Professional Documents
Culture Documents
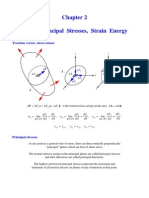
R R DX T: Plate Bending
Uploaded by
jianjungbdOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
R R DX T: Plate Bending
Uploaded by
jianjungbdCopyright:
Available Formats
y
x
y
+ collect
x
, E ,
y
x y
z
x
z
y
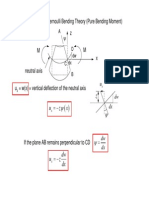
Plate Bending
not so long plate
previously have shown: M
2
x
w
d
d
2
:=
x
. this was for single axis bending. D
this relationship holds for the partial derivative in the respective direction fo both x and y;
assumptions:
plane cross section remains plane
small deflections w
max
< 3/4 t
stress < yield
w w(x, y) =
1
d
2
1
d
2
R
x
=
2
w(x,y)
R
y
=
dy
2
w(x,y)
dx
we are making no statement with respect to
y
(or any other ) as we did in long plate.
d
2
x
:=
R
1
x
z
x
:= z
d
d
x
2
2
w(x,y)
y
:=
R
1
y
z
y
:= z
dy
2
w(x,y)
x
x
x
:=
y
y
:=
y
y
E E E E
y
)
x
+
y
collect ,
x
, E
=>
x
:=
E
(
x
+
1
2
1 notes_23_plate_bending.mcd
dz
z
rx
ry
dy
dx
t
y
x y
t t
y
x
y
x y
y
substituting
into
y
:= z
d
2
2
w x, y)
x
:= z
d
2
2
w x, y)
x
:=
E
(
x
+ ( (
y
)
dy dx
1
2
x
E
|
z
d
d
d
w x, y) z
dy y
w x, y)
.
|
or ...
x
z
|
( (
|
1
2
\
dx x
(
d
d
d
(
( ) := z
1
E
2
\
d
d
x
2
2
w x, y) +
d
d
y
2
2
w x, y)
.
( (
similarly:
y
:= z
E
|
d
2
2
w x, y) +
d
2
2
w x, y)
|
1
2
\
dy dx
.
as in bending (applied in each of x and y direction): see figure Hughes 9.3 (below)
the lower case m denotes moment per unit length
note that the designation is changed: the subscript on the m refers to the direction of axial stress
t t
2
2
( (
( )z dz m
y
:= (
y
z dz m
x
:= (
x
z
( (
t
2 2
d d
w x, y) +
d d
w x, y) d d
w x, y) +
d
d
d
w x, y)
m
y
12
t
3
E
dy y
(
1 +
2
d
( (
1 d dx x
(
d dy y
m
x
1
t
3
E
dx x
12
1 +
2
with
E t
3
D :=
12
(
1
2
)
d
2
|
d
2 |(
(
|
d
2
d
2 |
m
x
:= D
2
w(x,y) +
2
w(x,y) m
y
:= D
2
w(x,y) +
2
w(x,y)
(
dx
\
dy
. \
dy dx
.
in the general plate case there may exist a twisting moment m
xy
we need to derive a similar expresssion for this moment
from basic shear strain relationships: :=
d
v +
d
u; := G and := G
d
v +
d
u
dx dy dx dy
2 notes_23_plate_bending.mcd
x y
t
yx
m
yx
x,u
dw/dx
u=-z*dw/dx
z
du/dy
dx
dy
dv/dx
y,v
from the geometry of the slope of w in each direction (x and y): u := z
d
w(x,y) and v := z
d
w(x,y)
dx dy
=> := 2Gz
d d
w x, y) and the twisting moment per unit length is determined by: (
dx y xd
t
2
(
(
minus sign comes from sense of mxy +
m
xy
:= ( z dz m
xy
1
t
3
G
d
d
d
w x, y)
and xy(+)*z(+) see figure Hughes 9.3
(
t
6 dy x
below
2
Et
3
(
x y
using: G:=
2 1
E
+
)
=> m
xy
:=
d
dx
|
\
d
d
w(x,y)
.
|
12
(
1 +
)
d |d
Et
3
(
1
)
multiply and divide by (1-) =>
m
xy
:=
dx y
w(x,y)
.
|
12
(
1 +
)
(
1
)
x
\
d
d |
d
Et
3
(
m
xy
:=
dx y
w(x,y)
.
|
12
(
1
2
)
(
1
)=>
m
xy
:= D 1
)
d
x
\
|
d
d
w(x,y)
|
.
