Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Final 091002
Uploaded by
kalidass88Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Final 091002
Uploaded by
kalidass88Copyright:
Available Formats
SEE2043
Q1.
Figure Q1(a)
(a) Given signal g(t) as in Figure Q1(a), graph the functions below :
(i).
) ( t g
(ii).
) (t g
(iii).
) 2 ( t g
(iv).
) 2 2 ( + t g
(v).
) 2 5 . 0 ( + t g
(vi).
) 1 ( ) 2 2 ( 5 . 0 + + t u t g
(6 marks)
(b) Convolution process is very important in communication system. Given
two signals as below:
2
g(t)
-3
t
3
-1
1
SEE2043
) 9 ( 2 ) 7 ( 2 2
4
3 ) ( +
,
_
t u t u
t
rect t x
and
) ( ) 1 ( 2 ) 2 ( 3 ) ( t u t u t u t h + +
Determine the output of the convolution between those two signals.
(10 marks)
(c) Figure Q1(b) shows the signal of
) (t y
. Determine:
(i). The general form of exponent Fourier series of the signal
) (t y
in
Figure Q1(b) (2 marks)
(ii). Find the exponent Fourier series for the signal in Figure Q1(c).
(7 marks)
3
) (t y
6
-1 -2 1 2
Figure Q1(b)
) (t y
t
SEE2043
4
-1 -2 1 2
-4
Figure Q1(c)
t
SEE2043
Q2 (a) Obtain the Fourier Transform for the following time domain signal.
Figure Q2(a)
(4 marks)
(b) A Linear Time Invariant (LTI) system used in valve control is shown in
the Figure Q2(b). The system is said to be injected with the input signal of
) 5 ( sin
5
) ( t c t x
. It was noted that the feedback signal,
Obtain:
(i) The Fourier transform of the input signal (3 marks)
(ii) The Fourier transform of the output signal.
(4 marks)
Figure Q2(b)
5
h
1
(t)
x(t) y(t)
(t)
SEE2043
(c) An ideal filter block diagram, which is assumed to be an LTI system is
shown in Figure Q2(c). The filtered signal of Y() is shown. If the
injected signal of
:
(i) Determine and plot the output of the mixer, E().
(4 marks)
(ii) Determine the specification of the filter transfer function,
H() and oscillator frequency,
o
in order to obtain the filtered
signal of y(t). Plot the output of the receivers mixer, F().
(10 marks)
6
H()
cos 100t cos
o
t
Figure Q2(c)
y(t) x(t)
E() F()
Transmitter
Receiver
Y()
6
59 60
SEE2043
Q3 (a) (i) Explain briefly the advantage of using laplace transform in solving
electrical engineering problems.
(2 marks)
(ii) What is the difference between laplace transform and fourier transform
in terms of their applications.
(2 marks)
x(t) h(t) y(t)
Figure Q3(a)
(b) The block diagram in Figure Q3(a) shows a system with ) ( ) (
2
t u e t h
t
and the input signal
) 3 ( ) ( ) ( t u t u t x
(i). Determine the laplace transform of signal
) (t x
and
) (t h
(2 marks)
(ii) By using the properties of laplace transform, obtain the
mathematical expression of signal
) (t y
.
(5 marks)
R1=10ohm
R2=3ohm
R3=7ohm
C=0.125F
s
L=2H
Vs=10volt
Figure Q3(b)
7
SEE2043
(c) An electrical circuit in Figure Q3(b) consisting of resistor R1 and R2, an
inductor L, a capacitor C and a voltage source
) (t v
. The switch is closed
for a long time before it is opened at s t 0 .
(i). Find the voltage across the capacitor and the current through the
inductor when the switch is closed for a long time
(4marks)
(ii). Sketch the electrical circuit by expressing the variables in laplace
transform when the switch is opened
(2marks)
(iii). Obtain the expression of the voltage across resistor R2, ) (
2
t V
R
when
the switch is opened.
(6 marks)
(iv). Determine the voltage across resistor R2 at time, s t 2
(2 marks)
8
SEE2043
Q4. (a) Given the transfer function of a network is
128 24
350 35
) (
2
2
+ +
+
s s
s
s H
(i) What are the constant term means for and the value? (2 marks)
(ii) Sketch the magnitude and phase Bode plots for the above transfer
function.
