Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Geology
Uploaded by
duncmcleodCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Geology
Uploaded by
duncmcleodCopyright:
Available Formats
BASIC GEOLOGY
2
Explain the main types of rocks
Identify rocks by their lithology
Explain the two main physical properties of reservoir
rocks
Describe four geological components of a prospect
Illustrate different types of petroleum reservoirs
Describe structural features that affect drilling
List methods used for evaluation during drilling
Learning Objectives
3
Geology is the science that deals with the history
and structure of the earth and its life forms,
especially as recorded in the rock record
During drilling rock characteristics and associated
drilling conditions can change many times
An understanding of the anticipated geology is
essential for properly designing the well and then
drilling it efficiently and safely.
Definition
4 Geologic Time Scale
ERA PERIOD EPOCH SUCCESSION OF LIFE
CENOZOIC
Quaternary
0 1 Million
Years
Recent
Pleistocene
Tertiary
65 Million Years
Pliocene
Miocene
Oligocene
Eocene
Paleocene
MESOZOIC
Cretaceous
Jurassic
Triassic
PALEOZOIC
Permian
Pennsylvanian
Mississippian
Devonian
Silurian
Ordovician
Cambrian
PRECAMBRIAN
5
Note the . In it is a nannofossil on the surface of this foraminifera
Microfossils found or extracted from drill
cuttings are the primary tool used by the oil
industry for age dating geologic strata.
Microfossils
6
IGNEOUS: Rocks formed by solidification of hot mobile
material termed magma.
Intrusive (solidifies underground)
Extrusive (volcanic eruption)
METAMORPHIC: Rocks formed by the transformation, in
the solid state, of pre-existing igneous or sedimentary
rocks as a result of high temperature and pressure.
SEDIMENTARY: Rocks formed from accumulations of
sediment, which may consist of rock fragments of
various sizes, the remains of animal and plants, the
product of chemical action or evaporation , or a
combination of these.
Types of Rocks
7 Distinction of Rocks for Petroleum
Igneous
Metamorphic
Non-
Reservoir
Sedimentary
Reservoir
8
Some Rock Samples
Reservoir
Reservoir
Reservoir
Reservoir
9
Description of Rock Cuttings
Shale, Clay, Claystone Argillaceous
Sandstone, Siltstone Arenaceous
Limestone, Dolomite Carbonates
Anhydrite, Salt Evaporites
Pyrite, Mica, Chert, Coal Other
10
Lithology
Shale
Sandstone
Limestone
Calcareous shale
Anhydrite
Argillaceous Limestone
Quartz
Conglomerate
Dolomite
Clay
Lignite
The Character of Rock Formations
11
Physical Properties of Reservoir Rocks
It is the percent volume
of pore space
Porosity
()
It is a measure of a
fluids ability to flow
through a porous media
Permeability
(k)
12
Physical Properties
Porosity ():
(
volume bulk
volume grain - volume bulk
100 = Porosity Percent
(
volume bulk
volume pore
100 = Porosity Percent
13
ABSOLUTE POROSITY: The percent of total voids in the
rock compared to the total rock volume
EFFECTIVE POROSITY: The percent of interconnected
void spaces in the rock compared to the total rock
volume
Physical Properties
14
Oil Reserves in Place
Oil In Place (Barrels) = 7,758 x V
o
x (1-S
w
)
Where,
V
o
= Volume of oil bearing rock in acre-feet
= Effective porosity, fraction
S
w
= Water saturation, fraction
15
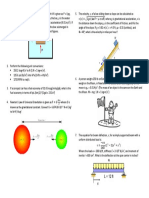
Permeability (k):
It is a measure of a fluids ability to flow through
a porous media
Where,
Q = flow rate, cc/sec
A = cross-sectional area of rock, cm
2
k = permeability, Darcy
= viscosity of the fluid, cp
AP = differential pressure, atm
L = length over which AP applies, cm
h = thickness of medium, cm
re = external radius
rw = well radius
L
P
k
A = Q
rw
re
Ln
P
hk
2 = Q
Linear horizontal flow Radial horizontal flow
Physical Properties
16
Physical Properties
Bulk Density (
b
):
It is the weight per unit volume of rock
In sedimentary rocks it is less than the density of the
matrix material due to rock porosity
Under normal compaction, the bulk density increases
with depth
Unit of measurement is gm/cc
Example:
Take rock with a specific gravity of 2.7 and a porosity of
10%. The pores are filled with salt water having a
specific gravity of 1.05. The bulk density of the shale
would then be (.9) (2.7) + (.1) (1.05) = 2.53
17
Prospect Components
1
Source Rock
2
Reservoir
3
Seal
4
Trap
18
SOURCE ROCK: Organic deposit that, when
heated, release oil and/or gas. These deposits
are usually formed in marine and lacustrine
environments. Most common rock type is shale.
