Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Api Grade
Uploaded by
Ankur YashOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Api Grade
Uploaded by
Ankur YashCopyright:
Available Formats
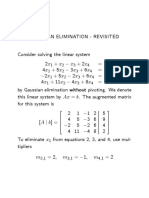
oil tions e n i Eng ssifica
cla
petrol engine oils diesel engine oils
SG
Introduced in 1989 to provide improved control of engine deposits, oil oxidation, rust and corrosion and engine wear relative to oils developed for previous categories.
CC
Introduced in 1961, lubricants of this type were intended for engines operating in moderate to severe duty service. Oils designed for this service provide protection from high temperature deposits and bearing corrosion. In 1975 oils with this designation were introduced for naturally aspirated, turbocharged or supercharged diesel engines and provided additional protection from high temperature deposits and bearing corrosion. For heavy duty turbocharged and supercharged diesel engines manufactured since 1983, and operated under low speed, high load and high speed, high load conditions. Improved control over cylinder and ring face scuffing as well as deposits were incorporated into CF-2 oils for severe duty two stroke diesels in 1994. May be used where CD-11 oils are recommended. Exceeding the requirements of CE oils, CF-4 oils provide improved control of oil consumption and reduces piston deposits. Introduced in 1990. Released in 1994 for severe duty diesel engines using fuels ranging from .05% sulphur to .50% sulphur. Intended for both high speed four stroke diesels used in both on and off highway applications. These oils provide effective control over high temperature piston deposits, wear corrosion, foaming, oxidation and soot accumulation. Especially effective in engines designed to meet 1994 emission standards and may also be used in engines requiring API CD, CE and CF4.
CH4
Cleaner emission engines and fuel technology demanded a higher standard of lubricant. CH4 was released in 1998 to comply with increased soot handling ability, piston ring wear, valve sliding wear (Cummins M11) and high sulphur fuel performance. Introduced in 2002 for oils use in high speed four stroke cycle diesel engines designed to meet 2004 exhaust emission standard. Formulated to use in engine where Exhaust Gas recirculation (ERG) and other after treatment devices may be used and where diesel fuel contains up to 0.05% by weight in sulphur content. CI4 oils can supersede API CH4, CG4 and CF4. In conjunction with CI4, CI4 + was implemented in 2004 to increase the level of protection against sootrelated viscosity increase and viscosity loss due to shear in diesel engines. Introduced in 2006 for high speed four stroke diesel engines to meet 2007 highway exhaust emission standards. These oils are especially effective at sustaining emission control system durability where Diesel Particulate Filters (PDF) and other advanced after treatment systems are used. Designed for use in all applications with diesel fuels up to 500ppmin sulphur content, however use of these oils with greater than 15ppm sulphur fuel may impact exhaust aftertreatment system durability and/or oil drain interval. Optimum protection in particulate filter blocking, catalyst poisoning, engine wear, piston deposits, low and high temperature stability, soot handling properties, oxidative thickening, foaming and viscosity loss due to shear. CJ4 exceeds performance criteria of CI4 plus, CI4, CH4 CG4 and CH4 oils.
SJ
Released in late 1996 to enhance the SH, now superseded, performance level. Improvements include better fuel economy, longer lubricant life and lower phosphorus levels. Released in 2001, more emphasis is placed on fuel economy, emission system protection, valve train wear, sludge deposits and oil consumption compared to SJ level lubricants. Lower viscosity grades require Group II or Group III base oils to meet SL volatility limits. 1998 to comply with increased soot handling ability, piston ring wear, valve sliding wear (Cummins M11) and high sulphur fuel performance.
CD
Ci4
(ISAC GF-3)
SL
CE
Ci4+
SM
CF2
Cj4
how to select engine oils
When selecting engine oil, there are two choices to be made: Viscosity Determined by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) this measures the resistance of oil to flow. The lower the number the less resistance to flow. For instance, 15W40 engine oil will flow more easily than 20W50 engine oil. Generally, as a rule, lighter grades of engine oil are for more modern cars, post 1990, and the heavier grades are for the earlier cars. Service Classification Petrol engine oils typically use a Service Classification (S) and Diesel engines use a commercial classification (C) when describing the performance characteristics of engine oils for use in passenger cars, trucks and other equipment.
