Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cubital Fossa and Anterior Forearm
Uploaded by
kcxieCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cubital Fossa and Anterior Forearm
Uploaded by
kcxieCopyright:
Available Formats
Cubital Fossa and Anterior Forearm
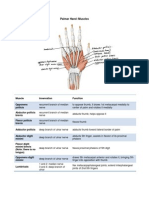
Muscle first layer Pronator teres Flexor carpi radialis Palmaris longus Flexor carpi ulnaris Flexor digitorum superficialis
Innervation Median Nerve Median Nerve Median Nerve Ulnar Nerve Median Nerve Lateral parts: Median Nerve (anterior interosseous branch), Medial part: ulnar nerve Anterior interosseous nerve from Median Nerve Anterior interosseous nerve from Median Nerve Radial nerve
Function Pronates and flexes forearm (at elbow) flexes and abducts hand (at wrist) Flexes hand (at wrist) and tenses palmar aponeurosis Flexes and adducts hand (at wrist) Flexes proximal interphalangeal joints of middle four digits, also flexes proximal phalanges at metacarpophalangeal joints Flexes distal interphalangeal joints of digits, 2,3,4,5; assists with wrist flexion
third layer
second layer
Flexor digitorum profundus
Flexor pollicis longus Pronator quadratus Brachioradialis
flexes phalanges of 1st digit (thumb) pronates forearm; deep fibers bind radius and ulna together weak flexion of forearm, maximal when forearm is midpronated position
te d in th e ex te ns or (p os ter ior ) co m pa rt m en t an d is th us su pp lie d by th e ra di al ne rv e
Cubital Fossa and Anterior Forearm - Arteries
Cubital Fossa and Anterior Forearm: Nerves
Cubital Fossa Boundaries Superiorly: imaginary line connecting medial and lateral epicondyles Medially: Pronator teres Laterally: Brachioradialis Contents Brachial, radial, ulnar artery Accompanying veins Biceps brachii tendon Median nerve Radial nerve (superficial + deep branches)
Affected structure Lateral Epicondyle
Clinical correlate Tennis elbow/lateral epicondylitis: results from repetitive use of superficial extensor muscles. Pain in lateral epicondyle, radiating down posterior surface of forearm. Golfer's elbow/medial epicondylitis Median nerve injury/palsy near cubital fossa results in hand of benediction
Medial Epicondyle
Median nerve
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Pediatrics NotesDocument25 pagesPediatrics Noteskcxie100% (12)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- ShoulderDocument4 pagesShoulderkcxieNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Fever of unknown origin evaluation and differentialsDocument3 pagesFever of unknown origin evaluation and differentialskcxieNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Toxicology TableDocument20 pagesToxicology TablekcxieNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Palmar HandDocument3 pagesPalmar HandkcxieNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Pelvic Cavity TableDocument2 pagesPelvic Cavity TablekcxieNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Genetic Conditions For USMLEDocument2 pagesGenetic Conditions For USMLEkcxieNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Posterior TriangleDocument4 pagesPosterior TrianglekcxieNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Lower LimbDocument1 pageLower LimbkcxieNo ratings yet
- Ankle and Sole of FootDocument4 pagesAnkle and Sole of FootkcxieNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Dorsal Forearm and HandDocument2 pagesDorsal Forearm and HandkcxieNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)