Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Receptor Pharmacology Cheat Sheet (4f6203b546fa5)
Uploaded by
sinthreckOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Receptor Pharmacology Cheat Sheet (4f6203b546fa5)
Uploaded by
sinthreckCopyright:
Available Formats
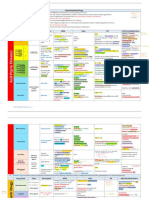
Overview of Receptor Pharmacology
Abbreviations: A, adrenaline; NA, noradrenaline; DA dopamine; 5HT, serotonin, PLC, phospholipase C; IP3, inositoltrisphosphate; DAG, diacylglycerol; AC, adenylate cyclase; NI, not important; PKA, protein kinase A; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; ACh, acetylcholine; MR, muscle relaxant Required information in bold. One agonist and antagonist per receptor is sufcient. Receptor family Adrenergic receptors Receptor subtype alpha 1 Physiological agonists NA > A Pharmacological agonists phenylephrine oxymetazoline Pharmacological antagonists prazosin Signalling mechanism Gq PLC IP3 + DAG Ca2+ Effect of agonist smooth muscle contraction, increased blood pressure decreased release of catecholamines from presynaptic neuron increased heart rate via PKAmediated increase in cardiac calcium channel activity Gs AC cAMP beta 2 A >> NA salbutamol terbutalin propranolol (non-selective) smooth muscle relaxation via phosphorylation of myosine increased lipolysis in adipose tissue, activation of brown adipose tissue used to treat asthma and COPD Note antagonists used as antihypertensives, agonists as decongestants presynaptic receptor, agonists used as antihypertensive agents agonists used to improve heart activity, antagonists to decrease its overactivation and as antihypertensives
alpha 2
A = NA
clonidine
NI
Gi AC cAMP
beta 1
A = NA
isoprenaline dobutamine
beta-blockers: propranolol (non-selective) atenolol (selective) pindolol (partial agonist)
beta 3
A > NA
NI
NI
possibly useful in the treatment of obesity
Information collated from http://www.iuphar-db.org/ Retrieved in March 2012.
Overview of Receptor Pharmacology
Receptor family Dopamine receptors Receptor subtype D1 Physiological agonists Pharmacological agonists NI Pharmacological antagonists NI Signalling mechanism Effect of agonist Note NI Gi AC cAMP
D2
DA
bromocriptine
antipsychotics: chlorpromazine haloperidol
inhibitory neurotransmission
agonists used to treat Parkinsons disease and excessive production of prolactin, antagonists are antipsychotics
D3 D4 Serotonin receptors 5HT1 5HT2 serotonin 5HT3
NI NI
NI NI
NI NI Gi AC cAMP
LSD
atypical antipsychotics: clozapine antiemetics: ondansetron
Gq PLC IP3 + DAG Ca2+ cation channel
stimulatory neurotransmission
receptor plays a role in hallucinations antagonists are used to combat vomiting during chemotherapy
NI
5HT4 Histamine receptors H1 histamine H2 NI anti-ulcer drugs: ranitidine NI antihistamines: loratadine
Gs AC cAMP Gq via beta-gamma subunits AC cAMP vasodilation, itching, bronchoconstricti on increased acid production in the stomach antagonists used to treat allergies
antagonists used to treat gastric hyperacidity and ulcers
Information collated from http://www.iuphar-db.org/ Retrieved in March 2012.
Overview of Receptor Pharmacology
Receptor family Cholinergic receptors Receptor subtype nicotinic (nAChR) Physiological agonists Pharmacological agonists nicotine succinylcholine decamethonium Pharmacological antagonists tubocurarine Signalling mechanism Effect of agonist Note cation channel membrane depolarisation excitatory transmission in autonomic ganglia and neuromuscular junction, antagonists used as nondepolarising MR, some agonists as depolarising MR mediates parasympathetic regulation of glandular secretion, ipratropium used in asthma, carbachol and pilocarpine to decrease intraocular pressure in glaucoma, pilocarpine also alleviates dry mouth mediates parasympathetic regulation of heart rate, atropine used to treat slow heart rate (bradycardia)
ACh M1 Gq PLC IP3 + DAG Ca2+ activation of glandular secretion
muscarine carbachol pilocarpine
atropine scopolamine hyoscyamine ipratropium Gi AC cAMP decreased heart rate via G-betagamma dimer mediated opening of K+ channels
M2
M3
Gq PLC IP3 + DAG Ca2+ Gi AC cAMP
M4
Information collated from http://www.iuphar-db.org/ Retrieved in March 2012.
