Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mech 325-Strength of Materials Syllabus
Uploaded by
picefeatiCopyright
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Mech 325-Strength of Materials Syllabus
Uploaded by
picefeatiCopyright:
DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING
Course Units Prerequisite Semester/SY Instructor & Department Head Dean Course Description : : : : : : MECH 325-Strength of Materials 5 MECH 315-Engineering Mechanics Second Semester, 1996-1997 Engr. Tomas U. Ganiron Jr, RCE, RJr.GE Engr. Jose M. Segovia, MSEE
Axial forces, stress, Strain, bending moment, shear and stress relationship, composite materials, Mohrs circle, combined stresses, deflection columns, and riveted and welded connections and reinforced beams. Course Objectives Upon successful completion of this course students will be able to do the following: 1. Understand the concepts of stress and strain; 2. Calculate stresses due to bending, shears, and torsion under plain and combined loading; 3. Analyze statically determinate and indeterminate structures; and 4. Determine the elastic stability of columns.
Course Distribution Week 1 2-3 4 5 TOPICS Orientation 1. Simple Stress and strain- Analysis of Internal Forces, Simple shearing and bearing stress, thin walled cylinders, Stress Strain diagram, Hookes law: Axial Deformation Statically indeterminate members, Thermal Stresses. 2. Shear and Moments Beams- Shear and Moment Interpretation of vertical shear and bending moment, relation between load, Shears, and Moment moving loads. 3. Stresses in Beams- Derivation of flexure formula, Economic sections Floor Framing Unsymmetrical beams, Analysis of flexure Action, Derivation of formula for horizontal shearing stress, design of flexure shear, Spacing of rivet or bolt in built beams. 4. Beam Deflections- Double integration method. Theorems of Area Moment method. Moment diagram by parts. Deflection of Cantilever beams. Deflections in simply supported beams misspend defection. Conjugate beams method. Deflection by the method. Deflections by the method of superposition. Prelim Examination 5. Restrained Beams- Redundant supports in propped and restrained beams. Application of double integration and superposition methods. Application of area moment methods. Restrained beam equivalent to simple beams. Design of restrained beams. 6. Continuous Beams- Generalized form of the three-moment equation. Factors and application of the three-moment equation. Reactions of continuous beams. Continuous beams with fixed ends. Deflections determined by the three- moment equation. Moment distribution. Midterm Examination 7. Reinforce Beams- Beams and different materials. Shearing stress and Deflection in composite beams. Reinforce concrete beams. Design of reinforces concrete beams. Beams of R.C., Shearing and bond stress.
6-7 8 9-10
11-12 13 14
15
16-17 18
8. Columns- Critical load. Long columns by Euler formula and its limitations. Intermediate columns empirical formulas. Eccentrically loaded columns. Secant formula 9. Riveted and Welded Connections- Types of riveted joints. Strength of a simple lap joint. Strength of a complex butt joint. Stresses in riveted joints. Structural riveted joints. Eccentrically loaded riveted connections. Welded connections. Eccentrically loaded welded connections. Final Examination
Textbook Strength of Materials by Ferdinand P Singer and Andrew Pytel,Harper and Row H. Kogakusha Publishers, New York
References
Mechanics of Materials by SI Version, end edition by Ferdinand P. Beer and E Russel Johnston (Jr); McGraw Hill, India Mechanics of Materials-SI Version 2nd Edition by EP Popov, Prentice Hall India Introduction to Solid Mechanics by D.H Shames, Prentice Hall Inc. Elements of strength of Materials by Timoshenko and Young Strength of Materials by DS Bedi; Khanna book Publishing Company, New Delhi. 7. Strength of materials by R.S Lehri and A.S. Lehri, S.K Kataria and Sons.
