Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MS2363 - Work in Tunneling, Fire & Electrical Safety
Uploaded by
HP LooiCopyright
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
MS2363 - Work in Tunneling, Fire & Electrical Safety
Uploaded by
HP LooiCopyright:
Seminar on MS 2363 : Work in Tunnelling
24 April 2012; Concorde Hotel, Shah Alam
Fire and Electrical Safety in Tunnel in MS2363
Ir. H.P. Looi Hon Secretary, ACEM (www.acem.com.my) Vice President , MGBC (www.mgbc.org.my)
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
MS 2363 Contents 4 The Control of Risk 12 - Methane 13 Fire & Smoke Control 14 Emergency Control 17 - Illumination 25 - Electrical
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
The Control of Risk (Section 4)
4 The Control of Risk Section 4
Contingencies
Identify Hazards
Assess Risk
Emergencies
Occupational Health
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
The Control of Risk (Section 4)
4 The Control of Risk Section 4
1.
2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Hazards Tunnel/ earth structure Methane Electrics Atmospheric pollution Water source Machines Lightings Obstructions, confined space Risks Assessment
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Collapse, cavities Fire, explosion, asphyxia Fire, shock, power failure Poisoning, dust, asphyxia Flooding, collapse, electrocution 6. Fire, noise, vibration, accidents 7. Egress/ingress, visual hazards 8. Accidents,
Identify hazards & assess Risks
C/ERP Contingency / Emergency Response Plan
CSHP Construction Safety & Health Plan
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
Methane (Section 12) Section 12 deals with Methane (CH4)
The principal risk of methane is Explosion
Identify source / occurrence Identify Risk Remove/ Control Risk
Decomposition of biomass Coal seams Marsh Water body Waste landfill
Explosion Fire Asphyxiation
Dilution Detection Monitor Ex proof equipment ERP
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
Methane (Section 12) Simplest of the alkane group CNH2N+1: Alkanes are colourless and odourless.
N 1 CNH2N+2 C1H4 Alkane Methane SGAIR Air = 1 0.55 Explosive Limit; Flash Point air/gas 5% - 15% -188C Ignition Temp. 537C
2
3 4 NG
C2H6
C3H8 C4H10
Ethane
Propane Butane
0.57
1.55 2.05 0.54 0.65
3% - 13%
2.4% - 9.5% 1.8% - 8.4% 5% - 15%
-135C
-104C -60C -
472C
540C 288C 704C
60% - 80% CH4
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
Methane (Section 12)
Methane is the most abundant occurring organic compound on earth. Methane is principally formed from natural decomposition of biomass
Methane seepage thro ground water and cracks in tunnel wall/linings. Water body
Tunnel
Leaking Gas Pipeline Fossil Pocket of methane biomass / trapped in rock Coal seams voids /shale seams Municipal Sanitary Landfill
Tunnel
hplooi (2012)
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
10
Methane (Section 12) 12.4 Detection & Monitoring
a) b) c) d) e) f) Along invert General body of air in tunnel At low level (sumps, pits etc) Methane layering sustepcted Voids above crown level Upwind of tunnel machinery, electrical gears etc.
hplooi (2012)
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
11
Methane (Section 12)
12.5 Danger Levels 4 Levels
1. 2% by volume (40% LEL) All persons withdrawn, electrical power to be isolated except to monitoring equipment. All equipment intrinsically safe (IEC60079-11). 2. 1.25% by volume (25% LEL) All non essential persons withdrawn, nonessential Ex-proof mech & elect equipment disconnected until concentration is reduced to 1% (20% LEL).