RESERVOIR: Container that holds sufficient
volumes of oil and/or gas. Most common rock
types include sandstone, limestone, and
dolomite.
Prospect Components
19
SEAL: Barrier that inhibits movement
of oil and/or gas. Common rock types
that act as seals are evaporites and
shales.
TRAP: Refers to the three dimensional
geometric configuration of the reservoir
and associated seal.
Prospect Components
20
Petroleum System Elements
Petroleum System Elements
Anticlinal Trap
Anticlinal Trap
(Impermeable)
Potential
Migration Route
Faults & Fractures
Unconformities
Salt Faces and Welds
Porous and Permeable Beds
Prospect Components
21
Flow of gas and oil from the source rock to the trap. Expulsion of oil and gas from the source
rock occurs because of volume increase during generation that fractures the shale.
Migration is usually upward through subsurface fractures due to buoyancy
(gas and oil are lighter than water).
Migration & Accumulation
22
Types of Petroleum Reservoirs
Anticline
Fault Trap
Stratigraphic Trap
Salt Dome
23
Oil
Anticlinal Trap
Gas
Reservoir
rock
Oil
Seal
Water
Fault trap requires:
Dipping Beds
Juxtaposition of impermeable
beds and/or
Smear/gouge seal as beds
move past each other
24
Fault Trap
25
A
B
C
A
B
C
Hanging wall
Foot wall
Normal Fault
Hanging wall moves down
relative to Footwall
Section will be missing faulted
out with normal faults
A
B
C
A
B
C
Hanging wall Foot wall
Reverse Fault
Hanging wall moves up
relative to Footwall
Section will be repeated with
reverse faults
Types of Faults
26 Stratigraphic Traps
27
Dome - An anticlinal structure, elliptical or
circular in outline. Often formed by intrusion
of igneous or diapiric sedimentary rock from
below.
Dome
28
Salt Dome
Cap Rock?
Salt Trap
29
The Science that deals with the composition and
physical phenomena of the earth and its liquid
and gaseous environments
Most commonly: Earth Magnetism, Gravity, and
Seismic Vibrations
Geophysics
30
Acquiring Seismic Data - Land
Vibrator Truck
(Energy Source)
Recording Truck
Geophone
(Receivers)
Returning Returning
Sound Waves Sound Waves
Vibrator Truck
(Energy Source)
Recording Truck
Geophone
(Receivers)
American Petroleum Institute, 1986
Returning Returning
Sound Waves Sound Waves
31
Acquiring Seismic Data - Marine
32
A Seismic Section
33
Gravity, seismic, and petrophysical log data are combined
3-D Earth Model
34
DIP
The angle at which a stratum or any planar
feature is inclined from the horizontal
The dip is at right angles to the strike
Structural Features
35 Structural Features
Structural features that affect drilling
performance:
Dip angle
Strike angle
Faults
Fractures
Vugs
Intercalation and lamination
Uplifted
Tectonic stresses and their direction
36
STRIKE
The course or bearing of the outcrop of an
inclined bed or structure on a level
surface; the direction or bearing of a
horizontal line in the plane of an inclined
stratum, joint, fault, cleavage plane, or
other structural plane
It is perpendicular to the direction of the
dip
Structural Features
37
Strike - parallel to the long axis of a structure or parallel to the direction or
trend taken by a structural element. Perpendicular to dip direction.
Dip - the maximum angle of a surface or structural element from horizontal.
Dip direction is perpendicular to strike.
