Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Report of Summit Power Ltd.
Uploaded by
Shaheen MahmudCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Report of Summit Power Ltd.
Uploaded by
Shaheen MahmudCopyright:
Available Formats
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Chapter-01 Introduction on Report
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
1.1 Origin
of the Report
BBA academic program is the building up to the theoretical knowledge about business administration which is the base of practical knowledge. For Example, in our 7th semester we are experiencing about the credit management system of an organization. Our course namely Credit Management introduces us how to manage the credit of an organization. For being practical knowledge, we select Summit Power Limited. And our key topic of study is Performance Evaluation and Credit Risk Management of Summit Power Limited. It was assigned to us by our course teacher, Md. Abdul Mannan. It was a challenge for us to complete a report on such an important topic. But we have completed this report successfully thanks to continuous supervision of our academic supervision Md. Abdul Mannan.
1.2 Background of the study
This report has been prepared based on Summit Power Ltd. All information is secondary and collected from Internet, Brochures, annual report etc. Based on this information ratio has been calculated. For the calculation of ratio has been calculated to measure the current position of the Summit Power Ltd. At the same time compare with the market performance.
1.3 Objective of the study
The objective of the report is to provide a clear description of Summit Power Ltd. It also provides an exposure of practices of different activities of Summit Power Ltd. Observing the existing rules for Credit Risk management policy and fulfilling the partial requirement of BBA program is another objective of the report. We have completed our report on Summit Power Ltd. And this report is about this organization. As one of the main objectives of report is to gather practical experience on credit risk management system, we have tried to put some of the experiences that we have learnt from our report.
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
1.3.1 Primary Objective:
Primary objective of this report is to measure and analyze the operational and financial performance of Summit Power Ltd.
To analysis the pros and cons of the conventional ideas about credit operation of Summit Power Ltd. To have better orientation on credit management activities specially credit policy and practices, credit appraisal, credit-processing steps, credit management of Summit Power Ltd. To analyze the credit risk management system of the Summit Power Ltd. under the guideline of the Bangladesh Bank (BB). To analyze the credit performance of SPL based on ratio analysis, SWOT
analysis, trend analysis and regression analysis.
1.3.2 The specific objectives of this report are
To present an overview of Summit Power Ltd. To appraise the performance of Summit Power Ltd. To apprise financial performance of Summit Power Ltd. To identify the problems of Summit Power Ltd. To recommend/ remedial measures of the development of Summit Power Ltd.
1. 4 Scope of the Report
The scope of credit risk management is vast and wide. Basically, this report is composed with two parts: Policy guideline and analysis. The policy guideline part includes the general procedures and techniques of credit risk management and the guideline imposed by the Bangladesh Bank. The analysis part includes how actually the SPL follows and practices credit risk management system. Together these statements give-
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
A proper and clear idea about the credit risk management techniques. The practice of credit risk management by the commercial bank of Whether the banks are success or not through using the credit risk
Bangladesh. management techniques.
1.5 Source
of information
Information collected to furnish this report is both from primary and secondary in nature. We collected primary information by direct conversation with the credit officers. Sources of secondary information were Annual Report of SPL. We also studied different books on Finance and Credit and searched through Internet for more information.
1.6 Limitations of the Report
limitations were:
In spite of having the wholehearted effort, there exits some limitations. The
Lack of in-depth knowledge and analytical ability for writing such report. Inadequacy and lack of availability of required Current data and official Limitation of time was a major constraint in making a complete study, due Lack of comprehension of the respondents was the major problem that As being students, it also created some problems as we were unable to
secrecy. to time limitation. created a lot of confusion regarding verification of conceptual question. acquire hands-on-experience in all the departments, due to the organizations policy of maintaining secrecy and also because we did not get the opportunity in all the departments.
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
1.7 Methodology
For preparing the Report, the following methodology is adopted
Populations and samples Sources of data:
This Report is an exploratory and descriptive one in nature. Among primary and secondary source most of the data has been collected from the secondary sources.
1)
Primary sources of information: Face to face conversation with the officials. Secondary sources of information:
1) 2)
Credit Policy Manual of the Banks. Prudential Guidelines on Credit Risk Management issued by Bangladesh Bank. Annual report of SPL. www.bangladesh-bank.org/ www.summitpower.org
3) 4) 5)
Analysis:
The following analysis have been done to measure the credit performance of the SPL Credit Risk Analysis following credit risk grading manual. Ratio analysis, SWOT analysis,
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Chapter-2 An overview of Summit Power Ltd
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
2.1
Background of the Summit Power Ltd
Summit Power Ltd. is the pioneer in the private sector power production field in Bangladesh. Summit Power is the largest local Independent Power Producer. SPL is also the first power generating company to be listed in the local stock exchanges. Summit Power Limited (SPL), a company Summit Group, is the first Bangladeshi Independent Power Producer (IPP) in Bangladesh and until now the only local company in private electricity generation and supply business providing power to national grid. SPL was incorporated in Bangladesh on March 30, 1997 as a Private Limited Company. On June 7, 2004 the Company was converted to Public Limited Company under the Companies Act 1994.
Summit Group is one of the leading investment and industrial business house in Bangladesh. The major sectors in which the group is currently investing in include power generation, port such as container freight station, tank terminal, shipping, property development, construction, civil & hydro engineering & trading. The sponsors of Summit group are interested in infrastructure sectors in Bangladesh and abroad. This has led to the establishment of the first barge mounted power plant in Bangladesh namely Khulna Power Co. Ltd, Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) plant in gas starved area at Mongla Bagerhat, 54 km long gas pipeline of 30 inches diameter from Ashugonj to Hobiganj, Container Freight Station in Chittagong etc. The company is also exploring energy markets in Sri Lanka and Vietnam which have emerging energy sector open to investment. Summit Power Limited has successfully established in the year 2001 three power plants each with 11 MW capacities for sale of electricity to Rural Electrification Board (REB) under build, own and operate basis at Savar, Narsingdi, and Comilla. The company has already expanded its total generation capacity to 105 MW. Summit Power Limited is going to implement another four power plants totaling a capacity of 110 MW through its two subsidiary companies Summit Uttaranchol Power Company Limited and Summit Purbanchol Power Company Limited.
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
2.2 At present Summit Power Ltd
Local Summit Group and US General Electric (GE) signed an agreement on Thursday with IDLC to receive $115 million from the World Banks Investment Promotion Facilitation Fund to implement two 341-megawatt power projects in Bibiyana. On the same day, the two companies signed another deal with Janata Bank and Industrial and Infrastructure Development Finance Company (IIDFC) to raise Tk 1,500 crore through zero-coupon bonds. This fund will be pumped into the Meghnaghat dual fuel 335MW power project. Summit was awarded the Bibiyana gas-fired projects and the Meghnaghat power project about four months back. The Bibiyana projects will need $560 million (Tk 3,920 crore) and Meghnaghat Tk 2,100 crore investment. The Thursdays deal ensures a large part of financing for these three power projects expected to begin production in early 2013 of the cheapest electricity costing less than Tk 2 per kilowatt hour. Summit Group Chairman Muhammed Aziz Khan said Janata Bank and IIDFC would provide Summit with Tk 1,500 crore against a sanction of Tk 2,100 crore financing. The remaining Tk 600 crore is deducted as advance interest for the next four years. As infrastructure like this has long gestation periods, zero-coupon bonds enable companies to implement these projects with an optimised cash flow. The bonds carry a 5 percent discount and 12 percent convertible to the shares of Summit Meghnaghat Power Company at net asset value of the company.
Summit Power Ltd has recently become the lowest in yet two more power tenders, Syedpur 100MW power plant and Shantahar 50MW power plant. Reports say the prime minister signed the work award orders on January 21.
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
2.3 Mission
To expand the company into a power generation capacity to the tune of 1000 MW, which is 20% of the electricity requirement of Bangladesh. Summit Power Limiteds motto: "Empowering Bangladesh, we can & we will."
2.4 Vision
their personal, social economic development.
To provide quality and uninterrupted electricity to vast majority of rural Bangladesh for
2.5 Objective
customers Efficient utilization of capital, machines, material and human resources Continuous management improvement of customer satisfaction and
Generate and provide uninterrupted reasonably priced electricity to our
resource
2.6 Projects
(a) Ashulia Power Plant:
This project was set up to provide electricity for Dhaka Palli Bidyut Samity under
15-years Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) with Rural Electrification Board (REB). An implementation agreement has also been signed with the government of Bangladesh (GoB). After signing expansion agreements with REB and GoB, Summit Power has increased
this plants production capacity by 33.75 MW with the total output being 45 MW.
(b) Narsingdi Power Plant:
This project was set up to provide electricity for Narsingdi Palli Bidyut Samity under 15years Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) with Rural Electrification Board (REB). An implementation agreement has also been signed with the government of Bangladesh (GoB).
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd After signing expansion agreements with REB and GoB, Summit power has increased this plants production capacity by 24.30 MW with the total output being 35 MW.
(c) Comilla Power Plant:
This project was set up to provide electricity for Comilla Palli Bidyut Samity under 15years Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) with Rural Electrification Board (REB). An implementation agreement has also been signed with the government of Bangladesh (GoB). After signing expansion agreements with REB and GoB, Summit power has increased this plants production capacity by 13.50 MW with the total output being 25 MW. Summit Uttaranchol Power Company Limited
(d) Ullapara Power Plant
This project was set up to provide electricity for Sirajganj Palli Bidyut Samity under 15years Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) with Rural Electrification Board (REB). An implementation agreement has also been signed with the government of Bangladesh (GoB). The total output being 11 MW.
