Professional Documents
Culture Documents
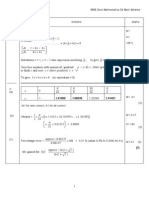
D 16) 1 (1 ) 4) 1 - (Arsinh: January 2006 6675 Pure Mathematics P5/FP2 Mark Scheme
Uploaded by
ykkamOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
D 16) 1 (1 ) 4) 1 - (Arsinh: January 2006 6675 Pure Mathematics P5/FP2 Mark Scheme
Uploaded by
ykkamCopyright:
Available Formats
January 2006 6675 Pure Mathematics P5/FP2 Mark Scheme
1
Question
Number
Scheme Marks
1
2
16 ) 1 ( 17 2
2 2
+ = + x x x
I = x
x
d
16 ) 1 (
1
4
1
2
}
+
= [ ]
4
) 1 - (
arsinh
x
or equiv. = arsinh
[ M1 does not require limits; A1 f.t. on completing square, providing arsinh ]
Into ln form
(
+ + 1
16
9
4
3
ln [ ; = ln2
[ If straight to ln form : B1, ln
(
+ + 16 ) 1 ( ) 1 (
2
x x M1
Using limits correctly M1A1 , ln2 A1 ]
(a) Using ; ) 1 (
2 2 2
= e a b [ 4 = 16 ) 1 (
2
e ] e =
2
5
or equiv. (1.12)
(b) Distance between foci = 2 a e [ 2 x 4 x
2
5
] ; = 4 5
[ A1 dependent on both Ms ]
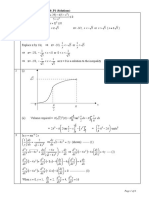
(c) Ellipse, centred on origin
Hyperbola, both branches
Totally correct, touching, with
correct intercepts
B1
M1 A1
M1A1
[5]
M1A1
(2)
M1A1
(2)
B1
B1
B1
(3)
[7]
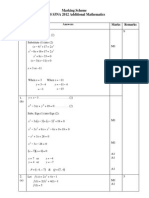
January 2006 6675 Pure Mathematics P5/FP2 Mark Scheme
2
3
4
, sin
d
d
, cos 1
d
d
t
t
y
t
t
x
= + = (both)
( ) t t t s d ) (sin ) cos 1 (
2 2
}
+ + = ; = t t d cos 2 2
}
+
Use of half-angle formula ] d cos 4 [
2
t t
}
; s =
|
.
|
\
|
(
2
(
) 0 (
2
sin 4
t
Using limits correctly and surd form; = 2 2 (allow )
2
4
(a) Using cosh
2
e e
x x
x
+
= and attempt to progress
Correct intermediate step as far as
(
|
|
.
|
\
| +
|
|
.
|
\
| + + +
2
e e
3
8
e e 3 e 3 e
4
3 3 x x x x x x
= x
x x
3 cosh
2
e e
3 3
=
+
(b) Using part (a) to reduce to cosh
2
x = [ 2 ]
Correct method to form ln x or find e
X
or e
2 x
x = ln ( ) 1 2 + , ln ( ) 1 2 or equivalent
or ln ( ) 2 2 3 + , ln ( ) 2 2 3 , ( after finding e
2 x
= )
B1
M1A1
M1A1
M1A1
[7]
M1
A1
A1 (3)
M1
M1
A1 A1
(4)
[7]
3
Question
Number
Scheme Marks
5
6
x x x
x x
y
tan tan sec .
sec
1
d
d
= = ; x =
x x x
dx
y
s
c
c
d tan 1 ( d
d
1 (
2
2
} }
+ = |
.
