Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ANOVA F-Test Explained
Uploaded by
Angeli FacunOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ANOVA F-Test Explained
Uploaded by
Angeli FacunCopyright:
Available Formats
ONE-FACTOR ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE The F-Test The analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a method for dividing the variation observed
erved into different parts. The ANOVA was developed by R.A. Fisher and reported by him in 1923. It is used when we wished to test the significance of the differences between two or more means obtained from independent samples. The F-Test is generally used for determining differences among more than two means. Three advantages for using the F-Test over the t-test when there are more than two means to compare: T-test is more laborious. The t-ratio has a statistical limitation which is the likelihood of increasing the probability of making alpha error. In the case of two or more way analyses of variance, the interaction effects between and among the variables can be measured. Relevant Example A. Sum of Squares. a) Deviation Method: This is the sum of the squared deviation s from a mean. This is done by squaring or multiplying by itself the deviations from the mean of the group of scores and adding these deviation scores together (x2). b) Raw Score Method: This is the sum of the squared raw scores (x2). Find the sum of squares from the data below. Deviation Method x x2 4 16 3 9 2 4 1 1 0 0 -1 1 -2 4 -3 9 -4 16 x = 0 x2 = 60 Deviation Method 1. Within-Groups Sum of Squares (SSw) - the sum of the squared deviations of individual scores from their group mean. SSw = Where: X= a deviation score (x- ) 2. Between-Groups Sum of Squares (SSb) - sum of the squared deviations of individual group mean from the mean of the total distribution. Raw Score Method X2 81 64 49 36 25 16 9 4 1 X2 = 285
X 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 X = 45
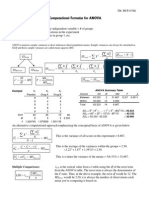
SSb = ( Where: = mean of any group = mean of the total distribution Number of scores in any group SSb = between groups sum of squares
)2N
3. Total Sum of Squares - sum of the squared deviation of every raw score from the mean of the total distribution. SSt = SSb + SSw 4. Mean Square (MS) - measure of variation obtained by dividing between-groups sum of squares by the appropriate degrees of freedom. MSb = SSb/dfb Where: MSb = mean square of the between-groups SSb = sum of squares of the between-groups dfb = degrees of freedom of the between-groups MSw = SSw/dfw Where: MSw = mean square of the within groups SSw = sum of squares of the within-groups dfw = degrees of freedom within groups dfb = k-1 dfw = N-k
Where: K= number of groups N= total number of scores in all groups combined Raw Score Method 1. Total Sum of Squares (SSt) (SS for total variability) SSt = X2 (Xt)2/N 2. Between-Groups Sum of Squares (SSb) (SS for between group variability) SSb = (X1)2/N1 + (X2)2/N2 + (X3)2/N3 - (Xt)2/Nt 3. Within-Groups Sum of Squares (SSw) (SS for within group variability) SSw = SSt - SSb 4. Degrees of freedom dfb = k - 1 dfw = Nt - k 5. Mean Square (MS) MSb = SSb/dfb MSw = SSw/dfw 6. F-Ratio F = MSb/MSw Related Output
X1 5 4 8 6 7 X = 30
X3 4 7 5 4 6 X = 26
Group 1 (N = 5) (Superior) x -1 -2 2 0 1 X=30/5=6 Group 3 (N = 5) (Average) x -1.2 1.8 -.2 -1.2 .8 X=26/5=5.2
