Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Site For Seeing Concurrent Prog
Uploaded by
Avishek BoseOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Site For Seeing Concurrent Prog
Uploaded by
Avishek BoseCopyright:
Available Formats
SITE FOR SEEING CONCURRENT PROGhttp://oracleappscommunity.
com/oracle/blog/1130/inventory-concurrent-programs/
SELECT THE PURCHASE ORDER AND THEN GIVE THE APPROPRIATE RECEIPT,THEN SHIPMENT NO.WILL BE AUTOMATICALLY GENERATED. CLICK ON FIND THE FOLLOWING SCREEN OPENS
CLICK ON INSPECT,THE FOLLOWING SCREEN OPENS
In the Quantity field, enter the positive or negative correction quantity for the current line. Making any entry on the line automatically selects the line. You can also use the line selector to select and deselect lines. You can also make corrections to quantities that you return to a supplier. For example, you receive 100 items, and you use a Return To Supplier transaction to return 10 items to the supplier because they were damaged. Then you realize that only 9 items were damaged. This means that, in the
Corrections window, you must enter a correction of -1 for the Return to Supplier transaction. Purchasing moves the item from the supplier to your receiving supply. If you additionally want to move the item from your receiving supply to your on-hand supply, you must additionally enter a correction of -1 for the Return to Receiving transaction. VIEW RECEIVING TRANSACTIONS
RECEIVING
CLICK ON FIND
NOTE: You cannot enter returns for internal shipments (that is, shipments with a Source Type of Internal).
MANAGE SHIPMENTS Use the Find Intransit Shipments window to find source documents for which you can enter shipment information. You can also use the Find Intransit Shipments window to view validated Advance Shipment Notices (ASNs). TRANSACTION STATUS SUMMARY
TRANSACTION MANAGER NAVIGATION: SETUPTRANSACTIONINTERFACE MANAGERS
The transaction managers execute the following processes: material transaction, demand reservation, move transaction, resource cost transaction, remote procedure call, and material cost transaction. These run at periodic intervals you
specify until you delete them with the concurrent manager. They control the number of transaction workers, processing intervals, and number of transactions processed by each worker during each interval. For descriptions of the available managers see: Transaction Managers. You must start the material cost transaction manager to cost material transactions. This manager processes costing of all material transactions. You must also start the move transaction manager so that assemblies received from an outside processing supplier can be moved to the next operation. You do not have to launch these transaction managers if you decide to process all your transactions on-line and do not use the transaction interface. The use of multiple transaction workers enables parallel processing of transactions. This is especially helpful when processing a large batch of transactions. To view and update the transaction managers: 1. Navigate to the Interface Managers window. All existing transaction managers and their current status are displayed. 2. Enter the maximum number of rows to assign to the worker. 3. For WIP Move Transactions only: Specify the processing timeout in hours and minutes. After this time the move transaction manager no longer processes pending transactions and marks them as an error. 4. Save your work. To launch a transaction manager: 1. Select a transaction manager in the Interface Managers window. 2. Choose Launch Manager from the Tools menu. The Launch Inventory Managers window appears displaying the transaction manager you choose as the process to be submitted. Note: If the transaction manager is already active, Oracle Inventory displays a warning before displaying the new window. 3. Select a resubmit level. You can enter the start date and time to resubmit the transaction manager or an interval of time that the transaction manager polls the interface table for pending transactions. 4. Choose Submit.
INTRANSIT INVENTORY INTER-ORGANISATION TRANSFER The items you transfer must exist in both organizations. You can also transfer expense and asset items from one organization to another using intransit inventory. For example, you can transfer item A from organization X to organization Y, even though item A is under lot control only in organization X (you can specify the lot numbers for item A in organization X during the transfer transaction). However, you cannot transfer item B from organization X to organization Y if item B is under lot control only in organization Y (you cannot specify lot numbers for item B in the destination organization because you are performing a direct transfer). BORROW PAYBACK TRANSACTION
Enter the date and time of entry for the transaction. The date you enter is controlled by the INV:Transaction Date Validation profile option.
