Professional Documents
Culture Documents
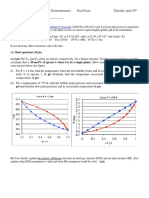
Bernoulli's Equation: Terms Term Meaning Relationship SI Units
Uploaded by
Mohammad OmarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bernoulli's Equation: Terms Term Meaning Relationship SI Units
Uploaded by
Mohammad OmarCopyright:
Available Formats
Bernoullis Equation
Terms
Term Meaning Relationship SI Units
a Acceleration -
(
2
sec
m
F Force on accelerati mass
(
2
sec
m kg
,
Newton (N)
g
Gravitational
Acceleration
-
2
sec
m
9.81
W Weight
g mass
(
2
sec
m kg
,
Newton (N)
A area
2
length [ ]
3
m
V Volume
3
length [ ]
3
m
Density
volume
mass
(
3
m
kg
Specific
Weight
g
volume
g mass
volume
weight
=
=
(
3
m
N
P Pressure
area
force
(
2
m
N
,
Pascal (Pa)
w Work
distance force
[ ] m N ,
Joule (J)
E Energy Ability to do work
[ ] m N ,
Joule (J)
z Elevation - [ ] m
Velocity
time
distance
(
sec
m
H
Hydraulic
Head
g g
P
z
g mass
Energy
2
2
+ + =
[ ] m
Derivation of Bernoullis Equation
Bernoullis Equation is the equation for the total energy in water normalized by the
product of the unit mass and gravitational acceleration.
The three types of energy in water are:
1. Potential Energy (EP) due to gravity
2. Kinetic Energy (Ek) due to motion
3. Non flow energy (En) associated with work on system by pressure and volume
(hydraulics)
=
=
=
) (
2
1
0 1
2
P P V E
m E
mgz E
n
k
p
Equations for different types of energy (Equation 1)
+ + + = mgz E E E E
n k P
2
2
1
m + ( )
0 1
P P V (Equation 2)
Remember:
m
V
V
m
= = (Equation 3)
Substituting equation 3 for the volume (V) in equation 2:
( ) ( )
0 1
2
0 1
2
2
1
2
1
P P
m
m mgz P P V m mgz E + + + + =
(Equation 4)
In natural systems we assume the P0 is atmospheric pressure (Pa), which one can
assume is a constant over the entire system. P1 is pore pressure (Pp) including
atmospheric pressure. So, we can express the difference between P1 and P0 as just the
pore pressure (Equation 5).
p a p a
a
p a
P P P P P P
P P
P P P
= + =
=
+ =
0 1
0
1
(Equation 5)
Equation 4 can be rewritten as:
P
m
m mgz E
+ + =
2
2
1
(Equation 6)
Finally, if one normalizes the energy (E) by the force of a unit mass of water (mg),
equation 6 can be rewritten as:
g
P
g
z H
mg
E
g
P
g
z
g m
P m
g m
m
g m
z g m
mg
mP
mg
m
mg
mgz
mg
E
+ + = =
+ + =
/
/
+
/
/
+
/
/
/
/
= + + =
2
2 2 2
2
2 2 2
(Equation 7)
Equation 7 defines hydraulic head (H) as the sum of three terms. Hydraulic head has
units of length. The three terms in the equation for hydraulic head are elevation head,
velocity head and pressure head (Equation 8).