CF4 Cg4
things to know
15
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Question: Without Computing A, ND Bases For Its Four Fundamental SubDocument1 pageQuestion: Without Computing A, ND Bases For Its Four Fundamental SubAnkur YashNo ratings yet
- Practical Applications of Bernoulli's EquationDocument12 pagesPractical Applications of Bernoulli's EquationAnkur Yash100% (1)
- De110e2 PDFDocument4 pagesDe110e2 PDFSureshkumar Kulanthai Velu100% (1)
- Manual Part 710 g7cDocument138 pagesManual Part 710 g7cJuan gabriel Orozco100% (3)
- Applied Thermal EngineeringDocument38 pagesApplied Thermal Engineeringzulfikar100% (1)
- Application For Marriage CertificateDocument11 pagesApplication For Marriage CertificateAnkur YashNo ratings yet
- 18.06 Problem Set 4 SolutionsDocument4 pages18.06 Problem Set 4 SolutionsAnkur YashNo ratings yet
- Sec 6-4 PDFDocument17 pagesSec 6-4 PDFRizky Budi AntonoNo ratings yet
- Thesis 2Document39 pagesThesis 2Ankur YashNo ratings yet
- Time Table: Fluid Mech. SOMDocument2 pagesTime Table: Fluid Mech. SOMAnkur YashNo ratings yet
- FEM (7 SEM.) : Fluid Mech. (3 Sem.) Fluid Mech. (3 Sem.) SOM SOM Fem LabDocument1 pageFEM (7 SEM.) : Fluid Mech. (3 Sem.) Fluid Mech. (3 Sem.) SOM SOM Fem LabAnkur YashNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Air Exchange Rates in Di Fferent Indoor Environments Using Continuous CO SensorsDocument8 pagesMeasurement of Air Exchange Rates in Di Fferent Indoor Environments Using Continuous CO SensorsAnkur YashNo ratings yet
- M Tech (RE) - CEE SyllabusDocument7 pagesM Tech (RE) - CEE SyllabusAnkur YashNo ratings yet
- Eia Q & ADocument10 pagesEia Q & AAnkur YashNo ratings yet
- 2.modes of Failure and Types of WearDocument5 pages2.modes of Failure and Types of WearMuhammad Arsalan KhanNo ratings yet
- GX120 - 160 - 200 OM EN Rev 3 3 21Document20 pagesGX120 - 160 - 200 OM EN Rev 3 3 21rendysuryadi174No ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Power PlantDocument16 pagesGas Turbine Power PlantSathya Raj SimiNo ratings yet
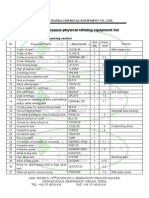
- 50TD Continuous Physical Refining Equipment ListDocument4 pages50TD Continuous Physical Refining Equipment ListWanda OilpressNo ratings yet
- of BPCL JaipurDocument15 pagesof BPCL JaipurRaman Kumar JhaNo ratings yet
- 374 837kW 508 1138PS : Marine Proplusion Diesel EngineDocument2 pages374 837kW 508 1138PS : Marine Proplusion Diesel EngineHendra SaputraNo ratings yet
- Off-Highway Rigid Truck: Standard Equipment WeightsDocument2 pagesOff-Highway Rigid Truck: Standard Equipment Weightsalfi rahman100% (1)
- Obd II CodesDocument21 pagesObd II CodesObd King TgiNo ratings yet
- Ventilation of Underground MinesDocument44 pagesVentilation of Underground Minestulus_tp11No ratings yet
- Write Up On DBRDocument24 pagesWrite Up On DBRDHARMENDRANo ratings yet
- Cummins Heavy Duty Product Guide PDFDocument22 pagesCummins Heavy Duty Product Guide PDFthailanNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Review of Rig Components Drilling System PDFDocument73 pagesCH 1 Review of Rig Components Drilling System PDFAnusha Anu100% (1)
- PolymerDocument89 pagesPolymerFatema Khatun100% (1)
- Coal GasificationDocument11 pagesCoal GasificationPratik RanjanNo ratings yet
- 01.section 01Document16 pages01.section 01kaushik.pooja12No ratings yet
- Catalogo Maxiforce 2017Document374 pagesCatalogo Maxiforce 2017Valeska Gonzales Rios100% (3)
- SUNY Maritime 8520 Teu Dual Fuel ContainershipDocument137 pagesSUNY Maritime 8520 Teu Dual Fuel Containershipntontarski100% (1)
- Claus Peter Halsig FLUORDocument24 pagesClaus Peter Halsig FLUORihllhm100% (1)
- Curso Common Rail Denso MedellinDocument120 pagesCurso Common Rail Denso MedellinArbey GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Ansari Shanawaz Ayaz S-Class ProjectDocument93 pagesAnsari Shanawaz Ayaz S-Class ProjectAli Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injector Pump PDFDocument16 pagesFuel Injector Pump PDFHrishikesh BedekarNo ratings yet
- Keenecatalog 2013Document44 pagesKeenecatalog 2013daks4uNo ratings yet
- Filters - Filter Details PDFDocument22 pagesFilters - Filter Details PDFPomaNo ratings yet
- Terminals of Ecm: DiagnosticsDocument6 pagesTerminals of Ecm: Diagnosticsbob loblawNo ratings yet
- Man B&W ManualDocument12 pagesMan B&W ManualJayantaDebnath50% (2)
- Study On Knocking Characteristics of Diesel Engine Through Vibration Monitoring.Document61 pagesStudy On Knocking Characteristics of Diesel Engine Through Vibration Monitoring.sahildhiman83% (6)
- Model 7012 HP SpecificationsDocument2 pagesModel 7012 HP SpecificationsMuhammad FaizalNo ratings yet