(e) Maona Power Plant
This project was set up to provide electricity for Maymensingh and Gazipur Palli Bidyut Samity under 15-years Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) with Rural Electrification Board (REB). An implementation agreement has also been signed with the government of Bangladesh (GoB). The total output being 33 MW.
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
(f) Jangalia Power Plant
This project was set up to provide electricity for Comilla Grid Substation under 15-years Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) with Bangladesh Power Development Board (BPDB). An implementation agreement has also been signed with the government of Bangladesh (GoB) The total output being 33 MW.
(g) Rupganj Power Plant
This project was set up to provide electricity for Narayanganj Palli Bidyut Samity under 15-years Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) with Rural Electrification Board (REB). An implementation agreement has also been signed with the government of Bangladesh (GoB). The total output being 33 MW.
2.7 Board of Directors
Chairman Managing Director Mr. Muhammed Aziz Khan Mr. Syed Ali Jowher Rizvi Mrs. Anjuman Aziz Khan Mrs. Sobera Ahmed Rizvi Mr. Mohammad Latif Khan Ms. Ayesha Aziz Khan Mr. Syed Yasser Haider Rizvi Ms. Adeeba Aziz Khan Mr. Syed Nasser Haider Rizvi Mr. Faisal Karim Khan Ms. Azeeza Aziz Khan Alternate
Directors
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
2.8Management Committees:
.
Audit Committee Mr. Abbas Uddin Ahmed Mr. Tauhidul Islam, Managing Director Ms. Ayesha Aziz Khan, Director(Finance) Mr. A.N.M Tariqur Rashid, Executive Director(P&D) Mr. Mahmud Hasan FCMA, Financial Controller Executive Committee Mr.Tauhidul Islam, Managing Director Mr. Md. Latif Khan, Director Ms. Ayesha Aziz Khan, Director (Finance) Dr. Mirza Khairuzzaman, Senior Executive Director Mr. A.N.M Tariqur Rashid, Executive Director(P&D) Mr. Mahmud Hasan FCMA, Financial Controller Purchase Committee Mr. Md. Latif Khan, Director Mr. Tauhidul Islam, Managing Director Mr. A.N.M Tariqur Rashid, Executive Director(P&D) Mr. Mahmud Hasan FCMA, Financial Controller Technical Committee Mr. A.N.M Tariqur Rashid, Executive Director(O&M) Mr. Solaiman Patwary, General Manager (O&M) Mr. Abdus Sobhan, General Manager (P&D) Md. Nazrul Islam Khan, Manager (E&I) Mr. A.K.M. Asadul Alam Siddique, Plant Manager Operation &smp; Maintenance Committee Mr. Faisal Karim Khan Mr. A.N.M Tariqur Rashid, Executive Director(O&M) Mr. Solaiman Patwary, General Manager (O&M) Md. Nazrul Islam Khan, Manager (E&I) In charge of Plants
Chairman Member Member Member Member Chairman Member Member Member Member Member Chairman Member Member Member Chairman Member Member Member Member Chairman Member Member Member Member
2.9 Senior Executives:
.
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd Dr. Mirza Khairuzzaman, Senior Executive Director A.N.M. Tariqur Rashid, Executive Director Md. Solaiman Patwary, General Manager (Operation & Maintenance) Md. Abdus Sobhan, General Manager (Planning & Development) Mahmud Hasan FCMA, Financial Controller & Company Secretary Md. Nazrul Islam Khan, Manager (Electrical & Instrumentation) Mr. A.K.M. Asadul Alam Siddique, Plant Manager, Comilla Power Plant Commander M Emdadul Haque, (E), psc, BN (Retd) Md. Sirajul Islam, Plant Manager,Narshingdi Power plant Md. Nazmul Hasan, Plant Manager, Rupganj Power Plant Md. Fazle Elahi Khan, Plant Manager, Jangalia Power Plant
2.10 Success Milestones:
. Incorporation of the company
Signing of Project Agreements With REB & GOB March 30, 1997 February 10, 2000 February 8, 2001
Commercial operation at Savar
Commercial operation at Madhabdi
Commercial operation at Comilla
Conversion from Private to Public Appointment of Issue Manager Credit Rating by CRISL Agreement with CDBL Approval of Prospectus from SEC Signing of Project Agreements for expansion at Madhabdi and Comilla with REB & GOB Publication of Prospectus
Subscription Opens Allotment of IPO shares Listing with CSE Listing with DSE First Trading in Stock Exchanges
April 1, 2001 June 08,2001 June 07, 2004 January 13, 2005
March 29, 2005
June 19,2005 June 25, 2005 June 28, 2005 June 28, 2005
August 27, 2005 October 03, 2005 October 23, 2005 November 10,2005 November 15,
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
2005 March 20, 2006
Signing of Project Agreements for expansion at Savar with REB & GOB
Commercial operation at Comilla expansion project Commercial operation at Madhabdi expansion project Incorporation of the Summit Purbanchol Power Company Limited (99%
November 15, 2006 December 16, 2006 August 15,
subsidiary of Summit Power Limited) 2007 Incorporation of the Summit Uttaranchol Power Company Limited (99% August 15, subsidiary of Summit Power Limited) Increase the Authorized Share Capital of the Company (SPL) through EGM for issuance of Rights Share at the ratio of 5:4 Signing of Project Agreements with REB, BPDB 7 GOB to implement total 110 MW power plants (04 nos) through its two subsidiary companies. Commercial Operation at Savar expansion project 2007 September 29, 2007 October 11, 2007 December 04, 2007
2.11 Financial Highlights:
.
Capital and Reserves
Basic Information Of current Year: Authorized Capital in BDT (mn) Paid-up Capital in BDT (mn) Reserve & Surplus in BDT (mn) : : : 10000.0 3034.0 1184.17
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
8%
Capital structure
21%
Authorized Capital in BDT* (mn) Paid-up Capital in BDT* (mn) Reserve & Surplus in BDT* (mn) 71%
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Assets, Liabilities and Oweners Equity:
Position of SPL in Accounting period 2009-10 Financial position
4352.97, 19%
698.52, 3% 10121.06, 43% 2223.94, 10% 5756, 25%
total assets total liability paid up capital net profit shareholder equity
Turnover: SPL has a upword turnover history over the last five year. It indicates this company is operated with smothness.
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Assests:
SPL strategically go ahead with a conception of increasing the total assets of it. The following table and graph show it clearly.
Year 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005
Current Assents Total Assents
1174 10121.1
642.55 6707.12
478.59 4097.69
253.79 2782.7
385.63 1588.23
Current Assets & Cureent Liabilities:
Every Organization needs to overlock on the position of current assets and cureent liabilities since it shows the effienciency of a company. Standard level of current assets and current liabilities ratio is 2:1. SPL showed over the last five year less current assets considering current liabities. The relevent information are:
Year 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Current Assets Current Liabilities 385.63 205.48 253.79 644.39 478.59 886.29 642.55 736.58 1174 1326
Gross Profit & Net Profit:
Over the last five years SPL is showing a unword rising of profitability which is shown in the following table and graph.
Year 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005
Gross Profit Net Profit
1510.03 698.52
945.86 460.21
586.62 268.1
310.16 175.1
283.89 174.21
Gross Profit Ratio: SPL showed a mixed performance for gross profit ratio. It shows performance over the capital. Following table and graph shows it clearly.
Year 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Gross Profit ratio (%)
52.98
54.43
51.07
53.08
54.49
Net Profit Ratio:
As like gross profit ratio, Net Profit Ratio also important since it show how much money is expanded for maintainance of an organization. SPL also showed around a flat level performance on it.
Year 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005
Net Profit Ratio (%)
24.59
26.48
23.34
29.96
33.43
Net Profit Ratio 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0
Return of Total Assets:
Taka (mn) 2009 2008 2007 Year 2006 2005
Net Profit Ratio (%)
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Return on total assets shows how effectively an organization works with its assets. In this consideration SPL is not successful. Since over the last five years it is declining the Return on total assests. The details are given below:
Year 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005
Return on total Assets (%) 6.9 6.86 6.54 6.29 10.97
Return on total Assets 12 10 Taka (mn) 6 4 2 0 2009 2008 2007 Year 2006 2005 8 Return on total Assets (%)
Earning Per Share:
EPS is a key elements of showing the performance to a company or earning per share. SPL showed around a flat rate of earning over the last five years. The following table and graph show it clearly.
Year 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005
Earning per share (Taka)
31.41
25.71
31.25
25.66
37.33
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Earning per share 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 2009 2008 2007 Year 2006 2005
Price Earning Ratio:
P/E ratio over the last five years was in upward movement of SPL. P/E Ratio is a very important element in investing of investor. It indicates the efficient performance of company.