Overview of Receptor Pharmacology
Receptor family Glutamatergic receptors Receptor subtype NMDA Physiological agonists Pharmacological agonists N-methyl-Daspartate Pharmacological antagonists ketamine phencyclidine Signalling mechanism cation channel (Na+ and Ca2+) Effect of agonist Note depolarisation, inux of calcium important in memory formation, excitotoxicity; antagonists cause dissociative hallucinations; only opens if glutamate is present AND membrane is depolarised
glutamate
AMPA kainate mGluR
AMPA kainic acid
cation channel cation channel G proteins
depolarisation depolarisation many roles in CNS; role in umami taste detection hyperpolarisation main inhibitory neurotransmitter
GABAergic receptors
GABAA
sedatives: benzodiazepines (BZD) barbiturates ethanol? GABA baclofen
picrotoxin umazenil (BZD antagonist)
chloride channel
GABAB
Gi AC cAMP
inhibitory transmission also via G-beta-gamma dimer mediated opening of K+ channels
Information collated from http://www.iuphar-db.org/ Retrieved in March 2012.
Overview of Receptor Pharmacology
Receptor family Voltage-gated sodium channels Receptor subtype NaV1.1 (neuronal bodies) NaV1.2 (fast, in axons) scorpion toxins aconitine tetrodotoxin local anaesthetics: lidocain cocaine tetrodotoxin Physiological agonists Pharmacological agonists Pharmacological antagonists Signalling mechanism Effect of agonist Note cation channel depolarisation
cation channel
depolarisation
depolarisati on
important in action potential propagation in nerve cells, specially axons
NaV1.4 (skeletal muscle) Voltage-gated calcium channels N-type or Q type (neuronal) L-type (long)
scorpion toxins
cation channel
depolarisation
NI
conotoxins
cation channel
depolarisation
important in synaptic exocytosis regulation responsible in part for in cardiac action potential, triggering Ca2+ release in skeletal muscle and contraction of vascular smooth muscles important for burst ring in neurons effects of opiates: analgesic, anti-anxiety, physical dependence
NI depolarisati on
nifedipine diltiazem verapamil
cation channel
depolarisation
T-type transient Opioid receptors mu delta kappa endorphins dynorphins enkephalins
NI
NI
cation channel
depolarisation
morphine
naloxone naltrexone
Gi AC cAMP plus other pathways
complex effects
Information collated from http://www.iuphar-db.org/ Retrieved in March 2012.
You might also like
- Pharmacology MnemonicsDocument17 pagesPharmacology MnemonicsAzfar AkramNo ratings yet
- Pharm MnemonicsDocument33 pagesPharm MnemonicsThomson George75% (4)
- Pharmacology ChartDocument6 pagesPharmacology ChartPaula67% (3)
- Adrenergics & Adrenergic BlockersDocument5 pagesAdrenergics & Adrenergic Blockersapi-3739910100% (4)
- Drugs WorksheetDocument16 pagesDrugs Worksheetninja-2001No ratings yet
- Drug Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesDrug Cheat SheetThomas Hart IIINo ratings yet
- Pharm 1.11 Insulin Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePharm 1.11 Insulin Cheat SheetSanobar Charania100% (1)
- Pharmacology Chart 3Document2 pagesPharmacology Chart 3Omar ClorNo ratings yet
- Anti-Infectives Course #25Document18 pagesAnti-Infectives Course #25Gina Giammalvo100% (2)
- Pharmacology Test 1Document39 pagesPharmacology Test 1Niki BolinNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Mnemonics (Part 01) by M IhtishamDocument32 pagesPharmacology Mnemonics (Part 01) by M Ihtishammuhammad ihtisham ul hassan100% (1)
- A New Way of Mnemonics - Hypertension-cough-asthma-NSAID - WMDocument26 pagesA New Way of Mnemonics - Hypertension-cough-asthma-NSAID - WMKartik Mendiratta100% (1)
- Pharm Drug Outline AdrDocument1 pagePharm Drug Outline AdrCess Lagera YbanezNo ratings yet
- Cholinergics and AnticholinergicsDocument5 pagesCholinergics and AnticholinergicscatislandbigredNo ratings yet
- Template Drug Card1Document1 pageTemplate Drug Card1Kay TaylorNo ratings yet
- Ace Inhibitors MnemonicDocument1 pageAce Inhibitors MnemonicGirish Waru0% (2)
- Mnemonic S 2Document9 pagesMnemonic S 2Anj Shrestha100% (2)
- Drug CardsDocument3 pagesDrug CardsDave HillNo ratings yet
- Drugclasses Pharmacologypart 1 PDFDocument25 pagesDrugclasses Pharmacologypart 1 PDFSutanya100% (2)