(6 marks)
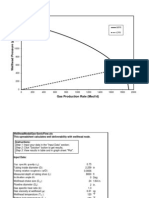
(b) Figure Q4 shows the magnitude frequency response of a low pass filter.
(i) Derive the transfer function of that filter. (9
marks)
(ii) By using suitable transformation, derive the transfer function of a high
pass filter from the transfer function obtained from question (b)(i).
(4 marks)
(iii) Explain your understanding on the damping factor,
effect in second
order low pass filter design. (2 marks)
(iv) What would happen to the amplitude response of the lowpass filter if
let say reduced by 15%. (2 marks)
Figure Q4
9
18.56
12
6.06 7.66
-
40dB/dec
9.0
Magnitude
H
(dB)
Actual Response
Asymptote
SEE2043
Q5. (a) Sketch a typical frequency response of the normalized Chebyshev low
pass filter. Please show clearly the maximum pass band frequency, the
minimum stop band frequency, maximum gain at the pass band, maximum
gain at the stop band, and ripple.
(6 marks)
(b) What is the difference between the frequency response of this filter with
the Butterworth filter.
(2 marks)
(c) You are required to design a Chebyshev filter. If 1
MAX
A ,
s rad
S
/ 844 . 1
, and
dB
S
20
, what is the required order of the
filter?
(4 marks)
(d) Obtain the normalized transfer function, H
n
(s), of the filter.
(3 marks)
(e) What is the actual transfer function of the filter, H(s), if the
s rad
P
/ 20 .
(3 marks)
(f) Obtain the Chebyshev circuit and clearly indicate the value of each
component in the circuit if the resistance at the load is given as 1000 and
s rad
C
/ 10
.
(7 marks)
10
SEE2043
LAMPIRAN ( APPENDIX )
F: MEREKABENTUK PENAPIS ANALOG
(Analog Filter Design)
CHEBYSHEV
( )
2
2
max
1 log 10
1
1
log 20 log 20
,
_
+
A A
,
1 10
10
max
A
( )
2
1
10 10
1
1
1 10 1 10 cosh
cosh
1
max
1
1
]
1
,
_
,
_
A
sn
s
n
,
_
,
_
1
cosh
1
cosh
1
n
p c
0 1
1
1
.... ) (
) (
a s a s a s
K
s T
K
s H
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
+ + + +
'
) ( ;
10
1
) ( ;
20
0
2
0
0
max
even genap n
a a
odd ganjil n a
K
A
n
BUTTERWORTH
n
c
j H
2
1
1
) (
,
_
,
1 ....
1
) (
1
) (
1
1
1
+ + + +
s a s a s s B
s H
n
n
n
n
n
1
1
]
1
,
_
+
n
c
j H
2
10
1 log 10 ) ( log 20
1
1
]
1
,
_
+
n
c
p
p
2
1 log 10
,
1
1
]
1
,
_
+
n
c
s
s
2
1 log 10
1 10
10
2
,
_
p
n
c
p
, 1 10
10
2
,
_
s
n
c
s
,
1
]
1
,
_
1 10
1 10
10
10
2
p
s
n
p
s
11
SEE2043
( ) [ ]
( )
sn
p s
n
log 2
1 10 1 10 log
10 10
[ ]
n
p
c
p
2 1
10
1 10
atau
[ ]
n
s
c
s
2 1
10
1 10
Jadual F.1: Pengiraan frekuensi sudut jalur henti ternormal,
sn
.
(Calculations of normalized stopband angle frequency)
Jenis penapis
(Types of filters)
Frekuensi sudut jalur henti ternormal,
sn
(Normalized stopband angle frequency)
Penapis lulus rendah, LPF
(Low Pass Filter)
p
s
Penapis lulus tinggi, HPF
(High Pass Filter)
s
p
Penapis lulus jalur, BPF
(Band Pass Filter)
( )
1 2 1
2
1 2 1
p p s
s p p
atau(or)
( )
1 2 2
2 1
2
2
p p s
p p s
, pilih yang lebih kecil
(choose smaller value)
Penapis jalur henti, BSF
(Band Stop Filter)
( )
2
1 2 1
1 2 1
s p p
p p s
atau(or)
( )
2 1
2
2
1 2 2
p p s
p p s
, pilih yang lebih kecil
(choose smaller value)
12
SEE2043
Jadual F.4: Pekali penapis Chebyshev untuk A
max
0.5, 1, 2 dan 3 dB.
