Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7 Tools of Statistical Process Control
Uploaded by
Sachin MethreeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
7 Tools of Statistical Process Control
Uploaded by
Sachin MethreeCopyright:
Available Formats
Explain the 7 tools of statistical process control?
Statistical process control: Statistical process control (SPC) is a method of quality control which uses statistical methods. SPC is applied in order to monitor and control a process. Monitoring and controlling the process ensures that it operates at its full potential. At its full potential, the process can make as much conforming product as possible with a minimum (if not an elimination) of waste (rework or trash). SPC can be applied to any process where the "conforming product" (product meeting specifications) output can be measured. Key tools used in SPC include control charts; a focus on continuous improvement; and the design of experiments. An example of a process where SPC is applied is manufacturing lines Objective analysis of variation SPC is a valuable process because it allows examination of specific parts of a process. In particular, it looks at the parts that may conceal sources of variation in the quality of the product. The examination involves objective analysis rather than subjective opinion. SPC also allows the strength of each source of variation to be determined numerically. If sources of variation are detected and measured, they may be amenable to correction. In turn, correction of variations may reduce waste in production and may improve the quality of the product that reaches the customer. SPC must be practiced in 2-phases, where in first phase of SPC to establish the process initially and after that in second phase during the production run. In the second phase, we need to decide the period to be examined, depending upon the change in 4-M conditions and wear rate of parts used in the manufacturing process (machine parts, Jigs and fixture and tooling standard. Statistical process control (SPC) is a method of quality control which uses statistical methods. SPC is applied in order to monitor and control a process. Monitoring and controlling the process ensures that it operates at its full potential. At its full potential, the process can make as much conforming product as possible with a minimum (if not an elimination) of waste (rework or trash). SPC can be applied to any process where the "conforming product" (product meeting specifications) output can be measured. Key tools used in SPC include control charts; a focus on continuous improvement; and the design of experiments The Seven Tools of Quality
1. Control chart 2. X-Bar and R Charts 3. Pareto chart 4. Flow chart 5. Cause and effect diagram 6. Histogram 7. Scatter diagram The Pareto graphically summarizes and displays the relative importance of the differences between groups of data. A Pareto chart can be constructed by segmenting the range of the data into groups. A flowchart is important project development and documentation tool.It visually records the steps, decisions, and actions of any manufacturing or service operation and defines the system, its key points, activities and role performances. A histogram is used to graphically summarize and display the distribution of a process dataset. It can be constructed by segmenting the range of the data into equalsized bins (segments, groups, or classes). The vertical axis of the histogram is the frequency (the number of counts for each bin), and the horizontal axis is labeled with the range of the response variable. Cause and Effect Diagram A problem is systematically tracked back to possible causes. The diagram organizes the search for the root cause of a problemA similar diagram can be used to systematically search for solutions to a problem. Scatter charts It is similar to a line graph except that the data point are plotted without a connecting line drawn between them. Scatter charts are suitable for showing how data points compare to each other. At least 2 measured objects are needed for the query (one for x-axis and one for y-axis) Control Charts A broken line graph illustrates how a process behaves over time. Samples are periodically taken, checked, or measured, and the results are plotted on the chart. The charts can show
how the specific measurement changes, how the variation in measurement changes, or how the proportion of defective pieces changes over time X-Bar and R Charts The most commonly used of the control charts and the most valuable.They are ideal tools to improve product quality and process control and help to drastically reduce scrap and rework while assuring the production of only Satisfactory products.They can be used for controlling every step of production process, for the acceptance/ rejection of lots, and for early detection of equipment or process failure Limitations SPC is applied to reduce or eliminate process waste. This, in turn, eliminates the need for the process step of post-manufacture inspection. The success of SPC relies not only on the skill with which it is applied, but also on how suitable or amenable the process is to SPC. In some cases, it may be difficult to judge when the application of SPC is appropriate.