Select the desired transaction type. The available choices are as follows:
Project Borrow- Borrows items from a project o Project Payback- Payback borrowed items to a project o Project Transfer- Transfer Items to another project
ABC ANALYSIS NAVIGATION:Go to Inventory Responsibilty ABC CodesABC Compiles The following screen opens
The criterion can be
CYCLE COUNT
Cycle Counting is:
performed periodically to ensure accuracy of inventory quantities and values a method of taking inventory that does not require the inventory organization to shut down in order to count actual inventory items
performed by an inventory organization at the discretion of the INV Administrator; conducting a Physical Inventory is an alternative method of taking inventory
Responsibility The INV Administrator is responsible for:
setting up the cycle count parameters and scheduling
The INV Inventory Specialist is responsible for:
printing cycle count requests performing the item counting entering actual item counts resolving inventory discrepancies in the database
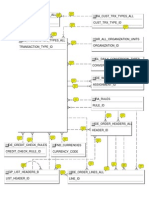
Save it Click on Items CST_COST_GROUPS HR_ALL_ORGANIZATION_UNITS_TL MTL_PICKING_RULES MTP_ATP_RULES BOM_RESOURCES
MFG_LOOKUPS FND_COMMON_LOOKUPS MTL_PARAMETERS HR_ORG_UNITS_NO_JOIN
Uncheck the Global check box if you want the location to only be available within the default Business Group of your current responsibility. Accept the
default if you want the location to be a global location and therefore available to all Business Groups. If you are setting up a global location, the location name must be unique across all Business Groups. If you are setting up a location for one Business Group, the location name must be unique within that Business Group and all global locations, but does not have to be unique across all Business Groups.
ACCOUNT ALIASES
An account alias is an easily recognized name or label representing a general ledger account number. You can view, report, and reserve against an account alias. During a transaction, you can use the account alias instead of an account number to refer to the account. The table associated with it is MTL_GENERIC_DISPOSITIONS
UOM Classes
You might also like
- CONSIGNED INVENTORY USER NOTESDocument7 pagesCONSIGNED INVENTORY USER NOTESNaveen SNNo ratings yet
- Defining Inventory Organization SetupDocument13 pagesDefining Inventory Organization Setupwondertiger2No ratings yet
- EAM StepsDocument9 pagesEAM Stepsvamc232855No ratings yet
- Oracle Finance Functional Interview Questions and AnswersDocument8 pagesOracle Finance Functional Interview Questions and AnswersMohd Nadeem AhmedNo ratings yet
- O2C Cycle PresentationDocument82 pagesO2C Cycle PresentationRNo ratings yet
- I ExpensesDocument21 pagesI ExpensesmanitenkasiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Receipt Accrual Process in PeopleSoft PurchasingDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Receipt Accrual Process in PeopleSoft PurchasingruzhaNo ratings yet
- GL Integration With Other ModulesDocument35 pagesGL Integration With Other ModulesVijaya GaliNo ratings yet
- Accounts Payable Interview Questions in R12 - Oracle Techno & FunctionalDocument15 pagesAccounts Payable Interview Questions in R12 - Oracle Techno & FunctionalDeepakNo ratings yet
- Configure WIP parameters to define modes of operationDocument7 pagesConfigure WIP parameters to define modes of operationSandeep TickooNo ratings yet
- Internal Order Process Setup in Oracle Order ManagementDocument14 pagesInternal Order Process Setup in Oracle Order ManagementRupak SinghNo ratings yet
- IExpense Implementation SetupsDocument16 pagesIExpense Implementation SetupsMarianoNo ratings yet
- IExpenses Setups in R12Document25 pagesIExpenses Setups in R12devender143No ratings yet
- Cycle CountDocument32 pagesCycle CountdeepakdkhoslaNo ratings yet
- Oracle SCM Inventory Interview Questions: Planning Methods and SetupDocument6 pagesOracle SCM Inventory Interview Questions: Planning Methods and SetupKarthikRamaswamy0% (1)
- Inventory Order Management GuideDocument7 pagesInventory Order Management GuideKoraganji VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Oracle Purchasing FAQ - by Dinesh Kumar SDocument22 pagesOracle Purchasing FAQ - by Dinesh Kumar Sdineshcse86gmailcomNo ratings yet