Grades Distribution Components Seatworks/Short Quizzes Projects Assignments Attendance Prelim Exam Midterm Exam Final Exam Total % Distribution 10 4 4 2 15 15 50 100
You might also like
- Mechanics of Materials 2: The Mechanics of Elastic and Plastic Deformation of Solids and Structural MaterialsFrom EverandMechanics of Materials 2: The Mechanics of Elastic and Plastic Deformation of Solids and Structural MaterialsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Case Study No. 11 - Hydroelectric Power Plant in The PhilippinesDocument26 pagesCase Study No. 11 - Hydroelectric Power Plant in The PhilippinespicefeatiNo ratings yet
- FEATI University, Civil Engineering Course Syllabus 1991-2002Document90 pagesFEATI University, Civil Engineering Course Syllabus 1991-2002Rebecca Perez100% (1)
- Structures Subjected To Repeated Loading-Stability and Strength - R Narayanan, 1990 PDFDocument259 pagesStructures Subjected To Repeated Loading-Stability and Strength - R Narayanan, 1990 PDFtmaNo ratings yet
- Stability of Structures: Principles and ApplicationsFrom EverandStability of Structures: Principles and ApplicationsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Hibbeler Structural Analysis 8th Chapter-4 Beam'sDocument45 pagesHibbeler Structural Analysis 8th Chapter-4 Beam'skyleNo ratings yet
- Case Study No. 4-Design of Water Distribution System Using Naugong Spring As An Additional Water Source For Laguna Water DistrictDocument18 pagesCase Study No. 4-Design of Water Distribution System Using Naugong Spring As An Additional Water Source For Laguna Water DistrictpicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Collapse PDFDocument98 pagesCollapse PDFSuresh nathanNo ratings yet
- Engineering ReviewDocument52 pagesEngineering ReviewChristine Verena Sarte100% (2)
- Elementary Mechanics of Solids: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structure and Solid Body MechanicsFrom EverandElementary Mechanics of Solids: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structure and Solid Body MechanicsNo ratings yet
- Lectures in Mechanics of Materials Ion Simulescu PDFDocument213 pagesLectures in Mechanics of Materials Ion Simulescu PDFRoberta LipăNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials: An Introduction to the Analysis of Stress and StrainFrom EverandStrength of Materials: An Introduction to the Analysis of Stress and StrainRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CE6306 Strength of Materials (SOM)Document127 pagesCE6306 Strength of Materials (SOM)goldencometNo ratings yet
- Basic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandBasic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Water Code of The PhilippinesDocument28 pagesWater Code of The PhilippinespicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Guideline Welding Coordination For ISO 1090-2Document33 pagesGuideline Welding Coordination For ISO 1090-2apostolidis83100% (1)
- Buckling and Ultimate Strength of Ship and Ship-like Floating StructuresFrom EverandBuckling and Ultimate Strength of Ship and Ship-like Floating StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
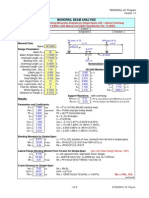
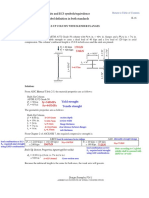
- MonorailDocument3 pagesMonorailHelard AlvarezNo ratings yet
- ME 201 Mechanics of SolidsDocument3 pagesME 201 Mechanics of SolidsSudeesh SudevanNo ratings yet
- BCE-14 Structural Mechanics - IDocument2 pagesBCE-14 Structural Mechanics - IUtkarsh ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering Revised Course Structure For M.Tech (Structural Engineering) (DT)Document13 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering Revised Course Structure For M.Tech (Structural Engineering) (DT)SaikrupaVempatiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Part 1Document32 pagesUnit 1 Part 1ramamurthiNo ratings yet
- Mech 302 - Strength of Materials SyllabusDocument3 pagesMech 302 - Strength of Materials SyllabusHarold TaylorNo ratings yet
- IK Gujral Punjab Technical University Jalandhar, Punjab, INDIA Study Scheme & Syllabus of B. Tech Mechanical Engineering Batch 2018 OnwardsDocument3 pagesIK Gujral Punjab Technical University Jalandhar, Punjab, INDIA Study Scheme & Syllabus of B. Tech Mechanical Engineering Batch 2018 OnwardsSurjit Kumar GandhiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Som SyllabusDocument1 pageAdvanced Som SyllabusRaj Kumar0% (1)
