Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SCIENCE Form 3-Excretion
Uploaded by
graciezaynCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SCIENCE Form 3-Excretion
Uploaded by
graciezaynCopyright:
Available Formats
SCIENCE - FORM 3 EXCRETION
HUMAN EXCRETION A. Excretory Organs and Excretory Products
1. (a) Excretion is the process of removing waste products from the body. (b) The products are produced during metabolism that occurs in the body. 2. (a) The body cells absorb oxygen and digested food from the blood. (b) At the same time it gives out waste products like carbon dioxide, excess water and urea to the blood. 3. (a) These waste products, also known as excretory substances, are poisonous to the body and must be removed. (b) They are carried by the circulatory system to the excretory organs to be removed from the body.
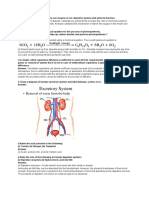
4. Excretion helps our body remove wastes to remain healthy. If wastes are not removed, toxic substances accumulate in the body. 5. The excretory organs in the human body are: (a) the skin (b) the lungs (c) the kidneys 6. Figure below shows the human excretory organs.
Human excretory organs Skin 1. Figure below shows the structure of the human skin.
Human skin as an excretory organ 2. We prespire through our skin and our perspiration or sweat is a solution of water, mineral salts and waste products. 3. (a) The skin structures involved in excretion consist of the capillaries, the sweat glands, the sweat ducts and the sweat pores. (b) Surrounding each sweat gland is a network of capillaries. 4. (a) When blood flows through the capillaries, waste products such as water,
urea and mineral salts are absorbed by the sweat glands. (b) These substances then pass through the sweat ducts and the sweat pores as sweat. (c) Finally, water in the sweat evaporates leaving mineral salts and a little urea on the skin. 5. Evaporation of the sweat helps to cool the skin and this helps to maintain the body temperature.
The 1. Figure below shows the structure of the
lungs human lungs. as carbon
2. During cells dioxide and water are
respiration, excretory produced.
substances
such
The lungs as excretory organs 3. The blood vessels carry the carbon dioxide and water from the body cells to the lungs. 4. These then diffuse out from the capillaries into the alveoli. 5. During exhalation, carbon dioxide and water vapour are expelled from the lungs when we breathe out. 6. Excretion of carbon dioxide and water can be represented as shown:
The kidneys 1. Figure below shows the human kidneys. 2. The kidneys are the principal organs of excretion. 3. They remove urea, uric acid, other nitrogenous substances, mineral salts and water from the body in the form of urine. This process is called urination.
4. Figure below shows the waster products excreted by the different excretory organs in our body and the processes involved.
B. The importance of Excretion
1. Excretory substances are produced during metabolism that occurs in our body. If these substances are allowed to accumulate, they endanger our health. 2. Carbon dioxide, urea and excess water are harmful to the body cells and must be removed. 3. Carbon dioxide dissolves in water to form an acid which will slow down many enzym reactions. A high concentration of this gas will also increase the breathing rate. 4. Urea is produced in the liver from excess amino acids in the body. It is a poisonous substance and will prevent enzyme reactions from taking place. 5. Excess water can cause a cell to swell and burst. Too much water in the body will also harm the lungs. 6. Bacteria thrives in dirty sweat and may cause boils or other skin diseases. So sweat must be created from the body. 7. Excretion maintains the chemical and water balance in the body. Excretion therefore regulates the blood concentration. 8. Sweating also controls the pH of body tissue fluids. It removes excess water and mineral salts. 9. The evaporation of sweat from the surface of the skin also helps to cool the body and this helps to maintain body temperature.
URINARY SYSTEM IN HUMANS
Figure 1: Human urinary system system in and female
Figure 2: Slide view of urinary males
1. The urinary system is part of the excretory system. 2. The urinary system consists of: (a) a pair of kidneys (b) a pair of ureters (c) a urinary bladder (d) urethra 3. The ureters are canals that connect the kidneys with the urinary bladder.
