Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Test 1 Bio f5 Daerah PD
Uploaded by
Annamal ArulnathanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Test 1 Bio f5 Daerah PD
Uploaded by
Annamal ArulnathanCopyright:
Available Formats
4551 UJIAN SETARA BIOLOGY 2012
UJIAN BULANAN 1
SETARA DAERAH PORT DICKSON BIOLOGY TING 5
INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS
1. Which of the following substances causes fibrinogen to change to fibrin ? A . Vitamin K B. Thrombin C. Calcium ion D. Thromboplastins 2. A mans foot bleeds non-stop after stepping on a sharp object . What will happen if his blood is unable to clot ? A. His blood pressure drops. B. His blood capillaries enlarge. C. The rate of heartbeat increases. D. The rate of respiration increases. 3. Through which vein does lymphatic fluid enter the bloodstream ? A. The aorta B. The jugular vein C. The subclavian vein D. The pulmonary vein
4. Vitamin K is essential for the : A. Formation of prothrombin B. Release of thrombokinase C. Conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin D. Conversion of prothrombin to thrombin
5. Which actions help to return low blood pressure to the normal value ? I A lower heartbeat rate II Weaker cardiac muscles III A narrowing of the blood vessels IV Contractions of the smooth muscles of the arteries
A. I and II B. I and III C. II and III D. III and IV
6. Which substances are found in the interstitial fluid ? I Platelets II Hormones A. I and II B. II and III C. III and IV D. I, II and III III Leucocytes IV Erythrocytes
7. The function of lymph nodes is to : A. Destroy old red blood cells B. Absorb fatty acids and glycerol from the lacteals C. Produce antibody-secreting cells D. Prevent accumulation of tissue fluid in the intercellular spaces
8. Which of the following is NOT a function of the lymphatic system ? A. Transport of fatty acids and glycerol from the small intestine B. Production of neutrophils that function as phagocytes in the immune system C. To return interstitial fluid to the circulatory system D. Production of antibodies
9. Blood clotting at a wound is brought about by the A. Platelets only B. Platelets and components of the plasma C. Erythrocytes and components of the plasma D. Erythrocytes and platelets
10. Which of the following statements are true about haemophilia ? I It is a deficiency disease II Haemophiliacs are unable to produce blood-clotting factors III One of the treatments for haemophillia is blood transfusion IV Haemophiliacs are more likely to be females than males A. I and III B. II and III C. I,II and III D. II,III and IV
11. What is the condition in which interstitial fluids collect in the intercellular space ? A. Oedema B. Emphysema C. Haemophilia D. Leukaemia
12. Which of the following is NOT likely to occur if the blood- clotting mechanism fails ? A. Blood pressure will drop B. Microscopic organism may enter cuts or open wounds C. Kidney function may be impaired D. The individual may be infected with the haemophilia virus
13. Tissue fluid is formed at capillary networks . Which of the following factors play a role in this process ? I Walls of capillaries are pemearble to some components of the blood II A high hydrostatic pressure at the arterial end of the capillary network III The presence of lymphatic capillaries close to the capillary network IV Active Transport A. I and II only B. I and IV only C. I,II and IV only D. II,III and IV only
14. Which of the following is the medium through which blood cells obtain nutrients and oxygen from the circulatory system ? A. Blood B. Lymph C. Interstitial fluid D. Plasma
15. Which statement best describes arteries ? A. Arteries carry oxygenated blood B. Arteries carry blood towards the lungs C. Blood flows in arteries is pulsatile D. Arteries are connected to veins by arterioles
16. A condition known as oedema is caused by the accumulation of A. Too much fluid in body tissues B. Too much lipids in body tissues
C. Toxic materials in the body tissues D. A parasitic roundworm in the lymphatic vessel
17. Lymph contains A. Lipids B. Starch C. Erythrocytes D. Plasma proteins