Year Price Earning Ratio (P/E) 2005 9.46 2006 20.64 2007 46.65 2008 46.69 2009 48.04
P/E (tk)
Taka (mn)
Earning per share (Taka)
Price Earning Ratio (P/E) 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 2005 2006 2007 Year 2008 2009 Price Earning Ratio (P/E)
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
2.12 Financial Position At a glance:
Financial Position of SPL for fiver years show how it is smoothly operated and continuoue its business actibities, Relevent financial information are given below:
Operating data (Take in million) Operating Expenses Turnover Gross Profit General & Admin Expenses Interest & Financial Charges Net Profit Balance Sheet data (Taka in million) Paid up Capital Shareholders Equity Total Debt Current Assets Current Liabilities Total Assets Total Liabilities Financial ratios Gross Profit ratio (%) Net Profit Ratio (%) Return on total Assets (%) Debt Equity ratio Others data Earning per share (Taka) Dividend (%) Total no. of shares outstanding Weighted average no. of shares outstanding Total no. of sponsors shares under lock in Total no, of free float shares 2009 1339.84 2849.87 1510.03 258.41 558.91 698.52 2009 2223.94 4352.97 4430.00 1174.00 1326.00 10121.06 5756.00 2009 52.98 24.59 6.90 56:44 2009 31.41 25.00 222,39,360 222,39,360 43,91,683 178,47,677 2008 791.93 1737.79 945.86 176.71 327.45 460.21 2008 1853.28 3654.44 2306.00 642.55 736.58 6707.12 3042.97 2008 54.43 26.48 6.86 45:55 2008 25.71 20.00 1,85,32,800 1,78,97,346 2007 1148.77 562.15 586.62 134.80 189.39 268.10 2007 858.00 1412.13 2268.12 478.59 886.29 4097.69 2685.56 2007 51.07 23.34 06.54 62:38 2007 31.25 20.00 85,80,000 2006 584.35 274.19 310.16 102.83 46.76 175.10 2006 715.00 1154.49 1494.80 253.79 644.39 2782.70 1628.21 2006 53.08 29.96 06.29 56:44 2006 25.66 20.00 71,50,000 2005 521.04 237.15 283.89 73.76 48.05 174.21 2005 650.00 1044.38 512.29 385.63 205.48 1588.23 543.85 2005 54.49 33.43 10.97 33:67 2005 37.33 20.00 65,00,000
79,84,167 68,25,000 46,66,667
45,00,000 45,00,000 45,00,000 43,91,683 1,41,41,117 40,80,000 20,00,000 26,50,000
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Chapter 3 An overview of Credit Management
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
3.1 Overview :
Credit is the heart of bank.The success and failure of bank depends largely on efficient handling of their fund.In the past i.e.70 to 80 years ago credit was simple because at that time lenders personally knew the borrowers.As commerce and industry grew, the activities of credit management have changed. In the past, credit management was only concerned about the protection of lenders own funds but in the modern banking lenders are not concerned about the protection of their own funds but also concerned with the future of the industry which borrowers own and the protection of borrowers fund.In credit management , a credit officer has to do a lot of works. For deciding to grant credit, he has to apply his common sense. Commonsense like, what he has to ensure the safety if ha wants to invests his own fund. For investing own funds one has to ensure the (1) Safety of his own money; (2) recovery of his own money; and (3) actual help to others in time of need (Srinivasa 1986,1). Like own funds, in making granting decision , a credit officer should satisfy himself/herself about the safety , recovery of his funds, and needs of the borrowers. In granting decision, a credit officer should be careful because a little bit of unconsciousness and ignorance can lead to heavy losses to the bank. This knowledge of lending cannot be taught nor learnt by reading a expertise book but by ones own experience and commonsense and helping attitude (Srinivasa 1986,2).
3.2 Definition of Credit :
Encyclopedia of Banking and Finance describes the origin and defines credit as.
Credit derived from Latin word credo means I believe, and usually define as the ability to buy with a promise to pay, or the ability to obtain title to, and receive goods for enjoyment in the present although payment is deferred to a future date.
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Credit is the provision of financial accommodation to a person, in return for a promise to repay it at some future date. It may be extended as cash, or supply of goods or services. The former type of credit is called lender credit and later is referred as vendor credit is, it enables a person to spend in excess of his/her actual
means in present.
3.3 Credit Management :
In the simplest form, management is the process of getting things done by others. In
the broader concept, management involves various systematic plan and actions to achieve the goal of the organization. Credit management is the process of accomplishing various tasks relating to deciding grant or not granting credit to others, determination of terms and conditions, proper documentation, frequent monitoring and reviewing the performance of borrowers and taking necessary steps to ensure smooth recovery of credit which ensure profit maximization of the bank. Bank in the developing countries often do not have a well developed credit
management process and the main deficiencies of this are : The absence of written policies.
The absence of portfolio concentration limits excessive centralization or decentralization of landing authority. Poor industry analysis. A cursory financial analysis of borrowers. An excessive reliance on collateral. Infrequent customer contact. The inadequate checks and balance in the credit process. Absence of loan supervision. A failure to improve collateral position as credit deteriorates. Poor control on loan documentation. Excessive overdraft lending. Incomplete credit files. The absence of asset classification and loan loss provisioning standards, and
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
A failure to control and audit the credit process effectively (Diana and Clayton 1997, 32).
3.4 Steps in credit management :
Credit management task starts from making strategic targets for credit markets and
end with recovery of credit. Broadly credit management involves the following main steps : First, one must determine priority sectors he/she is interested to lend and prohibited sectors he/she is not interested to lend (Credit policy formulation), Second, one must determine which borrowers are likely to pay their debt (Credit investigation and analysis). Third, one must decide how much credit he/she is prepare to extend in each borrower (Credit approval). Fourth, he/she must decide what evidence he/she need of indebtedness (Documentation. Fifth, after ha/she has granted credit, he/she has the problem of collecting the money when its becomes due. How does he/she keep track of payments ? (Monitoring, review, and loan recovery). By analyzing the above steps, the study identifies the following steps in credit management : Strategic plan for target credit markets. Credit policy formulation. Client request/relationship marketing. Loan interviewing. Credit investigation. Credit analysis. Preparation of credit analysis report/preparation of proposal. Loan sanction, loan structuring, loan negotiation. Loan documentation. Loan disbursement. Loan monitoring/review.
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Problem loan identification and resolution and Loan recovery.
3.5 Changing status & Qualification of Credit Management
(Evolution of credit management)
The major factor contributing to the changing status and qualifications for credit
management has been the rapid and tremendous growth of industry and commerce. When business was mostly under the control of a sole proprietor and relatively small in size, the approval of credit was simple and personal matter.50 to 70 years ago, it was customary that lenders were to visits market once or twice in a year. At that time borrowers were personally known to lenders, the size of business was small and for a number of years bookkeepers were in controls of the credit management task. With the pace of development of commerce, the personal relationship was lost and some other basis was needed to manage commerce credit. It was logical that the task should fall on someone within the company. As commerce and industry grew, it becomes apparent that the work of bookkeeper credit man would have to dividend. Parallel to the commercial and industrial developments of the last couple of centuries a high degree of administrative efficiency has been attained through better organization and specialization. With the organization of the national association of credit management in U.S.A in 1896 and several other developments supported the significance of professional credit management. Improved source of credit information; better accounting methods, redefinition of the techniques of financial statement analysis recognized the professional character of credit work. Significant relationships of credit to business finance , production , marketing and financial operations of the business sought out credit work as group and need an increased number of highly qualified people. The complexity of modern day business and the need for specialization created this condition, and it fostered the status held by todays credit managers.
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Now credit management has moved up to the status of an established business group, with prerogatives, responsibilities, standards and ethics.
3.6 Components of a Standard Credit Policy
aspects are1.Corporate mission statement 2. Analysis of the present credit portfolio 3. Board objectives of the policy 4. Preffered area of lending 5. Discouraged area of lending 6. Strategies to achieve the above objectives 7. Exposure limits 8. Liquid gap analysis 9. Spread Management 10. Credit expansion policy 11. Combating the growing menace of NPAs 12. Industry wise specialization and 13. Pricing strategy. In addition to the above components, credit policy may contain:
Gupta (1995) recommended thirteen aspects for a good lending policy. The
1. Specification of the lending authority given to each loan officer and loan committee (measuring the maximum amount and types of loan that each person and committee can approve and what signatures are required) 2. Credit granting Process. 3. Lines of responsibility in making assignments and reporting information within the loan department. 4. Operating procedures for soliciting, reviewing, evaluating and making decision on customer loan applications. 5. Lines of authority within the bank, detailing who is responsible for maintaining and reviewing the banks credit files, and 6. A discussion of the preferred procedures for detecting, analyzing, and working out problem loan situation.
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
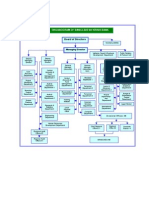
3.7 Flow Chart Of Credit Management :
From scholarly literature, the study develops the following flow chart of credit management Flow chart of CM Strategic plan for target market Credit policy formulation
Initiation, Client request, Relationship marketing
Client interview Credit investigation Credit analysis, purpose, business, Management figure, Credit rating Credit analysis report Credit approval Credit structuring, Pricing, Repayment Credit negotiation (Tenor, Pricing, Repayment, Security and others Documentation Credit disbursement Internal Audit Credit monitoring and review Handling problem credit Recovery of credit
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Chapter 4 Credit Risk Management- A Brief Discussion
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
4.1 Credit risk management:
Credit risk is the uncertainty in a counterparty's (also called an obligor's or credit's) ability to meet its obligations. The goal of credit risk management is to maximize a bank's risk-adjusted rate of return by maintaining credit risk exposure within acceptable parameters. Banks need to manage the credit risk inherent in the entire portfolio as well as the risk in individual credits or transactions. Banks should also consider the relationships between credit risk and other risks. The effective management of credit risk is a critical component of a comprehensive approach to risk management and essential to the long-term success of any banking organization. Because there are many types of counterparties--from individuals to sovereign governments-and many different types of obligations--Institutions manage it in different ways. In assessing credit risk from a single counterparty, an institution must consider three issues: Default probability:
What is the likelihood that the counterparty will default on its obligation either over the life of the obligation or over some specified horizon, such as a year? Calculated for a one-year horizon, this may be called the expected default frequency. Credit exposure:
In the event of a default, how large will the outstanding obligation be when the default occurs? Recovery rate:
In the event of a default, what fraction of the exposure may be recovered through bankruptcy proceedings or some other form of settlement? When we speak of the credit quality of an obligation, this refers generally to the counterparty's ability to perform on that obligation. This encompasses both the obligation's default probability and anticipated recovery rate.