4. The ureters function to channel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. 5. The urinary bladder functions to store urine. When it is filled with urine, the urge to urinate is felt. 6. The urethra functions to channel urine from the urinary bladder out of the body. 7. The renal artery transports oxygenated blood to the kidneys while the renal vein transports deoxygenated blood away from the kidneys. 8. The blood carried by the renal artery to the kidney is filtered and excretory products are then eliminated from the blood as urine.
A. Human kidneys
Longitudinal section of the human kidneys 1. The kidneys are situated to the left and right back section of the abdominal cavity. 2. Human kidneys are dark red in colour and is bean-shaped. 3. The internal structure of the kidneys is divided into: (a) the outer part which is dark red in colour named cortex (b) the inner part which is light red in colour named medulla
4. The medulla is pyramid-shaped. 5. The kidney pelvis is the part where the ureter begins. 6. Functions of the kidney include: (a) eliminating excess water and mineral salts from the body (b) regulating the amount of water and mineral salts in the body (c) regulating the blood concentration (d) helping to remove nitrogenous substances like urea and ric acid from the body
B. The importance of maintaining a healthy kidney
Substance content in blood plasma compared to urine 1. Under normal conditions, substances like protein (amino acids) and glucose are not found in the urine. If glucose is found in the urine, it is most likely that the person has diabetes. 2. If the kidneys do not function properly, toxic substances in the blood will accumulate and this will lead to death. 3. The kidneys will function properly if we : (a) drink a lot of clean water (b) avoid drinking alcohol (c) reduce drinking gassy drinks (d) reduce eating food with high sugar content 4. If the kidneys of a person do not function properly or if they are damaged, that person must get treatment by taking medicine given by a doctor. 5. A patient with a serious kidney condition must receive kidney dialysis
treatment by using body.
a dialysis machine to remove toxic substances from the
6. In severe conditions, patients have to undergo kidney dialysis treatment three times a week.
EXCRETION IN PLANTS
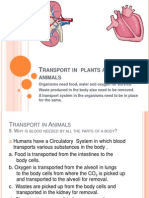
1. Plants do not have special excretory organs like humans. However, plants also need to excrete their waste products. 2. Plants have special processes for getting rid of waste products. 3. One of the ways plants excrete their waste products is by simple diffusion through their cell walls. 4. The main waste products formed in plants are water, carbon dioxide and oxygen. 5. Plants carry out two important processes. These are respiration and photosynthesis. (a) Respiration uses oxygen and produces carbon dioxide and water. Carbon dioxide and water are excretory products. (b) Photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide and water and produces oxygen and water and produces oxygen, which is a by-product. 6. Green plants make use of most of the waste products. 7. Water and carbon dioxide, produced during respiration, are used in photosynthesis. 8. Only a small quantity of the oxygen produced during photosynthesis is used up for respiration. 9. Most of the oxygen diffuses from the leaves into the air. 10. Water in the plants is obtained largely from the soil. Only a small percentage comes from respiration. 11. Any excess water in a plant is removed as water vapour during transpiration through the stomata on leaf surfaces. 12. The types and forms of minerals and nitrogenous products that are eliminated by plants are different from animals.
13. The excess minerals taken from the soil and not used up are stored in certain parts of the plant. They are removed as these parts die and drop off. 14. Plants also produce complex excretory substances in various forms. 15. (a) They include excretory substances such as oil, latex, gum, resin and tannin which are usually stored in different parts of the plant. (b) These plant parts may be the leaves, bark, stems, flowers, vacuoles and fruits. 16. When these parts drop off or die, the excretory substances in them will be removed. For example, calcium oxalate and calcium carbonate crystals are stored in the leaves and stems. These excretory substances are removed from the plant when the leaves drop off. 17. Volatile oil can be found on the petals of the flowers. This is removed through evaporation. 18. Latex, resin and gum are secreted by special cells or glands in the plant and then ooze out when these cells and glands are damaged. 19. Cinnamon, turpentine (from pine tree) and camphor are some examples of commercially important plant oils. 20. Table below shows the uses of plant excretory substances. 21. Some plant excretory products are dangerous and may cause a lot of harm. However is used correctly, these products can be very useful. (a) Morphine fromthe poppy fruit is used by doctors as a painkiller. (b) Nicotine from the tobacco keaves can also be used as a painkiller. (c) Cocaine from the coca plant is used as an anaesthetic. (d) Morphine, nicotine and cocaine are addictive drugs and are harmful if misused or abused. Drug abuse results in the loss of memory, reasoning ability and muscle coordination.