x2 1 4 4 0 1 x2 = 10 x2 1.44 3.24 .04 1.44 .64 2 x = 6.8
X2 5 6 6 8 3 X = 28
X4 4 4 7 4 5 X = 24
Group 2 (N = 5) (Above Average) x x2 -.6 .36 .4 .16 .4 .16 2.4 5.76 -2.6 6.76 X=28/5=5.6 x2 = 13.2 Group 4 (N = 5) (Below Average) x x2 .8 .64 .8 .64 2.2 4.84 .8 .64 .2 .04 2 X=24/5=4.8 x = 6.8
Xtotal = 108/20 = 5.4 Plugging the formula: SSw = 10 + 13.2 + 6.8 + 6.8 = 36.8 Between Groups Sum of Squares (SSb) SSb = (6 5.4)25 + (5.6 5.4)25 + (5.2 5.4)25 + (4.8 5.4)25 = 1.8 + .2 + .2 + 1.8 =4 Total Sum of Squares (SSt) SSt = 4 + 36.8 = 40.8 Mean Square (MS) dfb = 4 1 =3 dfw = 20 4 = 16 MSw = 5.4/16 = .338 MSb = 3.82/3 = 1.27 The F-Test of Ratio F = 1.27/.338 = 3.76
Raw Score Method On the following three groups of teaching attitude, test the null hypothesis that academic performance does not vary due to teaching attitude. = .01 Academic Performance Average X2 X22 87 7569 84 7056 86 7396 85 7225 83 6889 425 36135 85 5
SUMS Means N
Above Average X1 X12 89 7921 90 8100 93 8649 93 8649 91 8281 456 41600 91.2 5
X3 80 82 80 78 79 399 79.8 5
Below Average X32 6400 6724 6400 6084 6241 31849 Xt = 1280 Xt2 = 109684 Nt = 15
Total Sum of Squares (SSt) (SS for total variability) SSt = X2 (Xt)2/N = 109584 (1280)2/15 = 357.33 Between-Groups Sum of Squares (SSb) (SS for between group variability) SSb = (X1)2/N1 + (X2)2/N2 + (X3)2/N3 - (Xt)2/Nt = (456)2/5 + (425)2/5 + (399)2/5 - (1280)2/15 = 109552.4 109226.67 = 325.73 Within-Groups Sum of Squares (SSw) (SS for within group variability) SSw = SSt - SSb = 357.33 325.73 = 31.6 Degrees of freedom dfb = k 1 =31 =2 dfw = Nt k = 15 3 = 12 Mean Square (MS) MSb = SSb/dfb = 325.73/2 = 162.87 MSw = SSw/dfw = 31.6/12 = 2.63 F-Ratio F = MSb/MSw
= 162.87/2.63 = 61.93 Ho = X1 = X2 = X3 H1 = X1 X2 X3 Decision: Since Fcomputed > Ftab, then Reject Ho Accept H1 Conclusion: Academic performance vary due to teaching attitude.
You might also like
- Analysis of Variance PPT at BEC DOMSDocument56 pagesAnalysis of Variance PPT at BEC DOMSBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)100% (1)
- One Way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) : "Slide 43-45)Document15 pagesOne Way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) : "Slide 43-45)Dayangku AyusapuraNo ratings yet
- Pharmatox Analysis of Variance PresentationDocument44 pagesPharmatox Analysis of Variance PresentationCarlos AndradeNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Variance: Session 5Document25 pagesAnalysis of Variance: Session 5keziaNo ratings yet
- ANOVA PresentationDocument22 pagesANOVA PresentationNeeraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11: Statistical Inference by Dr. Javed Iqbal: Analysis of VarianceDocument7 pagesLecture 11: Statistical Inference by Dr. Javed Iqbal: Analysis of Variancesusheel kumarNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 3 AnovaDocument60 pagesPertemuan 3 AnovaKerin ArdyNo ratings yet
- Anova FinalDocument22 pagesAnova FinalHezekiah BatoonNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Variance: David Chow Nov 2014Document32 pagesAnalysis of Variance: David Chow Nov 2014Donald YumNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - AnovaDocument7 pagesModule 5 - AnovaIvy BautistaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 & 4 - Ignou Part 3Document19 pagesUnit 3 & 4 - Ignou Part 3Sree LathaNo ratings yet