- Key Users TrainingmaterialDocument32 pagesKey Users TrainingmaterialSayed RamadanNo ratings yet
- Order To Cash FlowDocument10 pagesOrder To Cash FlowBalaji ShindeNo ratings yet
- Short Notes On Oracle WIP User GuideDocument22 pagesShort Notes On Oracle WIP User Guidetsurendar0% (1)
- Interview QuestionsDocument58 pagesInterview QuestionsRipu Daman SinghNo ratings yet
- Internal Sales Order SetupDocument35 pagesInternal Sales Order SetupVeerendra ReddyNo ratings yet
- Oracle Credit CheckingDocument33 pagesOracle Credit CheckingVinita Bhatia100% (1)
- 1 PSFT Fundemental Finance Installation GLBU Setid and Table Set Sharing Setup 02-23-2014Document8 pages1 PSFT Fundemental Finance Installation GLBU Setid and Table Set Sharing Setup 02-23-2014Bala KulandaiNo ratings yet
- Period CloseDocument6 pagesPeriod CloseSuman BeemisettyNo ratings yet
- Back OrderDocument112 pagesBack OrderSourav KumarNo ratings yet
- OSPDocument8 pagesOSPvinoth13071972100% (1)
- Complete Order To CashDocument39 pagesComplete Order To CashDrAnand ShankarNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Oracle Receivables: Flow of Accounting InformationDocument10 pagesAccounting For Oracle Receivables: Flow of Accounting InformationAhmed Aljack SulimanNo ratings yet
- AP Concepts Part1 Oracle 11Document14 pagesAP Concepts Part1 Oracle 11JayantaNo ratings yet
- Oracle Inventory Interview QuestionsDocument42 pagesOracle Inventory Interview QuestionsPritesh Mogane100% (5)
- Setup Contingent Worker FunctionalityDocument12 pagesSetup Contingent Worker FunctionalityHameed KhanNo ratings yet
- Financials Option1Document23 pagesFinancials Option1KingshukNo ratings yet
- Run MRP, Convert Planned Order To Production Order, Settle Costs of Production OrderDocument58 pagesRun MRP, Convert Planned Order To Production Order, Settle Costs of Production OrderJayadeepauyaj UppalapatiNo ratings yet
- Oracle Apps Order Management Interview QuestionsDocument9 pagesOracle Apps Order Management Interview Questionsnet6351100% (2)
- Optimize Inventory Accuracy with Cycle CountingDocument7 pagesOptimize Inventory Accuracy with Cycle CountingvenkatsssNo ratings yet
- IntercompanyDocument48 pagesIntercompanyPritesh Mogane0% (2)
- Setting Up Transaction Types and Sources in Oracle ReceivablesDocument35 pagesSetting Up Transaction Types and Sources in Oracle Receivablesredro0% (1)
- Period Close PurchasingDocument11 pagesPeriod Close Purchasingora plsqlNo ratings yet
- Interco Transaction Flow and Troubleshooting GuideDocument8 pagesInterco Transaction Flow and Troubleshooting GuideNagarjunaNo ratings yet
- ERP DocumentDocument4 pagesERP DocumentTrietNo ratings yet
- Modified 31-JUL-2011 Type HOWTO Status MODERATEDDocument5 pagesModified 31-JUL-2011 Type HOWTO Status MODERATEDVaraprasad MedamNo ratings yet
- RMA Processing HELPDocument6 pagesRMA Processing HELPnaguraos4No ratings yet
- PO - Period Close ProcessDocument6 pagesPO - Period Close Processanishokm2992No ratings yet
- Issues On Purchasing & OMDocument4 pagesIssues On Purchasing & OMThammineni Vishwanath NaiduNo ratings yet
- Invenotry Period End Close ProcessDocument29 pagesInvenotry Period End Close ProcessSehowa Vrišti ThokaNo ratings yet
- Pick Release StatusDocument15 pagesPick Release StatusAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- Defining A Resource: PrerequisitesDocument4 pagesDefining A Resource: Prerequisitesapuri3No ratings yet
- How Is Bank Reconciliation Handled in SAPDocument10 pagesHow Is Bank Reconciliation Handled in SAPajay_bplNo ratings yet
- Setup and Usage of New Automatic Cash Application FunctionalityDocument20 pagesSetup and Usage of New Automatic Cash Application FunctionalityhuyhnNo ratings yet
- Period Close Process in Oracle InventoryDocument5 pagesPeriod Close Process in Oracle InventoryObulareddy BiyyamNo ratings yet
- EVO07 - Evolution Transaction TypesDocument21 pagesEVO07 - Evolution Transaction TypesDickson AllelaNo ratings yet
- Consigned Orders in PurchasingDocument28 pagesConsigned Orders in PurchasingOmer ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Inventory Period ClosingDocument8 pagesInventory Period ClosingUmair MehmoodNo ratings yet