You might also like
- Microsoft Word Chapter 3 ExcretionDocument7 pagesMicrosoft Word Chapter 3 ExcretionSylvaen WswNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ExcretionDocument7 pagesChapter 3 ExcretionkumaravelloNo ratings yet
- EXCRETIONDocument15 pagesEXCRETIONbrianbanda248No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - ExcretionDocument3 pagesChapter 3 - ExcretionSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-01 06 Life Processes: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 5Document5 pagesCbse Test Paper-01 06 Life Processes: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 5Saurabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument2 pagesExcretionSD card 32 gbNo ratings yet
- Ch-8 Excretion in Animals & PlantsDocument4 pagesCh-8 Excretion in Animals & PlantsRonnith NandyNo ratings yet
- PT3 Science Chapter 20 ExcretionDocument4 pagesPT3 Science Chapter 20 ExcretionSpike ChingyenNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - ExcretionDocument4 pagesLife Processes - ExcretionRajvir tradaNo ratings yet
- Biology #10 Excretion and OsmoregulationDocument5 pagesBiology #10 Excretion and OsmoregulationAkili ArmaniNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Excretory System NotesDocument2 pagesGrade 7 Excretory System NotespriyagvspvNo ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument36 pagesExcretionMeet vermaNo ratings yet
- Urinary System 7th Grade Deliverable.Document5 pagesUrinary System 7th Grade Deliverable.ansofy354No ratings yet
- 4cnGrxPn7rJRk0JiEyPn PDFDocument5 pages4cnGrxPn7rJRk0JiEyPn PDFAbuzar AzharNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-01 06 Life ProcessesDocument5 pagesCbse Test Paper-01 06 Life ProcessesManoj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cbse LP RevisionDocument18 pagesCbse LP RevisionKanak ChhajerNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument25 pagesSCIENCEcharu.chughNo ratings yet
- Sistem Ekskresi ManusiaDocument2 pagesSistem Ekskresi ManusiaLena EnjelinaNo ratings yet
- Ch.11. Transportation in Animals and PlantsDocument3 pagesCh.11. Transportation in Animals and PlantsSharath ChandraNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Life Processes NCERT SolutionsDocument11 pagesCH 6 Life Processes NCERT Solutionsaalia hasanNo ratings yet
- Biology For Form II-IV NotesDocument28 pagesBiology For Form II-IV NotesChrispin MsofeNo ratings yet
- TransportDocument26 pagesTransportBhaskar MajumdarNo ratings yet
- Excretory System HoDocument4 pagesExcretory System HodoraNo ratings yet
- Biology M8 Integumentary & Excretory SystemsDocument23 pagesBiology M8 Integumentary & Excretory SystemsDiana Dealino-SabandalNo ratings yet
- 0610 Biology EXCRETIONDocument27 pages0610 Biology EXCRETIONMunir LakhaNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Chapter 3 - Excretion PDFDocument2 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 3 - Excretion PDFFarah Sofea Razali57% (7)
- Chapter 3: Excretion 3.1 Excretion in HumanDocument2 pagesChapter 3: Excretion 3.1 Excretion in HumanSiti UmairahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Excretion 3.1 Excretion in HumanDocument2 pagesChapter 3: Excretion 3.1 Excretion in Humanayulg2No ratings yet
- 6 Life ProcessesDocument39 pages6 Life ProcessesPrashant Sirohi50% (2)
- Excretion CIS VIIIDocument6 pagesExcretion CIS VIIIelizabethNo ratings yet
- Life Processes Notes Grade 10Document6 pagesLife Processes Notes Grade 10Danny BlessyNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Excretion 220705180056Document11 pagesPhysiology of Excretion 220705180056raulbharati013No ratings yet