|
\
|
+ =
= ( ) ) ( tan sec ln ; d sec c x x x x + + =
}
or equivalent
Method to find c: c x s + + = = = ) 3 2 ( ln 0
3
, 0
c = ) 3 2 ( ln + or
12
5
tan ln
or 1.32
= s + ) tan (sec ln ) 3 2 ( ln + or equivalent
(a) x x
x
y
sinh cosh 3
d
d
2
=
x x x
x
y
2 3
2
2
sinh cosh 6 cosh 3
d
d
+ = or equivalent
Application of formula for radius of curvature [ =
( )
x x x
x x
2 3
2
3
2 4
sinh cosh 6 cosh 3
sinh cosh 9 1
+
+
]
Use of sinh
2
x = x
2
cosh 1
=
( )
)} 1 ( 2 { 3
) 1 ( 9 1
2 2
2
3
2 4
+
+
c c c
c c
=
( )
)} 2 3 { 3
1 9 9
2
2
3
4 6
+
c c
c c
AG
(b) cosh x =
4
5
Using found value of cosh x in formula for ; = 4.8
B1B1
M1
A1A1
M1
A1
A1
[8]
B1
M1A1
M1
M1
A1*
(6)
B1
M1A1
(3)
[9]
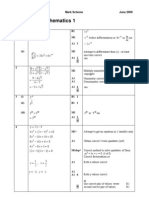
4
7
(a) x x x n x x I
n n
n
d ) 4 (
3
2
) 4 (
3
2
2
3 4
0
1
4
0
2
3
+
(
(
=
}
= x x x n
n
d ) 4 (
3
2
2
3 4
0
1
}
= x x x n x x x n
n n
d ) 4 (
3
2
d ) 4 ( 4
3
2
2
1 4
0
2
1 4
0
1
} }
n n n
I n I n I
3
2
3
8
1
=
[ ( )
1
8 3 2
= +
n n
I n I n ]
1
3 2
8
+
=
n n
I
n
n
I AG
(b) Relating
2
I to
0
I using result from (a)
2
I =
5
8
.
7
16
0
I =
105
2048
|
.
|
\
|
105
53
19
M1A1
A1
M1A1
A1*
(6)
M1
A1A1
(3)
[9]
5
8 (a) ar tanh
|
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
=
2
1
1
2
1
1
ln
2
1
2
1
or equivalent
=
(
+
+
+
1 2
1 2
x
1 2
1 2
ln
2
1
or equivalent
= ( ) ( ) 1 2 ln 1 2 ln
2
1
2
+ = + AG
Alternative Approach
If using = y ar tanh (sin x) |
.
|
\
|
=
2
1
tanh y [ or cosh
2
= y 2 ]
and then use exponentials:
Progression as far as ....... e ....... e
2y y
= = or M1
Converting to ln form M1
Answer as given A1*
Note: ( ) 2 2 3 ln
2
1
+ can earn M1M1 but for A1* there must be a
convincing further step.
(b) x
x
x
x
x x
y
sec
cos
cos
; cos .
sin 1
1
d
d
2 2
= =
=
Note: If x y sin tanh = is differentiated M1 requires ) ( f
d
d
x
x
y
=
(c) Attempt at by parts and use of result in (b)
=
}
+ x x x x x d d sec cos ) (sin tanh ar cos
= x x x + ) (sin tanh ar cos
Using limits correctly : = ( )
4
2 1 ln
2
1
+ + or exact equivalent
M1
M1
A1*
(3)
M1A1
(2)
M1
A1
M1
M1A1
(5)
[10 ]
6
9
(a) Correct method for finding
x
y
d
d
(
P
1
Gradient of normal = p
Equation of normal: ) )( ( 2
2
ap x p ap y =
3
2 ap ap px y + = + AG
(b) Using both equations and eliminating x or y
) ( ) ( 2 ) (
3 3
q p a q p a x q p + = may be unsimplified
) ( 2
2 2
q pq p a a x + + + =
Finding the other coordinate
) ( q p apq y + =
(c) Using pq = 3 in both x and y (in any form)
[ ) ( 3 ), 5 (
2 2
q p a y q p a x + = + + = ]
Complete method for relating x and y, independent of p and q
A correct equation, in any form
[ e.g. : ) 2 ( 9
2 2 2 2
pq q p a y + + = =
)
`
+ |
.