3. 0.5% by volume (10% LEL) No cutting, welding, abrasive disc cutter & non-Ex-proof locomotives. Non Ex-proof equipment to be shut down. 4. 0.25% by volume (5% LEL) all equipment to be Ex proof, Lightings, communication, fire detection, alarm & extinguishing systems to be Ex proof.
hplooi (2012)
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
12
Ex Protected Equipment IEC 600079 Series
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
13
Ex Protected Equipment IEC 600079 Series
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
14
Ex Protected Equipment IEC 600079 Series
Group II, Temp Class
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
15
Ex Protected Equipment IEC 600079 Series
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
16
Ex Protected Equipment IEC 600079 Series
IEC 60079 -1
Explosive Atmosphere Part 0: Equipment General Requirements Part 1: Equipment Protection by Flameproof Enclosures d
-2 -5
-6 -7 - 10 - 11 - 14 - 15 - 18 - 26
Part 2: Equipment Protection by Pressurised Enclosures Part 5: Equipment Protection by Powder Filling
Part 6: Equipment Protection by Oil Immersion Part 7: Equipment Protection by Increase Safety Part 10: Classification of Hazardous Areas Part 11: Equipment Protection by Intrinsic Safety Part 14: Electrical Installation, Design, Selection and Erection Part 15: Type of Protection n Part 18: Encapsulation m Part 26: Equipment with Protection Level (EPL)
p q
o e i n m GL
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
17
Ex Protected Equipment IEC 600079 Series
IEC 61241
Electrical Apparatus for Use in the Presence of Combustible Dust
-1 -4 - 10 - 11 - 18
Part 0: Equipment General Requirements
Part 1: Equipment Protection by Enclosures Part 4: Type of Protection pD Part 10: Classification of Areas where Combustible Dust are or may be Present Part 4: Protection by Intrinsic Safety Part 5: Protection by Encapsulation iD mD tD pD
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
19
Fire and Smoke (Section 13)
Strategies for Fire & Smoke Control
13.1 Storage of Combustible Materials 13.2 Welding & Cutting 13.3 Electrical Equipment Fires
Minimise storage in tunnels Proper storage of combustibles Signage Fire Extinguishing Equipment Ex lighting fixtures
Permit to work Adequate ventilation Prohibit hot work in areas classified Ex.
Refer Clause 25 (wirings) Protection against electric shock Ex standard wiring in Zone 1 area.
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
20
Fire and Smoke (Section 13)
Strategies for Fire & Smoke Control
13.4 Fire Precautions 13.5 Vulnerable items and locations
Timber in heading & face Stores Conveyours Cables & wirings Electrical installation Hydraulic oil Flame cutting/welding Compressed air Storage for explosives Shafts & openings
13.6 Escape routes
Fire mains and hose connections (MS1539-2) Hi risk areas, TBMs to have fixed fire extinguishing systems. Foam extinguishers for hydraulics & electrics Water spray at TBM Direct inject extinguishers for diesel engine
Refer Clause 25 (wirings) Protection against electric shock Ex standard wiring in Zone 1 area.
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
21
Fire and Smoke (Section 13)
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
22
Fire and Smoke (Section 13)
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
24
14 Emergency Control
14 Emergency Control
Emergency Response Plan Event classification Event response Access Lighting Smoke Control Rescue facilities Self rescuers Accounting
Emergency Command Centre
Forward Control (Bridgeheads)
Training
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
26
17 - Illumination
In sections where pedestrian access is prohibited and construction work is underway, fixed lighting may be omitted: 1. All vehicle to be fitted with head lamps 2. Personnel to wear hi-visibility clothes.
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
27
17 - Illumination
Emergency Lights to be located at the following:
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
29
25 Electrical Installation
25.1 Planning Electrical safety rules; Authorization certificates permit to work system Training including first aid techniques Testing, maintenance and inspections Liaison with local authorities Records and drawings Emergency Response
Standards to Comply: HV IEC 61936-1 LV MS 1979; MSIEC 60364 & MS1936
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
30
25 Electrical Installation
Additional Safeguards for Tunnels & Tunnelling Work HV may be required (1kV, 3.3kV, 6.6kV & 11kV Precautions/ allowance in confined space Wet conditions & high humidity Smoke & Fume hazards Explosive atmosphere Risk of mechanical damage Oxygen rich atmosphere LV 400V 3phase; 230V 1 phse Safe Voltage: 110V (using centre-tapped earth)
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
31
25 Electrical Installation
Additional Safeguards for Tunnels & Tunnelling Work
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
32
25 Electrical Installation
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
33
25 Electrical Installation
Exceptions to Ex Wirings: 1. Ventilation with monitoring to limit CH4 below 5% LEL 2. Power interlock; vent system to auto-isolate non-Ex type equipment 3. Failure of monitors automatically isolate non-Ex equipment.