(Coefficients of Chebychev filter for A
max
0.5, 1, 2 dan 3 dB)
n a
0
a
1
a
2
a
3
a
4
a
5
a
6
1 2.8627 0.5 db ripple
2 1.5162 1.4256
3 0.7156 1.5348 1.2529
4 0.3790 1.0254 1.7168 1.1973
5 0.1789 0.7525 1.3095 1.9373 1.172
6 0.0947 0.4323 1.1718 1.589 2.1718 1.159
7 0.044 0.2820 0.7556 1.6479 1.869 2.4126 1.1512
n a
0
a
1
a
2
a
3
a
4
a
5
a
6
1 1.9652 1 db ripple
2 1.1025 1.0977
3 0.4913 1.2384 0.9883
4 0.2756 0.7426 1.4539 0.9528
5 0.1228 0.5805 0.9743 1.6888 0.9368
6 0.0689 0.3070 0.9393 1.2021 1.9308 0.9282
7 0.0307 0.2136 0.5486 1.3575 1.4287 2.1760 0.9231
n a
0
a
1
a
2
a
3
a
4
a
5
a
6
1 1.3075 2 db ripple
2 0.8230 0.8038
3 0.3268 1.0221 0.7378
4 0.2057 0.5167 1.2564 0.7162
5 0.0817 0.4593 0.6934 1.4995 0.7064
6 0.0514 0.2102 0.7714 0.8670 1.7458 0.7012
7 0.0204 0.1660 0.3825 1.1444 1.0392 1.9935 0.6978
n a
0
a
1
a
2
a
3
a
4
a
5
a
6
1 1.0023 3 db ripple
2 0.7079 0.6448
3 0.2505 0.9283 0.5972
4 0.1769 0.4047 1.1691 0.5815
5 0.0626 0.4079 0.5488 1.4149 0.5744
6 0.0442 0.1634 69909 69060 1.6628 0.5706
7 0.0156 0.1461 0.3000 1.0518 0.8314 1.9115 0.5684
13
SEE2043
Jadual F.5: Transformasi frekuensi penapis
(Frequency Transformations of filter)
Jenis penapis
(Types of filters)
Transformasi
(Transformation)
Penapis lulus rendah, LPF
(Low Pass Filter)
p
s
, ( h Butterwort bagi ,
c
s
)
Penapis lulus tinggi, HPF
(High Pass Filter)
s
p
, ( h Butterwort bagi ,
s
c
)
Penapis lulus jalur, BPF
(Band Pass Filter)
( ) s
s
p p
p p
1 2
2 1
2
+
Penapis jalur henti, BSF
(Band Stop Filter)
( )
2 1
2
1 2
p p
p p
s
s
+
Jadual F.6(a): Pekali-pekali Polinomial Butterworth B
n
(s) = s
n
+a
n-1
s
n-1
+..+a
1
s+1
(Coefficients of Butterworth Polynomials)
n a
1
a
2
a
3
a
4
a
5
a
6
a
7
a
8
a
9
2 1.4142
3 2.0000 2.0000
4 2.6131 3.4142 2.6131
5 3.2360 6.2360 6.2360 3.2360
6 3.8637 7.4641 9.1416 7.4641 3.8637
7 4.4939 10.0978 14.5917 14.5917 10.0978 4.4939
8 6.1258 13.1370 21.8461 26.6883 21.8461 13.1370 6.1258
9 6.7587 16.5817 31.1634 41.9863 41.9863 31.1634 16.5817 6.7587
10 6.3924 20.4317 42/8020 64.8823 74.2334 64.8823 42.8020 20.4317 6.3924
Jadual F.6(b): Polinomial Butterworth dalam bentuk pemfaktoran Butterworth
(Butterworth Polynomials in Factorized Form)
n B
n
(s)
1 s + 1
2 s
2
+ 1.41421356s + 1
3 (s + 1) (s
2
+ s + 1)
4 (s
2
+ 0.76536686s + 1) (s
2
+ 1.84775907s + 1
5 (s + 1) (s
2
+ 0.61803399s + 1) (s
2
+ 1.931803399s + 1)
6 (s
2
+ 0.51763809s + 1) (s
2
+ 1.41421356s + 1) (s
2
+ 1.93185165s + 1)
7 (s + 1) (s
2
+ 0.44504187s + 1) (s
2
+ 1.24697960s + 1) (s
2
+ 1.80193774s + 1)
8 (s
2
+ 0.39018064s + 1) (s
2
+ 1.11114047s + 1) (s
2
+ 1.66293922s + 1) (s
2
+ 1.96157056s + 1)
9 (s + 1) (s
2
+ 0.34729636s + 1) (s
2
+ s + 1) (s
2
+ 1.53208889s + 1) (s
2
+ 1.87938524s + 1)
10 (s
2
+ 0.31286893s + 1) (s
2
+ 0.90798100s + 1) (s
2
+ 1.41421356s + 1) (s
2
+ 1.78201305s + 1)
(s
2
+ 1.97537668s + 1)
14
You might also like
- (Ebook) Mechanics of Machines Cleghorn) AnswersDocument23 pages(Ebook) Mechanics of Machines Cleghorn) AnswersWaqas Amjad25% (8)
- Mechanics of Machines Cleghorn AnswersDocument23 pagesMechanics of Machines Cleghorn AnswersAndrew Arnold67% (3)
- Sample Filter CalculationDocument20 pagesSample Filter CalculationAbraham JyothimonNo ratings yet
- 1982 - Holographic Antenna Measurements Further Technical ConsiderationsDocument20 pages1982 - Holographic Antenna Measurements Further Technical Considerationszan wang100% (1)