|
\
|
6
5
9
2
a
a x
a ]
) ( 9
2
a x a y + =
M1
A1
M1
A1*
(4)
M1
A1
A1
M1
A1
(5)
M1
M1
A1
A1
(4)
[13]
You might also like
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- C4 January 2006 Mark SchemeDocument6 pagesC4 January 2006 Mark Schemeshariz500No ratings yet
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsFrom EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Seafield 2013 M1 (Q&A)Document8 pagesSeafield 2013 M1 (Q&A)STPMmathsNo ratings yet
- FP3 P6 January 2006 Mark SchemeDocument5 pagesFP3 P6 January 2006 Mark SchemeFitri Azmeer NordinNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- c4 Jan 2008 MsDocument21 pagesc4 Jan 2008 MsMk D. AssassinoNo ratings yet
- GCE Maths Marking Scheme SolutionsDocument31 pagesGCE Maths Marking Scheme SolutionsElinorRoutleyNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- EDEXCEL PURE MATHEMATICS P5 MARK SCHEMEDocument8 pagesEDEXCEL PURE MATHEMATICS P5 MARK SCHEMEMichael HartNo ratings yet
- c4 Jan 2009 MsDocument25 pagesc4 Jan 2009 MsMk D. AssassinoNo ratings yet
- 3NA SA1 (AM Solution)Document8 pages3NA SA1 (AM Solution)johnlim199No ratings yet
- C4 Integration AnswersDocument9 pagesC4 Integration AnswersAhmad HussainNo ratings yet
- FP2 Practice Paper A Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesFP2 Practice Paper A Mark Schemejimbolina92100% (1)
- GCE Mathematics Core Mathematics C3 (6665) Mark Scheme January 2007Document7 pagesGCE Mathematics Core Mathematics C3 (6665) Mark Scheme January 2007Fahema ShafiNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Jan 2008Document59 pagesMark Scheme Jan 2008Lee StaplesNo ratings yet
- AI AA SL Core Diagnostic Test Ch. 1 3-5 Suggested SolutionsDocument26 pagesAI AA SL Core Diagnostic Test Ch. 1 3-5 Suggested SolutionsAlexandr BostanNo ratings yet
- 2016 2 KL SMK Methodist - Maths QADocument12 pages2016 2 KL SMK Methodist - Maths QAlingbooNo ratings yet
- Alevel C3C4Document59 pagesAlevel C3C4nuddin123No ratings yet
- (Maximum Mark: 7) : X GFX X XDocument5 pages(Maximum Mark: 7) : X GFX X Xsanand11No ratings yet
- C1 Core Mathematics Mark SchemeDocument12 pagesC1 Core Mathematics Mark Schemealyona1295No ratings yet
- FP2 Practice Paper B Mark SchemeDocument3 pagesFP2 Practice Paper B Mark Schemejimbolina92100% (2)
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument8 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2012: AEA Mathematics (9801)Document8 pagesMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2012: AEA Mathematics (9801)will bellNo ratings yet
- Kepong Baru 2012 M1 (A)Document8 pagesKepong Baru 2012 M1 (A)STPMmathsNo ratings yet
- C1 MS June 2009Document4 pagesC1 MS June 2009Chris WadsworthNo ratings yet
- Edexcel C3 June 2005 To June 2011 All Questions Mark SchemeDocument44 pagesEdexcel C3 June 2005 To June 2011 All Questions Mark SchemeOrhan AtestemurNo ratings yet
- SPM 2012 - FullDocument27 pagesSPM 2012 - FullWong Weng SonNo ratings yet
- Mathematics SPM 2011.powerpointDocument55 pagesMathematics SPM 2011.powerpointuzai88No ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Jan 2005Document116 pagesMark Scheme Jan 2005OE94No ratings yet
- Math Quest Math Methods VCE 12 (2016 Edition)Document542 pagesMath Quest Math Methods VCE 12 (2016 Edition)NhiNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument8 pagesAnswer All Questions in This SectionSK67% (3)
- 2005 Jan MS PDFDocument4 pages2005 Jan MS PDFeconomides1No ratings yet