head pressure
g
P
head velocity
g
head elevation z
2
2
(Equation 8)
You might also like
- Wholesale Real Estate Purchase Agreement PSA1Document1 pageWholesale Real Estate Purchase Agreement PSA1Charles Gonzales100% (6)
- Head To Toe AssessmentDocument3 pagesHead To Toe AssessmentCatherine Drew Sims100% (6)
- Label 304409446Document1 pageLabel 304409446darker111darkNo ratings yet
- Space Technology Section-A, Module - 1, Lecture-2: 1.2 Thrust From A Stationary Rocket Engine / MotorDocument7 pagesSpace Technology Section-A, Module - 1, Lecture-2: 1.2 Thrust From A Stationary Rocket Engine / MotorSid Siddapa SidhuNo ratings yet
- InSpectres CharacterSheetDocument1 pageInSpectres CharacterSheetmuzzylogic2555No ratings yet
- Xianyu Z.-Z. - Solutions To Peskin & SchroederDocument173 pagesXianyu Z.-Z. - Solutions To Peskin & SchroederAndres100% (3)
- PIPESIM 2009.1 Artificial Lift Design and Optimization HDocument110 pagesPIPESIM 2009.1 Artificial Lift Design and Optimization HMohammad Omar100% (2)
- Statistical Mechanics - Pathria Homework 2Document6 pagesStatistical Mechanics - Pathria Homework 2Ale Gomez100% (10)
- Dimensional AnalysisDocument13 pagesDimensional AnalysisahmedyasharNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Companies Emails - Ready To SentDocument10 pagesPetroleum Companies Emails - Ready To SentMohammad Omar85% (13)
- Contoh P&IDDocument1 pageContoh P&IDLudy Oji PrastamaNo ratings yet
- Peskin QFT SolutionsDocument173 pagesPeskin QFT SolutionsAmir Iqbal100% (12)
- SCI 121 - Introduction To Physics & Chemistry Formula Sheet 1 KinematicsDocument10 pagesSCI 121 - Introduction To Physics & Chemistry Formula Sheet 1 KinematicsTaco ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Pathria Solution1Document4 pagesPathria Solution1Mario Mede RiteNo ratings yet
- Design of Allyl TowerDocument11 pagesDesign of Allyl TowerMohammad OmarNo ratings yet
- Peskin&Schroeder Solution ManualDocument173 pagesPeskin&Schroeder Solution ManualJerad Williams100% (4)
- Mathematical Modeling of Gas TurbineDocument7 pagesMathematical Modeling of Gas TurbineKVVNo ratings yet
- UC Davis ENG 103 Midterm 2010 SolDocument4 pagesUC Davis ENG 103 Midterm 2010 SolgambitNo ratings yet
- Zeroth Law and Introductory ConceptsDocument13 pagesZeroth Law and Introductory ConceptsMohd Danial Muhd AliNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics A Full VersionDocument24 pagesAerodynamics A Full VersionVaishnavi SundarNo ratings yet
- Equations of Change ChE 131Document34 pagesEquations of Change ChE 131Johanna Martinne CanlasNo ratings yet
- AA200 CH 08 Entropy Generation and Transport CantwellDocument10 pagesAA200 CH 08 Entropy Generation and Transport CantwellsekharsamyNo ratings yet
- ∂ N ∂ T ∂ ∂ T Ηρdv+ Ηρ ⃗V ⋅ D ⃗ A: Derivation Of The Energy EquationDocument4 pages∂ N ∂ T ∂ ∂ T Ηρdv+ Ηρ ⃗V ⋅ D ⃗ A: Derivation Of The Energy EquationJaydee LuceroNo ratings yet
- Homework 5 Part (A) Write The Differential Equation(s) of Motion For The Following SystemDocument3 pagesHomework 5 Part (A) Write The Differential Equation(s) of Motion For The Following Systemgunawan refiadiNo ratings yet
- Termodinamika LanjutDocument44 pagesTermodinamika LanjutRyan Tw ChoumingNo ratings yet
- AE1104 Physics 1: List of EquationsDocument24 pagesAE1104 Physics 1: List of EquationssmithastellaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Forced Vibration of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom SystemsDocument4 pagesChapter 3 - Forced Vibration of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom SystemsAnonymous LcR6ykPBTNo ratings yet
- Physics 715 HW 1Document13 pagesPhysics 715 HW 1Antonildo PereiraNo ratings yet
