(c) equation represent circle for unique real value of
and , hence option
(d) is correct
22. If any two lines are parallel , then triangle is not formed
Now ,
1 2 3
5 1 3
, ;
2 3
m m m
= = =
3 5 6
2 5
= = ...(i)
or
3 1
9
3
= =
...(ii)
I
I
T
-
J
E
E
O
b
j
e
c
t
i
v
e
M
a
t
h
e
m
a
t
i
c
s
E
r
.
L
.
K
.
S
h
a
r
m
a
[180] Mathematics for I I T-J EE (Hints/Solutions)
If three lines are concurrent , then also triangle is not
formed
0 A =
5 2 12
1 3 5 0
3 1
=
5 =
6
5, 9, .
5
=
23.
24.
3 2 2
2 2 0 y x y y xy + =
2 2
( ) 2 ( ) 0 y y x y y x =
( )( 2) 0 y y x y x + =
Sides are given by 0, and 2 y y x x y = = + =
ABC A
is right-angled triangle
area of
1
(2)(1) 1
2
ABC A = = Square units.
Circumcentre of ABC A is (1 , 0)
Sides of ABC A are 2, 2 , 2
A is isosceles
25.
1 2 3
2
2 1
, and 1
2 5 7
p p
m m m
p p
= = =
If lines are parallel , then
1 2 3
m m m = =
2
2 1
1
2 5 7
p p
p p
= =
3 p =
If lines are concurrent , 0 A =
2
2 2 5 0
1 7 5 0
1 1 1
p p
p p
=
3 2
4 5 6 0 p p p + =
2
( 3)( 2) 0 p p p + =
3 p= is not applicable for concurrency ,
hence
2
2 0 p p + =
No value of p exist
26.
2 2 2
( ) (1 ) 0 y mx a m + =
2 2
1 and 1 y mx a m y mx a m = + + = +
...(i)
Similarly ,
2 2 2
( ) (1 ) 0 y nx a n + =
2 2
1 and 1 y nx a n y nx a m = + + = +
...(ii)
Equation (i) and (ii) represent parallel tangents to
circle
2 2 2
x y a + =
Equation (i) and (ii) form rohmbus but not a square
if 1 mn=
Statements (1) and (2) are true but the reasoning is not
correct.
27. 4 9 0 y kx k + =
9 4
, 0 (0, 9 4)
k
A and B k
k
+ | |
+
|
\ .
Now ,
9 4
9 4
k
OA OB k
k
+
+ = + +
4 4
9 9 4 13 9 k k
k k
= + + + = + +
( ) 13 2(6) OA OB + > +
min
( ) 25units OA OB + =
minimum area =2(9)(4) =72 Square units
Statement (1) and (2) are true but the reasoning in not
correct
28.
Let AM and BE meet at N.
Point 'E' is (2 , 2)
point 'M' is (1 , 1)
Now ,
4 1
3
0 1
AM
m
= =
and
2 0 1
2 4 3
BE
m
= =
+
( )( ) 1
AM BE
m m =
AM BE
Circles with EM and AB as diemeter touch each
other at N
Statements (1) and (2) are true and the reasoning is
correct.
I
I
T
-
J
E
E
O
b
j
e
c
t
i
v
e
M
a
t
h
e
m
a
t
i
c
s
E
r
.
L
.
K
.
S
h
a
r
m
a
[181] Mathematics for I I T-J EE (Hints/Solutions)
29.
2
4 9
1 1 1 0
2 3
m
m
=
2
13 30 0 m m + =
( 15)( 2) 0 m m + =
15or 2 m =
2 m=
is not applicable as it makes all the three lines
parallel and not concurrent
15 m =
is only applicable value for the
concurrency of three given lines
Statement (1) is true and statement (2) is false.
30.
In , tan
BD
BDC C
CD
A =
In , tan
BD
BDA A
AD
A =
: tan : tan CD AD C A =
: 3:1 CD AD =
Statements (1) and (2) are true and the reasoning is
also correct.
