Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Macro Environment
Uploaded by
poojasolCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Macro Environment
Uploaded by
poojasolCopyright:
Available Formats
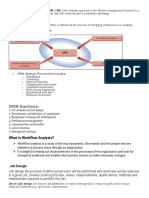
Macro environment analysis is a review of all the factors that a company is unable to control.
Companies conduct this analysis to stay abreast of the issue in the current business environment. A common tool for conducting a macro environment analysis is the PESTEL framework, which include factors from the political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal aspects in the business environment. The ultimate purpose of this analysis is to create a strategy that will leverage as many of these external factors as possible to the companys favor. Macro environment factors are uncontrollable external forces that affect how a business operates. They are largely out of the control of the business, and often require changes in operating, management, production, and marketing. Analysts often categorize them using the acronyms PEST or PESTEL. Broken down, PEST stands for political, economic, social, and technological concerns. PESTEL also includes environmental and legal factors.
A PESTLE analysis is a tool to help you do this. Each letter stands for an element of the organisations external operating environment. They stand for Political, Economic, Socio-cultural, Technological, Legal and Ecoenvironmental elements
Political influences: government stability ,government policy,government spending,education policies Economic influences: rates,inflation,unemployment business/economic cycles,bunding mechanisms,interest
Socio-cultural influences deal influences:mographics; attitudes to work and leisure; levels of education;health and lifestyle;social mobility. Technological influences: new development,rates of obsolescence discoveries,spread of new technologies,research,rates of
Eco-environment environmental protection laws,waste disposalenergy consumption,other resource consumption,sustainability Legal influences: welfare legislation,employment law,health and safety,consumer protection
Political Political macro environment factors include things like tax policies, governmentissued safety regulations, the availability of government contracts, and even shifts in the controlling political party. International laws, such as trade agreements and tariffs, may affect the supply and demand chains and available markets for many different companies as well. Economic A market boom, recession, or growing inflation problem can all change the way an organization plans for the future and operates in the present. Economic factors are often difficult to assess, since economic forecasts and analyses vary widely between experts.Unemployment levels, comparative foreign exchange rates, and the state of the global economy can all help or hurt a business' ability to get needed components and maintain a stable profit.
Social The mood and demographics of the population make up the social area of macroenvironment factors. For example, a society that places an emphasis on selfguided jobs with room for creativity may cause organizations to redefine job descriptions and adapt the model of the workplace to attract workers. Social trends, such as a preference for on-demand mobile media devices, can also influence which products a company manufacturers and where it chooses to spend advertising dollars. Technological Technological macro environment factors can influence how an organization does business. A new type of machinery, computer chip, or product created through research and development can help a company stay modernized and ahead of the market curve. Owners must be able to accurately identify which new developments will be truly useful, and which are just fads. Environmental Environmental concerns are important to businesses both in the short and long term. In the short-term, things like natural disasters can disrupt production and supply operations, or even destroy company assets. Programs such as environmental risk assessment can help companies prepare to handle many of the most likely short-term crises. In the long view, however, businesses may have an interest in ensuring that their supply chains are not destroyed by unsustainable practices. Legal Legal factors can limit or change how a business operates. For example, they may have to hire additional supervisory staff or purchase safety equipment after a new health and safety law is passed. Child labor laws often limit the hours a minor can work and require set break periods. If an organization employs several minors, it may have to hire additional help to cover the hours when the minors cannot legally work. Legal factors are determined by both local legislation and regional and national laws. In some cases, companies that do business internationally are also affected by international laws. Hedging Against the Macro Environment Generally, businesses have little to no control over their macro environment. They can, however, prepare for the unexpected by using a PEST or PESTEL analysis. For example, if a business has a manufacturing plant in an area prone to hurricanes, they could hedge against the possible loss by developing an action plan to relocate employees or supplies if threatened by a hurricane. Many organizations conduct regular analyses of the macroenvironment factors connected to them, and revise their strategies accordingly.