- ES 321 (Strength of Materials) SyllabusDocument2 pagesES 321 (Strength of Materials) SyllabusHarold TaylorNo ratings yet
- Theory of Soil MechanicsDocument5 pagesTheory of Soil MechanicsMuhammad ShahrulNo ratings yet
- ES 311 - (Mechanics) SyllabusDocument2 pagesES 311 - (Mechanics) SyllabusHarold TaylorNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids CT 205Document2 pagesMechanics of Solids CT 205Hassan0% (2)
- Mechanics of Solids: Mr. Y. B. Kumbhar Ybk - Aero@adcet - inDocument19 pagesMechanics of Solids: Mr. Y. B. Kumbhar Ybk - Aero@adcet - inYogesh KumbharNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - IDocument2 pagesStrength of Materials - IJosephNo ratings yet
- AU 3rd SEM - AU 2023-24030823012842Document11 pagesAU 3rd SEM - AU 2023-24030823012842badalmewada2002No ratings yet
- EMG 2303 Solid and Structural Mechanics 1 NotesDocument82 pagesEMG 2303 Solid and Structural Mechanics 1 Notesmusiomi200567% (3)
- Syllabus For: Applied Mathematics-III (Civil Engineering) Unit - I: Fourier Series (06Hrs)Document28 pagesSyllabus For: Applied Mathematics-III (Civil Engineering) Unit - I: Fourier Series (06Hrs)Udaysingh PatilNo ratings yet
- Solid Mechanics IIT DDocument1 pageSolid Mechanics IIT DVishalNo ratings yet
- Meng2082 Enrollment: Regular: Meng1081 Course Offered By: Ins Denus Caf Academic Year: 2017/201Document2 pagesMeng2082 Enrollment: Regular: Meng1081 Course Offered By: Ins Denus Caf Academic Year: 2017/201Yonas YGNo ratings yet
- Ce-5th & 6TH Sem23062018Document46 pagesCe-5th & 6TH Sem23062018John kantNo ratings yet
- ES 621: Advanced Solid Mechanics (3-0-0-4) : 1. Mathematical Background 2. Analysis of StressDocument2 pagesES 621: Advanced Solid Mechanics (3-0-0-4) : 1. Mathematical Background 2. Analysis of StressKhan Mohd SaalimNo ratings yet
- U15CET402 Strength of MaterialsDocument2 pagesU15CET402 Strength of MaterialsKarthiKeyanNo ratings yet
- ME 201 Mechanics of SolidsDocument2 pagesME 201 Mechanics of SolidsUnnikrishnan TGNo ratings yet
- M.Tec in Civil - Structural Design Engineering: Singhania UniversityDocument54 pagesM.Tec in Civil - Structural Design Engineering: Singhania UniversityPrashantNo ratings yet
- Strength of MateriaLS Course Outline For Civil Engineer, TarchaDocument3 pagesStrength of MateriaLS Course Outline For Civil Engineer, TarchaKebede HaileNo ratings yet
- 1 SemDocument12 pages1 SemShivam VermaNo ratings yet
- UNIT - II: Shear Force and Bending MomentDocument3 pagesUNIT - II: Shear Force and Bending MomentGopinath GangadhariNo ratings yet
- Mee214 Strength-Of-materials Ela 1.20 Ac19Document2 pagesMee214 Strength-Of-materials Ela 1.20 Ac19sharan chandranNo ratings yet
- Structural EngineeringDocument15 pagesStructural EngineeringSurender Reddy100% (1)
- ME530Document1 pageME530Vijay_DamamNo ratings yet
- 2 3-SomDocument67 pages2 3-SomGowtham SmartyNo ratings yet
- CE Strength of Materials I L T PC 3 0 0 3 ObjectivesDocument4 pagesCE Strength of Materials I L T PC 3 0 0 3 ObjectivesAnonymous H7nsyCogNo ratings yet
- Theory L/T (Hours Per Week) : 3/0, Credit: 3Document2 pagesTheory L/T (Hours Per Week) : 3/0, Credit: 3ashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- ENS 164 SyllabusDocument1 pageENS 164 SyllabusMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- 4.80 S.E Mechanical EngineeringDocument2 pages4.80 S.E Mechanical Engineeringq8400No ratings yet
- Civil EngineeringDocument1 pageCivil EngineeringRavi MehtaNo ratings yet
- NUS ME Core Modules 20190925 PDFDocument3 pagesNUS ME Core Modules 20190925 PDFHammadAzizNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering SyllabusDocument137 pagesCivil Engineering SyllabusH S Vishwanath ShastryNo ratings yet
- Me217strength of Materials L T P CDocument2 pagesMe217strength of Materials L T P ClogicvirusNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Kakinada KAKINADA - 533 003Document2 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Kakinada KAKINADA - 533 003rameshNo ratings yet
- Som Mech SyllabusDocument2 pagesSom Mech SyllabusVinay KorukondaNo ratings yet
- Ce 156Document4 pagesCe 156Teddy UlsNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Einstein Academy of Technology and ManagementDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: Einstein Academy of Technology and ManagementJITENDRA BISWALNo ratings yet
- Course On Structural StabilityDocument3 pagesCourse On Structural StabilityVenkatesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesStrength of Materials Lesson Planbalajimettur100% (1)