You might also like
- Analysis of Temperature Control of CSTR Using S FunctionDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Temperature Control of CSTR Using S FunctionSolecito FuentesNo ratings yet
- Calculation of The Total Drilling Cost For The Well 112-87Document5 pagesCalculation of The Total Drilling Cost For The Well 112-87Shaho Abdulqader Mohamedali100% (1)
- Chemicals Zetag MSDS Powder Magnafloc 1011 - 0810Document6 pagesChemicals Zetag MSDS Powder Magnafloc 1011 - 0810PromagEnviro.comNo ratings yet
- Howard Setteling Chamber CH 5Document16 pagesHoward Setteling Chamber CH 5RAHUL GNo ratings yet
- Energy Valorization of Biogas in Santa CatarinaDocument10 pagesEnergy Valorization of Biogas in Santa CatarinagrimdorlfNo ratings yet
- Selected Constants: Oxidation–Reduction Potentials of Inorganic Substances in Aqueous SolutionFrom EverandSelected Constants: Oxidation–Reduction Potentials of Inorganic Substances in Aqueous SolutionNo ratings yet
- Jntuworld: R07 Set No. 2Document6 pagesJntuworld: R07 Set No. 2Dolly PriyaNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Catalysts II: Scientific Bases for the Preparation of Heterogeneous CatalystsFrom EverandPreparation of Catalysts II: Scientific Bases for the Preparation of Heterogeneous CatalystsNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL-on Absorption - 2018 - SolutionDocument2 pagesTUTORIAL-on Absorption - 2018 - SolutionMayank Prasad100% (1)
- Test 1 Sample QuestionDocument7 pagesTest 1 Sample QuestionAnonymous GsiB6EMGNo ratings yet
- Final-Front Pages-2011 PME CodeDocument10 pagesFinal-Front Pages-2011 PME CodeJoseph R. F. DavidNo ratings yet
- FGC Group LLC - Consulting & Engineering - Products - Thermal Processing Equipment - Activated Carbon Plant PDFDocument3 pagesFGC Group LLC - Consulting & Engineering - Products - Thermal Processing Equipment - Activated Carbon Plant PDFCleverSeyramKetekuNo ratings yet
- AspirinDocument4 pagesAspiringenelleestremos100% (1)
- Removal of Steryl Glucosides in Palm Oil Based Biodiesel Using Silicate MagnesiumDocument7 pagesRemoval of Steryl Glucosides in Palm Oil Based Biodiesel Using Silicate MagnesiumNestor Armando Marin Solano100% (1)
- Report TemplateDocument9 pagesReport Templatedmscott10No ratings yet
- Koya University Faculty of Engineering School of Petroleum and Chemical Reservior LabDocument16 pagesKoya University Faculty of Engineering School of Petroleum and Chemical Reservior LabBakomora Evans WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Total Organic CarbonDocument10 pagesTotal Organic CarbonDeepti yadavNo ratings yet
- Assignment Tutorial WWWDocument5 pagesAssignment Tutorial WWWZariq NazaruddinNo ratings yet
- Oxygen TransferDocument37 pagesOxygen TransferKaycee ChirendaNo ratings yet
- Convergence Hints (Aspen)Document13 pagesConvergence Hints (Aspen)Saurabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Interphase Transport in Isothermal SystemDocument25 pagesInterphase Transport in Isothermal SystemMuhammad Yuzer IrosoneriNo ratings yet
- Rr410802 Chemical Reaction Engineering IIDocument8 pagesRr410802 Chemical Reaction Engineering IISrinivasa Rao G100% (3)
- B.Tech CH PDFDocument146 pagesB.Tech CH PDFAshutosh MishraNo ratings yet
- VRL Logistics & Navkar Corporation: Financial, Valuation, Business & Management AnalysisDocument5 pagesVRL Logistics & Navkar Corporation: Financial, Valuation, Business & Management AnalysisKaran VasheeNo ratings yet
- Energy Engineering-Lab Manuals PDFDocument82 pagesEnergy Engineering-Lab Manuals PDFUzair ArslanNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Biodiesel Production Using Aspen PlusDocument46 pagesOptimization of Biodiesel Production Using Aspen PlusKhairatun NisaNo ratings yet
- Separations and Reactors Design Project Production of Allyl ChlorideDocument8 pagesSeparations and Reactors Design Project Production of Allyl ChlorideAdelina SimionNo ratings yet