(
(
x
\
d
dx y
due to the complimentary nature of shear stress
xy
:=
yx
and due to the sign convention for + moment m
xy
:= m
yx
=> m
yx
:= D
(
1
)
d |
d
w(x,y)
|(
(
x
\
d
dx y
.
3 notes_23_plate_bending.mcd
m
yx
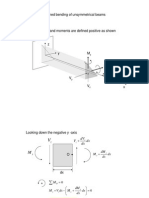
now for equilibrium of the dx, dy, dz segment:
see Hughes figure 9.3 forces and moments in a plate (below)
x
y
t
mx
my
my+dmy/dy*dy
mx+dmx/dx*dx
qx+dqx/dx*dx
qy+dqy/dx*dx
myx+dmyx/dy*dy
mxy+dmxy/dx*dx
qy
qx
mxy
myx
z
Hughes figure 9.3 forces and moments in a plate
q in this context is the shear force per unit length on each face:
q
x
* the distance dy is the force on the x face etc...
equilibrium of vertical forces => p is the lateral (+z direction) load per unit area - not shown on figure
q
x
+
|d
q
x
|
dx
(
(
dy q
x
dy +
q
y
+
|
\
d
d
y
q
y
.
|
dy
(
(
dx q
y
dx + p dxdy = 0
=>
d
d
x
q
x
+
d
d
y
q
y
+ p = 0
\
dx
.
moments wrt the x axis =>
m
xy
+
\
|
d
d
x
m
xy
|
.
dx
(
(
dy m
xy
dy + m
y
dx
m
y
+
|
\
d
d
y
m
y
.
|
dy
(
(
dx + q
y
dxdy = 0 =>
d
d
x
m
xy
d
d
y
m
y
+ q
y
= 0
and similarly: taking moments wrt the y-axis =>
d d
dy
m
yx
+
dx
m
x
q
x
= 0
or ... since
m
xy
:= m
yx
|
\
d
d
y
m
xy
|
.
+
d
d
x
m
x
q
x
= 0
4 notes_23_plate_bending.mcd
x y
substituting the moment relations
|d | d |d | d
+ q
x
:=
\
dy
m
xy
.
+
dx
m
x
and q
y
:=
\
dx
m
xy
.
dy
m
y
into the shear equation =>
d
d
x
|
\
d
d
y
m
xy
|
.
+
d
d
x
m
x
(
(
+
d
d
y
|
\
d
d
x
m
xy
.
|
+
d
d
y
m
y(
(
+ p = 0
d
2
d d d
2
2
m
x
2
dx y
m
yx
+
dy
2
m
y
+ p = 0
dx
d
substituting the relations fro m
x
, m
y
and m
xy
above =>
d d
(
d
2
2
d
d
x
2
2
w(x,y) +
\
|
d
d
y
2
2
w(x,y)
.
|
(
(
(
(
(
(
2
dx y
D 1
)
d
\
|
d
d
w(x,y)
|
(
(
(
(
+
d
2
2
|
d
2
2
w(x,y) +
d
d
x
2
2
w(x,y)
|
.
