Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 4 Plan
Uploaded by
api-201512422Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 4 Plan
Uploaded by
api-201512422Copyright:
Available Formats
Theatre 1: 2013-2014
UNIT 4: DIRECTING & PRODUCING
DIRECTING
Styles Fourth Wall: an imaginary wall between the audience and the actors in a representational play; the space that separates a performer or performance from an audience; the conceptual barrier between any ctional work and its viewers or readers Presentational Style: theatrical style in which the actors acknowledge the presence of the audience. Representational Style: theatrical style in which the actors do not acknowledge the presence of the audience but try to duplicate life. Casting Audition: a sample performance by an actor, singer, musician, dancer, or other performer that typically involves the performer displaying their talent through a previously memorized and rehearsed solo piece or by performing a work or piece given to the performer at the audition or shortly before; a systematic process in which industry professionals select performers (similar to a job interview). Cast by Type: to cast a show by choosing actors who t a particular character type. Cold Reading: auditioning with a script that you have not had the opportunity to read before the audition. Color-Blind Casting: casting without regard to race or ethnicity of the characters or actors. Doubling: having an a performer play two or more parts. Ensemble: the cast of a play other than the principals; supporting players. Nontraditional Casting: casting that ignores the general conventions of casting by type. Principal: an actor who has a major role in a musical show. Typecasting: choosing people who have certain qualities in real life to play characters with similar qualities. Understudy: someone who learns a role for the purpose of performing in the absence of the actor cast in that role. Call: to notify cast and crew of cues, rehearsal times, and the rise and fall of the curtain. Responsibilities/Duties Director's Notes: comments by the director on the performance of each actor and on the production in general, usually given before or after rehearsals. Pacing: the tempo of a performance as it progresses. Production Concept: how the play should look and feel. Sight Lines: lines indicating visibility of onstage and backstage areas from various points in the house. Special Roles Choreographer: an artist who designs (choreographs) dances for the stage. Dramaturgy: the art of dramatic composition and the representation of the main elements of drama on the stage; shaping a story into a form that may be acted. Dramaturgs forge a critical link between artists and institutions, and institutions and their communities. They work with their other artistic collaborators to hone their vision, focus their goals and nd outlets for their creative work on new and classical plays and dance pieces. Parts of Rehearsals/Performances Curtain Call: occurs at the end of a performance when individuals return to the stage to be recognized by the audience for their performance; also known as bows. - In musical theatre, the performers typically recognize the orchestra and its conductor at the end of the curtain call. - Luciano Pavorotti (an Italian operatic tenor) holds the record for receiving 165 curtain calls, more than any other artist. Dry Tech: a technical rehearsal without actors present. Intermission: a recess between parts of a performance or production. Paper Tech: a meeting of the stage crew and the stage manager to run through cues on paper and create a master cue sheet.
Read-Through: a complete reading of a play aloud by the assembled cast, usually at the rst rehearsal. Reader's Theatre: a performance created by reading a script based on a literary work. Technical Week (Tech Week): refers to the week prior to the opening night of a play, musical or similar production in which all of the technical elements (such as costumes, light, sound, and make-up) are present during rehearsal for the rst time. Projects Identify key directors in western and non-western professional theatre Analyze a text Divide a play/performance piece into smaller scenes or French scenes Notate a scene from a director's point of view Write a director's concept for a play Create character sketches Create a director's notebook Lead small groups in improvisational and scripted work Use correct theatre terminology to convey ideas Give constructive criticism Direct a short scene Apply research to enhance a performance piece Defend dramatic choices Apply symbolism to a scene