I
I
T
-
J
E
E
O
b
j
e
c
t
i
v
e
M
a
t
h
e
m
a
t
i
c
s
E
r
.
L
.
K
.
S
h
a
r
m
a
[182] Mathematics for I I T-J EE (Hints/Solutions)
1. ( ) ( ) 9 d OP d PQ + =
| | | | | 4| | 3| 9 x y x y + + + =
As 0; 0 x y > > is given , hence
| 4| | 3| 9 x y x y + =
4; 3 8
4; 3 4
4; 3 5
4; 3 No 'P' exists.
x y x y
x y y
x y x
x y
> > + =
< > =
`
> < =
< <
)
graph of the lines for different cases is shown in
figure.
Locus of point 'P' is union of 3 line segments of
the lines 4 0, 8and 5 0 y x y x = + = = .
2.
1 1 1
Area ( ) (1)(1) (4)(4)
2 2 2
ABC = A =
15
2
= Sq. units.
3. Pair of lines is ( 4)( 3) 0 x y =
4 and 3 x y = =
Triangle in consideration is right angled triangle
Circumcentre
9 7
,
2 2
| |
|
\ .
4. For given values of , and , the line can be
written as :
sin ( 4 2) cos (2 3) ( 1) 0 y x y x y x + + + =
(2 3) tan ( 4 2) 0 y x y x + + =
1 2
0 L L + =
the line passes through (1 , 2) as it satisfy the
line 1 0 y x = also
fixed point A is (1 , 2) which satisfy the curve of
option (d).
5. Let the line be ( 2) ( 1) y mx =
point 'P' is
2
1 , 2 and' ' Q
m
| |
|
\ .
is (0 , 2 m)
Now , area
( )
1 2
2
2
m
m
m
| |
=
|
\ .
1 4
4
2
m
m
| |
= +
|
\ .
(area) 4 (By ) AM GM > >
minimum area =4 square units.
6. (1 ) (1 ) (7 3 ) 0 y x + + + =
( 7) ( 3) 0 y x y x + + =
family of lines 'M' passes through (2 , 5)
Now , common member of L and M passes through the
points A (1 , 2) and (2 , 5)
2
3 3 1
1
y
y x
x
= =
I
I
T
-
J
E
E
O
b
j
e
c
t
i
v
e
M
a
t
h
e
m
a
t
i
c
s
E
r
.
L
.
K
.
S
h
a
r
m
a
[183] Mathematics for I I T-J EE (Hints/Solutions)
7.
1 2
( , ) and ( , )
2 2
y x y x
d P L d P L
+
= =
| | | | y x y x = +
0 xy =
8. Region 'R' is defined by
2 2 | | | | 4 2 y x y x s + + s
( ) ( )
2 2
area 4 2 2 2 =
24 = square units
9. Region 'R' is shown in the following graph.
from figure , point P is
( )
2 2 , 2 2 k and point Q
is
( )
2 , 2 k
1
(24)
3
PTS RUQ A A =
Now ,
( ) ( ) ( )
2
1 1
4 2 4 2 2 2 8
2 2
k k k =
( ) ( )
2 2
4 2 2 2 16 k k =
( )( )
6 2 2 2 2 16 k =
2 k =
10.
3 2 1 1 2 2
2 2 2 2 2 2
1
ax by c ax by c ax by c
a b a b a b
+ + + + + +
+ + =
+ + +
2 2
1 2 3 1 2 3
( ) ( ) (3) a x x x b y y y c a b + + + + + + = +
( ) { }
, (0, 0)
G G
x y
2 2
3c a b = +
now ,
1
2 2
2
2 2 2
2
9 3
a b
c a b
c
| |
+
= + =
|
|
\ .
11.
In , ABC A reflection of 'A' about the angular
bisectors lies on the side BC
' is ( 2, 1) and '' is (0, 3) A A
Equation of
BC
is
3 4
0 2
y
x
2 3 y x = +
( ) is (1, 5) and is 4, 5 B C
2 2
(5) (10) 5 5 BC = + =
5 P =
12.