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
4.2 Principles of Credit risk management: While financial institutions have faced difficulties over the years for a multitude
of reasons, the major cause of serious banking problems continues to be directly related to lax credit standards for borrowers and counterparties, poor portfolio risk management, or a lack of attention to changes in economic or other circumstances that can lead to a deterioration in the credit standing of a bank's counterparties. Banks need to manage the credit risk inherent in the entire portfolio as well as the
risk in individual credits or transactions. Banks should also consider the relationships between credit risk and other risks. A prudent Banker should always adhere to the following general principles of Background, Character and ability of the borrowers Purpose of the facility, Term of facility, Safety, Security, Profitability, Source of repayment, Diversity. Since exposure to credit risk continues to be the leading source of problems in banks world-wide, banks and their supervisors should be able to draw useful lessons from past experiences. Banks should now have a keen awareness of the need to identify, measure, monitor and control credit risk. While the exact approach chosen by individual supervisors will depend on a host of factors, including their on-site and off-site supervisory techniques and the degree to which external auditors are also used in the supervisory function. A further particular instance of credit risk relates to the process of settling financial transactions. If one side of a transaction is settled but the other fails, a loss may be incurred that is equal to the principal amount of the transaction. Even if one party is simply late in settling, then the other party may incur a loss relating to
lending funds to his customers.
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd missed investment opportunities. Settlement risk thus includes elements of liquidity, market, operational and reputational risk as well as credit risk.
4.3 Internal and external risk factors of credit risk:
The landing risk is to be primarily calculated from two angles, namely, Business risk and security risk. The Business risk is again divided under two categories of risk, i.e., industrial risk and company risk, which again divided into six categories. A form has been designed by the FSRP to help assessment of these risks. The form and a short description is given below Credit Risk
Business Risk
Security Risk
Industry Risk
Company Risk
Security Control Risk
Security covers Risk
Supply Risk
Sales Risks
Company Position Risk
Management Risk
Performance Risk
Resilience Risk
Management Competency
Management Integrity
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd Chart No-1: Flow chart of different Credit Risk
Tools used in Credit risk management Some tools used in credit risk management, like credit analysis, credit exposure, loan classification. These are describes below:
4.4 Credit analysis:
Credit analysis refers to the default risk analysis in which a loan officer attempts to evaluate a borrowers ability and willingness to repay. Generally through credit analysis the loan officer analyze all available information to determine whether the loan meets the banks risk-return objectives. To analyze credit three techniques are used: (i) a) Qualitative analysis, Quantitative analysis and Credit Risk Grading. Qualitative Analysis Character:
In the qualitative analysis the bank usually analyze the 5 Cs of the customer The loan officer must be convinced that the customer has a well-defined purpose for requesting bank credit and a serious intention to repay. If the officer is not sure exactly why the customer is requesting a loan, this purpose must be clarified to the banks satisfaction. To determine the character of the borrower, banker must investigate the following: Customers past payment records. Experience of other lenders with the customer. Purpose of loan. Customers track record in forecasting business or personal income. Credit Rating
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
a)
Capacity:
The loan officer must be sure that the customer requesting credit has the authority to request a loan and the legal standing to sign a binding loan agreement. Therefore the bank needs the following information: a) Identify of customer and guarantors. Description of history, legal structure, owners, nature of operation, products and Copies of resolution, partnership agreements, and other legal document Cash:
principal customers and suppliers for a business of the borrowers.
Here the loan officers analyze that whether they have ability to generate enough cash, in the form of cash flow, to repay the loan or not. b) Conditions:
The loan officer and credit analyst must be aware of recent trends in the borrowers line of work or industry and how changing economic conditions might affect the loan. To assess the situation the following points should be taken into consideration: a) Customers current position industry and expected market share. Customers performance vis--vis comparable firms in the same nature of Sensitivity of customer and industry to business cycles and changes in technology. Labor market condition of customers product, impact of inflation on the industry. Long run industry or job outlook. Regulations, political and environmental factors affecting the customer and / or Collateral:
business or industry.
his / her job, business and industry.
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd In assessing the collateral aspect of a loan request, the loan officer must ask, does the borrower possess adequate net worth or own enough quality assets to provide adequate support for the loan? The loan officer is particularly sensitive to such features as the age, condition, and degree of specialization of the borrowers assets. Bank has to consider: (i) Ownership of assets, Vulnerability of assets to obsolete Liquidation and degree in specialization of value of assets Liens, encumbrances and restrictions against property held Leases and mortgages issued against property and equipment Guarantees and warranties issued to others Banks relative position as creditors in placing a claim against borrowers assets Quantitative Analysis
Using Quantitative analysis refers to the analysis of financial statement ratios to know the past performance of a company. Some of the key ratios which serve as a tool for financial analysis are classified as 1) Financial Ratio 2) Turnover Ratio 3) Profitability Ratio Financial Ratio Financial ratios indicate about the financial position of the company. A company is deemed to be financially sound if it is in a position to carry on its business smoothly and meet its obligations-both long-term as well as short term-without strain. Some of the important financial ratios are: Fixed Asset Ratio, Current Ratio, Quick Ratio, Debt Equity Ratio etc. Turnover Ratio The turnover ratios indicate the efficiency with which the capital employed is rotated. They are also known as Activity or efficiency ratio. The overall profitability of the business depends on the turnover i.e. the speed at which the capital employed in the business rotates. The higher the rate of rotation, the greater the profitability. Some important turnover ratios are: Fixed Assets Turnover Ratio, Working Capital Turnover ratio etc. Profitability Ratio
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd Profitability is an indication of the efficiency with which the operations of the business are carried on. Poor operational performance may indicate poor sales and hence poor profits. Bankers look at the profitability ratio as an indicator whether or not the firm/company earns substantially more than it pays interest for the use of borrowed funds and whether the ultimate repayment of their debt appears reasonably certain. The important profitability ratios are: Overall Profitability Ratio, Gross Profit Ratio, Net Profit Ratio etc. (ii) Credit Risk Grading
Credit risk grading is an important part of credit analysis for credit risk management as it helps the banks & financial institutions to understand various dimensions of risk involved in different credit transactions. The aggregation of such grading across the borrowers, activities and the lines of business can provide better assessment of the quality of credit portfolio of a bank or a branch. At the pre-sanction stage, credit grading helps the sanctioning authority to decide whether to lend or not to lend, what should be the loan price, what should be the extent of exposure, what should be the appropriate credit facility, what are the various facilities, what are the various risk mitigation tools to put a cap on the risk level. At the post-sanction stage, the bank can decide about the depth of the review or renewal, frequency of review, periodicity of the grading, and other precautions to be taken. 4.5 Benefit of credit risk management: Maximize the value of your risk-management activities. Effective credit portfolio management is critical to the financial health of any company. This means setting the right credit amount and terms at account origination and, on revolving lines of credit, determining the right credit-line adjustments to profitably grow and retain existing customers. 1. 2. 3. 4. Gain a competitive advantage Maximize the portfolio profitability Make appropriate risk-reward decisions Gain more control and insight
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd 5. 6. Manage existing customers Maximize collections effectiveness
4.6 Basel Accord II Implementation in the Bangladesh Banking Sector:
Like many developing countries, implementation of Basel II is a challenging issue for banking sector of Bangladesh. Smooth transition to Basel II requires implementation of Basel Core Principles (BCPs) and the introduction of related risk management practices. In a recent self-assessment study by Bangladesh Bank shows that Bangladesh is largely compliant of BCPs. BB has also introduced risk management practices in the banking sector since October 2003 focusing on 5(five) core risk areas such as credit risk, asset and liability/balance sheet risk, foreign exchange risk, internal control and compliance risk and money laundering risk. This provides a basic foundation for implementation of the New Accord. However, the Accord is complex, requires good understanding of risk modeling, validation and a wide historical data base. Other challenges include human resources capacity building both in the central bank as well as in commercial banks. Since the Accord will affect different banks in varying degrees. If a bank's loan portfolio is allowed to be rated by external agencies such as credit rating agencies, cautious steps need to be adapted. Good corporate governance in rating agencies needs to be ensured to avoid cherry-picking. Since the New Accord will cause substantial change in inspection methodology, supervisory departments of BB require upgrading and strengthening their human resources capacity so as to avoid supervisory lapses and shoulder their responsibilities in a professionally competent manner.
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Chapter- 5 Credit assessment and risk grading
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
5.1 Credit assessment:
A thorough credit and risk assessment should be conducted prior to the granting of loans, and at least annually thereafter for all facilities. The results of this assessment should be presented in a Credit Application that originates from the relationship manager/account officer (RM), and is approved by Credit Risk Management (CRM). It is essential that RMs know their customers and conduct due diligence on new borrowers, principals, and guarantors to ensure such parties are in fact who they represent themselves to be. All banks should have established Know Your Customer (KYC) and Money Laundering guidelines which should be adhered to at all times. Credit Applications should summaries the results of the RMs risk assessment and include, as a minimum, the following details: o o o o Amount and type of loan(s) proposed. Purpose of loans. Loan Structure (Tenor, Covenants, Repayment Schedule, Interest) Security Arrangements.
5.2 Risk Grading:
All Banks should adopt a credit risk grading system. The system should define the risk profile of borrowers to ensure that account management, structure and pricing are commensurate with the risk involved. Risk grading is a key measurement of a Banks asset quality, and as such, it is essential that grading is a robust process. All facilities should be assigned a risk grade. Where deterioration in risk is noted, the Risk Grade assigned to a borrower and its facilities should be immediately changed. Borrower Risk Grades should be clearly stated on Credit Applications.