Structural Features
38
Description and analysis of cuttings
Mud weight - in & out
Gas detection and measurement
Detection of hydrocarbon shows
Logging while drilling
Rate of penetration
Torque and drag
Directional measurements
Temperature of drilling fluid
Chemical analysis of drilling fluid
Coring
Evaluation During Drilling
39 Depth Reference
7025
6525
-5000
Measured Depth (MD)
True Vertical Depth (TVD)
Subsea True Vertical Depth (SSTVD)
5075
5075
-5000
3000
Measured Depth (MD)
True Vertical Depth (TVD)
Subsea True Vertical Depth (SSTVD)
Below Mud Line (BML)
SEA
LEVEL
+1000
0
-1000
-2000
-3000
-4000
-5000
KB/RT - 25
KB/RT - 75
You might also like
- Tectonics of Sedimentary Basins: Recent AdvancesFrom EverandTectonics of Sedimentary Basins: Recent AdvancesCathy BusbyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- 1 IntroductionDocument14 pages1 Introductionbayoakac100% (1)
- Innovative Exploration Methods for Minerals, Oil, Gas, and Groundwater for Sustainable DevelopmentFrom EverandInnovative Exploration Methods for Minerals, Oil, Gas, and Groundwater for Sustainable DevelopmentA. K. MoitraNo ratings yet
- Determination of RW PDFDocument23 pagesDetermination of RW PDFAngelMesoNo ratings yet
- Depositional History of Franchthi Cave: Stratigraphy, Sedimentology, and Chronology, Fascicle 12From EverandDepositional History of Franchthi Cave: Stratigraphy, Sedimentology, and Chronology, Fascicle 12No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Final For PostingDocument75 pagesLecture 1 - Final For PostingWentao ZhouNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon Fluid Inclusions in Petroliferous BasinsFrom EverandHydrocarbon Fluid Inclusions in Petroliferous BasinsNo ratings yet
- Schlumberger Log Interpretation ChatsDocument287 pagesSchlumberger Log Interpretation ChatsSabrianto AswadNo ratings yet
- (Bernard Biju-Duval, Institut Français Du PétrolDocument658 pages(Bernard Biju-Duval, Institut Français Du PétrolMoisés CacamaNo ratings yet
- Basin Modeling SoftwaresDocument22 pagesBasin Modeling SoftwaresDarlly ReisNo ratings yet
- Wave Propagation in Drilling, Well Logging and Reservoir ApplicationsFrom EverandWave Propagation in Drilling, Well Logging and Reservoir ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Chapter-8 Sonic Logs: by Dr. Jorge Salgado GomesDocument20 pagesChapter-8 Sonic Logs: by Dr. Jorge Salgado GomesbrunoNo ratings yet
- Deepwater Sedimentary Systems: Science, Discovery, and ApplicationsFrom EverandDeepwater Sedimentary Systems: Science, Discovery, and ApplicationsJon R. RotzienNo ratings yet
- Water ResistivityDocument33 pagesWater ResistivityBrenda DavisNo ratings yet
- Exploration and Mapping TechniquesDocument12 pagesExploration and Mapping TechniquesEstephanny Watsson G. HzNo ratings yet
- Oilfield Review 2Document17 pagesOilfield Review 2Luis Alberto Colan GarciaNo ratings yet
- Shaly Sands: Shale Effects On Log Response and Log Analysis Depend OnDocument40 pagesShaly Sands: Shale Effects On Log Response and Log Analysis Depend OnwandaNo ratings yet
- 01 IntroductionToPetrophysics RAWDocument22 pages01 IntroductionToPetrophysics RAWBond Say HiiNo ratings yet
- Deep-Water Processes and Facies Models: Implications for Sandstone Petroleum ReservoirsFrom EverandDeep-Water Processes and Facies Models: Implications for Sandstone Petroleum ReservoirsNo ratings yet
- Geology of Carbonate Reservoirs: The Identification, Description and Characterization of Hydrocarbon Reservoirs in Carbonate RocksFrom EverandGeology of Carbonate Reservoirs: The Identification, Description and Characterization of Hydrocarbon Reservoirs in Carbonate RocksNo ratings yet
- Ophyscis Today Page 171 181Document543 pagesOphyscis Today Page 171 181anima1982100% (2)