You might also like
- Ethical Obligations and Decision Making in Accounting: Text and Cases Fifth EditionDocument174 pagesEthical Obligations and Decision Making in Accounting: Text and Cases Fifth EditionMERB Tzy0% (1)
- What Is Macro Environment AnalysisDocument3 pagesWhat Is Macro Environment AnalysisRobelyn D. LazaroNo ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument10 pagesExecutive SummaryaligaramNo ratings yet
- Micro and Macro Environment of BusinessDocument5 pagesMicro and Macro Environment of BusinessCyrus BondoNo ratings yet
- (Economic Themes) Impact of National Culture On International Human Resource ManagementDocument20 pages(Economic Themes) Impact of National Culture On International Human Resource ManagementAshleyKumarNo ratings yet
- Understanding Terminal, Instrumental Values and Employee AttitudesDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Terminal, Instrumental Values and Employee AttitudesFaaz Alwahab0% (1)
- Factors Affecting Organizational StructuresDocument4 pagesFactors Affecting Organizational StructuresDana Lutfi100% (1)
- Caribbean Business Environment PESTEL AnalysisDocument6 pagesCaribbean Business Environment PESTEL AnalysisXperiment Beatz50% (2)
- Discuss The Impact of PESTLEG On Success and FailureDocument4 pagesDiscuss The Impact of PESTLEG On Success and FailureTanaka M Kariri100% (2)
- The Macro Environment Factors Impacting OrganizationsDocument4 pagesThe Macro Environment Factors Impacting OrganizationsArafat RaufNo ratings yet
- Environmental Factors That Are Larger Societal Forces Affecting Your CompanyDocument3 pagesEnvironmental Factors That Are Larger Societal Forces Affecting Your CompanySuryaNo ratings yet
- Supply and Demand and The Labor MarketDocument4 pagesSupply and Demand and The Labor MarketbobzxzsNo ratings yet
- Individual Written AssignmentDocument26 pagesIndividual Written Assignmentovina peirisNo ratings yet
- Enviromental Factors Influencing HRM OpuDocument9 pagesEnviromental Factors Influencing HRM OpuAbul Hasnat88% (8)
- Theory of SellingDocument5 pagesTheory of SellingrajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Labor Market and Other Factors On The Changing Nature of Human Resource ManagementDocument48 pagesThe Impact of Labor Market and Other Factors On The Changing Nature of Human Resource ManagementMohammad Shoaib100% (1)
- Emerging Challenges of HRM in 21 Century: A Theoretical AnalysisDocument8 pagesEmerging Challenges of HRM in 21 Century: A Theoretical AnalysisZahid RizvyNo ratings yet
- Case Study Internal and External Environment Analysis On The Performance of Small and Medium Industries in IndonesiaDocument9 pagesCase Study Internal and External Environment Analysis On The Performance of Small and Medium Industries in IndonesiaDEDE NOVIARDINo ratings yet
- RecruitmentDocument21 pagesRecruitmentSunil Kumar100% (2)
- HRISDocument20 pagesHRISTeuku NoermanNo ratings yet
- Role of Entrepreneur in The Economic DevelopmentDocument6 pagesRole of Entrepreneur in The Economic Developmentsheikhirshad100% (2)
- Leaders Born or MadeDocument4 pagesLeaders Born or MadeshojesNo ratings yet
- Supply & DemandDocument13 pagesSupply & DemandTara MargaritaNo ratings yet
- Learning & GrowthDocument40 pagesLearning & GrowthAlamin SheikhNo ratings yet
- Challenges and Opportunities in Oraganisational BehaviourDocument5 pagesChallenges and Opportunities in Oraganisational BehaviourRamesh babuNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Human Resources Management at WalmartDocument13 pagesCase Study of Human Resources Management at WalmartRukshar Khan100% (1)
- Factors Affecting Business in NigeriaDocument9 pagesFactors Affecting Business in NigeriaKAYODE OLADIPUPONo ratings yet
- Porter's Five ForcesDocument27 pagesPorter's Five Forcesrenukashree100% (1)
- The Global Marketing Environment: Understanding Forces That Shape OpportunitiesDocument17 pagesThe Global Marketing Environment: Understanding Forces That Shape OpportunitiesIrfan QadirNo ratings yet
- Macro EnvironmentDocument11 pagesMacro EnvironmentMj Zafires100% (2)
