Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week 10
Uploaded by
007wasrOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Week 10
Uploaded by
007wasrCopyright:
Available Formats
12/12/2010
Why Evaluation
Does the Interface Meet the Usability Requirements?
Effective: completeness and accuracy Efficient: speed Engaging: Error tolerant Easy to learn
Evaluation
Dr. Ann Nosseir Stone et. al. ch 20-27 Benyon et. al. ch 12 & 21
Why Evaluation (cont.)
Exploring Other Concerns in Evaluations Why users are unable to complete tasks easily. Is the UI developed for all levels of users? Are all design features acceptable to users?
The Activities of Usability Evaluations
The Process of Usability Evaluation Is Iterative Techniques for Usability Evaluations
User Observations Inspections of the User Interface
Conform to usability standards?
Other Evaluation Techniques
Variations of user observation or inspection
12/12/2010
What Happens in a User Observation Evaluation Session? Welcome participant, explain purpose, make participant comfortable Ask participant to complete tasks while you observe and record Following completion of tasks, as for participants views, or to complete post-test questionnaire Thank participant.
Creating an Evaluation Strategy
What Is the Purpose of This Evaluation?
Does system meet usability requirements/concerns Qualitative Usability Requirements Desired features
Creating an Evaluation Strategy
Quantitative Usability Requirements/Usability Metrics
Explicit measures used: percentages, timings, or numbers are used.
It should be possible for the users to load any page of a web site in 10 seconds using a 56K modem. It should take no more than two minutes for an experienced user (one who has domain knowledge and has undergone the prescribed level of training when the new system is introduced) to enter a customers details in the hotels database
The users on an e-shopping site should be able to order an item easily and without assistance. Railway clerks work in extremely noisy environments, so any warning messages to them should be visually distinct and highlighted on the screens.
12/12/2010
Creating an Evaluation Strategy
Prioritizing Usability Requirements and Concerns
The usability requirements most important to the success of the system are given priority. Assign values to the five dimensions of usability, the Five Es.
The Five Es.
The Five Es.
High priority for online museum placed on engaging
Creating an Evaluation Strategy
What Type of Data Do I Want to Collect?
Quantitative data
Numeric content
Qualitative data
Non-numeric content
12/12/2010
Think of
What Am I Evaluating? What Constraints Do I Have?
Money Timescales Availability of usability equipment Availability of participants and the costs of recruiting them Availability of evaluators
Documenting the Evaluation Strategy
Choosing Your Users
Who Is a Real User?
Users who reflect the different skills, domain knowledge, system experience
Choosing Your Users
Ideas for Participants Offering Incentives
thank you letter, pay for out-of-pocket expenses, samples, gifts
Users Working Alone or in Pairs Number of Participants Recruiting Extra Participants
Recruiting Screeners and Pre-test Questionnaires
12/12/2010
Creating a Timetable
Decide the Duration of the Evaluation Session 30-90 minutes Create an Evaluation Timetable sessions, evaluation, reporting
Preparing Task Descriptions
the tasks the participant will perform while interacting with the prototype during the evaluation
Where Will You Do the Evaluation?
Field Studies users own environment Controlled Studies other than users environment
Preparing to Collect Evaluation Data
Timing and Logging Actions
Automatic Logging of Keystrokes and Mouse Clicks Specialist Logging Software for Usability Evaluations Choosing a Logging Product
12/12/2010
Think-Aloud and Offering Help
Using Cognitive Walkthrough Questions
Is there anything there that tells you what to do next? Is there a choice on the screen that lines up with what you want to do? If so, which one? Now that youve tried ti, has it done what you wanted it to do?
Taking Notes When Observing Users
Conducting Post-Session Discussions
Retrospective protocol Post-session interview / debrief
Questionnaires
Advantages
Cant forget to ask a question All participants see the same questions Ability to collect quantitative data
Disadvantages
Difficult to design Must predict topics the users will need Closed questions dont give reasons why the users answered the way that they have.
12/12/2010
Using Technologies to Help Recording
Video and Audio Recording Eye-Tracking Equipment Practitioners Choice of Technology
with
Facilitator
Note-Taker
Roles for Evaluators
Equipment Operator Observer Meeter and Greeter
What to Do If a Participant Does Not Agree to Be Recorded
Recruiter
The Lone Evaluator
Usability Defects (characteristics)
Reviewing the Data to Identify Usability Problems
Irritates or confuses the user Makes a system hard to install, learn, or use Causes mental overload for the user Causes poor user performance Violates design standards or guidelines Reduces trust or credibility of the system Tends to cause repeated errors Could make the system hard to market
12/12/2010
Working with Quantitative Data
Tabulations, charts, and rankings for visual rep. Descriptive statistics: mean (average), median (middle value), mode (most common value) Inferential statistics: tests of statistical significance yielding probability.