You might also like
- Performing ArtsDocument4 pagesPerforming ArtsThricia May DencoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12 Theater ProductionDocument26 pagesLesson 12 Theater Productionmary sunshine evangelistaNo ratings yet
- 4th Arts Lesson 3Document23 pages4th Arts Lesson 3Stephen LoboNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document5 pagesChapter 3geomoNo ratings yet
- Contempo TheaterDocument2 pagesContempo TheaterDerek AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Little-Prince TheatreDocument33 pagesLittle-Prince TheatreNK0% (1)
- Key Instructional Activities TheatreDocument2 pagesKey Instructional Activities TheatreJenmar VerzolaNo ratings yet
- Essay Questions - Winter Exam 2014: Proscenium Stage Is The Most Common Stage Used in Theaters. The AudienceDocument4 pagesEssay Questions - Winter Exam 2014: Proscenium Stage Is The Most Common Stage Used in Theaters. The AudienceRamona-MihaelaGheorgheNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Quarter 2Document2 pagesTopic 3 Quarter 2Marla Jemima HilisNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Speech & Theater Arts (Midterms)Document68 pagesGroup 2 - Speech & Theater Arts (Midterms)devilladaphneleighdNo ratings yet
- Elements of Drama and Theater (Presentation) Author Staff Site Universitas Negeri YogyakartaDocument29 pagesElements of Drama and Theater (Presentation) Author Staff Site Universitas Negeri YogyakartaMadhu MNo ratings yet
- Exposición de InglésDocument2 pagesExposición de InglésReyna GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Theatrical Elements PPT 071849Document44 pagesTheatrical Elements PPT 071849JasmineNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Theatre DirectingDocument13 pagesIntroduction To The Theatre Directingblv1227100% (1)
- Theatre VocabularyDocument9 pagesTheatre VocabularyAlyona BoichukNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 PlanDocument2 pagesUnit 3 Planapi-201512422No ratings yet
- Dramatic ConventionsDocument17 pagesDramatic ConventionsCherilyn MabananNo ratings yet
- Technical Vocabulary For Drama and TheaterDocument10 pagesTechnical Vocabulary For Drama and TheaterGrecilna B. ArelladoNo ratings yet
- Drama Study GuideDocument17 pagesDrama Study GuideMelody WolfeNo ratings yet
- Theatre TermsDocument3 pagesTheatre TermsLeonard CatubayNo ratings yet
- Theatre TerminologyDocument6 pagesTheatre TerminologyRaaj DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Dramatic ConventionsDocument16 pagesDramatic ConventionsCherilyn MabananNo ratings yet
- English Reviewr NiDocument7 pagesEnglish Reviewr NibaclignemricqNo ratings yet
- No. 5 CW 11 Elements of Drama To Be Discuss 1 SignedDocument26 pagesNo. 5 CW 11 Elements of Drama To Be Discuss 1 SignedaleluyanicoleNo ratings yet
- Teacher's Guide Pages 2. Learner's Materials Pages: A. Additional Materials From Learning Resource (LR) PortalDocument9 pagesTeacher's Guide Pages 2. Learner's Materials Pages: A. Additional Materials From Learning Resource (LR) PortalDaniel FabianNo ratings yet
- No. 6 - Art ProductionDocument30 pagesNo. 6 - Art Productionandie hinchNo ratings yet
- CREATIVE NONFICTION3Autosaved PDFDocument23 pagesCREATIVE NONFICTION3Autosaved PDFFrancis MadroñoNo ratings yet
- Drama SyllabusDocument5 pagesDrama Syllabusapi-233862230No ratings yet
- Chamber Theater ObserveDocument25 pagesChamber Theater ObserveMariel Maquiniana100% (1)
- Elements of DramaDocument21 pagesElements of DramaJann Kharla GularizaNo ratings yet
- 2170Document38 pages2170Princess MerryNo ratings yet
- What Is DramaDocument28 pagesWhat Is DramaGrace JeffreyNo ratings yet
- Bahan Ajar Pengkajian Drama InggrisDocument88 pagesBahan Ajar Pengkajian Drama Inggrisahmadjordi475No ratings yet
- Theater ArtsDocument14 pagesTheater ArtsRoriel Hernandez Benamir100% (2)