- User Guide For Material Managment in MAXIMODocument15 pagesUser Guide For Material Managment in MAXIMOLuiz JesusNo ratings yet
- Oracle Interview QuestionsDocument18 pagesOracle Interview Questionsabadrh100% (1)
- Creating a One-Piece Flow and Production Cell: Just-in-time Production with Toyota’s Single Piece FlowFrom EverandCreating a One-Piece Flow and Production Cell: Just-in-time Production with Toyota’s Single Piece FlowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Purchasing, Inventory, and Cash Disbursements: Common Frauds and Internal ControlsFrom EverandPurchasing, Inventory, and Cash Disbursements: Common Frauds and Internal ControlsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How to Create Continuous Production Flow?: Toyota Production System ConceptsFrom EverandHow to Create Continuous Production Flow?: Toyota Production System ConceptsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Types of Business by Legal OwnershipDocument9 pagesTypes of Business by Legal OwnershipAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- OM Interface & Base TablesDocument4 pagesOM Interface & Base TablesAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- Oracle Apps Integration with XML PublisherDocument4 pagesOracle Apps Integration with XML PublisherAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- Order To CashDocument18 pagesOrder To CashVenkatesh GurusamyNo ratings yet
- PLSQL DumpsDocument7 pagesPLSQL Dumpsmubark_ali100% (5)
- Oracle AlertDocument2 pagesOracle AlertAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- Flexfield DocumentDocument84 pagesFlexfield DocumentAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- Tracking Date in HRMS Payroll in OracleDocument3 pagesTracking Date in HRMS Payroll in OracleAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- InvDocument14 pagesInvAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- Data Migration-On Hand QtyDocument3 pagesData Migration-On Hand QtyAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- Container Type Setups Are Done in Inventory - Setups - Item - ContainerDocument5 pagesContainer Type Setups Are Done in Inventory - Setups - Item - ContainerAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- Can one operating unit user see sales orders of other unitsDocument44 pagesCan one operating unit user see sales orders of other unitsAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- OmDocument3 pagesOmAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- Workflow Training 2Document8 pagesWorkflow Training 2Avishek BoseNo ratings yet
- Registering New Reports Into Oracle ApplicationDocument10 pagesRegistering New Reports Into Oracle ApplicationmrsreekanthreddyNo ratings yet
- Registering New Reports Into Oracle ApplicationDocument10 pagesRegistering New Reports Into Oracle ApplicationmrsreekanthreddyNo ratings yet
- Pick Release To Ship ConfirmDocument7 pagesPick Release To Ship ConfirmAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- Registering New Reports Into Oracle ApplicationDocument10 pagesRegistering New Reports Into Oracle ApplicationmrsreekanthreddyNo ratings yet
- Cycle Count Flow Abc Codes Abc CompilesDocument26 pagesCycle Count Flow Abc Codes Abc CompilesAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- SQLDocument1 pageSQLAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- Trm115 Om SummaryDocument1 pageTrm115 Om SummaryAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- Trm115 Om SummaryDocument1 pageTrm115 Om SummaryAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- Trm115 Om SummaryDocument1 pageTrm115 Om SummaryAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- Trm115 Om SummaryDocument1 pageTrm115 Om SummaryAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- Trm115om WorkflowDocument1 pageTrm115om WorkflowAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- Trm115om WorkflowDocument1 pageTrm115om WorkflowAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- Trm115 Om SummaryDocument1 pageTrm115 Om SummaryAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- Trm115 Om SummaryDocument1 pageTrm115 Om SummaryAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- Trm115 Om SummaryDocument1 pageTrm115 Om SummaryAvishek BoseNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Adams Equity TheoryDocument1 page2.4 Adams Equity TheoryLoraineNo ratings yet