- ch04 2013Document21 pagesch04 2013angelli45No ratings yet
- Lesson 6.4 Simple Analysis of Variance FinDocument19 pagesLesson 6.4 Simple Analysis of Variance FinJeline Flor EugenioNo ratings yet
- How ANOVA Works: Fat For Frying DonutsDocument2 pagesHow ANOVA Works: Fat For Frying DonutsRessa AjaNo ratings yet
- ANOVA Analysis Comparing Majors' GPAsDocument7 pagesANOVA Analysis Comparing Majors' GPAsSam Rae LimNo ratings yet
- Anova 1Document20 pagesAnova 1Lorraine GalsimNo ratings yet
- One - Way Analysis of VarianceDocument14 pagesOne - Way Analysis of Variancemary magsipoc anaudNo ratings yet
- Lecture14 OneWayANOVADocument46 pagesLecture14 OneWayANOVAMutai VictorNo ratings yet
- One Way AnovaDocument30 pagesOne Way AnovaAshwin VelNo ratings yet
- Analysis of VarianceDocument62 pagesAnalysis of VarianceJohnasse Sebastian NavalNo ratings yet
- Repeated Measures ANOVA and Two-Factor (Factorial) ANOVADocument32 pagesRepeated Measures ANOVA and Two-Factor (Factorial) ANOVASrinivasagopalanNo ratings yet
- ANOVA MCQ (Free PDF) - Objective Question Answer For ANOVA Quiz - Download Now!Document10 pagesANOVA MCQ (Free PDF) - Objective Question Answer For ANOVA Quiz - Download Now!jayant bansalNo ratings yet
- EFM 515 Stats Lecture NotesDocument104 pagesEFM 515 Stats Lecture NotesKuda Keith MavhungaNo ratings yet
- 12 AnovaDocument43 pages12 AnovaBeing VikramNo ratings yet
- A V (Anova) : Nalysis of ArianceDocument8 pagesA V (Anova) : Nalysis of Arianceneeraj_kamboj2193No ratings yet
- Bio2 Module 3 - Comparison of MeansDocument19 pagesBio2 Module 3 - Comparison of Meanstamirat hailuNo ratings yet
- Materi 1 - One Way and Two Way ANOVADocument84 pagesMateri 1 - One Way and Two Way ANOVAThe Sun Will RiseNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Business: Analysis of VarianceDocument51 pagesStatistics For Business: Analysis of VarianceblahNo ratings yet
- Data AnalysisDocument4 pagesData AnalysisLoey ParkNo ratings yet
- Statistics Module 7Document13 pagesStatistics Module 7Lagcao Claire Ann M.No ratings yet
- Practice An OvaDocument11 pagesPractice An OvaHashma KhanNo ratings yet
- Statistics Module 7 RevisedDocument13 pagesStatistics Module 7 RevisedLynmar EnorasaNo ratings yet
- ANOVA and Chi SquareDocument67 pagesANOVA and Chi SquareSiva KarthikNo ratings yet
- Business Research Methods: Bivariate Analysis - Tests of DifferencesDocument56 pagesBusiness Research Methods: Bivariate Analysis - Tests of DifferencesLina Haytham HalasaNo ratings yet
- Analyze Variance (ANOVA) TechniquesDocument28 pagesAnalyze Variance (ANOVA) TechniquespatilmilindkNo ratings yet
- Anova: Analysis of Variation: Math 243 Lecture R. PruimDocument30 pagesAnova: Analysis of Variation: Math 243 Lecture R. PruimMahender KumarNo ratings yet
- Topic: ANOVA (Analysis of Variation) : Md. Jiyaul MustafaDocument49 pagesTopic: ANOVA (Analysis of Variation) : Md. Jiyaul MustafaBhagya PatilNo ratings yet
- One-Way Analysis of VarianceDocument21 pagesOne-Way Analysis of VarianceboodinNo ratings yet
- 16 AnovaDocument22 pages16 AnovamrNo ratings yet
- Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument4 pagesClick To Edit Master Subtitle StyleSudeep NairNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Rex Mabanta Ralph Stephen Bartolo Reynante LumawanDocument43 pagesPrepared By: Rex Mabanta Ralph Stephen Bartolo Reynante LumawanRicardo VelozNo ratings yet