(
(
(
dx
dx y
. dy
\
dy
= -p
the terms with cancel and the result is:
d
4
4
w(x,y) + 2
d
2
2
d
2
2
w(x,y) +
d
4
4
w(x,y) =
p
dx dx dy dy
D
5 notes_23_plate_bending.mcd
You might also like
- Mechanical Engineering Statics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesMechanical Engineering Statics Formula SheetAlexander Ari Nygaard100% (2)
- QM Notes Townsend PDFDocument439 pagesQM Notes Townsend PDFjake parkNo ratings yet
- Euler-Bernoulli Bending Theory (Pure Bending Moment) ψ z: dw u z dxDocument13 pagesEuler-Bernoulli Bending Theory (Pure Bending Moment) ψ z: dw u z dxeulerintegralNo ratings yet
- AP Calc - Instructor Solutions - Chapter 3Document43 pagesAP Calc - Instructor Solutions - Chapter 3Ishaan GuptaNo ratings yet
- 5.8.1 Governing Equations of Equilibrium of Composite LaminatesDocument11 pages5.8.1 Governing Equations of Equilibrium of Composite LaminatesStefano CanestrelliNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document29 pagesPart 1Boonme ChinnaboonNo ratings yet
- 5÷‹◊‹Ω·Document4 pages5÷‹◊‹Ω·liznNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - 2003 Twist Closed Sections: A) Equilibrium of Wall ElementDocument5 pagesLecture 5 - 2003 Twist Closed Sections: A) Equilibrium of Wall ElementjianjungbdNo ratings yet
- Unsymm BendingDocument29 pagesUnsymm BendingBia MughalNo ratings yet
- Método Por PartesDocument7 pagesMétodo Por PartesGuillermo Jesus Arce MezaNo ratings yet
- Jackson 6.1 Homework Problem SolutionDocument4 pagesJackson 6.1 Homework Problem SolutionJavierNo ratings yet
- Jackson 6.1 Homework Problem SolutionDocument4 pagesJackson 6.1 Homework Problem SolutionMatheus FagundesNo ratings yet
- 1st Order ODE and Its ApplicationsDocument76 pages1st Order ODE and Its ApplicationsMuhammad EhsanNo ratings yet
- FEA101 CourseNotesDocument149 pagesFEA101 CourseNotesRadhikaNo ratings yet
- Worksol2 16Document7 pagesWorksol2 16Joko IsnantoNo ratings yet
- Business Mathematics: Week 9: DifferentiationDocument15 pagesBusiness Mathematics: Week 9: DifferentiationBorhan Nordin DaudNo ratings yet
- Exercises-Exact EquationsDocument4 pagesExercises-Exact EquationsJake GuzmanNo ratings yet
- HW 1.2 SolutionsDocument6 pagesHW 1.2 SolutionsArini MelanieNo ratings yet
- Math24 Exact de (q1)Document4 pagesMath24 Exact de (q1)Rea AbuanNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus: A Little PebbleDocument18 pagesDifferential Calculus: A Little PebbleAshekin MahadiNo ratings yet
- AFEM ch20 SlidesDocument19 pagesAFEM ch20 SlidesERICSEPTIANNo ratings yet
- Vector Integration - GATE Study Material in PDFDocument10 pagesVector Integration - GATE Study Material in PDFTestbook BlogNo ratings yet
- Ploče Opterećenje Na Savijanje: y W X W W K Z W K Z y W y X W 2 X WDocument4 pagesPloče Opterećenje Na Savijanje: y W X W W K Z W K Z y W y X W 2 X WigorNo ratings yet
- Stress - Principal Stresses - Strain EnergyDocument11 pagesStress - Principal Stresses - Strain EnergymanjusitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - IntegrationDocument11 pagesChapter 3 - IntegrationMuhamad NazrinNo ratings yet
- Lec13 (1) Integrals TriplesDocument30 pagesLec13 (1) Integrals TriplesDavid Atilio Dominguez PozoNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Chapter 3 Problems: K (X + y ADocument8 pagesSolutions To Chapter 3 Problems: K (X + y AkalkinatorNo ratings yet
- Calculus: Differentiation RulesDocument17 pagesCalculus: Differentiation RulesAoSd' TikmanNo ratings yet
- HW 2.5 Solutions PDFDocument7 pagesHW 2.5 Solutions PDFharshasg92No ratings yet
- Calculus of Parametric EquationsDocument13 pagesCalculus of Parametric EquationsTwevleNo ratings yet