Let
AQ
BQ
=
2 2
,
1 1
k k
Q
| |
|
|
+ +
\ .
equation of line PQ is given by
2 2
1
1 1
k k
y x
| | | |
=
| |
| |
+ +
\ . \ .
2
1
0,
1
P k
| | | |
| |
+
\ . \ .
Now , area of
1
2
APQ A =
2
2 2
2
0 1
1
1 1
1
0 1
1
k
k k
k
+ +
| |
|
+
\ .
I
I
T
-
J
E
E
O
b
j
e
c
t
i
v
e
M
a
t
h
e
m
a
t
i
c
s
E
r
.
L
.
K
.
S
h
a
r
m
a
[184] Mathematics for I I T-J EE (Hints/Solutions)
(vertices in anticlockwise direction gives +ve area).
4
2
( 1)
k
APQ
A =
+
As
( )
8
3
AOB APQ A = A
4
4 2
2
1 8
3 10 3 0
2 3 ( 1)
k
k
| |
= + =
|
|
+
\ .
Not applicable because
lies on +ve -axis
3or 1/3
P y
=
3
QA
QB
= =
13. , and PR PQ PS are in harmonic progression
2 1 1
PQ PR PS
= +
2 1 1
0.
PQ PR PS
| |
=
|
\ .
14.
Let points M and N be (0 , (0, ) and(0, ) )
respectively
0 6
0 6 6 6
k k
h h
= =
...(i)
Similarly ,
3
3
k
h
=
...(ii)
Now , equation of OP is
y k
x h
= and the equation of
QN is 1
3
x y
+ =
3 3
Point ' ' is ,
3 3
h k
T
h k h k
| |
|
+ +
\ .
from (i) and (ii) ,
6 6
,
6 6
h k
T
h h
| |
|
+ +
\ .
Equation of MT is given by :
( )
6 3
3
6 3
0
6
3
6
k k
k
h h
y x
h
h
h
| |
|
+
=
|
|
|
+ \ .
3
2 (2 )
3
k
y x
h
| |
=
|
\ .
3
(2 ) ( 2) 0
3
k
y x
h
| |
+ =
|
\ .
( ) (2 ) ( 2) 0 is variable y x + =
MT
passes through fixed point (2 , 0)
| | 2 p =
15. (a) Line
1
is (3cos ) (4sin ) 12 L x y + =
1 4 3
area
2 cos sin
| || |
=
| |
\ .\ .
12
sin2
=
minimum area =12 square units for sin2 1 =
(b)
1 7cos 7sin
2 4 3
| || |
A =
| |
\ .\ .
49
sin
48
=
max
1
1
48
A = Square units
(c)
2 2
16 9
cos sin
AB
= +
2 2
16sec 9cosec = +
2 2
(16tan 16) (9cot +9) = + +
2 2
16tan 9cot +25 = +
min
( ) 7units ( ) AB By AM GM = >
(d)
1 2
and L L meet at (4cos , 3sin )
(4cos 3sin ) + = +
( ) 5 + >
16. (a) 0 0, and 0 , p q r p q = + + = =
and r are not all equal
1 2 3
0 L L L + + =
1 2 3
, , L L L are concurrent
(b) 0and 0 = =
1 2 3
, , L L L form triangle
I
I
T
-
J
E
E
O
b
j
e
c
t
i
v
e
M
a
t
h
e
m
a
t
i
c
s
E
r
.
L
.
K
.