- Thermal PhysicsDocument26 pagesThermal Physicsjmozo123No ratings yet
- Pressure Coupling / BarostatsDocument5 pagesPressure Coupling / BarostatsnootsamNo ratings yet
- Gibbs Paradox 1Document19 pagesGibbs Paradox 1John NelsonNo ratings yet
- Dimensional AnalysisDocument10 pagesDimensional Analysisyxc11No ratings yet
- Energy: Sub Chapter CoveredDocument31 pagesEnergy: Sub Chapter CoveredRenu SekaranNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Vacuum and The Photon NumberDocument9 pagesThe Structure of The Vacuum and The Photon NumberI.B. BirulaNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument13 pagesThermoMH MerhiNo ratings yet
- Gas Technology-4th Stage Lecture 3 27 November 2017 2Document13 pagesGas Technology-4th Stage Lecture 3 27 November 2017 2muhammadNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 Center of PressureDocument5 pagesExperiment 5 Center of Pressuresakura9999100% (4)
- Physics 262 Notes - Topic 2Document13 pagesPhysics 262 Notes - Topic 2romanberens2No ratings yet
- AdvHeatMass L 03 PDFDocument10 pagesAdvHeatMass L 03 PDFShanmukShannuNo ratings yet
- Exercícios Resolvidos - Cap. 02 (B) - AtkinsDocument26 pagesExercícios Resolvidos - Cap. 02 (B) - AtkinsRosiane VieiraNo ratings yet
- Exerc Cios Resolvidos - Cap. 02-Atkins (A) PDFDocument30 pagesExerc Cios Resolvidos - Cap. 02-Atkins (A) PDFSidnei SantosNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Formulas ShortcutsDocument15 pagesFluid Mechanics Formulas Shortcuts9444583008No ratings yet
- Fluid Disc. Ch6 STDDocument21 pagesFluid Disc. Ch6 STDLuay HameedNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 SolutionsDocument8 pagesAssignment 4 SolutionsSam KumagaiNo ratings yet
- $RVLROJZDocument7 pages$RVLROJZhusseinmarwan589No ratings yet
- Topic 3 Forced Vibration of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems - IDocument4 pagesTopic 3 Forced Vibration of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems - IstefanNo ratings yet
- Biryukov 2002Document5 pagesBiryukov 2002georgeqin75No ratings yet
- Graphite Oxide (GO) Decomposition Kinetics: Electronic Supplementary InformationDocument7 pagesGraphite Oxide (GO) Decomposition Kinetics: Electronic Supplementary Informationbai tap hoa vo coNo ratings yet
- Phys FormulasDocument5 pagesPhys FormulasIrina IvanovaNo ratings yet
- PART V - Gas Well TestingDocument98 pagesPART V - Gas Well TestingdarshanNo ratings yet
- Equation of State of TitaniumDocument6 pagesEquation of State of TitaniumKing OfheartsNo ratings yet
- PR 01 - Kelompok 06Document5 pagesPR 01 - Kelompok 06Jenny AzzahraNo ratings yet
- HW 1 SolutionDocument9 pagesHW 1 SolutionbharathNo ratings yet
- Applied Lecture 01 Solved PDFDocument12 pagesApplied Lecture 01 Solved PDFJessica GarrettNo ratings yet
- 1984, A Molecular Dynamics Method For Simulations in The Canonical Ensemblet by SHUICHI NOSEDocument14 pages1984, A Molecular Dynamics Method For Simulations in The Canonical Ensemblet by SHUICHI NOSEAnatoli KrasilnikovNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic EquationDocument10 pagesHydraulic EquationDheka 2022No ratings yet
- CBE3508 Sp21 FinalDocument6 pagesCBE3508 Sp21 Finalsasuke uchihaNo ratings yet
- Rock Climber 1) : CircuitDocument2 pagesRock Climber 1) : CircuitKarn KumarNo ratings yet
- Relativistic KinematicsDocument12 pagesRelativistic KinematicsAshim DuttaNo ratings yet
- Liouville's Theorem: 3N I I I I I 1Document18 pagesLiouville's Theorem: 3N I I I I I 1Sadaf KhanNo ratings yet
- Graetz ProblemDocument13 pagesGraetz ProblemBelialVKWWNo ratings yet
- Hoehler Appendix PDFDocument109 pagesHoehler Appendix PDFriletm86No ratings yet