- Calculation of Pressure Traverse Using Beggs and BrillDocument29 pagesCalculation of Pressure Traverse Using Beggs and BrillOba Fred Ajubolaka88% (8)
- Calculator Techniques RedefinedDocument55 pagesCalculator Techniques RedefinedJholo Bucton94% (16)
- WellheadNodalGas SonicFlowDocument7 pagesWellheadNodalGas SonicFlowthe_soldier_15_1No ratings yet
- A Unified Approach To The Design, Measurement, and Tuning of Coupled-Resonator FiltersDocument9 pagesA Unified Approach To The Design, Measurement, and Tuning of Coupled-Resonator Filtersmountainmn45No ratings yet
- ST - Anne'S: Multiple Choice Questions UNIT-2 (50X1 50 Marks)Document6 pagesST - Anne'S: Multiple Choice Questions UNIT-2 (50X1 50 Marks)St. Anne's CET (EEE Department)No ratings yet
- Ministry of Education Yangon Technological University Department of Electronic EngineeringDocument23 pagesMinistry of Education Yangon Technological University Department of Electronic Engineeringmw ccNo ratings yet
- Filt RosDocument15 pagesFilt RosTadeu FelixNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 PDFDocument34 pagesChapter 6 PDFPhan Phuong NgocNo ratings yet
- DSP QuestionsDocument8 pagesDSP Questionsjjshree79No ratings yet
- COMM 602: Digital Signal ProcessingDocument32 pagesCOMM 602: Digital Signal ProcessingMohamed YaseenNo ratings yet
- W9 - Lab 5 - Resonant Filters - 2021Document7 pagesW9 - Lab 5 - Resonant Filters - 2021VenkateshPatnalaNo ratings yet
- Digital State-Variable Filters: 1 Normalized Second-Order Continuous-Time Lowpass FilterDocument9 pagesDigital State-Variable Filters: 1 Normalized Second-Order Continuous-Time Lowpass FilterJennifer WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: Subject Code: Subject NameDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank: Subject Code: Subject NamemsurendiranNo ratings yet
- Filter Design 1Document31 pagesFilter Design 1sadyehclenNo ratings yet
- 2020 FinalDocument3 pages2020 FinalBen ChouNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 SolutionDocument5 pagesTutorial 3 SolutionMuhanad OfficerNo ratings yet
- IgbtDocument9 pagesIgbtKarthikrajan SendhilnathanNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Laboratory: Hamza OSAMA &haider Jamal&salah MahdiDocument27 pagesControl Systems Laboratory: Hamza OSAMA &haider Jamal&salah MahdiAhmed Mohammed khalfNo ratings yet
- Fi̇nal Çözümleri̇Document6 pagesFi̇nal Çözümleri̇ERCAN ÖZERDENNo ratings yet
- GP1A70R/GP1A71R: OPIC Photointerrupter With Encoder FunctionsDocument6 pagesGP1A70R/GP1A71R: OPIC Photointerrupter With Encoder FunctionsToai NguyenNo ratings yet
- Selected Solutions 9780123850591Document14 pagesSelected Solutions 9780123850591Coco SosoNo ratings yet
- Gate 23-09-2013Document7 pagesGate 23-09-2013Himanshu VasisthaNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal ProcessingDocument7 pagesDigital Signal ProcessingJagadeesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal ProcessingDocument7 pagesDigital Signal ProcessingAhsan MalikNo ratings yet
- Ee115hw+sol03 06 N PDFDocument6 pagesEe115hw+sol03 06 N PDFthinkberry22100% (1)
- Chapter 8 ProblemsDocument21 pagesChapter 8 Problemskhrid3100% (2)
- Lab 7 - Digital Filter On ArduinoDocument8 pagesLab 7 - Digital Filter On ArduinoIsmael RomeroNo ratings yet
- Question 09 10Document5 pagesQuestion 09 10Pc NgNo ratings yet
- Well Head NodalDocument7 pagesWell Head Nodalmath62210No ratings yet