S
h
a
r
m
a
[185] Mathematics for I I T-J EE (Hints/Solutions)
(c) 0and 0 = =
0 p q r = = =
1 2 3
, , L L L represent 2-dimensional space
(d) 0 p q r = = =
1 2 3
, , L L L are identical
17. Apply the concept of number of common tangents for
two circles under different conditions
(a)
from figure , n =3
(b) n =4
(c) n =2
(d) n =1
You might also like
- Solutions Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems 5edDocument496 pagesSolutions Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems 5edRicardo Vega100% (6)
- Technical Drawing School-Based Assessment Booklet-Guide: Building/Td DepartmentDocument45 pagesTechnical Drawing School-Based Assessment Booklet-Guide: Building/Td DepartmentArisha NicholsNo ratings yet
- GRE Magoosh Practice Questions Gre Magoosh Practice QuestionsDocument10 pagesGRE Magoosh Practice Questions Gre Magoosh Practice Questionsmtglahsib0% (2)
- Coordinate GeometryDocument32 pagesCoordinate GeometrythinkiitNo ratings yet
- Technology 1º & 2º ESODocument131 pagesTechnology 1º & 2º ESOalmarpaNo ratings yet
- Aieee Paper 2008Document30 pagesAieee Paper 2008Ravi LorventNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Exercise 6.coordinate Geometry 2Document11 pagesExercise 6.coordinate Geometry 2Chean Siang LongNo ratings yet
- Horizons Math Sampler - Odyssey AcademyDocument64 pagesHorizons Math Sampler - Odyssey AcademyasdfghNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Form 5 Additional Maths NoteDocument10 pagesForm 5 Additional Maths NoteEric WongNo ratings yet
- SPM Notes & Formulae MathematicsDocument9 pagesSPM Notes & Formulae MathematicsPatrick PhuahNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument184 pagesLecture Notes On Statics of Rigid BodiesLeandro S. DaceraNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument12 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument10 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument5 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument8 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument7 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm AAnupam PathiNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Home Practice Test/Mathematics: Circles HWT - 1Document6 pagesSolutions To Home Practice Test/Mathematics: Circles HWT - 1varunkohliinNo ratings yet
- Three Dimensional Geometry: Coordinate of A Point in SpaceDocument35 pagesThree Dimensional Geometry: Coordinate of A Point in SpacethinkiitNo ratings yet
- R X y X y X y X yDocument9 pagesR X y X y X y X yVincentiusSetiawanBiandaruNo ratings yet
- 3 Dimensional Geometry PDFDocument8 pages3 Dimensional Geometry PDFManoj RedhuNo ratings yet
- Straight Lines and Rectilinear FiguresDocument40 pagesStraight Lines and Rectilinear FiguresChona Escoton AlcaydeNo ratings yet
- I Year Straight Lines Practice Paper 1Document4 pagesI Year Straight Lines Practice Paper 1Qims QuestNo ratings yet
- Exercise 11.3 Page No: 235: NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12 Mathematics Chapter 11: Three-Dimensional GeometryDocument14 pagesExercise 11.3 Page No: 235: NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12 Mathematics Chapter 11: Three-Dimensional GeometryDamsNo ratings yet
- Vector AlgebraDocument16 pagesVector AlgebrasudersanaviswanathanNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument8 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Iitjee2008 1Document23 pagesIitjee2008 1Lokesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 Graphing Techniques SolutionsDocument22 pagesTutorial 6 Graphing Techniques SolutionsLawrenceJGLimesaNo ratings yet
- Class Test Maths: Vidyamandir ClassesDocument3 pagesClass Test Maths: Vidyamandir ClassesKAPIL SHARMANo ratings yet
- RT Solutions-22!01!2012 XIII VXY Paper II Code A SolDocument16 pagesRT Solutions-22!01!2012 XIII VXY Paper II Code A Solvishal110085No ratings yet
- Straigth Line Theory - EDocument24 pagesStraigth Line Theory - EthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Narayana Grand Test - 8Document12 pagesNarayana Grand Test - 8Meet ShahNo ratings yet