- LRS 10Document1 pageLRS 10anshuman432No ratings yet
- High Pressure Fluids Visualization CellsDocument4 pagesHigh Pressure Fluids Visualization Cellsapi-3703671No ratings yet
- Arc Discharge ApplicationDocument15 pagesArc Discharge ApplicationHong Chun LeeNo ratings yet
- Formal Report Dylan Novakowski, Ion ExchangeDocument22 pagesFormal Report Dylan Novakowski, Ion ExchangelucassenNo ratings yet
- Soran University Faculty of Engineering Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument25 pagesSoran University Faculty of Engineering Department of Chemical EngineeringHalo BashirNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment BasicsDocument62 pagesWater Treatment Basicsanac_mathNo ratings yet
- HumidificationDocument68 pagesHumidificationA AshokNo ratings yet
- Properties of Petroleum ProductsDocument30 pagesProperties of Petroleum ProductsBharath KumarNo ratings yet
- An Industrial Wastewater Contains 10 MG L ChlorophenolDocument5 pagesAn Industrial Wastewater Contains 10 MG L ChlorophenolsumitNo ratings yet
- Gas UnitDocument4 pagesGas UnitZalina SamsuddinNo ratings yet
- Scale-Up - Right First TimeDocument4 pagesScale-Up - Right First TimeDoddappa Anekal0% (1)
- Ethylene 2520oxide Methods 2520of 2520productionDocument25 pagesEthylene 2520oxide Methods 2520of 2520productionmartin_2104No ratings yet
- Condution Holman 10th-Ed PDFDocument167 pagesCondution Holman 10th-Ed PDFLizbeth Abril100% (1)
- Semiconductor Wastewater Treatment Using Tapioca Starch As A Natural CoagulantDocument9 pagesSemiconductor Wastewater Treatment Using Tapioca Starch As A Natural Coagulanthuonggiangnguyen3011No ratings yet
- GATE PSU Study Material Plant Design EconomicsDocument14 pagesGATE PSU Study Material Plant Design EconomicsJEFY JEAN ANo ratings yet
- Solid Phase Microextraction Theory and PracticeDocument9 pagesSolid Phase Microextraction Theory and PracticeBobbyGunarsoNo ratings yet
- Scale-Up: Training & Development Scale-Up S Lakshminarayanan, Technology TransferDocument72 pagesScale-Up: Training & Development Scale-Up S Lakshminarayanan, Technology TransferGopalVarthyaNo ratings yet
- Dehydration of Natural GasDocument9 pagesDehydration of Natural GasHuda ShahNo ratings yet
- Advanced Polymer TechnologyDocument4 pagesAdvanced Polymer Technologykhoa chauNo ratings yet
- CleaningandDescalingStainlessSteel 9001Document38 pagesCleaningandDescalingStainlessSteel 9001Kiran DuggarajuNo ratings yet
- Initial and Boundary Value Problems Involving Ordinary DifferentialDocument24 pagesInitial and Boundary Value Problems Involving Ordinary DifferentialMr. ONo ratings yet
- WorkDocument43 pagesWorkAkash GundaleNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy TOPSIS Method For Ranking Renewable Energy Supply Systems in TurkeyDocument9 pagesFuzzy TOPSIS Method For Ranking Renewable Energy Supply Systems in TurkeyJorge BessaNo ratings yet
- CHEN3005 Process Instrumentation and ControlDocument4 pagesCHEN3005 Process Instrumentation and ControlVincent Ys TanNo ratings yet
- Pervaporation of Ethanol-Water Solutions: Matthew Graham, Tsung-Ming Yeh, Benjamin Hsiao and Devinder MahajanDocument8 pagesPervaporation of Ethanol-Water Solutions: Matthew Graham, Tsung-Ming Yeh, Benjamin Hsiao and Devinder MahajanAnaclara LeitesNo ratings yet
- Growth Kinetics of Oleaginous Yeast, Rhodosporidium Toruloides, in High Salinity ConditionDocument79 pagesGrowth Kinetics of Oleaginous Yeast, Rhodosporidium Toruloides, in High Salinity ConditionShimme7No ratings yet
- A Study of Foaming and Carry-Over Problems in Oil and Gas SeparatorsDocument6 pagesA Study of Foaming and Carry-Over Problems in Oil and Gas SeparatorsWendy V. DomínguezNo ratings yet
- Derivates NotesDocument7 pagesDerivates NotesSachin MethreeNo ratings yet
- Satyam ScandalDocument25 pagesSatyam ScandalSachin MethreeNo ratings yet