- EE 164 Problem Set 5 SolutionDocument2 pagesEE 164 Problem Set 5 SolutionnenasukaNo ratings yet
- Ex Signal and SystemDocument25 pagesEx Signal and SystemNguyen Van HaiNo ratings yet
- Cusat DSP Question PaperDocument14 pagesCusat DSP Question PaperSabith PockerNo ratings yet
- D12se4 ExtcDocument10 pagesD12se4 ExtcNikhil HosurNo ratings yet
- Equalizer Design ExampleDocument10 pagesEqualizer Design ExamplehaimanhptitNo ratings yet
- Diseño Filtro ButterworthDocument6 pagesDiseño Filtro ButterworthPablo ObesoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Paper II - IES 2010 Question PaperDocument24 pagesElectrical Paper II - IES 2010 Question Paperaditya_kumar_meNo ratings yet
- Dds 80Document54 pagesDds 80Alicia SmithNo ratings yet
- Ss Prsolutions08Document9 pagesSs Prsolutions08watnottakenNo ratings yet
- Denon-AVR3300 RecDocument86 pagesDenon-AVR3300 RecErin RoffNo ratings yet
- DSP 2Document2 pagesDSP 2Sudhashree MutuswamyNo ratings yet
- 6th sem.-EC 1358-DSPDocument8 pages6th sem.-EC 1358-DSPGautham LogarajNo ratings yet
- II B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov - 2012 Signals and SystemsDocument8 pagesII B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov - 2012 Signals and Systemssateesh83No ratings yet
- 07-Élec-A7 (Version Anglaise) - Novembre 2011Document5 pages07-Élec-A7 (Version Anglaise) - Novembre 2011andrytahiryNo ratings yet
- International Islamic University, Islamabad: Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyDocument11 pagesInternational Islamic University, Islamabad: Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyLovely JuttNo ratings yet
- 5th OrderDocument14 pages5th OrderAbbas Sabbar GhaliNo ratings yet
- Exam+solution ET1303 080604Document17 pagesExam+solution ET1303 080604Jessica WrightNo ratings yet
- Discrete Wavelet Transform: A Signal Processing ApproachFrom EverandDiscrete Wavelet Transform: A Signal Processing ApproachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Fundamentals of Electronics 2: Continuous-time Signals and SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 2: Continuous-time Signals and SystemsNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics 2: Sequential and Arithmetic Logic CircuitsFrom EverandDigital Electronics 2: Sequential and Arithmetic Logic CircuitsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Digital Signal Processing Using the ARM Cortex M4From EverandDigital Signal Processing Using the ARM Cortex M4Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Discrete Fourier Analysis and Wavelets: Applications to Signal and Image ProcessingFrom EverandDiscrete Fourier Analysis and Wavelets: Applications to Signal and Image ProcessingNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNo ratings yet
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Hyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationFrom EverandHyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Advanced Coupling Matrix Synthesis Technique For UW FiltersDocument10 pagesAdvanced Coupling Matrix Synthesis Technique For UW FiltersFlorin CalinescuNo ratings yet
- Filter Approximation Theory: Butterworth, Chebyshev, and Elliptic FiltersDocument14 pagesFilter Approximation Theory: Butterworth, Chebyshev, and Elliptic FiltersRaghavendraRaoNo ratings yet