- CIRCLEA Theory Solved Example IitjeeDocument11 pagesCIRCLEA Theory Solved Example IitjeeShashank ShekharNo ratings yet
- 2012 ACJC Prelim H2 Math SolnDocument15 pages2012 ACJC Prelim H2 Math Solnckhowh_23284524667% (3)
- Y X y X: Exercise 5A (P. 5.18) Level 1 1. (A) The Equation of The Circle IsDocument9 pagesY X y X: Exercise 5A (P. 5.18) Level 1 1. (A) The Equation of The Circle IsSiu Ming LeeNo ratings yet
- 2010 AJC Paper 2solDocument5 pages2010 AJC Paper 2solFang Wen LimNo ratings yet
- Anderson Sec 2010 AM Prelim - P2Document5 pagesAnderson Sec 2010 AM Prelim - P2math3matics3No ratings yet
- (Final) HSC-Maths Board Question Paper With SolutionsDocument11 pages(Final) HSC-Maths Board Question Paper With SolutionsNeeraj RamkumarNo ratings yet
- Answer Technique MM 2Document34 pagesAnswer Technique MM 2Lä HäNäNo ratings yet
- Ceramah Maths 2011Document9 pagesCeramah Maths 2011soon siew leeNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Paper SolutionDocument29 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Paper SolutionSantanuNo ratings yet
- Rvhs h2 Math p1 SolutionsDocument13 pagesRvhs h2 Math p1 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Add Maths SPMDocument21 pagesAdd Maths SPMPusat Tuisyen Siswa MudaNo ratings yet
- FIITJEE Solutions To: IIT - JEE - 2009Document10 pagesFIITJEE Solutions To: IIT - JEE - 2009gautham28No ratings yet
- Regional Mathematical Olympiad-2013: Time: 3 Hours December 15, 2013Document4 pagesRegional Mathematical Olympiad-2013: Time: 3 Hours December 15, 2013Surya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Part - Iii: Mathematics: JEE (ADVANCED) 2013-Paper 1-PCM-17Document9 pagesPart - Iii: Mathematics: JEE (ADVANCED) 2013-Paper 1-PCM-17Mohammed IqbalNo ratings yet
- Iit - Jee Model Grand Test - Ii Paper - 1 SolutionsDocument6 pagesIit - Jee Model Grand Test - Ii Paper - 1 SolutionsSayan Kumar KhanNo ratings yet
- Maths 06Document14 pagesMaths 06Kashish ManochaNo ratings yet
- Acjc h2 Math p2 SolutionsDocument8 pagesAcjc h2 Math p2 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Maths QE Teacher NotesDocument19 pagesMaths QE Teacher NotessashaankNo ratings yet
- IIT JEE Maths TopicWisePreviousQuestionsWithAnswersDocument13 pagesIIT JEE Maths TopicWisePreviousQuestionsWithAnswersUtsavKumarNaretiNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee: Solution To Aieee-2005Document23 pagesFiitjee: Solution To Aieee-2005Kainshk GuptaNo ratings yet
- Name: - Class: - Class No.Document4 pagesName: - Class: - Class No.okuyotasNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Home Practice Test/Mathematics: Straight Line HWT - 1Document5 pagesSolutions To Home Practice Test/Mathematics: Straight Line HWT - 1varunkohliinNo ratings yet
- MAM2085F 2013 Exam SolutionsDocument8 pagesMAM2085F 2013 Exam Solutionsmoro1992No ratings yet
- Answers and Explanations: CAT 2005 Actual PaperDocument12 pagesAnswers and Explanations: CAT 2005 Actual PaperRiya GujralNo ratings yet
- Iit Jee 2008 Paper 1Document23 pagesIit Jee 2008 Paper 1Sai NarendraNo ratings yet
- WBJEE 2014 Mathematics Question Paper With SolutionsDocument20 pagesWBJEE 2014 Mathematics Question Paper With SolutionsLokesh Kumar0% (2)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- 22Document4 pages22PremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument6 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument11 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- 31Document8 pages31PremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument9 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument7 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument8 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument9 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument6 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument8 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument6 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument10 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument9 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Megalite PDFDocument9 pagesMegalite