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
5.3 Credit Risk Grading Definition:
A clear definition of the different categories of Credit Risk Grading is given as follows: Superior - (SUP) - 1 Credit facilities, which are fully secured i.e. fully cash covered. Credit facilities fully covered by government guarantee. Credit facilities fully covered by the guarantee of a top tier international Bank. Good - (GD) - 2 Strong repayment capacity of the borrower. The borrower has excellent liquidity and low leverage. The company demonstrates consistently strong earnings and cash flow. Borrower has well established, strong market share. Very good management skill & expertise. All security documentation should be in place. Credit facilities fully covered by the guarantee of a top tier local Bank. Aggregate Score of 85 or greater based on the Risk Grade Score Sheet. Acceptable - (ACCPT) - 3 These borrowers are not as strong as GOOD Grade borrowers, but still Borrowers have adequate liquidity, cash flow and earnings. Credit in this grade would normally be secured by acceptable collateral (1st Acceptable management. Acceptable parent/sister company guarantee. Aggregate Score of 75-84 based on the Risk Grade Score Sheet. Marginal/Watch list - (MG/WL) - 4
demonstrate consistent earnings, cash flow and have a good track record.
charge over inventory / receivables / equipment / property).
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd This grade warrants greater attention due to conditions affecting the borrower, the These borrowers have an above average risk due to strained liquidity, higher than Weaker business credit & early warning signals of emerging business credit The borrower incurs a loss. Loan repayments routinely fall past due. Account conduct is poor, or other untoward factors are present. Credit requires attention. Aggregate Score of 65-74 based on the Risk Grade Score Sheet. Special Mention - (SM) - 5 This grade has potential weaknesses that deserve managements close attention.
industry or the economic environment. normal leverage, thin cash flow and/or inconsistent earnings. detected.
If left uncorrected, these weaknesses may result in a deterioration of the repayment prospects of the borrower. Severe management problems exist. Facilities should be downgraded to this grade if sustained deterioration in An Aggregate Score of 55-64 based on the Risk Grade Score Sheet. Substandard - (SS) - 6 Financial condition is weak and capacity or inclination to repay is in doubt. These weaknesses jeopardize the full settlement of loans. Bangladesh Bank criteria for sub-standard credit shall apply. An Aggregate Score of 45-54 based on the Risk Grade Score Sheet. Doubtful - (DF) - 7 Full repayment of principal and interest is unlikely and the possibility of loss is However, due to specifically identifiable pending factors, such as litigation, Bangladesh Bank criteria for doubtful credit shall apply.
financial condition is noted (consecutive losses, negative net worth, excessive leverage),
extremely high. liquidation procedures or capital injection, the asset is not yet classified as Bad & Loss.
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd An Aggregate Score of 35-44 based on the Risk Grade Score Sheet. Bad & Loss - (BL) - 8 Credit of this grade has long outstanding with no progress in obtaining repayment Prospect of recovery is poor and legal options have been pursued. Proceeds expected from the liquidation or realization of security may be awaited.
or on the verge of wind up/liquidation.
The continuance of the loan as a bankable asset is not warranted, and the anticipated loss should have been provided for. This classification reflects that it is not practical or desirable to defer writing off this basically valueless asset even though partial recovery may be affected in the future. Bangladesh Bank guidelines for timely write off of bad loans must be adhered to. Legal procedures/suit initiated. Bangladesh Bank criteria for bad & loss credit shall apply. An Aggregate Score of less than 35 based on the Risk Grade Score Card.
At least top twenty-five clients/obligors of the Bank may preferably be rated by an outside credit rating agency.
5.4 How to Compute Credit Risk Grading:
The following step-wise activities outline the detail process for arriving at credit risk grading. Step I: Identify all the Principal Risk Components Credit risk for counterparts arises from an aggregation of the following: Financial Risk Business/Industry Risk Management Risk Security Risk Relationship Risk
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Step II: Allocate weights to Principal Risk Components According to the importance of risk profile, the following weights are proposed for corresponding principal risks. Principal Risk Components: Financial Risk Business/Industry Risk Management Risk Security Risk Relationship Risk Weight: 50% 18% 12% 10% 10%
Step III : Establish the Key Parameters Principal Risk Components Financial Risk Key Parameters: Leverage, Liquidity, Profitability & Coverage ratio Business/Industry Risk Size of Business, Age of Business, Business Outlook, Industry Growth, Competition & Barriers to Business. Management Risk Security Risk Experience, Succession & Team Work. Security Coverage, Collateral Coverage and Support. Relationship Risk Account Deposit. Table 7: Establishing key parameter in credit risk grading Conduct, Utilization of Limit,
Compliance of covenants/conditions & Personal
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Step IV
Assign weightages to each of the key parameters.
Key Parameters: Weight: 50% 15% 15% 15% 5% 18% Size of Business Age of Business Business Outlook Industry growth Market Competition Entry/Exit Barriers 5% 3% 3% 3% 2% 2% 12% Experience Succession Team Work 5% 4% 3% 10% 4% 4% 2% 10% Account conduct Utilization of limit Compliance of covenants /condition Personal deposit 5% 2% 2% 1%
Principal Risk Components: Financial Risk
Business/Industry Risk
Leverage Liquidity Profitability Coverage
Management Risk
Security Risk Security coverage Collateral coverage Support
Relationship Risk
After the risk has been identified & weights assignment process (as mentioned above), the next steps will be to input actual parameter in the score sheet to arrive at the scores corresponding to the actual parameters.
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Step V: Arrive at the Credit Risk Grading based on total score obtained The following is the proposed Credit Risk Grade matrix based on the total score obtained by an obligor. Number 1 Risk Grading Superior Short Name SUP Score 100% cash covered Government guarantee International Bank guarantees 85+ 75-84 65-74 55-64 45-54 35-44 <35
2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Good Acceptable Marginal/Watch list Special Mention Sub-standard Doubtful Bad & Loss
GD ACCPT MG/WL SM SS DF BL
Table 8: Credit Risk Grading matrix
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
5.5 CREDIT RISK GRADING SCORE SHEET:
Reference No: Borrower: Group Name (if any): Branch: Industry/Sector: Date of Financials: Completed by: Approved by:
Number Grading
Date:
Aggregate Score: _________
Risk Grading: _________
S h o r t
Score
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Superior Good
Acceptable
SUP GD ACCPT MG/WL SM SS DF BL
Fully cash secured, secured by Government/International Bank Guarantee 85+ 75-84 65-74 55-64 45-54 35-44 <35
Marginal/Watch list Special Mention Substandard Doubtful Bad & Loss
Criteria
Weight
Score Parameter
A. Financial Risk 1. Leverage: (15%)
50%
Actual Parameter
Score Obtained
Debt Equity Ratio () - Times Total Liabilities to Tangible Net worth All calculations should be based on annual financial statements of the borrower (audited preferred).
Less than 0.25 0.26 to 0.35 x 0.36 to 0.50 x 0.51 to 0.75 x 0.76 to 1.25 x 1.26 to 2.00 x 2.01 to 2.50 x 2.51 to 2.75 x More than 2.75
15 14 13 12 11 10 8 7 0
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
2. Liquidity: (15%) Current Ratio () - Times Current Assets to Current Liabilities Greater than 2.74 2.50 to 2.74 x 2.00 to 2.49 x 1.50 to 1.99 x 1.10 to 1.49 x 0.90 to 1.09 x 0.80 to 0.89 x 0.70 to 0.79 x Less than 0.70 Greater than 25% 20% to 24% 15% to 19% 10% to 14% 7% to 9% 4% to 6% 1% to 3% Less than 1% More than 2.00 More than 1.51 Less than 2.00 More than 1.25 Less than 1.50 More than 1.00 Less than 1.24 Less than 1.00 15 14 13 12 11 10 8 7 0 15 14 13 12 10 9 7 0 5 4 3 2 0
3. Profitability: (15%) Operating Profit Margin (%) Operating Profit 100 Sales
4. Coverage: (5%) Interest Coverage Ratio ()Times
Earning Before Interest & Tax (EBIT)
Interest on debt
Total ScoreFinancial Risk
50
Criteria
Weight
B. Business/Industry Risk 18% 1. Size of Business (Sales in BDT crore)
Parameter
Score
Actual Parameter
Score Obtained
The size of the borrowers business measured by the most recent years total sales. Preferably based on audited financial statements 2. Age of Business The number of years the borrower has been engaged in the primary line of business.