- HRM Practices at WIHGDocument121 pagesHRM Practices at WIHGPhilemon ZachariaNo ratings yet
- 34.factors Influencing Employee Job Satisfaction A Conceptual AnalysisDocument11 pages34.factors Influencing Employee Job Satisfaction A Conceptual AnalysisJawadNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument12 pagesHuman Resource Managementalam khanNo ratings yet
- Labour Market More NotesDocument5 pagesLabour Market More NotesSpencer HuNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of services marketing explainedDocument16 pagesFundamentals of services marketing explainedMedleen DembarembaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 HRP and HRDDocument9 pagesMODULE 2 HRP and HRDTitus ClementNo ratings yet
- Uses of Mobile PhonesDocument3 pagesUses of Mobile PhonesMUHAMMAD YAMEENNo ratings yet
- Leadership Style and GenderDocument101 pagesLeadership Style and GenderGreg JacksonNo ratings yet
- 12 Essential Traits of an EntrepreneurDocument9 pages12 Essential Traits of an Entrepreneursahil_bali86100% (1)
- The Essential Guide to HRMDocument3 pagesThe Essential Guide to HRMkhalid bashirNo ratings yet
- Definition of StaffingDocument5 pagesDefinition of StaffingJonthonBerwegaNo ratings yet
- Underpinning Theories and Models of HRMDocument25 pagesUnderpinning Theories and Models of HRMChris JumanNo ratings yet
- Motivating hospitality workersDocument12 pagesMotivating hospitality workersnoel sannaNo ratings yet
- What is Management in 40 CharactersDocument12 pagesWhat is Management in 40 CharactersShraddha Chhapolia100% (2)
- BLUE COLLAR JOBS Vs WHITE COLLAR JOBS.Document2 pagesBLUE COLLAR JOBS Vs WHITE COLLAR JOBS.Nelson VersozaNo ratings yet
- Measuring Employee Empowerment in OrganisationsDocument17 pagesMeasuring Employee Empowerment in OrganisationssauravwowNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScanningDocument4 pagesEnvironmental ScanningZolten CorporationNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument50 pagesRatio AnalysissshreyasNo ratings yet
- PESTEL Analysis of The Macro-EnvironmentDocument5 pagesPESTEL Analysis of The Macro-EnvironmentAna ParaschivNo ratings yet
- HRUSDocument12 pagesHRUSराकेश झाNo ratings yet
- Meaning of Human Resource Management HRMDocument3 pagesMeaning of Human Resource Management HRMsarvesh.bhartiNo ratings yet
- Impact of Information Technology On Organizational Performance: An Analysis of Qualitative Performance Indicators of Pakistan's Banking and Manufacturing CompaniesDocument13 pagesImpact of Information Technology On Organizational Performance: An Analysis of Qualitative Performance Indicators of Pakistan's Banking and Manufacturing CompaniesShahid AhmadNo ratings yet
- Diversification in The Context of Growth StrategiesDocument10 pagesDiversification in The Context of Growth StrategieskavenNo ratings yet
- Designing Repatriation Programs for ExpatriatesDocument6 pagesDesigning Repatriation Programs for ExpatriatesQalandar7464No ratings yet
- Notes For Lesson TwoDocument4 pagesNotes For Lesson TwoBetty MudondoNo ratings yet
- Faith ProcurementDocument9 pagesFaith ProcurementWomayi SamsonNo ratings yet
- Mco 06 em PDFDocument8 pagesMco 06 em PDFFirdosh Khan80% (5)
- Political PestelDocument19 pagesPolitical PestelS. GOWRINo ratings yet
- All About MarketingDocument26 pagesAll About Marketingsmit1522No ratings yet
- 3.1 Ifraz Mohammed_20231449_BSBOPS601 Business PlanDocument2 pages3.1 Ifraz Mohammed_20231449_BSBOPS601 Business PlanIfraz MohammadNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics ProjectDocument12 pagesApplied Economics ProjectPlied PlipperNo ratings yet
- Industry Data SpreadsheetDocument3 pagesIndustry Data SpreadsheetpoojasolNo ratings yet
- H9N2Document4 pagesH9N2poojasolNo ratings yet
- Anatomical and Physiological ChangesDocument25 pagesAnatomical and Physiological ChangespoojasolNo ratings yet
- International Marketing DefinitionDocument13 pagesInternational Marketing DefinitionpoojasolNo ratings yet
- Virus MorphologyDocument28 pagesVirus MorphologypoojasolNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument5 pagesINTRODUCTIONpoojasol0% (1)