- Positive Thinking: Powerpoint Slides by Megha SahayDocument18 pagesPositive Thinking: Powerpoint Slides by Megha SahaySachin MethreeNo ratings yet
- Business Cycle: Presented by Chandan Jagtap Ajit Mangarulakr Sachin MethreeDocument10 pagesBusiness Cycle: Presented by Chandan Jagtap Ajit Mangarulakr Sachin MethreeSachin MethreeNo ratings yet
- Team Work & Team Building: Powerpoint Slides by Megha SahayDocument6 pagesTeam Work & Team Building: Powerpoint Slides by Megha SahaySachin Methree100% (1)
- Statistical Process ControlDocument14 pagesStatistical Process ControlSachin MethreeNo ratings yet
- Corporate ExcellenceDocument21 pagesCorporate ExcellenceSachin MethreeNo ratings yet
- Unethical Issues in SportsDocument14 pagesUnethical Issues in SportsSachin Methree0% (1)
- Service Marketing Word FileDocument31 pagesService Marketing Word FileSachin MethreeNo ratings yet
- Statistical Process ControlDocument14 pagesStatistical Process ControlSachin MethreeNo ratings yet
- Cash MagtDocument12 pagesCash MagtSachin MethreeNo ratings yet
- 6 Product MarketDocument13 pages6 Product MarketSachin MethreeNo ratings yet
- CONTRIBN MADE by Deming, Juran and CrosbyDocument14 pagesCONTRIBN MADE by Deming, Juran and CrosbySachin Methree100% (1)
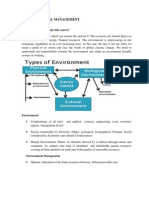
- Environment Mangament Notes 2Document24 pagesEnvironment Mangament Notes 2jayeshpereNo ratings yet
- Business Plan For LibraryDocument15 pagesBusiness Plan For LibrarySachin MethreeNo ratings yet
- Environment Mangament Notes 1Document40 pagesEnvironment Mangament Notes 1jayeshpereNo ratings yet
- Valuation of SecuritiesDocument8 pagesValuation of SecuritiesSachin MethreeNo ratings yet
- ERPDocument55 pagesERPSachin MethreeNo ratings yet
- Inventory ManagementDocument31 pagesInventory ManagementSachin MethreeNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow StatementDocument11 pagesCash Flow StatementSachin Methree100% (1)
- Under Water InspectionDocument87 pagesUnder Water InspectionFauzankalibataNo ratings yet
- Module 5 NotesDocument17 pagesModule 5 NotesDurga BudhathokiNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Money Scale (IMS)Document9 pagesThe Importance of Money Scale (IMS)Devina PrianandaNo ratings yet
- Total Population by Province, City, and Municipality: As of May 1, 2020 Province, City, and Municipality Total PopulationDocument53 pagesTotal Population by Province, City, and Municipality: As of May 1, 2020 Province, City, and Municipality Total PopulationJulius PalmeroNo ratings yet
- Smoothed Ratio Money ManagementDocument5 pagesSmoothed Ratio Money ManagementMauricio BurlacenkoNo ratings yet
- Topic 3b Simple Linear RegressionDocument17 pagesTopic 3b Simple Linear Regressionshaibu amanaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Gadgets in Learning AmongDocument45 pagesThe Impact of Gadgets in Learning AmongKen David BuenoNo ratings yet
- 2015 - Two Baselines Are Better Than One - Improving The Reliability of Computerized Testing in Sports NeuropsychologyDocument8 pages2015 - Two Baselines Are Better Than One - Improving The Reliability of Computerized Testing in Sports NeuropsychologyRaúl VerdugoNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument3 pagesSamplingsiaapaNo ratings yet
- Bayesian Analysis - ExplanationDocument20 pagesBayesian Analysis - ExplanationJamesNo ratings yet
- MA1014 Probability and Queueing TheoryDocument4 pagesMA1014 Probability and Queueing TheoryDivanshuSriNo ratings yet
- Our Lady of Lourdes College FoundationDocument35 pagesOur Lady of Lourdes College FoundationJerome EncinaresNo ratings yet
- PhDThesis Thomas Verbraken PDFDocument213 pagesPhDThesis Thomas Verbraken PDFsumit attharkarNo ratings yet
- Megalithic Aids To Navigation 1986 Ed 2011Document104 pagesMegalithic Aids To Navigation 1986 Ed 2011david_davidson_47No ratings yet
- Disk MagicDocument46 pagesDisk Magicbluegene74No ratings yet
- MultiLab CE Guia de UsuarioDocument98 pagesMultiLab CE Guia de Usuariovictor20008No ratings yet