You might also like
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument108 pagesIlovepdf MergedMZ MalikNo ratings yet
- Requirement Elicitation: Perancangan Sistem Informasi Logistik Teknik Logistik UISI 2017Document24 pagesRequirement Elicitation: Perancangan Sistem Informasi Logistik Teknik Logistik UISI 2017KarinaNo ratings yet
- Usability Testing (Kuantitatif)Document43 pagesUsability Testing (Kuantitatif)Furqan MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Identifying Needs and Establishing Requirements: HCI - Umber ShamimDocument53 pagesIdentifying Needs and Establishing Requirements: HCI - Umber ShamimMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Identifying Needs and Establishing Requirements: HCI - Umber ShamimDocument54 pagesIdentifying Needs and Establishing Requirements: HCI - Umber ShamimMuhammad Bilal100% (1)
- Lec 2001 8eDocument23 pagesLec 2001 8edwi krisbiantoroNo ratings yet
- Lec 11 - EvaluationDocument64 pagesLec 11 - EvaluationFRankNo ratings yet
- Lecture14-Designrules UserprofileDocument41 pagesLecture14-Designrules UserprofileRana TayyabNo ratings yet
- Review Ii: Course: COMP6176 / Human - Computer Interaction Year: 2015Document19 pagesReview Ii: Course: COMP6176 / Human - Computer Interaction Year: 2015Agus Sasmito HNo ratings yet
- What Is Design? A Simple Definition Is: - Achieving Within: Goals ConstraintsDocument27 pagesWhat Is Design? A Simple Definition Is: - Achieving Within: Goals ConstraintsHarshdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Kapita Selekta - Usability 2020Document31 pagesKapita Selekta - Usability 2020Restu Dharma yasaNo ratings yet
- 3concept of Software UsabilityDocument30 pages3concept of Software UsabilityMati ChalaNo ratings yet
- The Process of Interaction DesignDocument106 pagesThe Process of Interaction DesignEmran AljarrahNo ratings yet
- PDF Document (3) 2Document34 pagesPDF Document (3) 2WEI SZI LIMNo ratings yet
- Portfolio HF ResearcherDocument32 pagesPortfolio HF ResearcherDan ChiushunNo ratings yet
- Ucd DaDocument13 pagesUcd DaAndrei IordacheNo ratings yet
- Lec2 - Rqments Gatering 0KDocument28 pagesLec2 - Rqments Gatering 0Krachelortiz510No ratings yet
- 11 Evaluation Again s08 p1Document24 pages11 Evaluation Again s08 p1Hasna Hena MunniNo ratings yet
- COM 410-Part-1Document20 pagesCOM 410-Part-1mathew24No ratings yet
- Chapter Six: Evaluation Techniques and Universal DesignDocument27 pagesChapter Six: Evaluation Techniques and Universal DesignSun Love NewNo ratings yet
- Fact Finding MethodsDocument6 pagesFact Finding MethodspreeyalNo ratings yet
- Part 1 (Chapter 1-4) : Fundamental Components of Interactive SystemDocument46 pagesPart 1 (Chapter 1-4) : Fundamental Components of Interactive SystemM. Talha NadeemNo ratings yet
- Usability Inspection (Heuristic Evaluation)Document35 pagesUsability Inspection (Heuristic Evaluation)Furqan MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Design 2 (Chapter 5) : - Conceptual Design - Physical DesignDocument21 pagesDesign 2 (Chapter 5) : - Conceptual Design - Physical DesignDanial RajputNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 - EvaluationDocument27 pagesLecture 10 - EvaluationColinNo ratings yet
- Hci - 16Document36 pagesHci - 16Usama AhmedNo ratings yet
- Guided By: Prof. Nutan Software Engineering Nirmala Memorial FoundationDocument17 pagesGuided By: Prof. Nutan Software Engineering Nirmala Memorial FoundationSri Sai UniversityNo ratings yet
- Guided By: Prof. Nutan Software Engineering Nirmala Memorial FoundationDocument17 pagesGuided By: Prof. Nutan Software Engineering Nirmala Memorial FoundationVinayNo ratings yet
- HCI Sem1 202021 LU5Document57 pagesHCI Sem1 202021 LU5Diana IsmailNo ratings yet
- Usability Testing Workshop March2020Document89 pagesUsability Testing Workshop March2020jijiNo ratings yet
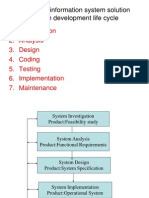
- Developing Information System SolutionDocument42 pagesDeveloping Information System SolutionAbhijeet Mahapatra71% (7)