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
34
25 Electrical Installation
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
35
25 Electrical Installation
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
36
25 Electrical Installation
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
37
25 Electrical Installation
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
38
25 Electrical Installation
UL 1581 Vertical Tray Flame Test
Similar to IEC60332-3 flame propagation test
30kW flame
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
39
25 Electrical Installation
NFPA 72 : 2002
UL 1666 Riser Flame Test Mimic a riser shaft 150kW burner for 30 mins. Pass if no flame appear at 2nd chamber. 30kW flame
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
40
25 Electrical Installation
NFPA 72 : 2002
NFPA262, UL910 Steiner Tunnel Test Standard for Plenum cables Test samples loaded into tunnel 25 by 1 88kW flame applied at control air flow of 240fpm Measure flame propagation on sample and smoke density
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
41
25 Electrical Installation
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
Seminar on MS 2363 : Work in Tunnelling
24 April 2012; Concorde Hotel, Shah Alam
Fire and Electrical Safety in Tunnel in MS2363
Ir. H.P. Looi Hon Secretary, ACEM (www.acem.com.my) Vice President , MGBC (www.mgbc.org.my)
Ir. H.P. Looi, 24 April 12
You might also like
- SS IEC 60598-2-22-2016 - Preview PDFDocument11 pagesSS IEC 60598-2-22-2016 - Preview PDFTai HuynhNo ratings yet
- Isolite MSDS - 1400 SeriesDocument8 pagesIsolite MSDS - 1400 SeriesMashudi FikriNo ratings yet
- Niosh PDD ShoDocument15 pagesNiosh PDD ShoMaza LufiasNo ratings yet
- Chemical Legislation in Malaysia: Purpose of AssessmentDocument8 pagesChemical Legislation in Malaysia: Purpose of AssessmentAwatifNo ratings yet
- Positioning of Sensors GuidelinesDocument3 pagesPositioning of Sensors GuidelinesMátyás DalnokiNo ratings yet
- Eqa 1974Document38 pagesEqa 1974cik_güzelNo ratings yet
- HIRARC Analysis Task: To Fell Down A Big Tree Using A ChainsawDocument1 pageHIRARC Analysis Task: To Fell Down A Big Tree Using A ChainsawAziful AimanNo ratings yet
- Distribution Code For Peninsular Malaysia Sabah F.T. Labuan Amendments 2017 - V5Document173 pagesDistribution Code For Peninsular Malaysia Sabah F.T. Labuan Amendments 2017 - V5May OngNo ratings yet
- Trainer: S. Balamurugan B.E.., M.E (ISE) : Ehs Solutions Maduravoyal, ChennaiDocument75 pagesTrainer: S. Balamurugan B.E.., M.E (ISE) : Ehs Solutions Maduravoyal, ChennaiBala SbNo ratings yet
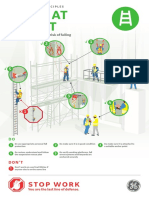
- LSP - Work at Height ENGDocument1 pageLSP - Work at Height ENGYosuaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Acts & RegulationsDocument50 pagesEngineering Acts & RegulationsPrasanthRaoNo ratings yet
- BEM Code of Ethics - Ir. Yim Hon WaDocument53 pagesBEM Code of Ethics - Ir. Yim Hon WaAnonymous DJrec2No ratings yet
- Safety Engineering Certificate CoursesDocument3 pagesSafety Engineering Certificate CoursesjoemsambiNo ratings yet
- Bitumen: Safety Data SheetDocument10 pagesBitumen: Safety Data SheetJaharudin Juhan100% (1)
- Case Study 1 (OSHA)Document14 pagesCase Study 1 (OSHA)Geetha SivakumarNo ratings yet
- NIT Rourkela-Safety EngineeringDocument23 pagesNIT Rourkela-Safety Engineeringshahnawaz ahmedNo ratings yet