- MMS Complete Syllabus NewDocument126 pagesMMS Complete Syllabus NewsiddheshkaraneNo ratings yet
- Risk Management in Project Management (Project Management)Document31 pagesRisk Management in Project Management (Project Management)حفيظ الدين محمد كيلاني100% (2)
- Unit 4 Hypothesis Formulation and Sampling: StructureDocument16 pagesUnit 4 Hypothesis Formulation and Sampling: StructureBhupenderSinghNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Performance Prognostic For Condition-Based Maintenance PDFDocument10 pagesGas Turbine Performance Prognostic For Condition-Based Maintenance PDFEddy PachecoNo ratings yet
- Methods and Instruments For Noncontact DiagnosticsDocument10 pagesMethods and Instruments For Noncontact DiagnosticsjohnnysNo ratings yet
- Bjmq3013 Syllabus 2016 Bom StudentDocument4 pagesBjmq3013 Syllabus 2016 Bom Studentwong6804No ratings yet
- An Empirical Analysis of Money Demand Function in Nepal: Birendra Bahadur BudhaDocument17 pagesAn Empirical Analysis of Money Demand Function in Nepal: Birendra Bahadur BudhaIsmith PokhrelNo ratings yet
- SCM - Session 8 (Forecasting)Document21 pagesSCM - Session 8 (Forecasting)Bushra Mubeen SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Data Description PDFDocument2 pagesChapter 6 Data Description PDFSUE YINNo ratings yet
- 0cafccf7 PDFDocument20 pages0cafccf7 PDFNana MacabandoNo ratings yet
- Sample Size CalculationDocument13 pagesSample Size Calculationwanna learnNo ratings yet
- Review On Prediction Algorithms in Educational Data Mining: A.Dinesh Kumar, R.Pandi Selvam, K.Sathesh KumarDocument8 pagesReview On Prediction Algorithms in Educational Data Mining: A.Dinesh Kumar, R.Pandi Selvam, K.Sathesh KumarnpraveenaNo ratings yet
- 08 Natural Language Processing in TensorflowDocument29 pages08 Natural Language Processing in TensorflowAkbar ShakoorNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Statistical Signal ProcessingDocument303 pagesFundamentals of Statistical Signal Processingansumanhello67% (3)
- From Vision to Version - Step by step guide for crafting and aligning your product vision, strategy and roadmap: Strategy Framework for Digital Product Management RockstarsFrom EverandFrom Vision to Version - Step by step guide for crafting and aligning your product vision, strategy and roadmap: Strategy Framework for Digital Product Management RockstarsNo ratings yet
- CATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part I : Getting Started and Sketcher WorkbenchFrom EverandCATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part I : Getting Started and Sketcher WorkbenchRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Designing SCADA Application Software: A Practical ApproachFrom EverandDesigning SCADA Application Software: A Practical ApproachNo ratings yet
- Autodesk Fusion 360: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users (3rd Edition)From EverandAutodesk Fusion 360: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users (3rd Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- SketchUp Success for Woodworkers: Four Simple Rules to Create 3D Drawings Quickly and AccuratelyFrom EverandSketchUp Success for Woodworkers: Four Simple Rules to Create 3D Drawings Quickly and AccuratelyRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- AutoCAD 2010 Tutorial Series: Drawing Dimensions, Elevations and SectionsFrom EverandAutoCAD 2010 Tutorial Series: Drawing Dimensions, Elevations and SectionsNo ratings yet
- Autodesk Fusion 360 Black Book (V 2.0.6508) Part 2: Autodesk Fusion 360 Black Book (V 2.0.6508)From EverandAutodesk Fusion 360 Black Book (V 2.0.6508) Part 2: Autodesk Fusion 360 Black Book (V 2.0.6508)No ratings yet
- Certified Solidworks Professional Advanced Surface Modeling Exam PreparationFrom EverandCertified Solidworks Professional Advanced Surface Modeling Exam PreparationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)