- Eme 3046Document3 pagesEme 3046kskajskNo ratings yet
- Osmania University ME SE Structures SyllabusDocument36 pagesOsmania University ME SE Structures SyllabusRahul Dragoon100% (2)
- Open ElectivesDocument231 pagesOpen ElectivesGaneshNo ratings yet
- Bmee202l Mechanics-Of-Solids TH 1.0 67 Bmee202lDocument3 pagesBmee202l Mechanics-Of-Solids TH 1.0 67 Bmee202lKrijayNo ratings yet
- Case Study No. 10-Construction of Box Culverts in The PhilippinesDocument33 pagesCase Study No. 10-Construction of Box Culverts in The PhilippinespicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Design Coordinates, Inc.Document14 pagesDesign Coordinates, Inc.picefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study No. 12-Presidential Decree No. 1067Document25 pagesCase Study No. 12-Presidential Decree No. 1067picefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study No. 3-Molino Dam in Bacoor, CaviteDocument27 pagesCase Study No. 3-Molino Dam in Bacoor, CavitepicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Foundation Constructions System in Makati CityDocument17 pagesAdvanced Foundation Constructions System in Makati CitypicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study No. 1-Groundwater Supply of Cavite ProvinceDocument25 pagesCase Study No. 1-Groundwater Supply of Cavite ProvincepicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study No. 9-Philippines' Integrated Stormwater ManagementDocument23 pagesCase Study No. 9-Philippines' Integrated Stormwater ManagementpicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study No. 7 - Contingency Plan of Manila WaterDocument20 pagesCase Study No. 7 - Contingency Plan of Manila WaterpicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study No. 5-Pasig River Open Channel in AquacultureDocument30 pagesCase Study No. 5-Pasig River Open Channel in AquaculturepicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study 10-Shaping A Regional IP Tool & Folk Art and The Opportunities of The Modern WorldDocument41 pagesCase Study 10-Shaping A Regional IP Tool & Folk Art and The Opportunities of The Modern WorldpicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study No. 6-Road and Drainage Improvement Project in Caloocan CityDocument19 pagesCase Study No. 6-Road and Drainage Improvement Project in Caloocan CitypicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study No. 2 - Lumot Lake in LagunaDocument25 pagesCase Study No. 2 - Lumot Lake in LagunapicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study 12A-From Herbal Folklore To Modern MedicineDocument10 pagesCase Study 12A-From Herbal Folklore To Modern MedicinepicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study 13-A Color For All Seasons & A New Variety of SuccessDocument81 pagesCase Study 13-A Color For All Seasons & A New Variety of SuccesspicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study No. 8-Managing Floods in Metro ManilaDocument22 pagesCase Study No. 8-Managing Floods in Metro ManilapicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study 11-Rising Above The Competition & Thriving On IP ProtectionDocument36 pagesCase Study 11-Rising Above The Competition & Thriving On IP ProtectionpicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study 6-Developing Affordable Software For Small Business & Mary Engelbreit - Artist and EntrepreneurDocument31 pagesCase Study 6-Developing Affordable Software For Small Business & Mary Engelbreit - Artist and EntrepreneurpicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study 3-A Green Stone Age For The Future & Combining Innovative Technology With Artisanal ProductionDocument27 pagesCase Study 3-A Green Stone Age For The Future & Combining Innovative Technology With Artisanal ProductionpicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study 5-The CyberTracker & The Protection of Computer ProgramsDocument13 pagesCase Study 5-The CyberTracker & The Protection of Computer ProgramspicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study 9-Strategic Partnership Linked To IP in The Development & Planting The Seeds of InnovationDocument26 pagesCase Study 9-Strategic Partnership Linked To IP in The Development & Planting The Seeds of InnovationpicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study 4-Creating An Innovative Environment With Licensing & Insulating A Nation's HomesDocument25 pagesCase Study 4-Creating An Innovative Environment With Licensing & Insulating A Nation's HomespicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study 12B-The Gugo Queen - An Inventor's TaleDocument9 pagesCase Study 12B-The Gugo Queen - An Inventor's TalepicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2 - Copyright in The Digital Age & Keeping Track of Things With MAMORIODocument25 pagesCase Study 2 - Copyright in The Digital Age & Keeping Track of Things With MAMORIOpicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study 8-Electrifying Economic Development & From Heavy To Light Accelerating Commercialization Through Open InnovationDocument22 pagesCase Study 8-Electrifying Economic Development & From Heavy To Light Accelerating Commercialization Through Open InnovationpicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study 7 - A Bold Step Into The Modern Economy & A Remote Solution For A Global OpportunityDocument24 pagesCase Study 7 - A Bold Step Into The Modern Economy & A Remote Solution For A Global OpportunitypicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Roads in Metro ManilaDocument22 pagesSustainable Roads in Metro ManilapicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1 - The Importance of Copyright and Patent Protection & The Poetry of ArchitectureDocument25 pagesCase Study 1 - The Importance of Copyright and Patent Protection & The Poetry of ArchitecturepicefeatiNo ratings yet
- 1980 The Phase Diagram of NaNO3-KNO3 PDFDocument12 pages1980 The Phase Diagram of NaNO3-KNO3 PDFAdrian CaraballoNo ratings yet
- DURALCAN Geiler ParraDocument3 pagesDURALCAN Geiler ParraGeiler ParraNo ratings yet
- Significant Changes in ACI 318-11Document4 pagesSignificant Changes in ACI 318-11cabpcabpNo ratings yet
- Example of Application of AISI 360 10 and Parallel With EC3Document5 pagesExample of Application of AISI 360 10 and Parallel With EC3Aakash KhatriNo ratings yet
- Articulo Coniin 3Document3 pagesArticulo Coniin 3Marlu Garcia BarajasNo ratings yet
- Stress-Based Uniaxial Fatigue Analysis Using Methods Described in FKM-GuidelineDocument40 pagesStress-Based Uniaxial Fatigue Analysis Using Methods Described in FKM-GuidelineclevercogNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Assignment 1Document2 pagesThermodynamics Assignment 1Chadaram Jagadish JagadishNo ratings yet
- Deicon: Viscoelastic Tuned Mass DamperDocument1 pageDeicon: Viscoelastic Tuned Mass Damperkiran2381No ratings yet
- M.O.M Complex Engineering ProblemDocument4 pagesM.O.M Complex Engineering ProblemBilal KhanNo ratings yet
- 4 A Comparative Study Od Concretes Reinforced With Carbon, Polythylene, and Steel Fibers and Their Improvement by Latex AdditionDocument5 pages4 A Comparative Study Od Concretes Reinforced With Carbon, Polythylene, and Steel Fibers and Their Improvement by Latex AdditionJORGRULESNo ratings yet
- AUTODYN - Chapter 9 - Material - Models PDFDocument47 pagesAUTODYN - Chapter 9 - Material - Models PDFFabiano OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document26 pagesWeek 2Laureano Gomez Zabala100% (3)
- Compressive Mechanical Properties of HTPB Propellant at Low - 2017 - Results inDocument6 pagesCompressive Mechanical Properties of HTPB Propellant at Low - 2017 - Results inEduardo CandelaNo ratings yet
- SIT Thesis FormatDocument18 pagesSIT Thesis FormatPrathikNo ratings yet
- Review Onna Nope Rovs Kites MaterialDocument10 pagesReview Onna Nope Rovs Kites MaterialAmal SKNo ratings yet
- Torayca Carbon Fiber Summary DataSheet PDFDocument1 pageTorayca Carbon Fiber Summary DataSheet PDFaleatoryoNo ratings yet
- Corbec Guide-Pliage Eng CourrielDocument36 pagesCorbec Guide-Pliage Eng CourrielOlgalycosNo ratings yet
- Shear Force and Bendind MomentDocument8 pagesShear Force and Bendind MomentAshish AgarwalNo ratings yet
- C 904 - 01 - QzkwnaDocument3 pagesC 904 - 01 - QzkwnaLipikaNo ratings yet
- Elastomers Desmodur MX100 Data BrochureDocument4 pagesElastomers Desmodur MX100 Data BrochureJORGE BRAVONo ratings yet
- (L2) - (JLD 3.0) - Semiconductors - 24th DecDocument66 pages(L2) - (JLD 3.0) - Semiconductors - 24th DecAshfaq khanNo ratings yet
- Shape Memory AlloysDocument25 pagesShape Memory AlloysGanesh YNo ratings yet
- EC2 BetonDocument13 pagesEC2 BetonBlaKy2No ratings yet
- Super Conductor and Magnetism MCQDocument5 pagesSuper Conductor and Magnetism MCQliveNo ratings yet