- Akta Kualiti Alam Sekitar (Buangan TerjadualDocument25 pagesAkta Kualiti Alam Sekitar (Buangan Terjadualshafie.buang67% (3)
- Modul EQA 2014Document102 pagesModul EQA 2014Nursyafika JasmiNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument43 pagesReportMohd AlifNo ratings yet
- 8 NADOPOD RegulationsDocument26 pages8 NADOPOD Regulationsayie874100% (1)
- Fire DrillDocument2 pagesFire DrillCHERRY ANN OLAJAY100% (1)
- JKJ 103 Report For DoshDocument9 pagesJKJ 103 Report For DoshMohd Fadli100% (1)
- MS 2542 2013 PrepdfDocument5 pagesMS 2542 2013 PrepdfAlphonse D'EscargotNo ratings yet
- Fee 2010Document22 pagesFee 2010gohviccNo ratings yet
- Moreover,: A 116-Page Report Was Released by The Penang State Commission of Inquiry (SCI) On The Worksite IncidentDocument4 pagesMoreover,: A 116-Page Report Was Released by The Penang State Commission of Inquiry (SCI) On The Worksite IncidentAsogan JagaNo ratings yet
- 03 Fire Protection Spec-Uptown21Document20 pages03 Fire Protection Spec-Uptown21laurenjiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: OSHA 1994Document37 pagesChapter 9: OSHA 1994Aldric Tinker Toyad100% (1)
- Metal Sealant: Main ApplicationDocument2 pagesMetal Sealant: Main ApplicationHung Mai VanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Practice - Workplace Safety and Health 2016Document65 pagesEngineering Practice - Workplace Safety and Health 2016MiguelaTayNo ratings yet
- Root Cause Analysis Example Near Miss Asphalt Drop FULLDocument9 pagesRoot Cause Analysis Example Near Miss Asphalt Drop FULLnayakya100% (1)
- Tunneling Work SafetyDocument1 pageTunneling Work SafetyHazim HasanNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet CB-9099: 1. Product and Company IdentificationDocument6 pagesSafety Data Sheet CB-9099: 1. Product and Company IdentificationJust Rysdan0% (1)
- MR Am Karuppanan - UITM PUNCAK ALAMDocument40 pagesMR Am Karuppanan - UITM PUNCAK ALAMakubestlah100% (3)
- Ec 704Document1 pageEc 704Saiful AyyasNo ratings yet
- Valerie Lab ReportDocument10 pagesValerie Lab ReportvalerieNo ratings yet
- STR GL Hal Hse SQ 501Document12 pagesSTR GL Hal Hse SQ 501jose gregorio mata cabezaNo ratings yet
- BMSM BriefingDocument41 pagesBMSM BriefingPeter NgNo ratings yet
- OSHCIM Guidelines PDFDocument39 pagesOSHCIM Guidelines PDFZiThiamNo ratings yet
- PBU Unit PaintingDocument3 pagesPBU Unit Paintingmangeshkoli20078932No ratings yet
- Exam Paper Occupational 2 PDFDocument8 pagesExam Paper Occupational 2 PDFHema0% (1)
- Fire Life Safety TrainingDocument29 pagesFire Life Safety Trainingdiegos70100% (1)
- NIOSH Headquarters (Bandar Baru Bangi) : NIOSH Northern Regional Office (P.Pinang)Document2 pagesNIOSH Headquarters (Bandar Baru Bangi) : NIOSH Northern Regional Office (P.Pinang)ismawi74No ratings yet
- Installation Maintenance of Water Heater - ST - Updated PDFDocument17 pagesInstallation Maintenance of Water Heater - ST - Updated PDFHong Leong KuNo ratings yet
- Table 1: New Malaysia Ambient Air Quality StandardDocument1 pageTable 1: New Malaysia Ambient Air Quality StandardBoyHaha0% (1)
- Safety Induction TAWJV Revised4Document53 pagesSafety Induction TAWJV Revised4Adiel Yoga KharismaNo ratings yet
- 001 Bentonite Dril RigDocument5 pages001 Bentonite Dril RigAb AUNo ratings yet
- Daily SSS Work Report 2 July 2019 - Copy 1Document7 pagesDaily SSS Work Report 2 July 2019 - Copy 1Ahmad FaridNo ratings yet
