Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1
Uploaded by
latecircleOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Uploaded by
latecircleCopyright:
Available Formats
financial analisyst
Introduction
Dixon Corporation , a U .S .-based chemical company , is mulling on buying a plant from American Chemical Corp . American Chemical 's Collinsville plant makes sodium chlorate for the and pulp industry . Dixon will have to pay 12 million as purchase price for the plant . It may also pay 2 .25 million to complete the laminate technology developed by the plant 's research and development staff , which is expected to improve the plant 's efficiency Dixon already has transacted business with some of American Chemical 's major customers . Dixon , however , believes that
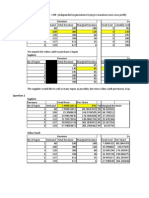
the acquisition will enable it to widen product lines and penetrate the and pulp industry Analysis To determine the economic feasibility of the acquisition , we can compute for the NPV of the acquisition , with or without the new technology . The NPV will show whether the Collinsville purchase will increase shareholder 's wealth or lead the company to insolvency . Under the net present value method , the weighted average cost of capital is used as the discount rate to calculate the present value of future cash inflows Hence , for the case study , we will compute for the WACC , prepare projected cash flows then compute the NPV Solution WACC The all-equity beta ) of Dixon is 1 .06 . We assume that we could have a beta of 1 .9 for the production of sodium chlorate , basing from the betas of other chemical firms . We could re-lever Dixon 's beta by using its 35 target capital structure . Using the formula ?levered equity ?all-equity [1 (1-t D /E] 1 .09 [1 (1-0 .48 0 .35 /0 .65] , we 'll have a ?levered of 1 .40 We compute for the WACC , the required rate of return for equity , using the Capital Asset Pricing Model . We use the 9 .5 yield on Treasury bonds , and the 8 .4 equity risk premium . Using the formula r rf ?leveredRP , we get 9 .5 1 .40 8 .4 21 .26 . We presuppose that the Dixon 's debt will solely be used for the Collinsville acquisition Assuming debt at 11 .25 , we can compute for the aftertax cost of debt as (1-0 .48 11 .25 equaling 5 .85
We can now compute for the weighted average of the costs of debt and equity funds , noting that target debt-to-equity ratio is 35 . The WACC using the formula WACC D /V After-tax cost of debt E /V Cost of equity 0 .35 5 .85 0 .65 21 .26 16 Cash Flow We use the historical cash flow for 1980 to 1984 , and projected cash flow for 1985 to 1989 , using this information -- Historical data will be used for property plant and equipment and depreciation costs -- Prices increase 8 annually -- Power expenditures increase 12 each year -- Net working capital is 9 of revenues -- we use the average figures for 1980 to 1984 to project other costs - non-power variable costs rate is 11 per year , selling expenses increase 7 , fixed cost increase 6 , R D expenses...
You might also like
- American Chemical CompanyDocument7 pagesAmerican Chemical Companycmarshall22340% (5)
- American Chemical Corporation Case StudyDocument11 pagesAmerican Chemical Corporation Case StudyRahul Pandey100% (6)
- Dixon's Purchase On Collinsville: The Victory of LaminateDocument9 pagesDixon's Purchase On Collinsville: The Victory of LaminateJing LuoNo ratings yet
- Shrieves Casting Company Chapter 12 (11ed-11) Cash Flow Estimation and Risk AnalysisDocument12 pagesShrieves Casting Company Chapter 12 (11ed-11) Cash Flow Estimation and Risk AnalysisHayat Omer Malik100% (1)
- American Chemical CorporationDocument5 pagesAmerican Chemical Corporationjlvaldesm100% (1)
- Sampa Video, Inc Case StudyDocument26 pagesSampa Video, Inc Case StudyFaradilla Karnesia100% (2)