- Modeling The Earth For Oil Exploration: Final Report of the CEC's Geoscience I Program 1990-1993From EverandModeling The Earth For Oil Exploration: Final Report of the CEC's Geoscience I Program 1990-1993No ratings yet
- Advanced - Log InterpretationDocument11 pagesAdvanced - Log Interpretationعبد العزيز مروى100% (1)
- Size of ReservoirDocument15 pagesSize of ReservoirKonul AlizadehNo ratings yet
- GeoLog - Installation Manual v1.0Document13 pagesGeoLog - Installation Manual v1.0riki1989zainNo ratings yet
- Interpretations of Logs-3Document137 pagesInterpretations of Logs-3Shalihan MustafaNo ratings yet
- CH-4 Log Correlation Techniques 22 48-1-10 PDFDocument22 pagesCH-4 Log Correlation Techniques 22 48-1-10 PDFRenato AlgarateNo ratings yet
- EGB373 Summary PermeabilityDocument1 pageEGB373 Summary PermeabilityWinston BoonNo ratings yet
- Optimal Seismic Deconvolution: An Estimation-Based ApproachFrom EverandOptimal Seismic Deconvolution: An Estimation-Based ApproachNo ratings yet
- How To Compute Petrophysicals Cutoffs With GeolOilDocument3 pagesHow To Compute Petrophysicals Cutoffs With GeolOilpahlawankemalemanNo ratings yet
- PetroMod TecLinkDocument2 pagesPetroMod TecLinkAnggara Putra100% (1)
- Multifrequency Electromagnetic Data Interpretation for Subsurface CharacterizationFrom EverandMultifrequency Electromagnetic Data Interpretation for Subsurface CharacterizationNo ratings yet
- Seismics BasicsDocument86 pagesSeismics Basicssandeepmev100% (1)
- Going Beyond Exploration: HeadlinesDocument18 pagesGoing Beyond Exploration: HeadlinesibidaboNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5. Neutron LoggingDocument72 pagesLecture 5. Neutron LoggingDimash AbdrakhmanovNo ratings yet
- Lamcount: Reservoir DescriptionDocument1 pageLamcount: Reservoir DescriptionWahid MiaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Thin Beds PDFDocument26 pagesEvaluation of Thin Beds PDFMustapha BouregaaNo ratings yet
- 2 Mechanisms Basin FormationDocument24 pages2 Mechanisms Basin FormationMuhamadKamilAzharNo ratings yet
- Seismic Inversion For Reservoir CharacterizationDocument5 pagesSeismic Inversion For Reservoir CharacterizationMahmoud EloribiNo ratings yet
- Downhole LoggingDocument54 pagesDownhole LoggingMohammadFaisalQureshiNo ratings yet
- Resistivity LogDocument14 pagesResistivity LogMuhammad NursalamNo ratings yet
- Seismicreflections ExxonDocument25 pagesSeismicreflections ExxonAamir LokhandwalaNo ratings yet
- Caliper & Temperature LoggingDocument23 pagesCaliper & Temperature Loggingsdb158100% (1)
- Gamma Ray LogsDocument31 pagesGamma Ray LogsAlyani KornerNo ratings yet
- SPE-194775-MS Laser Gun: The Next Perforation TechnologyDocument15 pagesSPE-194775-MS Laser Gun: The Next Perforation TechnologyEdi Agurto CarrascoNo ratings yet
- Permeability From Production Logs - Method and ApplicationDocument16 pagesPermeability From Production Logs - Method and ApplicationTwirX100% (1)
- Dipmeter MeasurementsDocument18 pagesDipmeter Measurementsmahmoud_al_kafajiNo ratings yet
- 10 - Shaly SandDocument31 pages10 - Shaly SandLyn KenNo ratings yet
- The Organic Content of The Bone Spring Formation As Evaluated by The Delta Log R Method of Log AnalysisDocument98 pagesThe Organic Content of The Bone Spring Formation As Evaluated by The Delta Log R Method of Log Analysisragingpheonix87100% (1)
- Engineering Geology Presentation PDFDocument65 pagesEngineering Geology Presentation PDFBenjamin AttwellNo ratings yet
- Formation Evaluation and Well Log CorrelationDocument27 pagesFormation Evaluation and Well Log CorrelationNguyen Truong SonNo ratings yet