- Tun Hussein Onn 2013 M1 (A)Document6 pagesTun Hussein Onn 2013 M1 (A)STPMmathsNo ratings yet
- Math Challenge Problem SolutionsDocument3 pagesMath Challenge Problem Solutions72 Tanvir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Subject Review of IB 2023 Year - 1Document63 pagesSubject Review of IB 2023 Year - 1Duru SavdaNo ratings yet
- 2014 2 NSEMBILAN KGVseremban Maths QADocument7 pages2014 2 NSEMBILAN KGVseremban Maths QASK0% (1)
- 2014 2 WPERSEKUTUAN SMKMethodistKL Maths QADocument6 pages2014 2 WPERSEKUTUAN SMKMethodistKL Maths QASK100% (2)
- 2010 AJC Paper 1solDocument6 pages2010 AJC Paper 1solnothingtodo1992No ratings yet
- 2014 2 MELAKA SMK Gajah Berang - MATHS QADocument6 pages2014 2 MELAKA SMK Gajah Berang - MATHS QASK67% (3)
- C2 Mock Paper MSDocument5 pagesC2 Mock Paper MSZaviyaniNo ratings yet
- January 2005 6664 Core Mathematics C2 Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesJanuary 2005 6664 Core Mathematics C2 Mark SchemeAravind PerinpanathanNo ratings yet
- 2008 h2 Math Prelim p1 (Solns)Document19 pages2008 h2 Math Prelim p1 (Solns)Utsav NiroulaNo ratings yet
- 2016 Calculus Exam 2Document13 pages2016 Calculus Exam 2lllloNo ratings yet
- Maths Paper 1 Nov Making 2003Document10 pagesMaths Paper 1 Nov Making 2003PriscaNo ratings yet
- FX X X X Orx X X X FX X X: Test 1 SolutionsDocument4 pagesFX X X X Orx X X X FX X X: Test 1 SolutionsexamkillerNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Solution 9Document4 pagesWorksheet Solution 9abdelrahmanhelal13No ratings yet
- Co-Ordinate Geometry A-1Document6 pagesCo-Ordinate Geometry A-1amanNo ratings yet
- Penilaian Menengah Rendah: Final Answer (A) in Its Simplest FormDocument51 pagesPenilaian Menengah Rendah: Final Answer (A) in Its Simplest FormNorliha JamilNo ratings yet
- Sem 0203 Test 1Document2 pagesSem 0203 Test 1Adel AshyapNo ratings yet
- C3 January 2006 Mark SchemeDocument6 pagesC3 January 2006 Mark SchemeTaqsim RajonNo ratings yet
- JC2 Mid-Year Exam SolutionsDocument15 pagesJC2 Mid-Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- One Mark For Each Intercept Down Ward.: A A X yDocument14 pagesOne Mark For Each Intercept Down Ward.: A A X yKarabo MailulaNo ratings yet
- Test 3 - SMJKCH (Kota Bharu) - AnsDocument8 pagesTest 3 - SMJKCH (Kota Bharu) - AnsLIM YEE WEN MoeNo ratings yet
- MathDocument7 pagesMathglitteryanonNo ratings yet
- Maths MSDocument12 pagesMaths MSUNDERWORLD MAFIANo ratings yet
- MATH161 Exam 2 Solutions and FormulasDocument4 pagesMATH161 Exam 2 Solutions and FormulasRoba El GhorNo ratings yet
- C4 Mock MSDocument5 pagesC4 Mock MSmahamidahmedNo ratings yet
- UKMT Senior Math Challenge questionsDocument2 pagesUKMT Senior Math Challenge questionsykkamNo ratings yet
- Additional Math OCR 04 JUN With MsDocument17 pagesAdditional Math OCR 04 JUN With MsykkamNo ratings yet
- d1 QP Jannny 200132Document13 pagesd1 QP Jannny 200132Tom SnellingNo ratings yet
- s1 QP SpecimenDocument5 pagess1 QP SpecimenKasra AnsariNo ratings yet
- Journal of Environmental Sciences research on morphology changes of coking coal during cokingDocument4 pagesJournal of Environmental Sciences research on morphology changes of coking coal during cokingJohan Pranata BarusNo ratings yet
- Partial Differential Equations Formula SheetDocument3 pagesPartial Differential Equations Formula SheetnewyorkstudyNo ratings yet
- What Happens When Warm Air RisesDocument30 pagesWhat Happens When Warm Air RisesCriselAlamag100% (1)