- Bio Answers CH 1-5Document4 pagesBio Answers CH 1-5ROHAN 99No ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument7 pagesLife ProcesseskrithicktcrNo ratings yet
- CQ Class10 Bio Life Processes T1Document8 pagesCQ Class10 Bio Life Processes T1Tapas Banerjee100% (1)
- The Excretory System: by Group 1Document35 pagesThe Excretory System: by Group 1Gresia FalentinaNo ratings yet
- Excretion & Osmoregulation: 16. Highlights of This TopicDocument41 pagesExcretion & Osmoregulation: 16. Highlights of This TopicSAGAR PADALKARNo ratings yet
- Excretion & OsmoregulationDocument41 pagesExcretion & OsmoregulationSAGAR PADALKARNo ratings yet
- Excretion & OsmoregulationDocument35 pagesExcretion & OsmoregulationSAGAR PADALKARNo ratings yet
- Transportation in Animals and PlantsDocument3 pagesTransportation in Animals and Plantsravilulla100% (1)
- Excretion: The KidneysDocument7 pagesExcretion: The KidneysLulu BandaNo ratings yet
- 2021 12 03 VII Science 1Document5 pages2021 12 03 VII Science 1Daily Current affairsNo ratings yet
- EASE Module 8 The Integumentary and Excretory SystemsDocument24 pagesEASE Module 8 The Integumentary and Excretory SystemsPrescy Gonzaga100% (1)
- BYJU'S Learn Portal LoginDocument5 pagesBYJU'S Learn Portal LoginRohith ReddyNo ratings yet
- Excretion and Waste Management TestDocument5 pagesExcretion and Waste Management Testapi-635512040No ratings yet
- Life Processes: Difference Between Living and Non-LivingDocument5 pagesLife Processes: Difference Between Living and Non-LivingHarshil RastogiNo ratings yet
- Life ProoDocument6 pagesLife ProoItz me KARTIKKKNo ratings yet
- Al Wadi International School Biology Grade 9 13. Excretion in Humans NotesDocument42 pagesAl Wadi International School Biology Grade 9 13. Excretion in Humans NotesMohammed HelmyNo ratings yet
- UNIT 10 Excretion in Humans NotesDocument27 pagesUNIT 10 Excretion in Humans NotescyumadripNo ratings yet
- 6-Life ProcessesDocument39 pages6-Life ProcessesKaushal Solanke0% (1)
- Life ProcessesDocument7 pagesLife Processestasmitha98No ratings yet
- HSB Notes-15 May, 2020: The Testes As An Endocrine GlandDocument5 pagesHSB Notes-15 May, 2020: The Testes As An Endocrine GlandshaniaNo ratings yet
- 10 Biology WorksheetDocument2 pages10 Biology Worksheetranjan pataliNo ratings yet
- 1ST Term S3 BiologyDocument36 pages1ST Term S3 BiologyFaith Opadele100% (2)
- The 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksFrom EverandThe 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksNo ratings yet
- Kidney Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandKidney Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers HomeostasisFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers HomeostasisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Directed Number Form 2Document19 pagesDirected Number Form 2graciezaynNo ratings yet
- Coordinates Form 2Document17 pagesCoordinates Form 2graciezayn100% (1)
- Science Form 3 Chapter 1 - Respiration (Notes)Document4 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 1 - Respiration (Notes)Autumn JJ40% (5)
- Maths FractionDocument39 pagesMaths FractionSherlock Wesley ConanNo ratings yet
- Polygons Form 1Document38 pagesPolygons Form 1graciezaynNo ratings yet
- Solid Geometry Form 2Document18 pagesSolid Geometry Form 2graciezayn67% (3)
- Circles Form 2Document22 pagesCircles Form 2graciezayn100% (6)
- Percentage Form 1Document22 pagesPercentage Form 1graciezaynNo ratings yet