- Cholinergics and Cholinergic BlockersDocument5 pagesCholinergics and Cholinergic Blockersapi-3739910100% (3)
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument16 pagesPharmacology Summarysechzhen96% (46)
- Pharmacology Important Things To RememberDocument5 pagesPharmacology Important Things To RememberHydie100% (1)
- Drugs Cards 208Document11 pagesDrugs Cards 208SOOOS94100% (3)
- Top-200-Drug ETSYDocument31 pagesTop-200-Drug ETSYBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Final Study GuideDocument28 pagesPharmacology Final Study GuideAnthony Palladeno100% (1)
- Pharmacology Mnemonics PDFDocument27 pagesPharmacology Mnemonics PDFHasanAli100% (2)
- Complete Drug GuideDocument225 pagesComplete Drug GuideJessica 'Baker' IsaacsNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PharmacologyDocument89 pagesRespiratory PharmacologyEka PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Adrenergic DrugsDocument52 pagesTopic 2 - Adrenergic DrugsAngeli Gregorio100% (1)
- Whole Pharmacology Classification: Adrenergic Antagonists Alpha Adrenergic Antagonists Alpha 1 AntagonistsDocument17 pagesWhole Pharmacology Classification: Adrenergic Antagonists Alpha Adrenergic Antagonists Alpha 1 AntagonistsFlorina TrutescuNo ratings yet
- GI Drugs PDFDocument6 pagesGI Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Cholinergic Drug MnemonicsDocument1 pageCholinergic Drug Mnemonicssunshine151100% (1)
- Nursing Pharmacology Drug Study GuideDocument15 pagesNursing Pharmacology Drug Study GuideChelsea SmithNo ratings yet
- Family Names of DrugsDocument1 pageFamily Names of DrugsangelNo ratings yet
- Ninja - Anti-HTN PDFDocument6 pagesNinja - Anti-HTN PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (2)
- Comprehensive Pharmacology SummaryDocument25 pagesComprehensive Pharmacology Summarybhaveshnidhi64100% (1)
- NCLEX Review: Pharmacology Charlene Natale, BSN, RNDocument43 pagesNCLEX Review: Pharmacology Charlene Natale, BSN, RNMenly Susada100% (1)
- Nursing School Drug ChartDocument13 pagesNursing School Drug ChartEve Lester100% (3)
- Pharm-Drugs ChartsDocument21 pagesPharm-Drugs ChartsCandace Flowers100% (3)
- Agents Causing Coma or SeizuresDocument3 pagesAgents Causing Coma or SeizuresShaira Aquino VerzosaNo ratings yet
- Drugs MnemonicsDocument6 pagesDrugs MnemonicsDarrylJavier100% (1)
- A-Autonomic Drugs: 1) CholinergicDocument28 pagesA-Autonomic Drugs: 1) CholinergicMahmoud Ahmed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Printable Drug Template CardDocument2 pagesPrintable Drug Template CardJennifer LeNo ratings yet
- Overview of by Mechanism 2Document16 pagesOverview of by Mechanism 2daven100% (1)
- Pain and Inflammation Med ChartsDocument4 pagesPain and Inflammation Med Chartssurviving nursing school100% (1)
- 1430 Drug CardsfinalDocument7 pages1430 Drug CardsfinalLizSherman100% (1)
- Drug SuffixesDocument3 pagesDrug SuffixesjeromeasuncionNo ratings yet
- 4 Adrenergic AgonistsDocument46 pages4 Adrenergic Agonistsmatchees-gone rogueNo ratings yet
- ADR PharmacologyDocument30 pagesADR PharmacologySumanth Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AgentsDocument77 pagesAdrenergic AgentsMa8 Au8No ratings yet
- MX Accion AdrenergecosDocument7 pagesMX Accion Adrenergecosetbriali84No ratings yet
- Adrenergic Agonist & Antagonist: - Guide: DR R K Solanki Sir DR Neelam Mam DR Kailash MittalDocument83 pagesAdrenergic Agonist & Antagonist: - Guide: DR R K Solanki Sir DR Neelam Mam DR Kailash MittalDivya Rekha KolliNo ratings yet
- Day 22 Signaling 1: General Concepts and cAMP Pathway: - You Should Be Able To ExplainDocument20 pagesDay 22 Signaling 1: General Concepts and cAMP Pathway: - You Should Be Able To Explainshouq huusainNo ratings yet
- Atrial Natriuretic PeptideDocument4 pagesAtrial Natriuretic PeptideZiedTrikiNo ratings yet
- Anti-Hypertensive DrugsDocument56 pagesAnti-Hypertensive Drugsapi-3815243No ratings yet
- Antiepileptics Class PPT - DR Anoosha BhandarkarDocument64 pagesAntiepileptics Class PPT - DR Anoosha BhandarkaranooshabhandarkarNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Receptor: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesAdrenergic Receptor: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaChandra TappyNo ratings yet