18. Which of the following structures acts as a filter in the human lymphatic system ? A. Lymph nodes B. Spleen C. Lymphatic duct D. Lymphatic vessels
19. The interstitial fluid returns to the blood circulatory system through I the minute spaces between tissue cells II the venous end of the capillaries III the capillary walls into interstitial space IV the thoracic duct and right lymphatic duct
A. I and III only B. II and IV only C. I,II and III only D. II,III and IV only
20. Which of the following are needed to convert the protein, prothrombin to thrombin ? A. Calcium ions + vitamin K B. Vitamin K + iodine ions C. Iodine ions + vitamin C D. Vitamin C + calcium ions
21. What will happen to the interstitial fluid that fails to return to the circulatory system ? A. It causes elephantiasis B. It causes oedema C. It causes high fever D. It causes stomachache
22. A clot formation inside an unbroken blood vessel is known as A. An embolus B. A fibrin C. Thrombosis D. Arteriosclerosis
23. Which of the following is the correct sequence of events in the blood clotting mechanism ? I Thrombin catalyses the conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin II Blood clot hardens when it is exposed to air to form a scab III The aggregation of platelets forms a plug called a platelet plug IV Thromboplastins convert prothrombin to thrombin A. IV,I,III,II B. I,IV,II,III C. IV,I,II,III D.III,IV,I,II
24. Which valve prevents the backflow of blood into the right ventricle ? A. Tricuspid valve B. Bicuspid valve C. Semi-lunar valve D. Ventricle valve
25. The flow of blood in veins is aided by A. A tension generated by the beating of the heart B. The action of muscles in the wall of the vein C. Constriction of skeletal muscle between which the vein is located D. Active transport
STRUCTURAL QUESTIONS : ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS
Q1
LUNG CAPILLARIES
GILL CAPILLARIES
SYSTEMIC CAPILLARIES OF P
SYSTEMIC CAPILLARIES OF Q
Diagram shows the blood circulatory systems of organism P and Q. a.State the type of blood circulatory system of 1. P 2. Q -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------(2M)
b.State one similar characteristic between the blood circulatory system of P and Q
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------(2M)
c. Organism P has two ventricles while Q has one ventricle. State 2 advantages of having two ventricles.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------(2M)
d. Explain the bloodflow in the circulatory system of P. --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------(5M)
e. The rate of oxygen supply to body cells in P is faster than in Q, even though they are of the same size. Explain why.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------(2M)
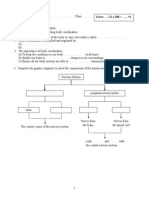
Q2. FIGURE 4 shows the relationship between a part of the blood circulatory system, the lymphatic system and blood cells.
Fluid R Venule Arteriol
Figure 4
a (i) Label the parts marked R, S, T and U. R: ...................................................... S: .................................................... T: ------------------------------------------------------U: -------------------------------------------(2M)
(ii) Draw arrows to show the flow of fluid between both systems.
(2M)
(b) (i) What is the difference in composition of fluid R compared to the fluid in U?
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ (1M )
(ii)State the reason for this difference.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------(1M)
The lymphatic system acts as a complement to the blood circulatory system in terms of transport and body defence. (c) (i) Describe the above statement from the aspect of transport of substances.
(2M) (ii) Describe the above statement from the aspect of body defence.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------(2 M)
(d) (i) What happens if fluid R is excessive in the intercellular space?
(1M) (ii ) State why a patient suffering from elephantiasis has swollen hands and legs.
(1M)
ANSWERS 1. 2. B A 3. 4. C D 5. 6. D B
7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25.