- Integers Form 1Document17 pagesIntegers Form 1graciezayn50% (2)
- Maths DecimalsDocument38 pagesMaths DecimalsSherlock Wesley ConanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics F1-Algebraic ExpressionsDocument5 pagesMathematics F1-Algebraic ExpressionsgraciezaynNo ratings yet
- Christine Campbell Thomson (Ed) - at Dead of Night (1931)Document256 pagesChristine Campbell Thomson (Ed) - at Dead of Night (1931)Gia MantovaniNo ratings yet
- Normal Menstrual Cycle The ProcessDocument6 pagesNormal Menstrual Cycle The ProcessBrett StevensonNo ratings yet
- Duck Production and Management StrategiesDocument665 pagesDuck Production and Management StrategiesCamila Andrea Ruge SánchezNo ratings yet
- Applications of Calcium and Its Supplement Derived From Marine OrganismsDocument8 pagesApplications of Calcium and Its Supplement Derived From Marine OrganismsDewi SariNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 1 ENGLISHDocument22 pagesSample Paper 1 ENGLISHDhawan ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- MushroomPlague HighQualityDocument22 pagesMushroomPlague HighQualityCaio CostaNo ratings yet
- 12 de Thi Thu Tieng Anh Co Dap AnDocument176 pages12 de Thi Thu Tieng Anh Co Dap Anhoa taphuancukuin2018No ratings yet
- Fibrous Dysplasia - PolyostoticDocument75 pagesFibrous Dysplasia - PolyostoticKush PathakNo ratings yet
- Development of Face &it's Applied AspectsDocument95 pagesDevelopment of Face &it's Applied AspectsHansa KunduNo ratings yet
- Anthrax 2012 ReportDocument6 pagesAnthrax 2012 ReportAko Gle C MarizNo ratings yet
- Leaps and Bounds: Question BankDocument19 pagesLeaps and Bounds: Question Banksarbani dewanjiNo ratings yet
- Selective Reading Sample Test QuestionsDocument12 pagesSelective Reading Sample Test QuestionsRagini Bajpai100% (2)
- Pop Q ReferenceDocument18 pagesPop Q ReferenceEdwin KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Schleich Knights MagazineDocument16 pagesSchleich Knights Magazinebananica28100% (1)
- Tensile Strength of FibersDocument26 pagesTensile Strength of FibersSandip Bakshi50% (2)
- Final Assessing Female and Male Genitourinary SystemDocument7 pagesFinal Assessing Female and Male Genitourinary SystemJo Marchianne PigarNo ratings yet
- History of Southern AfricaDocument117 pagesHistory of Southern AfricaBharatonNo ratings yet
- Grinnell JournalingDocument8 pagesGrinnell JournalingAnonymous vqO6zPNo ratings yet
- Sangkap NG MenudoDocument30 pagesSangkap NG MenudoNics GozunNo ratings yet
- Basic Horse TrainingDocument10 pagesBasic Horse TrainingMary Dixon100% (1)
- Uas GenapDocument10 pagesUas GenapDream32apNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesDigestive SystemAngelaOrosiaDenilaNo ratings yet
- Soluciones Del Simple Past or Present SimpleDocument4 pagesSoluciones Del Simple Past or Present SimpleVirginia Moreno Lopez0% (2)
- Globalization in FisheriesDocument7 pagesGlobalization in Fisheriesnylra MNo ratings yet
- Tortle VariantsDocument4 pagesTortle VariantsCarter RobinsonNo ratings yet
- 378310-Abyssal Incursion Printer FriendlyDocument25 pages378310-Abyssal Incursion Printer FriendlyOlimac BravoNo ratings yet
- 21,000 SecretsDocument9 pages21,000 SecretsHaley Claire GustafsonNo ratings yet
- FERTILIZATIONDocument180 pagesFERTILIZATIONPaul Kevin Mendoza67% (3)
- CAR Emergency Meeting On Dengue August 1, 2019Document41 pagesCAR Emergency Meeting On Dengue August 1, 2019Kenneth MarquezNo ratings yet
- The Cat of The Cane-BrakeDocument11 pagesThe Cat of The Cane-Brakepaunero1222No ratings yet