- Sandstone Vs Carbonate ReservoirDocument3 pagesSandstone Vs Carbonate ReservoirTri HaryantaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Gamma Ray LogDocument39 pagesLecture 7 Gamma Ray LogNaser Khan100% (2)
- Alternative Shaly Sands Water Saturation Equations ComparisonDocument32 pagesAlternative Shaly Sands Water Saturation Equations ComparisonKartiko WibowoNo ratings yet
- Borehole ImagingDocument18 pagesBorehole ImagingkietniNo ratings yet
- CGE 674 CGE 674 CGE 674 CGE 674 Formation Evaluation Formation Evaluation Formation Evaluation Formation EvaluationDocument65 pagesCGE 674 CGE 674 CGE 674 CGE 674 Formation Evaluation Formation Evaluation Formation Evaluation Formation EvaluationNamwangala Rashid NatinduNo ratings yet
- Petrel EnglishDocument52 pagesPetrel EnglishMiguel Angel Catunta Zarate100% (1)
- 1 Well Logging - IntroductionDocument16 pages1 Well Logging - IntroductionMuhammad RaiesNo ratings yet
- Pressure Ratings Stainless Steel PipeDocument4 pagesPressure Ratings Stainless Steel PipeduncmcleodNo ratings yet
- 4 1-4 4Document2 pages4 1-4 4duncmcleodNo ratings yet
- Kinley CutterDocument1 pageKinley CutterduncmcleodNo ratings yet
- P Is Given To As 300 Pounds, Find The Volume of The Box Submerged inDocument1 pageP Is Given To As 300 Pounds, Find The Volume of The Box Submerged induncmcleodNo ratings yet
- Stuck Pipe PDFDocument27 pagesStuck Pipe PDFduncmcleod100% (1)
- Kbg-2 Mandrel SLB Product SheetDocument2 pagesKbg-2 Mandrel SLB Product SheetduncmcleodNo ratings yet
- Oilfield Ownership 3-2012Document1 pageOilfield Ownership 3-2012duncmcleodNo ratings yet
- IED-Review Engineering Formula SheetDocument10 pagesIED-Review Engineering Formula Sheetedhy_03100% (1)
- Plugs and ProfilesDocument43 pagesPlugs and ProfilesTariq SaydawiNo ratings yet
- Titan C ManualDocument26 pagesTitan C Manualduncmcleod100% (3)
- Cheat SheetDocument34 pagesCheat SheetbambamaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Progress ReportDocument48 pagesMidterm Progress ReportduncmcleodNo ratings yet
- GVSTDocument1 pageGVSTduncmcleodNo ratings yet
- Oilfield Resume EbookDocument60 pagesOilfield Resume EbookduncmcleodNo ratings yet
- Casing Sizes and DriftsDocument2 pagesCasing Sizes and DriftsAbdulaziz AbdullahNo ratings yet
- TSH TT PH4-PH6-CS 1Document8 pagesTSH TT PH4-PH6-CS 1Jesus Mishell Perez HuertaNo ratings yet
- Premium Connections Catalogue ENGDocument134 pagesPremium Connections Catalogue ENGsubzwarijNo ratings yet
- HE Drilling JarsDocument32 pagesHE Drilling Jarsmr_heeraNo ratings yet
- Casing Sizes and DriftsDocument2 pagesCasing Sizes and DriftsAbdulaziz AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 1.7 Pressure Drop CalculationsDocument29 pages1.7 Pressure Drop Calculationsduncmcleod100% (1)
- Common Rig MathDocument17 pagesCommon Rig MathSanjay Mishra86% (7)
- Greater Prudoe Bay Area MapDocument1 pageGreater Prudoe Bay Area MapduncmcleodNo ratings yet
- Casing Sizes and DriftsDocument2 pagesCasing Sizes and DriftsAbdulaziz AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Barite Product Data SheetDocument1 pageBarite Product Data SheetduncmcleodNo ratings yet
- University of Oklahoma School of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering AME 4163/4553: Senior Design Practicum Information For Student ParticipantsDocument33 pagesUniversity of Oklahoma School of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering AME 4163/4553: Senior Design Practicum Information For Student ParticipantsduncmcleodNo ratings yet
- Press Fit PDFDocument9 pagesPress Fit PDFMohd Hilmi IzaanNo ratings yet
- Technical Rockwell Automation FactoryTalk HistorianDocument6 pagesTechnical Rockwell Automation FactoryTalk HistorianAmit MishraNo ratings yet