- 2013 Homework 013solDocument1 page2013 Homework 013soleouahiauNo ratings yet
- Pure Math Cape Unit 1 Parametric DifferentiationDocument8 pagesPure Math Cape Unit 1 Parametric DifferentiationHugh IngramNo ratings yet
- Polar Coordinates: Axi-Symmetric ProblemsDocument8 pagesPolar Coordinates: Axi-Symmetric ProblemsalshaijiNo ratings yet
- Useful MathsDocument1 pageUseful MathsIan LeeNo ratings yet
- Defslt Lec # 03 13-01-21Document7 pagesDefslt Lec # 03 13-01-21AkashNo ratings yet
- X W Q T A T: Plate Bending IntroductionDocument2 pagesX W Q T A T: Plate Bending IntroductionjianjungbdNo ratings yet
- Murray Klamkin Problems 1nbsped 091955816x - CompressDocument1 pageMurray Klamkin Problems 1nbsped 091955816x - CompressRaju RajNo ratings yet
- MAS 201 Spring 2021 (CD) Differential Equations and ApplicationsDocument10 pagesMAS 201 Spring 2021 (CD) Differential Equations and ApplicationsBlue horseNo ratings yet
- CH 03Document22 pagesCH 03Atif AbbasiNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Double IntegralsDocument8 pages2.1 Double Integralsmukesh3021No ratings yet
- Differentiation RevisionDocument4 pagesDifferentiation RevisionMavakise CalvinNo ratings yet
- HomogeneasDocument5 pagesHomogeneasBladimir BahenaNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations HandoutsDocument4 pagesDifferential Equations HandoutsEllimacOdnumrebNo ratings yet
- Functions With Several VariablesDocument36 pagesFunctions With Several VariablesBlackBunny103No ratings yet
- Chap 3 Differential EquationsDocument29 pagesChap 3 Differential Equationsprakash silvarajanNo ratings yet
- 05 FiniteElementMethodDocument83 pages05 FiniteElementMethodmileNo ratings yet
- General Solution Procedure: D W DDDocument6 pagesGeneral Solution Procedure: D W DDSenior JuniorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document15 pagesLecture 3ansgcekNo ratings yet
- Class - Test 2 SolnDocument5 pagesClass - Test 2 SolniitkgpdelNo ratings yet
- Answer: M 1Document36 pagesAnswer: M 1Desmond MunisNo ratings yet
- MTH132 Section 1 & 12, Quiz 3: Name (Print Clearly) : Student NumberDocument2 pagesMTH132 Section 1 & 12, Quiz 3: Name (Print Clearly) : Student Numbermasyuki1979No ratings yet
- Y GT2 A Lec 04 Triple Int 1415Document14 pagesY GT2 A Lec 04 Triple Int 1415Bell PhamNo ratings yet
- L53-Parametric Surfaces and Surface IntegralsDocument28 pagesL53-Parametric Surfaces and Surface IntegralsQuynh-AnhNo ratings yet
- Triple IntegralDocument10 pagesTriple IntegralEnrique MirazoNo ratings yet
- Exercises: Double and Triple Integrals Solutions Math 13, Spring 2010Document8 pagesExercises: Double and Triple Integrals Solutions Math 13, Spring 2010Colls MuntadaNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations #2: Separable Differential EquationsDocument2 pagesDifferential Equations #2: Separable Differential EquationsJunhel Libre JuarezNo ratings yet
- Principal StressesDocument5 pagesPrincipal Stressesavinashn1No ratings yet
- 5 HaftaDocument9 pages5 HaftaUmut UralNo ratings yet
- Plane Stress: Notes 10. September 2014Document4 pagesPlane Stress: Notes 10. September 2014grvmaurya999No ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- 4 Notes 15 Pure Warp PDFDocument6 pages4 Notes 15 Pure Warp PDFjianjungbdNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - 2003 Twist Closed Sections: A) Equilibrium of Wall ElementDocument5 pagesLecture 5 - 2003 Twist Closed Sections: A) Equilibrium of Wall ElementjianjungbdNo ratings yet
- 3 Notes 24 Plate Bendin PDFDocument9 pages3 Notes 24 Plate Bendin PDFjianjungbdNo ratings yet