- Aspeon Sparkling Water, Inc. Capital Structure Policy: Case 10Document16 pagesAspeon Sparkling Water, Inc. Capital Structure Policy: Case 10Alla LiNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Project Management (Fourth Edition)From EverandEarned Value Project Management (Fourth Edition)Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- Re-Evaluation of DNV Simplified Formulae For Crane Tip MotionsDocument10 pagesRe-Evaluation of DNV Simplified Formulae For Crane Tip Motionsguxiaom100% (1)
- Readable Elaine Kirn - Pamela Hartmenn, - 2009 - Interactions 1 - EnG 106 - 2020S - TEXTDocument256 pagesReadable Elaine Kirn - Pamela Hartmenn, - 2009 - Interactions 1 - EnG 106 - 2020S - TEXTle huy100% (1)
- Solutions Class Examples AFM2015Document36 pagesSolutions Class Examples AFM2015SherelleJiaxinLiNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting OverviewDocument31 pagesCapital Budgeting OverviewJomarTianesCorunoNo ratings yet
- Fin 612 Managerial Finance Week Six Assignment Your Assignment - CompressDocument3 pagesFin 612 Managerial Finance Week Six Assignment Your Assignment - CompressBala GNo ratings yet
- Case 14Document4 pagesCase 14Diksha MulaniNo ratings yet
- MIN 100 Investment Analysis: University of Stavanger E-MailDocument52 pagesMIN 100 Investment Analysis: University of Stavanger E-MailSonal Power UnlimitdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Cost of CapitalDocument52 pagesChapter 9 Cost of CapitalksachchuNo ratings yet
- TeamD WCA No1 Fall2014Document6 pagesTeamD WCA No1 Fall2014goldengirl2015No ratings yet
- ValuationDocument85 pagesValuationsamNo ratings yet
- WACCDocument30 pagesWACCIvan ChiuNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting and Valuation With Leverage: P.V. ViswanathDocument33 pagesCapital Budgeting and Valuation With Leverage: P.V. ViswanathAnonymous fjgmbzTNo ratings yet
- AmericanDocument4 pagesAmericanskull13No ratings yet
- American Chemical Corporation: Financial Analysis: June 2010Document9 pagesAmerican Chemical Corporation: Financial Analysis: June 2010BenNo ratings yet
- 13 American Chemical Corporation - Group 13Document5 pages13 American Chemical Corporation - Group 13Anonymous MpSSPQi0% (1)
- Acf302: Corporate Finance: Capital Budgeting and Valuation With Leverage - Part IDocument43 pagesAcf302: Corporate Finance: Capital Budgeting and Valuation With Leverage - Part IXue Meng LuNo ratings yet
- M12 Berk0821 04 Ism C12Document14 pagesM12 Berk0821 04 Ism C12Linda VoNo ratings yet
- Wacc NTDocument41 pagesWacc NTsachin2727No ratings yet
- Soalan FinanceDocument27 pagesSoalan FinanceNur Ain SyazwaniNo ratings yet
- American Chemical CorporationDocument8 pagesAmerican Chemical CorporationAnastasiaNo ratings yet
- The Weighted Average Cost of Capital and Company Valuation: Fundamentals of Corporate FinanceDocument30 pagesThe Weighted Average Cost of Capital and Company Valuation: Fundamentals of Corporate FinancedewimachfudNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3-ch12Document65 pagesLecture 3-ch12Linda VoNo ratings yet
- Sampa VideoDocument18 pagesSampa Videomilan979No ratings yet
- Quiz 3Document131 pagesQuiz 3afeeraNo ratings yet
- QUIZ3Document131 pagesQUIZ3Syed BakhtyarNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance PDFDocument56 pagesCorporate Finance PDFdevNo ratings yet
- ValuationDocument3 pagesValuationRendry Da Silva SantosNo ratings yet
- I5 Im10bDocument7 pagesI5 Im10btarick06No ratings yet
- FM414 LN 6 Master Copy Presentation Solutions - Valuation - 2024 ColorDocument16 pagesFM414 LN 6 Master Copy Presentation Solutions - Valuation - 2024 ColorAntonio AguiarNo ratings yet
- Ch13Document44 pagesCh13Vindy Artissya Ryzkha100% (1)
- Cost of CapitalDocument57 pagesCost of CapitalEmily Rose Zafe0% (1)
- Case Study 2 WriteupDocument7 pagesCase Study 2 Writeupapi-553175823No ratings yet
- Fin315 - Business Finance Chapter 10 and 11 NAME (PLEASE PRINT)Document8 pagesFin315 - Business Finance Chapter 10 and 11 NAME (PLEASE PRINT)Ryan Xuan0% (1)
- Business Finance Module Assignment.Document14 pagesBusiness Finance Module Assignment.Master's FameNo ratings yet