- FLUIDME Quiz 02 AnswersDocument5 pagesFLUIDME Quiz 02 AnswersSam Denielle TugaoenNo ratings yet
- Slide Micro Teaching 5.3Document18 pagesSlide Micro Teaching 5.3Mastura MohamadNo ratings yet
- L-3/T-2/CE Date: 07/08/2016Document30 pagesL-3/T-2/CE Date: 07/08/2016নীল জোছনা0% (1)
- CH 3 Concept of ViscosityDocument11 pagesCH 3 Concept of ViscosityJenny ChenNo ratings yet
- Art AnalysisDocument3 pagesArt AnalysisCheeny VelascoNo ratings yet
- Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman Equation ExplainedDocument7 pagesHamilton-Jacobi-Bellman Equation ExplainedMakinita CerveraNo ratings yet
- Skema Chemistry Paper 3Document8 pagesSkema Chemistry Paper 3nurul atiqahNo ratings yet
- University of Engineering and Technology Peshawar, PakistanDocument54 pagesUniversity of Engineering and Technology Peshawar, PakistanJoachim GardNo ratings yet
- System Modelling and SimulationDocument260 pagesSystem Modelling and SimulationArvind Kumar100% (13)
- Maximum Material Boundary (MMB) and Its Advantages in GD&T Analysis PDFDocument6 pagesMaximum Material Boundary (MMB) and Its Advantages in GD&T Analysis PDFSangeethaNo ratings yet
- Thesis MainDocument144 pagesThesis MainIvan GrkajacNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchangers Types & Applications, LMTD Derivation & ProblemsDocument11 pagesHeat Exchangers Types & Applications, LMTD Derivation & Problemsananth2012No ratings yet
- Mean Deviation - Wolfram MathWorldDocument4 pagesMean Deviation - Wolfram MathWorldbraulio.dantas-1No ratings yet
- Engineering Failure Analysis: Ayad Subhy, Davide Lo Presti, Gordon AireyDocument11 pagesEngineering Failure Analysis: Ayad Subhy, Davide Lo Presti, Gordon AireyMohamed BoudabbousNo ratings yet
- BEYOND SYLLABUS: CURVED, COMPOSITE, UNSYMMETRICAL BEAMSDocument11 pagesBEYOND SYLLABUS: CURVED, COMPOSITE, UNSYMMETRICAL BEAMSVignesh VickyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Thermal Expansion: EXERCISE 122, Page 266Document9 pagesChapter 22 Thermal Expansion: EXERCISE 122, Page 266NurulAinMatAron0% (1)
- Homework #02 (Phy 112) SolutionsDocument19 pagesHomework #02 (Phy 112) SolutionsKvn4N6No ratings yet
- Astronomy Unit Resources SchoolpointeDocument17 pagesAstronomy Unit Resources SchoolpointeShekel DeninoNo ratings yet
- MCQ Electromagnetism Self-AssessmentDocument2 pagesMCQ Electromagnetism Self-AssessmentJunaidKhanNo ratings yet
- Physics Questions Part 3Document8 pagesPhysics Questions Part 3Muhammad HuzaifaNo ratings yet
- The Planets Comparative Superlative - 87358Document2 pagesThe Planets Comparative Superlative - 87358Maria AdamNo ratings yet
- Pure Substances Mixtures and SolutionsDocument18 pagesPure Substances Mixtures and SolutionsJoanna Angela LeeNo ratings yet
- On Errors of Fit and Accuracy in Matching Synthetic Seismograms and Seismic TracesDocument21 pagesOn Errors of Fit and Accuracy in Matching Synthetic Seismograms and Seismic TracesBSSNo ratings yet
- Cluster ExpansionDocument4 pagesCluster ExpansionflytrapsolNo ratings yet
- Materials Finer Than 75 - M (No. 200) Sieve in Mineral Aggregates by WashingDocument3 pagesMaterials Finer Than 75 - M (No. 200) Sieve in Mineral Aggregates by WashingLucio Rodriguez SifuentesNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics PDFDocument51 pagesElectrostatics PDFSaksham GuptaNo ratings yet
- BelowsDocument35 pagesBelowstejassidhpuraNo ratings yet