- Wheat as an alternative to reduce corn feed costsDocument4 pagesWheat as an alternative to reduce corn feed costsYuariza Winanda IstyanNo ratings yet
- Shri Siddheshwar Co-Operative BankDocument11 pagesShri Siddheshwar Co-Operative BankPrabhu Mandewali50% (2)
- Sierra Wireless AirPrimeDocument2 pagesSierra Wireless AirPrimeAminullah -No ratings yet
- M Series CylindersDocument61 pagesM Series CylindersAndres SantanaNo ratings yet
- (NTA) SalaryDocument16 pages(NTA) SalaryHakim AndishmandNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgment: George & Also To Our Group Guide Asst. Prof. Simy M Baby, For Their Valuable Guidance and HelpDocument50 pagesAcknowledgment: George & Also To Our Group Guide Asst. Prof. Simy M Baby, For Their Valuable Guidance and HelpKhurram ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Activate Adobe Photoshop CS5 Free Using Serial KeyDocument3 pagesActivate Adobe Photoshop CS5 Free Using Serial KeyLukmanto68% (28)
- Hollow lateral extrusion process for tubular billetsDocument7 pagesHollow lateral extrusion process for tubular billetsjoaopedrosousaNo ratings yet
- Superior University: 5Mwp Solar Power Plant ProjectDocument3 pagesSuperior University: 5Mwp Solar Power Plant ProjectdaniyalNo ratings yet
- Accident Causation Theories and ConceptDocument4 pagesAccident Causation Theories and ConceptShayne Aira AnggongNo ratings yet
- UKBM 2, Bahasa InggrisDocument10 pagesUKBM 2, Bahasa InggrisElvi SNo ratings yet
- The Punjab Commission On The Status of Women Act 2014 PDFDocument7 pagesThe Punjab Commission On The Status of Women Act 2014 PDFPhdf MultanNo ratings yet
- HSPA+ Compressed ModeDocument10 pagesHSPA+ Compressed ModeAkhtar KhanNo ratings yet
- Admission Checklist (Pre-) Master September 2021Document7 pagesAdmission Checklist (Pre-) Master September 2021Máté HirschNo ratings yet
- Terminología Sobre Reducción de Riesgo de DesastresDocument43 pagesTerminología Sobre Reducción de Riesgo de DesastresJ. Mario VeraNo ratings yet
- HealthFlex Dave BauzonDocument10 pagesHealthFlex Dave BauzonNino Dave Bauzon100% (1)
- Liability WaiverDocument1 pageLiability WaiverTop Flight FitnessNo ratings yet
- Discount & Percentage Word Problems SolutionsDocument4 pagesDiscount & Percentage Word Problems SolutionsrheNo ratings yet
- Itec 3100 Student Response Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesItec 3100 Student Response Lesson Planapi-346174835No ratings yet
- Research Design Elements for ScenariosDocument25 pagesResearch Design Elements for Scenariosrohizal ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Pass Issuance Receipt: Now You Can Also Buy This Pass On Paytm AppDocument1 pagePass Issuance Receipt: Now You Can Also Buy This Pass On Paytm AppAnoop SharmaNo ratings yet
- Domestic Water Consumption in ChennaiDocument18 pagesDomestic Water Consumption in Chennaimaaz0% (1)
- Book Two - 2da. EdiciónDocument216 pagesBook Two - 2da. EdiciónJhoselainys PachecoNo ratings yet
- Chi Square LessonDocument11 pagesChi Square LessonKaia HamadaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Employee Turnover and Job Satisfaction A Case Study of Amari Hotels and Resorts Boondarig Ronra and Assoc. Prof. Manat ChaisawatDocument26 pagesFactors Affecting Employee Turnover and Job Satisfaction A Case Study of Amari Hotels and Resorts Boondarig Ronra and Assoc. Prof. Manat ChaisawathumeragillNo ratings yet
- Lead Magnet 43 Foolproof Strategies To Get More Leads, Win A Ton of New Customers and Double Your Profits in Record Time... (RDocument189 pagesLead Magnet 43 Foolproof Strategies To Get More Leads, Win A Ton of New Customers and Double Your Profits in Record Time... (RluizdasilvaazevedoNo ratings yet
- Shubh AmDocument2 pagesShubh AmChhotuNo ratings yet
- Mosaic Maker - Instructions PDFDocument4 pagesMosaic Maker - Instructions PDFRoderickHenryNo ratings yet
- Reynold's Number Flow ExperimentDocument8 pagesReynold's Number Flow ExperimentPatrick GatelaNo ratings yet