- AEF - CF - LECTURE - 4 Wacc Og TaxDocument32 pagesAEF - CF - LECTURE - 4 Wacc Og TaxFrederikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: NPV and Capital Budgeting: Assigned Problems Are 3, 7, 34, 36, and 41. Read Appendix ADocument8 pagesChapter 7: NPV and Capital Budgeting: Assigned Problems Are 3, 7, 34, 36, and 41. Read Appendix AmajorkonigNo ratings yet
- 11 FM 9Document9 pages11 FM 9asih359No ratings yet
- Cost of CapitalDocument16 pagesCost of CapitalRuchi SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Cost of CapitalDocument45 pagesThe Cost of CapitalBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)No ratings yet
- The Cost of Capital: Taufikur@ugm - Ac.idDocument31 pagesThe Cost of Capital: Taufikur@ugm - Ac.idNeneng WulandariNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument17 pagesUntitledEhab M. Abdel HadyNo ratings yet
- Week 12 Lecture SlidesDocument29 pagesWeek 12 Lecture Slidesnikoleta demosthenousNo ratings yet
- (123doc) - Testbank-Chap18-Corporate-Finance-By-Ross-10thDocument6 pages(123doc) - Testbank-Chap18-Corporate-Finance-By-Ross-10thHa Lien Vu KhanhNo ratings yet
- EFN406 Module 09 Notes 2022Document6 pagesEFN406 Module 09 Notes 2022zx zNo ratings yet
- Sample Problems - Principles of Corporate Finance Dec 2015Document26 pagesSample Problems - Principles of Corporate Finance Dec 2015ahmetdursun03100% (4)
- Technical Analysis N Cost of CapitalDocument29 pagesTechnical Analysis N Cost of CapitalMahbubur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Financing and Valuation: Principles of Corporate FinanceDocument19 pagesFinancing and Valuation: Principles of Corporate FinanceNar NarNo ratings yet
- Lockheed Tri Star and Capital Budgeting Case Analysis: ProfessorDocument8 pagesLockheed Tri Star and Capital Budgeting Case Analysis: ProfessorlicservernoidaNo ratings yet
- Summary Mankeu CH 14Document18 pagesSummary Mankeu CH 14Yoga Pratama Rizki FNo ratings yet
- Cost of Capital PPT at Bec Doms On FinanceDocument44 pagesCost of Capital PPT at Bec Doms On FinanceBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)No ratings yet
- Corporate Value Creation: An Operations Framework for Nonfinancial ManagersFrom EverandCorporate Value Creation: An Operations Framework for Nonfinancial ManagersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Applied Corporate Finance. What is a Company worth?From EverandApplied Corporate Finance. What is a Company worth?Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Avramov Etal MomentumDocument28 pagesAvramov Etal MomentumlatecircleNo ratings yet
- Data DrivenDocument1 pageData DrivenlatecircleNo ratings yet
- Baba Packer Interest ParityDocument22 pagesBaba Packer Interest ParitylatecircleNo ratings yet
- T R A F: He Oad Head For The EdDocument15 pagesT R A F: He Oad Head For The EdlatecircleNo ratings yet
- Case 7 PetrozuataDocument13 pagesCase 7 PetrozuatalatecircleNo ratings yet
- Time Series Momentum - Journal of Financial Economics 2012Document23 pagesTime Series Momentum - Journal of Financial Economics 2012Absolute ReturnNo ratings yet
- Northwestern University J.L. Kellogg Graduate School of ManagementDocument52 pagesNorthwestern University J.L. Kellogg Graduate School of ManagementlatecircleNo ratings yet
- Northwestern University J.L. Kellogg Graduate School of ManagementDocument24 pagesNorthwestern University J.L. Kellogg Graduate School of ManagementChura HariNo ratings yet
- Solver To Solve Video VaultDocument2 pagesSolver To Solve Video VaultlatecircleNo ratings yet
- Boehmer Jones Zhang ShortsDocument37 pagesBoehmer Jones Zhang ShortslatecircleNo ratings yet
- Brunnermeier MKT Fun LiquidityDocument38 pagesBrunnermeier MKT Fun Liquidityfreemind3682No ratings yet
- ShortbtmDocument46 pagesShortbtmlatecircleNo ratings yet
- Solver To Solve Video VaultDocument2 pagesSolver To Solve Video VaultlatecircleNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain NotesDocument2 pagesSupply Chain NoteslatecircleNo ratings yet