- TE 2003&2008 PatternDocument623 pagesTE 2003&2008 PatternAshashwatmeNo ratings yet
- Lab 5. FIR & IIR Filters in Matlab: Filter DesignDocument12 pagesLab 5. FIR & IIR Filters in Matlab: Filter DesignDrakshayaniMurgodNo ratings yet
- CU7202-MIC and RF System DesignDocument16 pagesCU7202-MIC and RF System DesignSaadNo ratings yet
- 3 Design of RF and Microwave FiltersDocument44 pages3 Design of RF and Microwave Filterswearole100% (2)
- Response of A Digital Filter. Filter Design. or Matrix.: Theta Angle (Z)Document2 pagesResponse of A Digital Filter. Filter Design. or Matrix.: Theta Angle (Z)Benj MendozaNo ratings yet
- Advanced EDC & PDC NotesDocument19 pagesAdvanced EDC & PDC NotesSashikanth BethaNo ratings yet
- Active Compensation For High-Frequency Effects in Op-Amp Circuits With Applications For Active RC Filters (CATHERINE VERA)Document5 pagesActive Compensation For High-Frequency Effects in Op-Amp Circuits With Applications For Active RC Filters (CATHERINE VERA)Catherine VeraNo ratings yet
- DSP Lab RecordDocument97 pagesDSP Lab RecordLikhita UttamNo ratings yet
- Filtros de Segundo OrdenDocument30 pagesFiltros de Segundo OrdenAlex Fernando Coro LuzuriagaNo ratings yet
- 4 CSE 447 Digital FilterDocument82 pages4 CSE 447 Digital FilterAriful Islam ShantoNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Analog FiltersDocument453 pagesDesign and Analysis of Analog Filterspouty567100% (4)
- Filter Design Assignment 2016-17 EE 338: Digital Signal ProcessingDocument17 pagesFilter Design Assignment 2016-17 EE 338: Digital Signal ProcessingShashank OvNo ratings yet
- DSP manual-KIOTDocument62 pagesDSP manual-KIOTTalemaNo ratings yet
- Diplexer For UHF Military Applications (Master's Thesis)Document76 pagesDiplexer For UHF Military Applications (Master's Thesis)wearoleNo ratings yet
- Lab.6&7. IIR FiltersDocument8 pagesLab.6&7. IIR FiltershimNo ratings yet
- Filter DesignDocument22 pagesFilter DesignAbdul Rozaq SyamsuddinNo ratings yet
- U20ECCJ03 DSP Question Bank (June 2023) (Updated)Document7 pagesU20ECCJ03 DSP Question Bank (June 2023) (Updated)Veera VenkatNo ratings yet
- DSP Manual HamdardDocument52 pagesDSP Manual HamdardMuhammad IrfanNo ratings yet
- Normalized Filter Design TablesDocument72 pagesNormalized Filter Design TablessdeirNo ratings yet
- ELE 3212 - SS LabDocument49 pagesELE 3212 - SS LabsheetalprachandraNo ratings yet
- Band Pass Filter Design Part 2. Band Pass Filters From First Principles Richard Harris G3OTKDocument11 pagesBand Pass Filter Design Part 2. Band Pass Filters From First Principles Richard Harris G3OTKopachecoNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Different Orders of Active-Rc Butterworth FilterDocument124 pagesDesign and Analysis of Different Orders of Active-Rc Butterworth FilterPradeep Kumar Goud NadikudaNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing IIR Filter Design Via Impulse InvarianceDocument11 pagesDigital Signal Processing IIR Filter Design Via Impulse Invariancedeepak reddyNo ratings yet
- DSPDocument28 pagesDSPPalani GnanavelNo ratings yet
- Electronic Device Floyd FiltersDocument25 pagesElectronic Device Floyd FiltersEdgar PeninsulaNo ratings yet
- Microwave FiltersDocument34 pagesMicrowave FiltersLinh TajNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Chbyshev Filter (21-MS-TE-05)Document6 pagesAssignment 2 Chbyshev Filter (21-MS-TE-05)Amanullah sasoliNo ratings yet