- EPIGENETICS DRUG THERAPYpptx - 240118 - 070801Document43 pagesEPIGENETICS DRUG THERAPYpptx - 240118 - 070801Maryam HaniniNo ratings yet
- L20 Signal Transduction and Mechanism of Hormone ActionDocument51 pagesL20 Signal Transduction and Mechanism of Hormone Actionyebadem228No ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetic Drug Interactions: Ika Puspita Sari Bagian Farmakologi & Farmasi Klinik Fakultas Farmasi UGMDocument31 pagesPharmacokinetic Drug Interactions: Ika Puspita Sari Bagian Farmakologi & Farmasi Klinik Fakultas Farmasi UGMNasyrah OchaNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On-: Dr. Nikhil Oza Intern BvdumcDocument43 pagesA Presentation On-: Dr. Nikhil Oza Intern BvdumcMaheboob GanjalNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Maths Project On Prime NumbersDocument13 pagesClass 12 Maths Project On Prime Numbersanon_3835245630% (1)
- Tuesday, 16 November 2021 - Afternoon Discovering ElectronicsDocument20 pagesTuesday, 16 November 2021 - Afternoon Discovering Electronicsnvmalt070No ratings yet
- c083c282a43655ec69532f2704c3993aDocument12 pagesc083c282a43655ec69532f2704c3993aAneilRandyRamdialNo ratings yet
- Reloved - October 2015Document116 pagesReloved - October 2015Barron Fields67% (3)
- Comparative Performance of Some Cattle Breeds Under Barani Conditions of PakistanDocument4 pagesComparative Performance of Some Cattle Breeds Under Barani Conditions of PakistanMasood HassanNo ratings yet
- Inform LetterDocument2 pagesInform LetterMc Suan75% (4)
- Comparison of 3 Tests To Detect Acaricide ResistanDocument4 pagesComparison of 3 Tests To Detect Acaricide ResistanMarvelous SungiraiNo ratings yet
- Listening - Homework 2: Brushes 285 RamdhanieDocument4 pagesListening - Homework 2: Brushes 285 RamdhanieBao Tran NguyenNo ratings yet
- The Joy Luck Club Book 1Document12 pagesThe Joy Luck Club Book 1loronalicelNo ratings yet
- SSCNC Turning Tutorial ModDocument18 pagesSSCNC Turning Tutorial ModYudho Parwoto Hadi100% (1)
- Bio (RocessDocument14 pagesBio (RocessVijay SansanwalNo ratings yet
- Communication Guide: For Vita 62 Compliant VPX Power SuppliesDocument8 pagesCommunication Guide: For Vita 62 Compliant VPX Power Suppliesk.saikumarNo ratings yet
- Poems Prescribed For 2012-2014 English B CSEC ExamsDocument24 pagesPoems Prescribed For 2012-2014 English B CSEC ExamsJorge Martinez Sr.100% (2)
- Spectroscopy (L-26 To 29)Document81 pagesSpectroscopy (L-26 To 29)Vashistha GargNo ratings yet
- Conformational Analysis: Carey & Sundberg: Part A Chapter 3Document53 pagesConformational Analysis: Carey & Sundberg: Part A Chapter 3Dr-Dinesh Kumar100% (1)
- SCIENCEEEEEDocument3 pagesSCIENCEEEEEChristmae MaganteNo ratings yet
- TS SR Chemistry Imp Questions PDFDocument5 pagesTS SR Chemistry Imp Questions PDFUnknown Khan100% (3)
- Drug Study LidocaineDocument15 pagesDrug Study LidocaineFrancym R. BatengaNo ratings yet
- Plato: Epistemology: Nicholas WhiteDocument2 pagesPlato: Epistemology: Nicholas WhiteAnonymous HCqIYNvNo ratings yet
- Dialog Bahasa InggirsDocument2 pagesDialog Bahasa InggirsKeRtha NeghaRaNo ratings yet
- Mini Project 1 - 1Document9 pagesMini Project 1 - 1Sameer BaraNo ratings yet
- Siemens Internship ReportDocument84 pagesSiemens Internship Reportujjawalbhojawala100% (1)
- Pre RmoDocument4 pagesPre RmoSangeeta Mishra100% (1)
- Abnormalities of Placenta, Amniotic Fluid and Cord: Prepared By, B. Ezhilarasi, Nursing TutorDocument21 pagesAbnormalities of Placenta, Amniotic Fluid and Cord: Prepared By, B. Ezhilarasi, Nursing TutorGopala KrishnanNo ratings yet
- QuantAssay Software Manual 11-Mar-2019Document51 pagesQuantAssay Software Manual 11-Mar-2019LykasNo ratings yet
- Cell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsDocument6 pagesCell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsRPh Krishna Chandra JagritNo ratings yet
- Siprotec 7ut82 ProfileDocument2 pagesSiprotec 7ut82 ProfileOliver Atahuichi TorrezNo ratings yet
- Texto CuritibaDocument1 pageTexto CuritibaMargarida GuimaraesNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument61 pagesCase StudyA GNo ratings yet