- Masters 121113Document5 pagesMasters 121113poojasolNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Email: EmailDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Email: EmailpoojasolNo ratings yet
- Adms and Exam ScheduleDocument3 pagesAdms and Exam ScheduleMohammad AzimNo ratings yet
- Microscopic TechniquesDocument60 pagesMicroscopic TechniquesRonaldo Júnior FernandesNo ratings yet
- Ring Spinning Frame GuideDocument12 pagesRing Spinning Frame Guidepoojasol0% (1)
- BusinessetiquettepowerpointslidesDocument56 pagesBusinessetiquettepowerpointslidespoojasolNo ratings yet
- Joseph ConradDocument4 pagesJoseph ConradpoojasolNo ratings yet
- Diversification Strategy PresentationDocument49 pagesDiversification Strategy PresentationChandeep WadhwaNo ratings yet
- An Tar Tic ADocument12 pagesAn Tar Tic ApoojasolNo ratings yet
- An Tar Tic ADocument12 pagesAn Tar Tic ApoojasolNo ratings yet
- Middle East Real Estate Forum Post Event Brochure PDFDocument55 pagesMiddle East Real Estate Forum Post Event Brochure PDFAnonymous YsumsYNo ratings yet
- Realestate Appraiser Course ListDocument33 pagesRealestate Appraiser Course ListcutmytaxesNo ratings yet
- Role of the Sleeping PartnerDocument15 pagesRole of the Sleeping PartnerKhalid AsgherNo ratings yet
- Oracle Payments R12 User GuideDocument184 pagesOracle Payments R12 User GuideppmurilloNo ratings yet
- A Casestudy On Sap BW Aspects in Divestiture Project of A Large Automotive CustomerDocument11 pagesA Casestudy On Sap BW Aspects in Divestiture Project of A Large Automotive CustomerBryan AdamsNo ratings yet
- Final PTCL Project CompleteDocument83 pagesFinal PTCL Project CompleteMuhammad Zubair100% (4)
- ZaraDocument25 pagesZarakarish_sadaranganiNo ratings yet
- The Customer JourneyDocument1 pageThe Customer JourneyIDG_World100% (3)
- Trading Checklist 1Document12 pagesTrading Checklist 1rangghjNo ratings yet
- Vakrangee LimitedDocument3 pagesVakrangee LimitedSubham MazumdarNo ratings yet
- Herbert Simon Model of Decision MakingDocument3 pagesHerbert Simon Model of Decision MakingSachin Raikar100% (2)
- Sai Khant Kyaw Za - Task 2Document4 pagesSai Khant Kyaw Za - Task 2Lean CosmicNo ratings yet
- Challan Form (Cash Voucher) Challan Form (Cash Voucher)Document6 pagesChallan Form (Cash Voucher) Challan Form (Cash Voucher)prasannalakshmi_gurralaNo ratings yet
- EStmtPrintingServlet 3Document5 pagesEStmtPrintingServlet 3Ahmad Al FaizNo ratings yet
- WEEK15-17 ENTR 6152 Entrepreneurial Leadership in An Organization 2 PDFDocument29 pagesWEEK15-17 ENTR 6152 Entrepreneurial Leadership in An Organization 2 PDFMoca ΔNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management - Business Plan ClothesDocument35 pagesStrategic Management - Business Plan ClothesMuhammad Dzikri Tesla BuwonoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Project Report for Khushi Mandap DecoratorsDocument50 pagesDetailed Project Report for Khushi Mandap DecoratorsNeha Marathe100% (1)
- Signature____________DateDocument4 pagesSignature____________DateSpencer DavidNo ratings yet
- Metorex Ar Dec10Document148 pagesMetorex Ar Dec10Take OneNo ratings yet
- Indo US Ventures Case DebriefDocument19 pagesIndo US Ventures Case DebriefYazad AdajaniaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Plan PresentationDocument7 pagesMarketing Plan Presentationapi-454161052No ratings yet
- Ruston, Louisiana: Zion Traveler Baptist ChurchDocument19 pagesRuston, Louisiana: Zion Traveler Baptist ChurchGilbert LomofioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 SlidesDocument60 pagesChapter 1 Slides임민수No ratings yet
- Module 6 - Lect 3 - Role of CBDocument22 pagesModule 6 - Lect 3 - Role of CBBHAVYA GOPAL 18103096No ratings yet
- Starbucks Case AnalysisDocument17 pagesStarbucks Case Analysisytsell30No ratings yet
- Ohsas 18001Document2 pagesOhsas 18001InnoviaNo ratings yet
- ADEVA Task#1Document3 pagesADEVA Task#1Maria Kathreena Andrea AdevaNo ratings yet
- Anwesha Roy - 30701017043Document17 pagesAnwesha Roy - 30701017043Anwesha RoyNo ratings yet