C B B B A D A C C A A A B A B C D C C
Q1 a(i) Double circulatory system (ii) Single circulatory system b. c. Closed circulatory system where blood flows in blood vessels (i) no mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood (ii) efficient and rapid delivery to specific tissues d Deoxygenated blood flows into right atrium via vena cava. Deoxygenated blood then flows into right ventricle. Deoxygenated blood flows into pulmonary artery to lungs Gaseous exchange occurs at the lungs Oxygenated blood flows into left atrium via pulmonary vein. Oxygenated blood flows into left ventricle Oxygenated blood is pumped to body tissues via aorta
e. Q2 a(i) R interstitial fluid S body cells T lymph capillary U blood capillary Oxygenated blood in P flows at a higher pressure Erythrocytes in P transport MORE oxygen than Q
(ii) { ARROWS FROM BLOOD CAPILLARIES INTO SPACE BETWEEN BODY CELLS AND THEN TO LYMPHCAPILLARIES } b(i) Fluid R does not contain red blood cells while fluid U contains red blood cells (ii) Too large to move through the capillary wall c(i) lymphatic system transports fatty acid and glycerol from the ileum (ii) lymph nodes contain lymphocytes that produce antibodies to fight infections d(i) swelling of tissue or oedema occurs. (ii) round worms living in the lymphatic vessels restrict flow of lymph
You might also like
- WORKSHEET 2.1 Animal and Plant Cell - LatestDocument4 pagesWORKSHEET 2.1 Animal and Plant Cell - LatestAnnamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 2.2 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesWORKSHEET 2.2 Cell Structure and FunctionAnnamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- Latihan Penilaian Bio Ting 4 Bab 2 (Struktur Sel Dan Fungsinya)Document10 pagesLatihan Penilaian Bio Ting 4 Bab 2 (Struktur Sel Dan Fungsinya)Mastura Haji Ariffin50% (2)
- WORKSHEET 2.1 Animal and Plant Cell - LatestDocument4 pagesWORKSHEET 2.1 Animal and Plant Cell - LatestAnnamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 2.1 Animal and Plant Cell - LatestDocument4 pagesWORKSHEET 2.1 Animal and Plant Cell - LatestAnnamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- Borang Headcount MatapelajaranDocument2 pagesBorang Headcount MatapelajaranAnnamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- Biology Quiz Form 5Document1 pageBiology Quiz Form 5Annamal Arulnathan100% (1)
- Locomotion Support StudentDocument28 pagesLocomotion Support StudentCt FatimahNo ratings yet
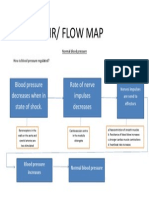
- CARTA ALIR Blood Pressure1Document1 pageCARTA ALIR Blood Pressure1Annamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- Ringkasan RPT 2014 SNF4Document12 pagesRingkasan RPT 2014 SNF4Annamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- ST AnthonyDocument2 pagesST AnthonyAnnamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- CARTA ALIR Blood Pressure 2Document1 pageCARTA ALIR Blood Pressure 2Annamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- A Bone To The Dog Is Not CharityDocument2 pagesA Bone To The Dog Is Not CharityAnnamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- 10 CommandmentDocument1 page10 CommandmentAnnamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 5 Chapter 2:locomotion and Support: To: Mrs AnnamalDocument25 pagesBiology Form 5 Chapter 2:locomotion and Support: To: Mrs AnnamalAnnamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- Science f4 ExercisesDocument5 pagesScience f4 ExercisesAnnamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- Kertas Soalan Bio t4Document2 pagesKertas Soalan Bio t4Annamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- Peka F51Document3 pagesPeka F51Annamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Science RINGKASDocument1 pageYearly Plan Science RINGKASAnnamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- Blood ClottingDocument15 pagesBlood ClottingAnnamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- Latihan Sains t4 Bab 2Document1 pageLatihan Sains t4 Bab 2Shahezan ShahNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Science RingkasDocument1 pageYearly Plan Science RingkasAnnamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Metastasis 2Document28 pagesMetastasis 2RaNa MaYaaNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Breast CancerDocument72 pagesCase Study: Breast CancerJoy Mariel Isadora BurgosNo ratings yet