- Micro-Chaos in Digital Control: Summary. in This Paper We Analyze A Model For The Effect of Digital Control On OneDocument34 pagesMicro-Chaos in Digital Control: Summary. in This Paper We Analyze A Model For The Effect of Digital Control On OneGeorge HallerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document33 pagesChapter 02westly_castro100% (3)
- Logical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeFrom EverandLogical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeNo ratings yet
- Commensurabilities among Lattices in PU (1,n). (AM-132), Volume 132From EverandCommensurabilities among Lattices in PU (1,n). (AM-132), Volume 132No ratings yet
- Mel242 32Document35 pagesMel242 32Mohammad OmarNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter UkDocument1 pageCover Letter UkNayan MallickNo ratings yet
- BP Egypt: Master'S Degree Scholarships University of CambridgeDocument2 pagesBP Egypt: Master'S Degree Scholarships University of CambridgeMohammad OmarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Reinforced Concrete Desing - c2004Document2 pagesAdvanced Reinforced Concrete Desing - c2004Sai RajNo ratings yet
- High End SCADA SolutionsDocument2 pagesHigh End SCADA SolutionsQuantumAutomationNo ratings yet
- Mastering 3D PrintingDocument2 pagesMastering 3D PrintingTamás KissNo ratings yet
- Nicardipine Quick ReferenceDocument1 pageNicardipine Quick ReferenceLisa Trisnawati ChaniagoNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Listening 2 PDFDocument6 pagesStep by Step Listening 2 PDFtuyentruongNo ratings yet
- Briggs HaldaneDocument2 pagesBriggs HaldaneSri Dwi AryaniNo ratings yet
- PallikoodamDocument16 pagesPallikoodamSuMana50% (4)
- Pricing in International Market by Amritraj D BangeraDocument10 pagesPricing in International Market by Amritraj D BangeraAmritraj D.BangeraNo ratings yet
- Rspca and PetaDocument1 pageRspca and Petasophie_sherlock4917No ratings yet
- Asme CCase 2067-2Document2 pagesAsme CCase 2067-2ADAMJSRAONo ratings yet
- Deskilling Devices UsedDocument3 pagesDeskilling Devices UsedRuchika Puri0% (1)
- IV Drip Rate HandoutDocument3 pagesIV Drip Rate HandoutMaria MarieNo ratings yet
- Miller Welding Project: Adjustable Stand: Materials and ToolsDocument4 pagesMiller Welding Project: Adjustable Stand: Materials and ToolskokiskoNo ratings yet
- RSA Industries, India - Products - Care - Polymeric Non Ionic Fabric Softener - Fabric Softener (RSF-H-SOFT)Document3 pagesRSA Industries, India - Products - Care - Polymeric Non Ionic Fabric Softener - Fabric Softener (RSF-H-SOFT)crplzNo ratings yet
- Brochure MT-50T SRH Eng PDFDocument2 pagesBrochure MT-50T SRH Eng PDFpramodtryNo ratings yet
- Pantaloons Retail India Limited: Group MembersDocument6 pagesPantaloons Retail India Limited: Group MembersSakshi GuptaNo ratings yet
- 739695Document2 pages739695Виталий Захарчук100% (1)
- Cold Fast Embers Historic: Braised Pork & Fried Clam Po BoyDocument2 pagesCold Fast Embers Historic: Braised Pork & Fried Clam Po BoyDaniel GerzinaNo ratings yet
- Abhijeet FerrolysDocument6 pagesAbhijeet FerrolysNareshkumar KoppalaNo ratings yet
- Statistical Multipath Model Lecture4 PDFDocument16 pagesStatistical Multipath Model Lecture4 PDFkivetiNo ratings yet
- Ocean Waves ThrowDocument1 pageOcean Waves ThrowJill KrahlingNo ratings yet
- ElectricalDocument1 pageElectricalJprince1920No ratings yet
- إدارة الجودة الشاملة لضمان جودة الخدمات الصحية في المستشفيات - د. بن نافلة قدور، د. مزريق عاشورDocument20 pagesإدارة الجودة الشاملة لضمان جودة الخدمات الصحية في المستشفيات - د. بن نافلة قدور، د. مزريق عاشورhossam626No ratings yet
- 37 - Acute Rheumatic FeverDocument1 page37 - Acute Rheumatic FevernasibdinNo ratings yet
- Centrifuge DSC 156TDocument2 pagesCentrifuge DSC 156TRose Lynn Anne BesaNo ratings yet