> 60.00 30.00 59.99 10.00 29.99 5.00 - 9.99 2.50 - 4.99 < 2.50 > 10 years > 5 - 10 years 2 - 5 years < 2 years
5 4 3 2 1 0 3 2 1 0
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Criteria Weight
3. Business Outlook
A critical assessment of the medium term prospects of the borrower, taking into account the industry, market share and economic factors. 4. Industry Growth 5. Market Competition
Favorable Stable Parameter Slightly Uncertain Cause for Concern Strong (10%+) Good (>5% - 10%) Moderate (1% - 5%) No Growth (<1%) Dominant Player Moderately Competitive Highly Competitive Difficult Average Easy
3 2 Score 1 0 3 2 1 0 2 1 0 2 1 0 18
Actual Parameter Score Obtained
6. Entry/Exit Barriers
Total ScoreBusiness/Industry Risk
Criteria
C. Management Risk
Weight
12 %
Parameter More than 10 years in the related line of business 510 years in the related line of business 15 years in the related line of business No experience Ready Succession Succession within 1-2 years Succession within 2-3 years Succession in question Very Good Moderate Poor Regular Conflict
Score 5 3 2 0 4 3 2 0
Actual Paramete r
Score Obtained
1. Experience
(Management & Management Team)
The quality of management based on the aggregate number of years that the Senior Management Team has been in the industry. 2. Second Line/ Succession
3. Team Work
Total Score-Management Risk
3 2 1 0 12
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Criteria D. Security Risk
Weight 10%
Score Parameter Fully pledged facilities/substantially cash covered/Reg. Mortg, for HBL Registered Hypothecation (1st charge/1st Pari passu charge) 2nd Charge/Inferior charge Simple hypothecation/negative lien on assets. No security Registered Mortgage on Municipal Corporation/Prime area property. Registered Mortgage on Pourashava/semi-urban area property Equitable Mortgage or No property but plant & machinery as collateral Negative lien on collateral No collateral Personal guarantee with high net worth or Strong Corporate Guarantee Personal Guarantees or Corporate Guarantee with average financial strength No Support/Guarantee 4 3 2 1 0
Actual Score Parameter Obtained
1. Security Coverage (Primary)
2. Collateral Coverage (Property Location)
4 3 2 1 0
3. Support (Guarantee)
1 0 10
Total Score- Security Risk
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Criteria E. Relationship Risk 1. Account Conduct
Weight 10%
Parameter More than 3 (three) years accounts with faultless record Less than 3 (three) years accounts with faultless record Accounts having satisfactory dealings with some late payments Frequent Past dues & Irregular dealings in account More than 60% 40% - 60% Less than 40% Full Compliance Some Non-Compliance No Compliance
Score 5 4 2 0
Actual Score Parameter Obtained
2. Utilization of Limit (actual/projection) 3. Compliance of Covenants / Conditions 4. Personal Deposits
2 1 0 2 1 0 1
Personal accounts of the key business Sponsors/ Principals are The extent to which the bank maintained in the bank, with maintains a personal banking significant deposits relationship with the key business No depository relationship sponsors/principals. Total Score-Relationship Risk Grand Total- All Risk
0 10 100
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Chapter-6 Performance Evaluation of Summit Power Ltd
.
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
The overall performance of SPL is in line with the first generation of electricity company. Besides, the SPL has been facing decline trend in some of the performance parameters compared to its previous performance up to 30th June 2009.However, some of the parameters has again shown upward trend in 31st August 2008 performance. The overall Performance of the SPL is analyzed below: 6.1 CREDIT RISK GRADING SCORE SHEET Of SUMMIT POWER Ltd as the financial performance 2009-2010:
Reference No: Borrower: Group Name (if any): Branch: Industry/Sector: Date of Financials: Completed by: Approved by:
Number
Date: Summit Power Ltd
Aggregate Score: ______85___
Power and Electricity 2009-2010
Risk Grading:
___Good______
Grading
S h o r t
Score
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Superior Good
Acceptable
SUP GD ACCPT MG/WL SM SS DF BL
Fully cash secured, secured by Government/International Bank Guarantee 85+ 75-84 65-74 55-64 45-54 35-44 <35
Marginal/Watch list Special Mention Substandard Doubtful Bad & Loss
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Criteria
Weight
Score Parameter
A. Financial Risk 1. Leverage: (15%)
50%
Actual Parameter
Score Obtained
Less than 0.25 0.26 to 0.35 x Debt Equity Ratio () - Times 0.36 to 0.50 x Total Liabilities to Tangible Net 0.51 to 0.75 x worth 0.76 to 1.25 x 1.26 to 2.00 x All calculations should be based 2.01 to 2.50 x on annual financial statements of 2.51 to 2.75 x the borrower (audited preferred). More than 2.75 2. Liquidity: (15%) Greater than 2.74 2.50 to 2.74 x Current Ratio () - Times 2.00 to 2.49 x Current Assets to Current 1.50 to 1.99 x Liabilities 1.10 to 1.49 x 0.90 to 1.09 x 0.80 to 0.89 x 0.70 to 0.79 x Less than 0.70 3. Profitability: (15%) Greater than 25% Operating Profit Margin (%) 20% to 24% 15% to 19% Operating Profit 10% to 14% 100 7% to 9% Sales 4% to 6% 1% to 3% Less than 1% 4. Coverage: (5%) More than 2.00 Interest Coverage Ratio () More than 1.51 Less than Times 2.00 More than 1.25 Less than Earning Before Interest & Tax (EBIT) 1.50 Interest on debt More than 1.00 Less than 1.24 Less than 1.00 Total ScoreFinancial Risk
15 14 13 12 11 10 8 7 0 15 14 13 12 11 10 8 7 0 15 14 13 12 10 9 7 0 5 4 3 2 0
1.27
10
0.89
25%
15
50
38
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Criteria Weight Score
B. Business/Industry Risk 18% 1. Size of Business (Sales in BDT crore)
Parameter
Actual Parameter
Score Obtained
The size of the borrowers business measured by the most recent years total sales. Preferably based on audited financial statements 2. Age of Business The number of years the borrower has been engaged in the primary line of business. 3. Business Outlook A critical assessment of the medium term prospects of the borrower, taking into account the industry, market share and economic factors. 4. Industry Growth 5. Market Competition
> 60.00 30.00 59.99 10.00 29.99 5.00 - 9.99 2.50 - 4.99 < 2.50 > 10 years > 5 - 10 years 2 - 5 years < 2 years Favorable Stable Slightly Uncertain Cause for Concern Strong (10%+) Good (>5% - 10%) Moderate (1% - 5%) No Growth (<1%) Dominant Player Moderately Competitive Highly Competitive Difficult Average Easy
5 4 3 2 1 0 3 2 1 0 3 2 1 0 3 2 1 0 2 1 0 2 1 0 18
169
13
Favorable
20%
Dominant Player Difficult
6. Entry/Exit Barriers
Total ScoreBusiness/Industry Risk
18 Actual Paramete r 13
Criteria
C. Management Risk
Weight Parameter
Score 5 3 2 0
Score Obtained 5
1. Experience
More than 10 years in the related line of business 510 years in the related The quality of management based line of business on the aggregate number of years 15 years in the related that the Senior Management line of business Team has been in the industry. No experience
(Management & Management Team)
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
2. Second Line/ Succession Ready Succession Succession within 1-2 years Succession within 2-3 years Succession in question Very Good Moderate Poor Regular Conflict 4 3 2 0 Ready Succession 4
3. Team Work
Total Score-Management Risk Criteria D. Security Risk Weight 10%
3 2 1 0 12 Score
Very Good
12 Actual Score Parameter Obtained Reg. Mortg, for HBL 4
Parameter Fully pledged facilities/substantially cash covered/Reg. Mortg, for HBL Registered Hypothecation (1st charge/1st Pari passu charge) 2nd Charge/Inferior charge Simple hypothecation/negative lien on assets. No security Registered Mortgage on Municipal Corporation/Prime area property. Registered Mortgage on Pourashava/semi-urban area property Equitable Mortgage or No property but plant & machinery as collateral Negative lien on collateral No collateral Personal guarantee with high net worth or Strong Corporate Guarantee Personal Guarantees or Corporate Guarantee with average financial strength No Support/Guarantee 4 3 2 1 0
1. Security Coverage (Primary)
2. Collateral Coverage (Property Location)
4 3 2 1 0 Plant & machinery as collateral Personel guarantee whith high net worth or strong Corporate Gurrantee 7 1
3. Support (Guarantee)
1 0 10
Total Score- Security Risk
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Criteria E. Relationship Risk 1. Account Conduct
Weight 10%
Parameter More than 3 (three) years accounts with faultless record Less than 3 (three) years accounts with faultless record Accounts having satisfactory dealings with some late payments Frequent Past dues & Irregular dealings in account More than 60% 40% - 60% Less than 40% Full Compliance Some Non-Compliance No Compliance
Score 5 4 2 0
Actual Score Parameter Obtained More than 3 years accounts with faultless record 5
2. Utilization of Limit (actual/projection) 3. Compliance of Covenants / Conditions 4. Personal Deposits
2 1 0 2 1 0 1
>60%
Full Compliance
2 1
Personal accounts of the key business Sponsors/ Principals are The extent to which the bank maintained in the bank, with maintains a personal banking significant deposits relationship with the key business No depository relationship sponsors/principals. Total Score-Relationship Risk Grand Total- All Risk
0 10 100
Personal accounts of the key business sponsors
10 85
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
6.2 SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is a basic, straightforward model that provides direction and serves as a basis for the development of marketing plans. It accomplishes this by assessing an organizations strengths (what an organization can do) and weaknesses (what an organization cannot do) in addition to opportunities (potential favorable conditions for an organization) and threats (potential unfavorable conditions for an organization). SWOT analysis is an important step in planning and its value is often underestimated despite the simplicity in creation The following will briefly introduce the SUMMIT POWERS internal strengths and weaknesses, and external opportunities and threats as explored in the past few years.
Strength
Summit Power is the largest local Independent Power Producer. Satisfactory and superior asset and service quality. Good internal capital generation. Diversified product lines. Experienced, expert and efficient management team especially in credit department. Quality risk assessment tools. Strong policy and guideline Reputation in Stock market Environmental stewardship 13 Strong financial performance Strong market position
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Moderate MIS Moderate corporate unable to fulfill the demand of power Weak Liquidity Position Dependence On Purchased Power Limited Hydroelectric Generation
Dependency on Coal
Weaknesses
Opportunities
Creation of brand image New product innovation Government support Efficient utilization of capital, machines, material and human resources Summit power is interested in infrastructure sectors in Bangladesh Focus on Renewable Energy Implementation of New Technologies 14 Increasing Demand for Electricity Increased Market competition Regulatory Obligations Legal Proceedings Seasonal Variations and Climate Conditions Economic Slowdown in Bangladesh
Threat
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Chapter-7 Findings & Conclusion
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
7.1 Findings
following Findings have been found.