- Interaction Design: Natnael GonfaDocument40 pagesInteraction Design: Natnael GonfaMebiratu BeyeneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Human-Computer InteractionDocument30 pagesChapter 12 - Human-Computer InteractionHIRSIONo ratings yet
- What Is Usability?: - Usability Is A Measure of How Easy It Is To Use SomethingDocument14 pagesWhat Is Usability?: - Usability Is A Measure of How Easy It Is To Use SomethingAbhinav DakshaNo ratings yet
- Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Document45 pagesSystems Development Life Cycle (SDLC)javauaNo ratings yet
- Got Data, Now What? Analyzing Usability Study Results: Lynn Silipigni Connaway June 26, 2005Document40 pagesGot Data, Now What? Analyzing Usability Study Results: Lynn Silipigni Connaway June 26, 2005lunaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Requirements ModelingDocument50 pagesLesson 4 - Requirements ModelingChlorine CINo ratings yet
- Software Engineering - 1: Lecture #1Document14 pagesSoftware Engineering - 1: Lecture #1Enggielita FitriNo ratings yet
- Hci 10Document29 pagesHci 10SARMAD BEHZAD BUTTNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Evaluation TechniquesDocument41 pagesUnit 7: Evaluation TechniquesKiruthiga DeepikaNo ratings yet
- Online ExaminationDocument30 pagesOnline ExaminationArihant BothraNo ratings yet
- Hci 2Document35 pagesHci 2venkateshNo ratings yet
- Pressman CH 7 Requirements EngineeringDocument34 pagesPressman CH 7 Requirements Engineeringnishasaiyed2304No ratings yet
- KmkloDocument69 pagesKmklomohsinNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For SoftwareDocument29 pagesImportant Questions For Softwarep229321No ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document35 pagesChapter 12Ammar YasserNo ratings yet
- User-Interface DesignDocument28 pagesUser-Interface DesignAarav GKNo ratings yet
- User Centered DesignDocument23 pagesUser Centered Designrm adderNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Requirements ModelingDocument28 pagesChapter Two: Requirements Modelingjurihu143No ratings yet
- 03 Ch2 UX Design Process - IntroDocument16 pages03 Ch2 UX Design Process - Introstudy nowNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document59 pagesChapter 7Efoy TechNo ratings yet
- Usability Engineering : Metrics and Measures For EvaluationsDocument24 pagesUsability Engineering : Metrics and Measures For Evaluationsblack smithNo ratings yet
- Practical Tips Successful BI Project: Milena GerovaDocument33 pagesPractical Tips Successful BI Project: Milena GerovapitupskripteNo ratings yet
- HCI Lect - 18 Evaluation Through Expert AnalysisDocument31 pagesHCI Lect - 18 Evaluation Through Expert AnalysisAqsaNo ratings yet
- Human Computer Interaction Introduction and OverviewDocument27 pagesHuman Computer Interaction Introduction and OverviewAdika Dwi Ananda PutraNo ratings yet
- UXDD Module 6Document9 pagesUXDD Module 6prasad GadeNo ratings yet
- Fiber Distributed Data Interface A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandFiber Distributed Data Interface A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- Lec2 SRS 1 2014 (Compatibility Mode)Document37 pagesLec2 SRS 1 2014 (Compatibility Mode)007wasrNo ratings yet
- Con CurrencyDocument46 pagesCon Currency007wasrNo ratings yet
- Acy 2013 - 2014 - V 13 - 12 May 2014 - AfDocument12 pagesAcy 2013 - 2014 - V 13 - 12 May 2014 - Af007wasrNo ratings yet
- Sheet (6) - Risk ManagementDocument3 pagesSheet (6) - Risk Management007wasrNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Model AnswersDocument5 pagesAssignment 1 Model Answers007wasrNo ratings yet
- Derby BackupDocument17 pagesDerby Backup007wasrNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - 21.11.2013Document3 pagesAssignment 2 - 21.11.2013007wasrNo ratings yet
- Univ Dec Hum RightDocument6 pagesUniv Dec Hum Right007wasrNo ratings yet
- Mutual Exclusion: by Shiran MizrahiDocument67 pagesMutual Exclusion: by Shiran Mizrahi007wasrNo ratings yet
- ARM Assembler: Structure / LoopsDocument61 pagesARM Assembler: Structure / Loops007wasrNo ratings yet