- Solver To Solve Video VaultDocument2 pagesSolver To Solve Video VaultlatecircleNo ratings yet
- Weissss TemplateDocument9 pagesWeissss TemplatelatecircleNo ratings yet
- Woodford Rules Jackson Hole WyomingDocument97 pagesWoodford Rules Jackson Hole WyominglatecircleNo ratings yet
- Port OptimisationDocument64 pagesPort OptimisationlatecircleNo ratings yet
- Self Incompatibility: Dr. L.K.GangwarDocument38 pagesSelf Incompatibility: Dr. L.K.GangwarSiddhant Singh100% (1)
- Euler - Concerning The Shortest Line On Any SurfaceDocument16 pagesEuler - Concerning The Shortest Line On Any Surfacegromit9999No ratings yet
- Visual Development Milestones and Visual Acuity Assessment in ChildrenDocument2 pagesVisual Development Milestones and Visual Acuity Assessment in ChildrenNikhil Maha DevanNo ratings yet
- Case MyelitisDocument34 pagesCase Myelitisyolanda nurlizaNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document3 pagesWeek 1Markdel John EspinoNo ratings yet
- Contact ListDocument3 pagesContact Listapi-468161460No ratings yet
- Narrative Report On Brigada Eskwela Jingle 2020Document1 pageNarrative Report On Brigada Eskwela Jingle 2020MARICEL CAINGLESNo ratings yet
- Pain Assessment AND Management: Mr. Swapnil Wanjari Clinical InstructorDocument27 pagesPain Assessment AND Management: Mr. Swapnil Wanjari Clinical InstructorSWAPNIL WANJARINo ratings yet
- Culture Shock Refers To The Feelings of Confusion and Uncertainty That You Experience When You Come Into Contact With A New CultureDocument13 pagesCulture Shock Refers To The Feelings of Confusion and Uncertainty That You Experience When You Come Into Contact With A New CultureRetno WulanNo ratings yet
- Volt Am Metric Determination of Ascorbic Acid in Vitamin C SupplementsDocument2 pagesVolt Am Metric Determination of Ascorbic Acid in Vitamin C SupplementshebieNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Rainfall and Temperature Variability To Guide Sorghum (Sorghum Bicolar) Production in Maitsebri District, Northwestern Tigray, EthiopiaDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Rainfall and Temperature Variability To Guide Sorghum (Sorghum Bicolar) Production in Maitsebri District, Northwestern Tigray, EthiopiafffNo ratings yet
- HM3 ChaosHallsDocument36 pagesHM3 ChaosHallsBrady Mcghee100% (2)
- Customer Communication.Document3 pagesCustomer Communication.wilson wambuguNo ratings yet
- SU05Document114 pagesSU05saopaulo100% (1)
- The Impact of Dementia On The ClinicalDocument8 pagesThe Impact of Dementia On The ClinicalihsansabridrNo ratings yet
- RR 1116Document72 pagesRR 1116Кирилл КрыловNo ratings yet
- Past Simple PDFDocument4 pagesPast Simple PDFderlinNo ratings yet
- Corrective Action Report (CAR) : Form1001 CAR-KMR - e Page 1 of 1 Revision: 6 Reference: Organizational Instruction 8.5.01Document1 pageCorrective Action Report (CAR) : Form1001 CAR-KMR - e Page 1 of 1 Revision: 6 Reference: Organizational Instruction 8.5.01JOECOOL67No ratings yet
- Sagittarius The HeroDocument2 pagesSagittarius The HeroСтеди Транслейшънс0% (1)
- Junto, Brian Cesar S.Document1 pageJunto, Brian Cesar S.Brian Cesar JuntoNo ratings yet
- National Social Protection Strategy GhanaDocument95 pagesNational Social Protection Strategy GhanaSisiraPinnawalaNo ratings yet
- 4 5 and 6 - Approaches To HR MeasurementDocument14 pages4 5 and 6 - Approaches To HR MeasurementRahul RaoNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter-Alexis ReedDocument1 pageCover Letter-Alexis Reedapi-252291947No ratings yet
- Journal of Cognitive Liberties׃ Vol. 4, No. 2 (2003)Document97 pagesJournal of Cognitive Liberties׃ Vol. 4, No. 2 (2003)HoorayFrisbeeHeadNo ratings yet
- Buad 306 HW 2Document4 pagesBuad 306 HW 2AustinNo ratings yet
- American Colonial Empire - Julian GoDocument6 pagesAmerican Colonial Empire - Julian GoBert M DronaNo ratings yet
- y D Starter PDFDocument13 pagesy D Starter PDFnazar750No ratings yet
- Take Home Assignment 2Document2 pagesTake Home Assignment 2Kriti DaftariNo ratings yet