- CPD Hours GuidelineDocument7 pagesCPD Hours Guidelinejohn labuNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safe Work PracticeDocument138 pagesElectrical Safe Work PracticeIjaz HussainNo ratings yet
- 10 Permit To Work Procedure Rev.d 301014Document11 pages10 Permit To Work Procedure Rev.d 301014Murdiyanto100% (1)
- Duw10022-C05 - Fire SafetyDocument46 pagesDuw10022-C05 - Fire SafetyMuhd Imran Kasyidi Omar100% (1)
- Operational Control Procedures BhelDocument124 pagesOperational Control Procedures BhelKrishnan Rajappan100% (3)
- Electrical Equipment in HazardousDocument17 pagesElectrical Equipment in HazardousZen LohNo ratings yet
- Fire Leak FinalDocument46 pagesFire Leak FinalRemington ManalotoNo ratings yet
- Shell Hazardous Area Classification FundamentalsDocument30 pagesShell Hazardous Area Classification Fundamentalsthekevindesai100% (17)
- Electrical Equipment in Hazardous AreasDocument14 pagesElectrical Equipment in Hazardous Areasger80No ratings yet
- Recurring Accidents-Confined Spaces v2Document24 pagesRecurring Accidents-Confined Spaces v2Himanshu ChichraNo ratings yet
- Electrical Equipment in Hazardous Areas - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument12 pagesElectrical Equipment in Hazardous Areas - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMrNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area ClassificationDocument9 pagesHazardous Area ClassificationyogitatanavadeNo ratings yet
- Answers To Offshore Tech ExamsDocument14 pagesAnswers To Offshore Tech ExamsEkiyo PiusNo ratings yet
- Power&EMC Earthing Mar19Document3 pagesPower&EMC Earthing Mar19HP LooiNo ratings yet
- Power&EMC Earthing Mar19 PDFDocument65 pagesPower&EMC Earthing Mar19 PDFHP LooiNo ratings yet
- Site Source Energy PlantDocument6 pagesSite Source Energy PlantHP LooiNo ratings yet
- IET Lecture LV Wiring Design September 14Document36 pagesIET Lecture LV Wiring Design September 14HP LooiNo ratings yet
- Common Practice Problems Electrical Part 1 (21may11)Document55 pagesCommon Practice Problems Electrical Part 1 (21may11)HP Looi100% (1)
- Common Practice Issues For Electrical 2011Document39 pagesCommon Practice Issues For Electrical 2011HP LooiNo ratings yet
- MS1525:2007 (Lighting) Public, 17june13Document19 pagesMS1525:2007 (Lighting) Public, 17june13HP LooiNo ratings yet
- Fire Detection Alarm System - 6 Oct 2009Document83 pagesFire Detection Alarm System - 6 Oct 2009HP Looi0% (1)
- Common Practice Problems Electrical Part 1 (21may11)Document55 pagesCommon Practice Problems Electrical Part 1 (21may11)HP Looi100% (1)
- GBIT Melaka 3novDocument56 pagesGBIT Melaka 3novHP LooiNo ratings yet
- GBI Township 3nov2011Document56 pagesGBI Township 3nov2011HP LooiNo ratings yet
- GFCO Certification ManualDocument72 pagesGFCO Certification Manualatila117No ratings yet
- Pipes On DeckDocument34 pagesPipes On DeckNataly Janataly100% (1)
- BrochureDocument8 pagesBrochurevacmanilaNo ratings yet
- Maxillofacial Trauma and Management - Dental Ebook & Lecture Notes PDF Download (Studynama - Com - India's Biggest Website For BDS Study Material Downloads)Document24 pagesMaxillofacial Trauma and Management - Dental Ebook & Lecture Notes PDF Download (Studynama - Com - India's Biggest Website For BDS Study Material Downloads)Vinnie SinghNo ratings yet
- Tata Steel Ratio AnalysisDocument41 pagesTata Steel Ratio AnalysisGourav VallakattiNo ratings yet