- ANOVA Test StatisticDocument32 pagesANOVA Test StatisticMary KabembaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of VarianceDocument25 pagesAnalysis of Variancejerzone88100% (1)
- Anova - One Way Sem 1 20142015 DKDocument8 pagesAnova - One Way Sem 1 20142015 DKAnonymous jxnjKLNo ratings yet
- ANOVA analysis of variance experimentDocument29 pagesANOVA analysis of variance experimentFarrukh JamilNo ratings yet
- ANOVA Analysis of Variance TechniquesDocument57 pagesANOVA Analysis of Variance TechniquesLiza Lorena C. JalaNo ratings yet
- M8 ANOVA and Kruskall Wallis - Pelajar 12042018-20191108123443Document59 pagesM8 ANOVA and Kruskall Wallis - Pelajar 12042018-20191108123443Centuren RennNo ratings yet
- Comp Formulas A NovaDocument2 pagesComp Formulas A NovaNibir MahantaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Variance (Anova)Document22 pagesAnalysis of Variance (Anova)YalliniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 15 ANOVA (Analysis of Variance)Document6 pagesLesson 15 ANOVA (Analysis of Variance)Maria PappaNo ratings yet
- Ed105 ADocument14 pagesEd105 Aapi-268563289No ratings yet
- One-Way ANOVA: Test Differences Between Multiple Sample MeansDocument7 pagesOne-Way ANOVA: Test Differences Between Multiple Sample MeansRaphael BalitaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Varience-One Way Analysis (Original Slide)Document25 pagesAnalysis of Varience-One Way Analysis (Original Slide)Hilmi DahariNo ratings yet
- ANOVA For One Way Classification TheoryDocument4 pagesANOVA For One Way Classification TheoryAtul JhariyaNo ratings yet
- Anova: Analysis of Variation: Math 243 Lecture R. PruimDocument30 pagesAnova: Analysis of Variation: Math 243 Lecture R. PruimLakshmi BurraNo ratings yet
- Chapter Seven: Multi-Sample MethodsDocument52 pagesChapter Seven: Multi-Sample MethodsFiza MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Chapter Seven: Multi-Sample MethodsDocument52 pagesChapter Seven: Multi-Sample MethodsFiza MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13 Analysis of VarianceDocument36 pagesLesson 13 Analysis of VarianceNicole Daphnie LisNo ratings yet
- Anova Slides PresentationDocument29 pagesAnova Slides PresentationCarlos Samaniego100% (1)
- Starch and SucroseDocument5 pagesStarch and SucroseAngeli Facun100% (1)
- Analysis of Iron in Razor Blade Using Redox Titration and Blank TitrationDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Iron in Razor Blade Using Redox Titration and Blank TitrationAngeli FacunNo ratings yet
- Answers to Questions About Dye Synthesis and PropertiesDocument4 pagesAnswers to Questions About Dye Synthesis and PropertiesAngeli FacunNo ratings yet
- Winkler DO MethodDocument5 pagesWinkler DO MethodAngeli FacunNo ratings yet
- How to Make Macopa Ice CreamDocument4 pagesHow to Make Macopa Ice CreamAngeli FacunNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Iron in Razor Blade Using Redox Titration and Blank TitrationDocument1 pageAnalysis of Iron in Razor Blade Using Redox Titration and Blank TitrationAngeli Facun100% (1)
- Phylum Mollusca: Littorina SPDocument10 pagesPhylum Mollusca: Littorina SPAngeli FacunNo ratings yet
- 5 - Asesmen Klinis (Tes Proyektif)Document10 pages5 - Asesmen Klinis (Tes Proyektif)Syifa SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Educational Assessment Mcqs For PSC HeadmasterDocument24 pagesEducational Assessment Mcqs For PSC Headmastersrinivasana66% (128)