PDFAnup SharmaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry EquationsDocument6 pagesTrigonometry EquationsPremNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Newton's Laws of MotionDocument13 pagesChapter 5 Newton's Laws of MotionPremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument7 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument7 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm AAnupam PathiNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument5 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- DocDocument1 pageDocPremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument10 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Books List PDFDocument4 pagesBooks List PDFRohit Kumar100% (2)
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument10 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument10 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Books For AIEEEDocument2 pagesBooks For AIEEEbanur2No ratings yet
- Mathematics Nine (9) Summative Assessment 9.4.3 I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The Correct Letter of Each ItemDocument3 pagesMathematics Nine (9) Summative Assessment 9.4.3 I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The Correct Letter of Each ItemGen-GenAlcantaraBaldadoNo ratings yet
- Fss Prelims Am p2 2009Document6 pagesFss Prelims Am p2 2009math3matics3No ratings yet
- The Art of Problem Solving Online Classes Introduction To Geometry Challenge Set 7Document7 pagesThe Art of Problem Solving Online Classes Introduction To Geometry Challenge Set 7Sara YeoNo ratings yet
- Wa0013.Document13 pagesWa0013.Nirmala DeviNo ratings yet
- 1st Summative 3rd Quarter in MathDocument2 pages1st Summative 3rd Quarter in MathRemore VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Connect: Pythagoras' Theorem: Study/Maths/Maths-A-To-Z/-/Maths - Glossary/Rid5/203/Right+Angled+TriangleDocument7 pagesConnect: Pythagoras' Theorem: Study/Maths/Maths-A-To-Z/-/Maths - Glossary/Rid5/203/Right+Angled+TriangleTalha AzanNo ratings yet
- Dayanand Anglo Vedic Public School, Airoli QUESTION BANK (SA-1) 2015-16 Class-Ix Sub - EnglishDocument18 pagesDayanand Anglo Vedic Public School, Airoli QUESTION BANK (SA-1) 2015-16 Class-Ix Sub - EnglishParth DevNo ratings yet
- Mathematical FinanceDocument13 pagesMathematical FinanceAlpsNo ratings yet
- Links To RememberDocument52 pagesLinks To Rememberjong bariquitNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry SyllabusDocument9 pagesTrigonometry SyllabusYAREN OZCANNo ratings yet
- 10 Mathbasic sp01Document19 pages10 Mathbasic sp01danielstabinNo ratings yet
- 10 Mathematics Sample Paper 13Document4 pages10 Mathematics Sample Paper 13Prashant ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Coordinate GeometryDocument29 pagesCoordinate Geometryinba673No ratings yet
- Exterior Angles of A Triangle PDFDocument2 pagesExterior Angles of A Triangle PDFSeanNo ratings yet
- What Is Angle Bisector TheoremDocument8 pagesWhat Is Angle Bisector TheoremTabish RozaanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 59-Routine and NonRoutine Problems in Real-Life Situations Involving PerimeterDocument40 pagesLesson 59-Routine and NonRoutine Problems in Real-Life Situations Involving Perimetermay bondocNo ratings yet
- F5B 2Document100 pagesF5B 2flora studyNo ratings yet
- Level 7 Technical Drawing Curriculum GuideDocument17 pagesLevel 7 Technical Drawing Curriculum GuideMary Rose Masinopa0% (1)
- Projection of Planes (CAED)Document5 pagesProjection of Planes (CAED)Akarsh manNo ratings yet
- Intermediate GeometryDocument16 pagesIntermediate GeometryD.SREEPRANAD 7a2020No ratings yet
- Application of Determinant To Determine The Area of PlaneDocument14 pagesApplication of Determinant To Determine The Area of PlanekanasaputrasNo ratings yet
- Ais TargetDocument6 pagesAis TargetwaicleeNo ratings yet
- What Is SymmetryDocument13 pagesWhat Is SymmetryMainul AbedinNo ratings yet
- 微臣GRE数学词汇2 0Document10 pages微臣GRE数学词汇2 0xueqiyao40No ratings yet
- Floor LoadDocument9 pagesFloor LoadAbhijit RanjanNo ratings yet