- Minimalist CV ResumeDocument1 pageMinimalist CV ResumeSijith MathewNo ratings yet
- White Paper - Data Communication in Substation Automation System SAS - Part 1 Original 23353Document5 pagesWhite Paper - Data Communication in Substation Automation System SAS - Part 1 Original 23353sabrahimaNo ratings yet
- ZPPF ChallanDocument1 pageZPPF ChallanGunasekhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Resource Planning: Computerized AccountingDocument14 pagesEnterprise Resource Planning: Computerized Accountingjivesh ranjan tiwariNo ratings yet
- 3rd Term s1 Agricultural Science 1Document41 pages3rd Term s1 Agricultural Science 1Adelowo DanielNo ratings yet
- TQM - Juran ContributionDocument19 pagesTQM - Juran ContributionDr.K.Baranidharan100% (2)
- Management Thoughts Pramod Batra PDFDocument5 pagesManagement Thoughts Pramod Batra PDFRam33% (3)
- RODEL LUZ y ONG, Petitioner, People of The Philippines, Respondent. FactsDocument1 pageRODEL LUZ y ONG, Petitioner, People of The Philippines, Respondent. FactsBee Raagas100% (1)
- BS en 12285-1-2003 (2006)Document162 pagesBS en 12285-1-2003 (2006)dahzahNo ratings yet
- QUIZ - PFRS 1 - FIRST TIME ADOPTION OF PFRSsDocument2 pagesQUIZ - PFRS 1 - FIRST TIME ADOPTION OF PFRSsGonzalo Jr. Ruales86% (7)
- Region VIII Schools Division of Tacloban City DLC V Sto. Niño Extension, Tacloban CityDocument3 pagesRegion VIII Schools Division of Tacloban City DLC V Sto. Niño Extension, Tacloban CityRikka EspedillaNo ratings yet
- Brigada EskwelaDocument4 pagesBrigada EskwelaJas Dela Serna SerniculaNo ratings yet
- 6 Elements of A Healthy ChurchDocument2 pages6 Elements of A Healthy ChurchJayhia Malaga JarlegaNo ratings yet
- BioEdit Version 7.0.0 PDFDocument192 pagesBioEdit Version 7.0.0 PDFJovanderson JacksonNo ratings yet
- Lower Gasket Kit (S/N E/ 9Fz999 & Below) : Model Number: 335 Serial Number: A9KA11001 & Above, AAD111001 & AboveDocument2 pagesLower Gasket Kit (S/N E/ 9Fz999 & Below) : Model Number: 335 Serial Number: A9KA11001 & Above, AAD111001 & Abovezeeshan tanveerNo ratings yet
- Contingent Liabilities For Philippines, by Tarun DasDocument62 pagesContingent Liabilities For Philippines, by Tarun DasProfessor Tarun DasNo ratings yet
- Amended Formal ComplaintDocument87 pagesAmended Formal ComplaintWXYZ-TV Channel 7 DetroitNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Dairy Waste Water Using Adsorbents From Solid WasteDocument7 pagesTreatment of Dairy Waste Water Using Adsorbents From Solid WasteIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Test Help StatDocument18 pagesTest Help Statthenderson22603No ratings yet
- Single Line DiagramDocument1 pageSingle Line DiagramGhanshyam Singh100% (2)
- EIV Operation ManualDocument339 pagesEIV Operation ManualJJSNo ratings yet
- PV1800VPM SEREIS (1-5KW) : Pure Sine Wave High Frequency Solar Inverter With MPPT InsideDocument4 pagesPV1800VPM SEREIS (1-5KW) : Pure Sine Wave High Frequency Solar Inverter With MPPT InsideHuber CallataNo ratings yet
- Triptico NIC 16Document3 pagesTriptico NIC 16Brayan HMNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To SAP Business One CloudDocument14 pagesAn Introduction To SAP Business One CloudBharathkumar PalaniveluNo ratings yet
- Read Me - CADWorx Plant 2019 SP2 HF1Document4 pagesRead Me - CADWorx Plant 2019 SP2 HF1Himanshu Patel (Himan)No ratings yet