- Elements of DramaDocument20 pagesElements of DramaCarlos TabangayNo ratings yet
- Intro To Stage ActingDocument23 pagesIntro To Stage ActingBABIELYN BELAMIDENo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document21 pagesChapter 1PNRNo ratings yet
- Elements of Drama TheatreDocument23 pagesElements of Drama Theatrederghal100% (1)
- Elementsoftheaterbyshairalim 160731094015Document11 pagesElementsoftheaterbyshairalim 160731094015Shayne De Castro VisayanaNo ratings yet
- Theatre VocabularyDocument4 pagesTheatre VocabularyRubén LópezNo ratings yet
- Elements of DramaEDIDocument23 pagesElements of DramaEDIMARY ANGELINE BUGAYNo ratings yet
- Elements of DramaDocument19 pagesElements of DramaOmnia OthmanNo ratings yet
- Outline of Performing ArtsDocument3 pagesOutline of Performing Artsdobojac73No ratings yet
- Introduction To The Theatre DirectingDocument13 pagesIntroduction To The Theatre Directingblv1227100% (1)
- Theater: Grades Prek - 12Document10 pagesTheater: Grades Prek - 12Takhai MohamedNo ratings yet
- Final Study Guide THE 191Document7 pagesFinal Study Guide THE 191Maggie ReillyNo ratings yet
- Elements of DramaDocument20 pagesElements of DramaKorfa Alutaya100% (1)
- UGRC 160-Introduction To Literature Session 11Document8 pagesUGRC 160-Introduction To Literature Session 11OFORINo ratings yet
- Theater Glossary: A Tempo: A Musical Marking Meaning That The Music Has Returned To The Original Speed of The SongDocument7 pagesTheater Glossary: A Tempo: A Musical Marking Meaning That The Music Has Returned To The Original Speed of The SongSarah Bird PassemarNo ratings yet
- Stage Direction and TerminologyDocument2 pagesStage Direction and TerminologybgentryNo ratings yet
- Directing Lot2 PDFDocument90 pagesDirecting Lot2 PDFRalph AbaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7. Drama and TheaterDocument22 pagesLesson 7. Drama and TheaterPatrick SapieraNo ratings yet
- What I S D Rama?Document47 pagesWhat I S D Rama?Didith RobielosNo ratings yet
- Words and Terms You Should KnowDocument31 pagesWords and Terms You Should KnowetetwNo ratings yet
- Patch UpDocument11 pagesPatch UpellamaybullosNo ratings yet
- Original Performance With The Use of MediaDocument25 pagesOriginal Performance With The Use of MediaPom Gach71% (7)
- Elements of Drama CW - AutoRecoveredDocument42 pagesElements of Drama CW - AutoRecoveredYhed ZmadNo ratings yet
- Elt 213 (Reporting)Document47 pagesElt 213 (Reporting)trishagamayNo ratings yet
- What Are The Elements of DramaDocument17 pagesWhat Are The Elements of DramaFatria MointiNo ratings yet
- Break a Leg!: An Actor's Guide to Theatrical Practices, Phrases, and SuperstitionsFrom EverandBreak a Leg!: An Actor's Guide to Theatrical Practices, Phrases, and SuperstitionsNo ratings yet
- l9 1 Probability NotesDocument12 pagesl9 1 Probability Notesapi-201512422No ratings yet
- Jordankirby Resume April2016Document1 pageJordankirby Resume April2016api-201512422No ratings yet
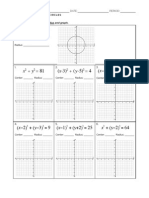
- Activitysheet CirclesDocument2 pagesActivitysheet Circlesapi-201512422No ratings yet
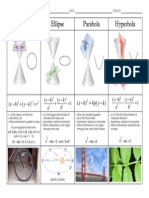
- Conicsections ReferencesheetDocument1 pageConicsections Referencesheetapi-201512422No ratings yet
- Unit11 PlanDocument1 pageUnit11 Planapi-201512422No ratings yet
- Lessonplan GraphingcirclesDocument2 pagesLessonplan Graphingcirclesapi-201512422No ratings yet
- Unit 6 PlanDocument1 pageUnit 6 Planapi-201512422No ratings yet
- Unit 9 PlanDocument1 pageUnit 9 Planapi-201512422No ratings yet
- Unit12 PlanDocument1 pageUnit12 Planapi-201512422No ratings yet
- Unit 8 PlanDocument1 pageUnit 8 Planapi-201512422No ratings yet
- Unit10 PlanDocument1 pageUnit10 Planapi-201512422No ratings yet
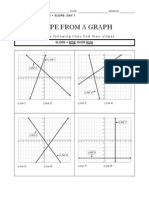
- Slope Worksheet 1graphsDocument2 pagesSlope Worksheet 1graphsapi-201512422No ratings yet
- Unit 5 PlanDocument2 pagesUnit 5 Planapi-201512422No ratings yet
- Unit 7 PlanDocument1 pageUnit 7 Planapi-201512422No ratings yet
- Jordankirby Classroommanagement March2013Document18 pagesJordankirby Classroommanagement March2013api-201512422No ratings yet
- Unit 2 PlanDocument2 pagesUnit 2 Planapi-201512422No ratings yet
- Unit 3 PlanDocument2 pagesUnit 3 Planapi-201512422No ratings yet