By analyzing the credit risk and their performance in last financial year the
According to the credit risk grading score, SPL achieved 85 out of 100 which indicate a sound business operation in current financial year. As per Credit Risk Grade, SPL is categorized in group of Good. SPL is one of the leading companies in Electricity & Power sector. The annual turnover of SPL is around increased by double. Paid up capital is increased by 400 million of SPL. So it is a good point to consider as increasing growth of SPL. The current ratio of SPL in financial year is 0.89. It indicates a less amount of current assets considering the Ideal ratio. They are very much strong in capital adequacy and asset quality, but their liquidity management was not good in the last five years. The profitability ratio indicates that in last five years SPLs profitability condition was good. The credit policy of SPL is very restrictive and defensive. As a result, its loan management is very constructive. The expansion of business activity in current years indicates the successive period of this is continuing. In last five years the maximum portion of total income of SPL comes from the selling the power and electricity which is very demanded commodity for the public concern.
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
7.2 Recommendation .
At first the SPL should find out the way to Reduce its bad loan amount further, to improve is loan performance quality. SPL holds huge reserves and fund that are not utilized. As a result, huge opportunity cost is incurred by SPL. So, it should be utilized more its reverse money in productive sector.
SPL should give more emphasize on liquidity management in a balanced way. SPLs training programs can encourage their trainees to seek additional education including computer classes, accounting, MBA programs and foreign language instruction. So the training should be fully fledged. Due to the unwanted increase of the oil price the world economy as well as Bangladesh economy is facing a big challenging situation. So the SPL is recommended to very careful to sanction further new plants and power stations. An industry wise integrated Credit Risk Grading system should be developed. So that risk can measure for different industry of business. Power sector is a large plant and long projected activities so it moves by a team effort. So, strong co-ordination with the related divisions and departments is very important SPL is a leading company in Bangladesh for power sector, and there have a lot of chances for expanding business in this sector. Bangladesh Government also facilitates more in this sector for improving the power sector. So, it can a good chance for SPL for optimizing its business. The above recommendations will be advantageous for the commercial banks if these are attained in case of credit risk management. As a result nonperforming
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
loan will be reduced as well as the financing will steer the wheel strongly in the economy of Bangladesh.
7.3 Conclusion .
Credit risk management practices in Bangladesh are not well developed. Now NCBs & PCB have significant amount of Bad loans and non performing loan. Even though Bangladesh Bank have taken various steps to minimize credit risk in NCBs and PCBs. The Lending Risk Analysis (LRA) manual introduced in 1993 by the Bangladesh Bank has been in practice for mandatory use by the Banks & financial institutions for loan size of BDT 1.00 crore and above. However, the LRA manual suffers from a lot of subjectivity, sometimes creating confusion to the lending Bankers in terms of selection of credit proposals on the basis of risk exposure. Meanwhile, in 2003 end Bangladesh Bank provided guidelines for credit risk management of Banks wherein it recommended, the introduction of Risk Grade Score Card for risk assessment of credit proposals. Since the two credit risk models are presently in vogue, the Governing Board of Bangladesh Institute of Bank Management (BIBM) under the chairmanship of the Governor, Bangladesh Bank decided that an integrated Credit Risk Grading Model be developed incorporating the significant features of the above mentioned models with a view to render a need based simplified and user friendly model for application by the Banks and financial institutions in processing credit decisions and evaluating the magnitude of risk involved therein. further the most important guidelines on Managing Core Risk in Banking developed by the focus group under the auspices of Bangladesh bank already implemented within the given deadline, have made new dimension in the whole banking arena. Following implementation of guidelines on credit risk management, entire credit operation has been streamlined with maintaining separate demarcation among the department under credit risk management.
Page 31
Credit Risk Grading of Summit Power ltd
Bibliography
1. Annual Report- 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009 of The SPL. 2. SPL website: http://www.summitpower.org 3. Summit group: www.summitgroupbd.com
4. Research Methodology, By-Richard Daniel & John Morgan, Published in USA, 2005 By International Research Institute of Minnesota. 5. Prudential guidelines of credit risk management.
6. Managing core risks in Banking : Credit Risk Management-Published by:
Bangladesh Bank-2005 7. Bangladesh Bank circular and guidelines-BRPD Circular No.18 dated 11.12.2008 8. Credit Risk Grading Manual_ Introduced by Bangladesh Bank, November 2005 9. Annual Term paper of Bangladesh Bank-2007 10.
11.
Economic Term paper of Bangladesh-2007 Bangladesh Bank Website. http://www.bangladesh-bank.org/ Guidelines of Basel-II implementation, By Bangladesh Bank-2009 Yahoo : http://www.yahooanswer.com/ Goggle : http://www.google.com.bd/ Wikipedia : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Main_Page Essentials of Managerial Finance by Scoot Besley & Eugene F. Brigham
Ask : www.ask.com
12.
13. 14. 15.
16.
17.
Page 31
You might also like
- CityCell history and operationsDocument25 pagesCityCell history and operationsNinad KhanNo ratings yet
- Pathao: An Emerging Motorcycle-Ride Service in Bangladesh: Southern AsiaDocument12 pagesPathao: An Emerging Motorcycle-Ride Service in Bangladesh: Southern AsiaMuhammad Towfiqul IslamNo ratings yet
- Marketing Activities of Products and Services of The City Bank LimitedDocument61 pagesMarketing Activities of Products and Services of The City Bank LimitedZiaul Onim0% (1)
- Union Bank Limited Internship ReportDocument60 pagesUnion Bank Limited Internship Reportsaleemkhp50% (2)
- Internship Report On Bank Asia LimitedDocument20 pagesInternship Report On Bank Asia LimitedGold Leaf0% (1)
- Information of Abdul Monem Ltd.Document16 pagesInformation of Abdul Monem Ltd.Moinuddin Ahmed100% (1)
- Rural Revenue Franchisee Scheme 2013Document18 pagesRural Revenue Franchisee Scheme 2013Siddhartha60% (5)
- Energy Crisis in BangladeshDocument3 pagesEnergy Crisis in Bangladeshc_masudNo ratings yet
- Business Glossary (Shetu Ranjan Biswas) PDFDocument36 pagesBusiness Glossary (Shetu Ranjan Biswas) PDFMd. Erfan AhmedNo ratings yet
- BkashDocument15 pagesBkashkhanjahid100% (2)
- Brief History of Insurance Company in BangladeshDocument6 pagesBrief History of Insurance Company in BangladeshSarjeel Ahsan Niloy100% (2)
- Internship Report on Performance Analysis of Mobile Financial IndustriesDocument83 pagesInternship Report on Performance Analysis of Mobile Financial IndustriesWahidul Haque Khan SanielNo ratings yet
- INTERNSHIP REPORT ON FahiM. (16-12-19)Document31 pagesINTERNSHIP REPORT ON FahiM. (16-12-19)shahanara basherNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Building Systems LimitedDocument116 pagesBangladesh Building Systems Limitedshobu_iuj100% (1)
- INTERNSHIP PROPOSAL On Green BankingDocument7 pagesINTERNSHIP PROPOSAL On Green Bankingsourav4730No ratings yet
- Brac Bank PresentationDocument24 pagesBrac Bank PresentationSumi Islam100% (2)
- Internship Report RSDocument58 pagesInternship Report RSLayes AhmedNo ratings yet
- Problems On Hire Purchase and LeasingDocument5 pagesProblems On Hire Purchase and Leasingprashanth mvNo ratings yet
- 5th Semester AssignmentsDocument17 pages5th Semester Assignments181 Mudasar PatoliNo ratings yet
- Electric Vehicles in India: A Literature ReviewDocument3 pagesElectric Vehicles in India: A Literature ReviewSatyendra Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Banking System in Bangladesh (Law of Practice in BabkindDocument10 pagesPresentation On Banking System in Bangladesh (Law of Practice in BabkindAbbasi Hira33% (3)
- Citycell The Failure StoryDocument14 pagesCitycell The Failure StoryJaniva SultanaNo ratings yet
- Foreign Exchange Operations of Janata Bank LTDDocument81 pagesForeign Exchange Operations of Janata Bank LTDMd Alimur Razee Real71% (7)
- Mitsubishi plans big for Bangladesh auto marketDocument5 pagesMitsubishi plans big for Bangladesh auto marketSakib Mohammed MalikNo ratings yet
- Term Paper: "Metro Rail Project: Dream and Challenges"Document6 pagesTerm Paper: "Metro Rail Project: Dream and Challenges"Jahidur_rahimNo ratings yet
- Focus WrittingDocument32 pagesFocus Writtingshuvrosaha007100% (2)
- An Overview of BRAC Bank LimitedDocument4 pagesAn Overview of BRAC Bank LimitedHuq Ziaul100% (1)
- FIN 603 Corporate Social Responsibilities of Banks Term Paper ResubmissionDocument33 pagesFIN 603 Corporate Social Responsibilities of Banks Term Paper ResubmissionNuzhat Binta RahmanNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Money Market BangladeshDocument25 pagesPresentation On Money Market BangladeshAminul Haque100% (1)
- Citycell by AbirDocument67 pagesCitycell by Abirrigan_nsuuNo ratings yet
- Mobile Banking in Bangladesh: Costs, Services, SecurityDocument11 pagesMobile Banking in Bangladesh: Costs, Services, SecurityTuly gomesNo ratings yet
- The Bkash Banking Company and Summary of It'S Marketing StrategyDocument19 pagesThe Bkash Banking Company and Summary of It'S Marketing StrategyRita AhmedNo ratings yet