- CV SummaryDocument8 pagesCV SummaryafrisNo ratings yet
- Gacl Testing Data SheetDocument2 pagesGacl Testing Data SheetVIKASH RAINo ratings yet
- Stats Activity 8Document2 pagesStats Activity 8Shekinah GellaNo ratings yet
- F-TEST AND ONE-WAY ANOVA ANALYSISDocument17 pagesF-TEST AND ONE-WAY ANOVA ANALYSISJyle Mareinette ManiagoNo ratings yet
- Excercise-A Independent Sample Case - Parametric Approach Q-1A)Document11 pagesExcercise-A Independent Sample Case - Parametric Approach Q-1A)Mohammad Talha QureshiNo ratings yet
- Rayan Kittaneh VTSP VMware Server Virtualization Test ResultsDocument2 pagesRayan Kittaneh VTSP VMware Server Virtualization Test ResultsRay0% (1)
- APTET 2014 Social Question Paper II With Solutions PDFDocument47 pagesAPTET 2014 Social Question Paper II With Solutions PDFgayathriNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology TechniquesDocument34 pagesResearch Methodology TechniquesKirithiga SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Output SPSS: Tests of NormalityDocument6 pagesOutput SPSS: Tests of NormalityariNo ratings yet
- Statistical TreatmentDocument3 pagesStatistical Treatmentblazer1012000100% (1)
- Statistics For Managers Using Microsoft Excel: 6 Global EditionDocument64 pagesStatistics For Managers Using Microsoft Excel: 6 Global Edition015Devina UlimaNo ratings yet
- Pages From FX207-Essentials of MCMI-IV Assessmen - Seth D. GrossmanDocument3 pagesPages From FX207-Essentials of MCMI-IV Assessmen - Seth D. GrossmanKaisar Ono100% (1)
- Jhoemer B. Ariola Lyndonne Dredd P. MagbitangDocument16 pagesJhoemer B. Ariola Lyndonne Dredd P. MagbitangLyndonne PadronNo ratings yet
- Free Software Testing Course ContentDocument6 pagesFree Software Testing Course ContentReddy KrishNo ratings yet
- Neet Ug Result TelanganaDocument1,096 pagesNeet Ug Result TelanganaRavuri Krishna Chaitanya0% (1)
- Agile Testing Mindset ManifestoDocument2 pagesAgile Testing Mindset ManifestochangNo ratings yet
- IIM CAT - 2009 Scorecard - SinghDocument1 pageIIM CAT - 2009 Scorecard - Singhkkvv11No ratings yet
- Multi Answer Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument1 pageMulti Answer Multiple Choice Questionsrakibdx001No ratings yet
- CCSP GuidelinesDocument42 pagesCCSP GuidelinesAzhagendranNo ratings yet
- GCSE Maths 314648 Foundation Tier Terminal Unit 3 Section B Mark Scheme (Specimen)Document3 pagesGCSE Maths 314648 Foundation Tier Terminal Unit 3 Section B Mark Scheme (Specimen)gcsemathstutor100% (1)
- ShowPdf PDFDocument347 pagesShowPdf PDFRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- National Testing Agency (NTA) : Category Wise Cut-Off NTA Score For JEE (Advanced) - 2019 Based On Paper-1Document1 pageNational Testing Agency (NTA) : Category Wise Cut-Off NTA Score For JEE (Advanced) - 2019 Based On Paper-1Jayesh KumavatNo ratings yet
- Research Center Soil Tests Bridge ProjectDocument10 pagesResearch Center Soil Tests Bridge ProjectS Azhar ATNo ratings yet
- AnovaDocument105 pagesAnovaasdasdas asdasdasdsadsasddssaNo ratings yet
- DgnsttrudntsDocument107 pagesDgnsttrudntsVincent HilarioNo ratings yet
- Norm and Criterion Referenced TestDocument14 pagesNorm and Criterion Referenced TestDr. Nisanth.P.M80% (5)
- Test Item Analysis Calculator 2019Document4 pagesTest Item Analysis Calculator 2019Reysa m.duatin100% (1)