- l9 1 Quiz VBDocument1 pagel9 1 Quiz VBapi-201512422No ratings yet
- Acting QuizDocument1 pageActing Quizapi-201512422No ratings yet
- Unit 1 PlanDocument2 pagesUnit 1 Planapi-201512422No ratings yet
- Refmat Mathg07Document2 pagesRefmat Mathg07api-201512422No ratings yet
- Staar Formula Chart Grade8Document2 pagesStaar Formula Chart Grade8api-201512422No ratings yet
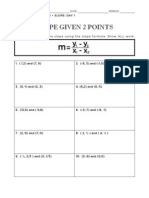
- Slope Worksheet 2pointsDocument1 pageSlope Worksheet 2pointsapi-201512422No ratings yet
- l9 1 Quiz VaDocument1 pagel9 1 Quiz Vaapi-201512422No ratings yet
- ThefourthwallDocument1 pageThefourthwallapi-201512422No ratings yet
- Lessonplan Algebrai Slope Notes SlopedudeDocument1 pageLessonplan Algebrai Slope Notes Slopedudeapi-201512422No ratings yet
- Finding The Slope of A LineDocument31 pagesFinding The Slope of A Lineapi-201512422No ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument5 pagesResearch Methodologysonal gargNo ratings yet
- Learning Area Grade Level Quarter Date: English 10 4Document4 pagesLearning Area Grade Level Quarter Date: English 10 4Yuki50% (8)
- Say. - .: Examining Contemporary: Tom Daley's Something I Want To Celebrity, Identity and SexualityDocument5 pagesSay. - .: Examining Contemporary: Tom Daley's Something I Want To Celebrity, Identity and SexualityKen Bruce-Barba TabuenaNo ratings yet
- Cohort 2 Assignment Essay FinalDocument4 pagesCohort 2 Assignment Essay Finalapi-652640066No ratings yet
- Eniserver Quickstart EDocument14 pagesEniserver Quickstart EYESSER CHANNANo ratings yet
- HeartCry Magazine Summer 2022 WebsiteDocument29 pagesHeartCry Magazine Summer 2022 WebsiteefraNo ratings yet
- Final Research Proposal-1Document17 pagesFinal Research Proposal-1saleem razaNo ratings yet
- THE STUDY OF THE TESTIMONIES. - No. 1. A Series Presented at The 1893 General Conference Session by ELDER J. N. LOUGHBOROUGHDocument16 pagesTHE STUDY OF THE TESTIMONIES. - No. 1. A Series Presented at The 1893 General Conference Session by ELDER J. N. LOUGHBOROUGHKunedog1No ratings yet
- 1903 Er19031211Document22 pages1903 Er19031211Tullio OpattiNo ratings yet
- Akbar Early YearsDocument25 pagesAkbar Early YearsSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Abella vs. CSCDocument17 pagesAbella vs. CSCRocky Diente SenupeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument21 pagesIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human Personanon_254928515No ratings yet
- 5.1 ReteachDocument2 pages5.1 ReteachCarlos Pastrana0% (1)
- Data ListDocument239 pagesData Listpriyanka chithran100% (1)
- CONTARE Notes and ReviewerDocument4 pagesCONTARE Notes and ReviewerApong VillegasNo ratings yet
- Suitcase Lady Christie Mclaren ThesisDocument7 pagesSuitcase Lady Christie Mclaren ThesisWriteMyPaperForMeCheapNewHaven100% (2)
- Brahm Dutt v. UoiDocument3 pagesBrahm Dutt v. Uoiswati mohapatraNo ratings yet
- E2.d Solar System FlipbookDocument39 pagesE2.d Solar System FlipbookSaurabh100% (1)
- HRA Strategic PlanDocument40 pagesHRA Strategic PlanjughomNo ratings yet
- Food and Medicine Label 1-50Document11 pagesFood and Medicine Label 1-50Muthia KumalaNo ratings yet
- A Translation Quality Assessment of Two English Translations of Nazım HikmetDocument14 pagesA Translation Quality Assessment of Two English Translations of Nazım HikmetIntzarEltlNo ratings yet
- Applications of Digital - Image-Correlation Techniques To Experimental MechanicsDocument13 pagesApplications of Digital - Image-Correlation Techniques To Experimental MechanicsGustavo Felicio PerruciNo ratings yet
- Emotional IntelligenceDocument5 pagesEmotional Intelligenceマリージョー 玄波楼No ratings yet
- 4.5 Roces v. HRETDocument1 page4.5 Roces v. HRETZepht Badilla100% (1)
- Professional Ethics in Human ValuesDocument25 pagesProfessional Ethics in Human Valuesdips03275% (4)
- PERENNIALISMDocument2 pagesPERENNIALISMDaisy Rose TangonanNo ratings yet
- Mendezona vs. OzamizDocument2 pagesMendezona vs. OzamizAlexis Von TeNo ratings yet
- MailEnable Standard GuideDocument53 pagesMailEnable Standard GuideHands OffNo ratings yet
- RCBC Capital Corporation Vs Banco de OroDocument18 pagesRCBC Capital Corporation Vs Banco de OroLove HatredNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document7 pagesPresentation 1Funio KhanNo ratings yet