- LFSC Grade 10 P2 MEMO ENG FinalDocument11 pagesLFSC Grade 10 P2 MEMO ENG FinalLucky Jr MonobeNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsDocument35 pagesLymphatic System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsAlyssum MarieNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Medical Language For Modern Health Care 4th Edition David Allan Rachel BascoDocument13 pagesSolution Manual For Medical Language For Modern Health Care 4th Edition David Allan Rachel BascoChristopherRamosfgzo100% (40)
- Lymphatic System OutlineDocument4 pagesLymphatic System OutlineMelljonhNo ratings yet
- 3 Interview Transcripts From A Magnificent New NormalDocument49 pages3 Interview Transcripts From A Magnificent New NormalsiesmannNo ratings yet
- Congenital ChylothoraxDocument6 pagesCongenital ChylothoraxromeroclaualeNo ratings yet
- Greenmedinfo Intentional Movement The Path To Restoring Your Vital SelfDocument21 pagesGreenmedinfo Intentional Movement The Path To Restoring Your Vital SelfsiesmannNo ratings yet
- First Aid and Pre-Hospital Management of Venomous SnakebitesDocument12 pagesFirst Aid and Pre-Hospital Management of Venomous SnakebitesSiti Nurhasanah MustafaNo ratings yet
- 15a. First Aid ManualDocument73 pages15a. First Aid ManualchimaraiykeNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Lymphoid Organs Sr. Sarupya Mercy College PalakkadDocument28 pagesImmunology: Lymphoid Organs Sr. Sarupya Mercy College PalakkadTahir AzizNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Objectives WAPT 2022Document5 pagesHuman Anatomy Objectives WAPT 2022ExcelNo ratings yet
- Physiotheraphy Role in Pain ManagementDocument63 pagesPhysiotheraphy Role in Pain Management姐姐雯No ratings yet
- ANPH M3 CU15. Lymphatic SystemDocument22 pagesANPH M3 CU15. Lymphatic Systemmark tuazonNo ratings yet
- Lung Anatomy - Overview, Gross Anatomy, Microscopic AnatomyDocument15 pagesLung Anatomy - Overview, Gross Anatomy, Microscopic Anatomyأحمد نور الهدايةNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 - Transport in Animals: Blood and Lymph VesselsDocument15 pagesTopic 9 - Transport in Animals: Blood and Lymph Vesselsgytfnhj.comNo ratings yet
- Eqb - Breast: Le DischargeDocument22 pagesEqb - Breast: Le DischargeSagarRathodNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Lymphadenectomy Step-By-Step Surgical EducaDocument5 pagesPelvic Lymphadenectomy Step-By-Step Surgical EducaVlad GrigoreNo ratings yet
- Syllabus JKSSB Theatre Assistant Theatre Nurse Health Family Welfare AssistantDocument10 pagesSyllabus JKSSB Theatre Assistant Theatre Nurse Health Family Welfare AssistantLone NissarNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System and Body DefensesDocument74 pagesThe Lymphatic System and Body DefensesWyncess Joy Unza CamiloNo ratings yet
- Non-Cardiogenic Pulmonary EdemaDocument7 pagesNon-Cardiogenic Pulmonary EdemadarmariantoNo ratings yet
- Visible Body Module # 32 Lymphatic System Anatomy NotesDocument15 pagesVisible Body Module # 32 Lymphatic System Anatomy NotesAmelia Follmer100% (1)
- Handouts Lymphatic System F11Document7 pagesHandouts Lymphatic System F11Kelly TrainorNo ratings yet
- Kisl 07 01 1024405Document16 pagesKisl 07 01 1024405Guillermo Angel Herrera ChavezNo ratings yet
- The Lympho Glandular and Intugmentary System: Presenter: Abdurke Dido - Physician (MD) May 22,2011Document62 pagesThe Lympho Glandular and Intugmentary System: Presenter: Abdurke Dido - Physician (MD) May 22,2011Worku KifleNo ratings yet
- Breastcancerorg Pathology Report Guide 2013Document27 pagesBreastcancerorg Pathology Report Guide 2013GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Definition and General Features 4.i 5.12.Document216 pagesDefinition and General Features 4.i 5.12.Elma RamakicNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument53 pagesThe Circulatory SystemVera June RañesesNo ratings yet
- B SC Nursing Syllabus INC PDFDocument183 pagesB SC Nursing Syllabus INC PDFsohini bhattacharyaNo ratings yet