- Internship On Janata BankDocument36 pagesInternship On Janata BankJahedarunNo ratings yet
- BCBL Internship ReportDocument37 pagesBCBL Internship ReportSinthiya AkterNo ratings yet
- South Bangla Agriculture & Commerce Bank LTDDocument35 pagesSouth Bangla Agriculture & Commerce Bank LTDNafiz Niaz50% (4)
- Bkash: Financial: Technology Innovation For Emerging MarketsDocument8 pagesBkash: Financial: Technology Innovation For Emerging MarketsAditya AnandNo ratings yet
- Akij Group's CSR initiatives through Ad-din HospitalDocument4 pagesAkij Group's CSR initiatives through Ad-din Hospitalanisulislam asifNo ratings yet
- Industrial Tour Report (JEWEL - MANAGEMENT-CU)Document37 pagesIndustrial Tour Report (JEWEL - MANAGEMENT-CU)Mohammad Jewel100% (2)
- Green Banking and Its Practices in Bangladesh. (ID-07303125)Document35 pagesGreen Banking and Its Practices in Bangladesh. (ID-07303125)Maidul Hayder Limon91% (11)
- Service Marketing Report 2Document39 pagesService Marketing Report 2Ehsan VillaNo ratings yet
- Introductory Page: Introduction of The BusinessDocument17 pagesIntroductory Page: Introduction of The BusinessKhaleeq Ur Rehman0% (1)
- Survey QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesSurvey QuestionnaireSaief Dip100% (1)
- Report On "Production Management"Document15 pagesReport On "Production Management"Zannatun NayeemNo ratings yet
- Functions of Central and Commercial BanksDocument11 pagesFunctions of Central and Commercial BanksDeepjyotiNo ratings yet
- 4rafiul Intern Report PDFDocument53 pages4rafiul Intern Report PDFAktader Ahmad Farhan100% (2)
- Assignment On Brac BankDocument15 pagesAssignment On Brac Bankakhtar140100% (1)
- Janata Bank Micro CreditDocument25 pagesJanata Bank Micro CreditMahfoz KazolNo ratings yet
- Agrani Bank Internship ReportDocument71 pagesAgrani Bank Internship ReportRobiRashedNo ratings yet
- Problems and Prospects of Real Estate Business in BangladeshDocument38 pagesProblems and Prospects of Real Estate Business in BangladeshSurajit SarbabidyaNo ratings yet
- Financial Performance Analysis of Mutual Trust Bank Ltd.Document41 pagesFinancial Performance Analysis of Mutual Trust Bank Ltd.Myeidislam100% (3)
- ACN 403 ReportDocument12 pagesACN 403 ReportIubianNo ratings yet
- Lease Financing for Entrepreneurs in BangladeshDocument11 pagesLease Financing for Entrepreneurs in BangladeshHasibul IslamNo ratings yet
- Corporate Social Responsibilities of FSIBLDocument47 pagesCorporate Social Responsibilities of FSIBLMasumur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Valuation & Fin Moduling PDFDocument14 pagesValuation & Fin Moduling PDFTohidul Anwar ChyNo ratings yet
- Strategic Analysis: BAT Nestle GPDocument26 pagesStrategic Analysis: BAT Nestle GPAbul HasnatNo ratings yet
- Priya Thesis SoftDocument26 pagesPriya Thesis SoftAPRATIM BHUIYANNo ratings yet
- CRG and Project SuccessDocument35 pagesCRG and Project SuccessNishat FarjanaNo ratings yet
- Financial Performance of EXIM BankDocument52 pagesFinancial Performance of EXIM BankMirtun Joy100% (2)
- Credit Management of Agrani Bank LimitedDocument52 pagesCredit Management of Agrani Bank Limitedorda55555100% (7)
- Comparative Analysis of NPAs in Public and Private Sector BanksDocument77 pagesComparative Analysis of NPAs in Public and Private Sector BanksNikhil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Group 7 Section BDocument25 pagesGroup 7 Section BShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- Android Tutorial PDFDocument34 pagesAndroid Tutorial PDFThế AnhNo ratings yet
- DocDocument1 pageDocShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- Statistical InformationDocument1 pageStatistical InformationShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- OrganogramDocument1 pageOrganogramShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument210 pagesFinal ReportShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- Guide EngDocument219 pagesGuide EngShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- Succession Planning Ensures Optimum ProductivityDocument12 pagesSuccession Planning Ensures Optimum ProductivityShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- Bank Credit Trends in BangladeshDocument259 pagesBank Credit Trends in BangladeshShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- Report For SirDocument57 pagesReport For SirMostafizur RahmanNo ratings yet
- AssumptionsDocument3 pagesAssumptionsShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- Last Four Years Activities of BKBDocument4 pagesLast Four Years Activities of BKBShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- Accrual PrincipleDocument3 pagesAccrual PrincipleShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- CSR in Bangladesh BankingDocument3 pagesCSR in Bangladesh BankingShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- HRMDocument57 pagesHRMShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- Report For SirDocument57 pagesReport For SirMostafizur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Slide of ProductivityDocument15 pagesSlide of ProductivityShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- Phrase and IdiomsDocument14 pagesPhrase and IdiomsShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- Transfer PricingDocument17 pagesTransfer PricingShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- Responsibility AccountingDocument39 pagesResponsibility AccountingShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- OMDocument8 pagesOMShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- Job Circular of Different OrganizationDocument1 pageJob Circular of Different OrganizationShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- Operations ManagementDocument175 pagesOperations ManagementAnurag Saikia100% (2)
- MBA SyllabusDocument18 pagesMBA SyllabusShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- College LevelDocument42 pagesCollege LevelShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- Managerial AssaignmentDocument20 pagesManagerial AssaignmentShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- Bank Head Office AddressesDocument6 pagesBank Head Office AddressesShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument1 pageDocumentShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- Target Market Segmentation and Positioning StrategiesDocument5 pagesTarget Market Segmentation and Positioning StrategiesShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- Annual Report ComparisonDocument7 pagesAnnual Report ComparisonShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Sociological PerspectivesDocument39 pagesModule 1 Sociological PerspectivesCristine BalocaNo ratings yet
- 05 Mesina v. PeopleDocument7 pages05 Mesina v. PeopleJason ToddNo ratings yet
- (13-14) - Modeling of Thermal SystemsDocument33 pages(13-14) - Modeling of Thermal SystemsmawooaNo ratings yet
- Human Rights Project, 2018Document25 pagesHuman Rights Project, 2018Vishal Jain100% (3)
- What Is Link AdaptationDocument4 pagesWhat Is Link AdaptationAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Meena ResumeDocument3 pagesMeena ResumeAnonymous oEzGNENo ratings yet
- CSEC English B June 2013 P2Document7 pagesCSEC English B June 2013 P2Jhanett RobinsonNo ratings yet
- My Experience With DreamsDocument7 pagesMy Experience With DreamsPamela Rivera SantosNo ratings yet
- Enuma Elish LitChartDocument20 pagesEnuma Elish LitChartsugarntea24No ratings yet
- Accenture 2014 Celent Claims ABCD Acn Duck Creek Dec14Document28 pagesAccenture 2014 Celent Claims ABCD Acn Duck Creek Dec14Ainia Putri Ayu KusumaNo ratings yet
- EDIBLE PLANTSDocument10 pagesEDIBLE PLANTSBotany DepartmentNo ratings yet
- Significance of Research in Education - Research ArticleDocument18 pagesSignificance of Research in Education - Research ArticleSalex E. AliboghaNo ratings yet
- Disirders of Synaptic Plasticity and Schizophrenia - J.smythiesDocument559 pagesDisirders of Synaptic Plasticity and Schizophrenia - J.smythiesBrett CromptonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 22 NDocument6 pagesLecture 22 Ncau toanNo ratings yet
- MRI BRAIN FINAL DR Shamol PDFDocument306 pagesMRI BRAIN FINAL DR Shamol PDFDrSunil Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- English 7 1st Lesson Plan For 2nd QuarterDocument4 pagesEnglish 7 1st Lesson Plan For 2nd QuarterDiane LeonesNo ratings yet
- Mugunthan ResumeDocument4 pagesMugunthan Resumeapi-20007381No ratings yet
- Individual Assignment I Google Search Network CampaignDocument15 pagesIndividual Assignment I Google Search Network CampaignMokshita VajawatNo ratings yet
- Vegetation of PakistanDocument10 pagesVegetation of PakistanAhmad sadiqNo ratings yet
- Optimizing RMAN RecoveryDocument61 pagesOptimizing RMAN RecoveryVijay ParuchuriNo ratings yet
- Corruption PDFDocument11 pagesCorruption PDFkaleemullahNo ratings yet
- Wildlife Ecology - Unit 14 - Week (12) - RevisionDocument1 pageWildlife Ecology - Unit 14 - Week (12) - RevisionAdityaNo ratings yet
- TR Massage Therapy NC IIDocument162 pagesTR Massage Therapy NC IIAljon Fortaleza Balanag100% (4)
- O'laco Vs Cocho ChitDocument16 pagesO'laco Vs Cocho ChitAngel Pagaran AmarNo ratings yet
- Demand Letter Jan 16Document8 pagesDemand Letter Jan 16jhean0215No ratings yet
- Foreclosing Modifications - How Servicer Incentives Discourage Loan ModificationsDocument86 pagesForeclosing Modifications - How Servicer Incentives Discourage Loan ModificationsRicharnellia-RichieRichBattiest-CollinsNo ratings yet
- What Is The Advantages and Disadvantages of Analog and Digital InstrumentDocument22 pagesWhat Is The Advantages and Disadvantages of Analog and Digital Instrumentabishek_bhardwa866645% (20)
- Antenna & Wave Propagation - Course OutlineDocument2 pagesAntenna & Wave Propagation - Course OutlineSabuj AhmedNo ratings yet
- NIH Strategic Plan For Data ScienceDocument26 pagesNIH Strategic Plan For Data ScienceAristide AhonzoNo ratings yet