- 13CSCI01I: Analysis of Algorithms Assignment #1: Assigned: Wednesday 23/10/2013 Deadline: Thursday 31/10/2013Document5 pages13CSCI01I: Analysis of Algorithms Assignment #1: Assigned: Wednesday 23/10/2013 Deadline: Thursday 31/10/2013007wasrNo ratings yet
- HWK 1Document2 pagesHWK 1007wasrNo ratings yet
- Greedy Practice ProblemsDocument3 pagesGreedy Practice Problems007wasrNo ratings yet
- Univ Dec Hum RightDocument6 pagesUniv Dec Hum Right007wasrNo ratings yet
- Lecture07 UmlDocument44 pagesLecture07 Uml007wasrNo ratings yet
- Phase 4: Implementation Deadline: Week 12 Weight: 35% of The Project WeightDocument1 pagePhase 4: Implementation Deadline: Week 12 Weight: 35% of The Project Weight007wasrNo ratings yet
- Unplugged 09 Minimal Spanning TreesDocument5 pagesUnplugged 09 Minimal Spanning Trees007wasrNo ratings yet
- Friday Night Mishaps, Listening Plus TasksDocument3 pagesFriday Night Mishaps, Listening Plus TasksCristina Stoian100% (1)
- Natureview Case StudyDocument3 pagesNatureview Case StudySheetal RaniNo ratings yet
- SH Case3 Informants enDocument1 pageSH Case3 Informants enHoLlamasNo ratings yet
- Parkin 8e TIF Ch27Document51 pagesParkin 8e TIF Ch27Pranta SahaNo ratings yet
- Culvert StatementDocument4 pagesCulvert StatementRubul Prasad DasNo ratings yet
- Birhane, E. 2014. Agroforestry Governance in Ethiopa Report WP 5Document50 pagesBirhane, E. 2014. Agroforestry Governance in Ethiopa Report WP 5woubshetNo ratings yet
- Broken Squares - Unfreezing Team Building ExerciseDocument4 pagesBroken Squares - Unfreezing Team Building Exerciselilywhite786No ratings yet
- Drishti IasDocument36 pagesDrishti Ias23010126269No ratings yet
- Case Study TemplateDocument4 pagesCase Study Templateapi-355498849No ratings yet
- Rationale of Labour Welfare To Employers and EmployeesDocument20 pagesRationale of Labour Welfare To Employers and Employeesajit yadav100% (1)
- Evolve Instagram Marketing Guide - From Zero To 10k PDFDocument132 pagesEvolve Instagram Marketing Guide - From Zero To 10k PDFAnjit Malviya100% (2)
- Age of Sigmar AoS - Battletome - Hedonites of Slaanesh - Errata 2023-01Document4 pagesAge of Sigmar AoS - Battletome - Hedonites of Slaanesh - Errata 2023-01Ughu RajaNo ratings yet
- Bhrighu Saral Paddhati - 1Document212 pagesBhrighu Saral Paddhati - 1ErrovioNo ratings yet
- RMK Akl 2 Bab 5Document2 pagesRMK Akl 2 Bab 5ElineNo ratings yet
- Calcium Carbonate Lab ReportDocument2 pagesCalcium Carbonate Lab ReportAlexander Weber0% (1)
- Corruption CricketDocument21 pagesCorruption CricketAshwin NaraayanNo ratings yet
- Danmachi Volume 15Document319 pagesDanmachi Volume 15Muhammad Fazrul Rahman100% (1)
- Activity 1 Which Is WhichDocument1 pageActivity 1 Which Is WhichRhanna Lei SiaNo ratings yet
- Kinematic Tool-Path Smoothing For 6-Axis Industrial Machining RobotsDocument10 pagesKinematic Tool-Path Smoothing For 6-Axis Industrial Machining RobotsToniolo LucaNo ratings yet
- Ezra Pound - PersonaeDocument34 pagesEzra Pound - PersonaedanielrdzambranoNo ratings yet
- Mps Item Analysis Template TleDocument11 pagesMps Item Analysis Template TleRose Arianne DesalitNo ratings yet
- We Don't Need No MBADocument9 pagesWe Don't Need No MBAsharad_khandelwal_2No ratings yet
- Monthly Film Bulletin: 1T1IcqDocument12 pagesMonthly Film Bulletin: 1T1IcqAlfred_HitzkopfNo ratings yet
- Different Varieties of English C1 WSDocument5 pagesDifferent Varieties of English C1 WSLaurie WNo ratings yet
- Simile ListDocument3 pagesSimile ListFiona SohNo ratings yet
- Tle9cookery q1 m7 Presentingandstoringarangeofappetizer v2Document30 pagesTle9cookery q1 m7 Presentingandstoringarangeofappetizer v2Almaira SumpinganNo ratings yet
- Reply Speeches What Are They?Document2 pagesReply Speeches What Are They?Yan Hao Nam89% (9)
- Karbohidrat: Gula, Pati & SeratDocument20 pagesKarbohidrat: Gula, Pati & SeratAlfi Syahrin SiregarNo ratings yet
- How To Perform A Financial Institution Risk Assessment: Quick Reference GuideDocument15 pagesHow To Perform A Financial Institution Risk Assessment: Quick Reference GuideYasmeen AbdelAleemNo ratings yet