- V13 D03 1 PDFDocument45 pagesV13 D03 1 PDFFredy Camayo De La CruzNo ratings yet
- A-1660 11TH Trimester From Mcdowell To Vodafone Interpretation of Tax Law in Cases. OriginalDocument18 pagesA-1660 11TH Trimester From Mcdowell To Vodafone Interpretation of Tax Law in Cases. OriginalPrasun TiwariNo ratings yet
- Lecture BouffonDocument1 pageLecture BouffonCarlos Enrique GuerraNo ratings yet
- Request For Proposals/quotationsDocument24 pagesRequest For Proposals/quotationsKarl Anthony Rigoroso MargateNo ratings yet
- Passage Planning: Dr. Arwa HusseinDocument15 pagesPassage Planning: Dr. Arwa HusseinArwa Hussein100% (3)
- FIGMADocument22 pagesFIGMACessNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Lab AnswersDocument3 pagesPeriodic Table Lab AnswersIdan LevyNo ratings yet
- Action Plan in T.L.E Project Title Objectives Activities Person-In-Charge Time Frame Success IndicatorDocument1 pageAction Plan in T.L.E Project Title Objectives Activities Person-In-Charge Time Frame Success IndicatorEdelmar BenosaNo ratings yet
- ING C1 CO JUN2016 CorrectorDocument6 pagesING C1 CO JUN2016 CorrectoraciameNo ratings yet
- The Teacher Research Movement: A Decade Later: Cite This PaperDocument13 pagesThe Teacher Research Movement: A Decade Later: Cite This PaperAlexandre NecromanteionNo ratings yet
- Swiss Army Triplet 1Document2 pagesSwiss Army Triplet 1johnpwayNo ratings yet
- Rosewood Case AnalysisDocument5 pagesRosewood Case AnalysisJayant KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Yu ZbornikDocument511 pagesYu ZbornikВладимирРакоњацNo ratings yet
- 3-A Y 3-B Brenda Franco DíazDocument4 pages3-A Y 3-B Brenda Franco DíazBRENDA FRANCO DIAZNo ratings yet
- Monster Hunter: World - Canteen IngredientsDocument5 pagesMonster Hunter: World - Canteen IngredientsSong HoeNo ratings yet
- MC4 CoCU 6 - Welding Records and Report DocumentationDocument8 pagesMC4 CoCU 6 - Welding Records and Report Documentationnizam1372100% (1)
- The Sandbox Approach and Its Potential For Use inDocument13 pagesThe Sandbox Approach and Its Potential For Use invalentina sekarNo ratings yet
- Some Studies On Structure and Properties of Wrapped Jute (Parafil) YarnsDocument5 pagesSome Studies On Structure and Properties of Wrapped Jute (Parafil) YarnsVedant MahajanNo ratings yet
- Installation of Submarine PE PipesDocument84 pagesInstallation of Submarine PE Pipeswaseemiqbal133100% (2)
- School Activity Calendar - Millsberry SchoolDocument2 pagesSchool Activity Calendar - Millsberry SchoolSushil DahalNo ratings yet
- Buddha Mind PDFDocument32 pagesBuddha Mind PDFVishal GadeNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Familiarize The VmgoDocument10 pagesWeek 1 Familiarize The VmgoHizzel De CastroNo ratings yet
- S4 Computer Sciences Exercises PDFDocument2 pagesS4 Computer Sciences Exercises PDFHenriette Desanges UwayoNo ratings yet
- Zillah P. Curato: ObjectiveDocument1 pageZillah P. Curato: ObjectiveZillah CuratoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Concepts About Educational TechnologyDocument17 pagesLesson 1 Concepts About Educational TechnologyMarvin ContigaNo ratings yet
- Ec 0301Document25 pagesEc 0301Silvio RomanNo ratings yet
- 00022443the Application of A Continuous Leak Detection System To Pipelines and Associated EquipmentDocument4 pages00022443the Application of A Continuous Leak Detection System To Pipelines and Associated EquipmentFaizal AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Kursus Jabatan Kejuruteraan Mekanikal Sesi Jun 2014Document12 pagesKursus Jabatan Kejuruteraan Mekanikal Sesi Jun 2014ihsanyusoffNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Flight Control SystemDocument25 pagesAircraft Flight Control Systemthilina jayasooriyaNo ratings yet