- X W Q T A T: Plate Bending IntroductionDocument2 pagesX W Q T A T: Plate Bending IntroductionjianjungbdNo ratings yet
- Loads: Primary Stress Allocation, Loads and Design ApproachDocument9 pagesLoads: Primary Stress Allocation, Loads and Design ApproachjianjungbdNo ratings yet
- Shiphandling PDFDocument2 pagesShiphandling PDFjianjungbdNo ratings yet
- Basic Ship-HandlingDocument4 pagesBasic Ship-HandlingjianjungbdNo ratings yet
- Show That The Set of All Solutions To The Nonhomoge-: Spanning SetsDocument10 pagesShow That The Set of All Solutions To The Nonhomoge-: Spanning SetsVictoria RojasNo ratings yet
- Long Answer Type Questions (Part 4)Document15 pagesLong Answer Type Questions (Part 4)Hf vgvvv Vg vNo ratings yet
- Advanced Dynamics: Donald T. GreenwoodDocument24 pagesAdvanced Dynamics: Donald T. GreenwoodSasidhar JannuNo ratings yet
- Strain Energy Density FunctionDocument3 pagesStrain Energy Density Functionjavier_maldonado_12No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Field Theory I (EFT I) /: Dr.-Ing. René MarkleinDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Field Theory I (EFT I) /: Dr.-Ing. René Markleinbhuvana_eeeNo ratings yet
- Uncertainty Principles and Fourier Analysis: Alladi SitaramDocument4 pagesUncertainty Principles and Fourier Analysis: Alladi SitaramVinayak SavarkarNo ratings yet
- Stability Analysis For OdesDocument13 pagesStability Analysis For OdesAbdul Latif AbroNo ratings yet
- Gravity Part 3Document5 pagesGravity Part 3netname1No ratings yet
- Compressibility of Gases - Concept of Corresponding StatesDocument3 pagesCompressibility of Gases - Concept of Corresponding StatesShabir MansuriNo ratings yet
- Alt STD ModelDocument3 pagesAlt STD ModelChris AntoniadesNo ratings yet
- Weigand Introduction To String TheoryDocument178 pagesWeigand Introduction To String TheoryAxel PhilipNo ratings yet
- Observer Effect and Deepak ChopraDocument6 pagesObserver Effect and Deepak ChopraArmands Leimanis100% (1)
- ETD Assignment Presentation 21Document2 pagesETD Assignment Presentation 21shiva snekhaNo ratings yet
- Spectra of CR III ComplexesDocument3 pagesSpectra of CR III ComplexesM Zeeshan aliNo ratings yet
- Molecular SymmetryDocument9 pagesMolecular SymmetryH SNo ratings yet
- Born Approximation Validity Conditions: Ik X 2 3 0 Ik - X X - 0 0 0Document1 pageBorn Approximation Validity Conditions: Ik X 2 3 0 Ik - X X - 0 0 0Keerthi KeerthNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of ElementsDocument27 pagesDual Nature of ElementsTarnate Tacay100% (1)
- Very Special RelativityDocument121 pagesVery Special RelativityGospod Bog100% (1)
- Chapter 17 Electric Fields (A2)Document45 pagesChapter 17 Electric Fields (A2)Pathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- Tanabe Sugano DiagramsDocument16 pagesTanabe Sugano DiagramsKiran WasimNo ratings yet
- MA4006: Exercise Sheet 4: SolutionsDocument12 pagesMA4006: Exercise Sheet 4: SolutionsG SREEHARINo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicasDocument21 pagesThermodynamicasTom Psy100% (1)
- Section 2-3 MatricesDocument17 pagesSection 2-3 MatricesManuela ZahariaNo ratings yet
- CHE222 Material ScienceDocument4 pagesCHE222 Material ScienceJoseph-celestine DonaldNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 8: Solution-NGPE - 2014 PDFDocument1 pagePage 1 of 8: Solution-NGPE - 2014 PDFsampannkumarNo ratings yet
- Instructions: R A R A A RDocument3 pagesInstructions: R A R A A RanhhaikimdongNo ratings yet
- Ncs Mock Exam 2 Xii MathDocument6 pagesNcs Mock Exam 2 Xii MathSania GeorgeNo ratings yet
- BIBO Stability ProofDocument7 pagesBIBO Stability Prooftasos7639No ratings yet