Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Modul MAP 2010 Item Pack
Uploaded by
hamraa84Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Modul MAP 2010 Item Pack
Uploaded by
hamraa84Copyright:
Available Formats
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
1. FUNCTIONS
"IMPORTANT NOTES AND FORMULAE
RELATIONS Relation is a connection between two sets. The relation between two sets can be represented by : (a) An arrow diagram
Set A subtract 1 from Set B
2 3 5
1 2 4
(b) Ordered pairs {(2, 1), (3, 2), (5, 4)} (c) A graph Set B
4 3 2 1 0 1
2 3 4 5
Set A
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
Domain, codomain, object, image and range of a relation The arrow diagram shows the relation squares of between set A and set B.
squares of
1 2 4 Set A
1 4 16 25
Set B
Domain = {1, 2, 4} Codomain = {1, 4. 16, 25} 1, 2 and 4 are objects 1, 4, 16 are images Range = {1, 4, 16} Types of relations (a) One-to-one relation
Set A
one half of
Set B
4 8 10
2 4 5
(b) Many-to-one relation
Set A
factor of
Set B
6 12 14
3 7
(c) One-to-many relation
Set A
multiple of
Set B
3 5
6 9 10
2
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
(d) Many-to-many relation
Set A prime factor of Set B
6 9
2 3
FUNCTIONS A function is a type of relation where each object in the domain has only one image in the codomain. A one-to-one relation and many-to-one relation can be a function. Function notation
Set A
f
Set B
x is the object y is the image of x under f.
In function notation, y is expressed in terms of x. Example. f : x 2x 1 or f (x) = 2x 1
COMPOSITE FUNCTIONS g f A B x y
C z
f ( x) = y g(y) = z g[f (x)] = z
gf
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
INVERSE FUNCTIONS o For a function f : x y, the inverse function is denoted as f A x f B y
1
: y x.
f 1 For example : Given that f : x 2x + 1, find f Solution : Method 1 Let y = 2x + 1 2x = y 1 y 1 x= 2 x 1 f 1 ( x ) = 2
1
(x).
Method 2 Let f
1
( x) = a
f (a) = x Since f (x) = 2x + 1 f (a) = 2a + 1 = x x 1 a= 2
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 1JJ
1. Diagram 1 shows the relation between set A and set B. Rajah 1 menunjukkan hubungan di antara set A dan set B.
a b c
Set A
p q r s
Set B
Diagram 1 / Rajah 1 State Nyatakan (a) the range of the relation, julat hubungan itu, (b) the type of the relation. jenis hubungan itu.
Answer : (a) .. (b) .. 2. Diagram 2 shows the function f : x 2 m x . Rajah 2 menunjukkan fungsi f : x 2 m x . x 3 5
Diagram 2 / Rajah 2
2m x 9 a
Find Cari (a) the value of m, nilai bagi m, (b) the value of a. nilai bagi a.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
Answer : (a) m = .... (b) a = .....
5
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
3.
In Diagram 3, the functions g maps x to y and the function h maps y to z. Dalam Rajah 3, fungsi g memetakan x kepada y dan fungsi h memetakan y kepada z g h y x z 2 3 8
Diagram 3 / Rajah 3
Determine Tentukan (a) g 1 (8) , (b) h (8), (c) hg (3) . Answer : (a) (b) (c) .
4.
The relation between set X and set Y is defined by the set of ordered pairs {(4,2), (4,4), (9,3)}. Hubungan antara set X dan set Y ditakrifkan oleh pasangan tertib {(4,2), (4,4), (9,3)}. State Nyatakan (a) the range of the relation, julat hubungan itu, (b) the images of 4. imej bagi 4.
Answer : (a) .. (b) ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
5.
Diagram 5 shows the relation between two sets of elements. Rajah 5 menunjukkan hubungan antara dua unsur set. f (x)
4
(4, 5)
(4, 3)
(8, 3)
(1, 2)
Diagram 5 / Rajah 5
State Nyatakan (a) the type of relation, jenis hubungan, (b) f 1 (3) . Answer : (a) .. (b) .. 6. In Diagram 6, set B shows the images of certain elements of set A. Dalam Rajah 6, set B menunjukkan imej bagi unsur-unsur tertentu set A.
0 2 4 2 Set A (a) State the value of k. Nyatakan nilai k.
1 5 17 k Set B
Diagram 6 / Rajah 6
(b) Using the function notation, express f in terms of x. Dengan menggunakan tatatanda fungsi, ungkapkan f dalam sebutan x. Answer : (a) k = ... (b) ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
7.
Given f : x 4 x + 3, find Diberi f : x 4 x + 3, cari (a) the image of 3, imej bagi 3, (b) the object which has the image of 5. objek yang mempunyai imej 5.
Answer : (a) (b)
8.
a , x k, where a and k are constant. 1 x a , x k, dengan keadaan a dan k ialah pemalar. Rajah 8 menunjukkan fungsi h : x 1 x a x 1 x
Diagram 8 shows the function h : x
3 1
Diagram 8 / Rajah 8
(a) Determine the value of k. Tentukan nilai k. (b) Find the value of a. Cari nilai bagi a.
Answer : (a) k = ...... (b) a = ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
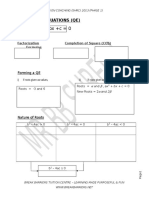
2. QUADRATIC EQUATIONS
"IMPORTANT NOTES AND FORMULAE
Quadratic equations and their roots
o A quadratic equation is an algebraic equation which has only one unknown and the highest power of the unknown is 2. o The general form of quadratic equation is : ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b and c are constants. o The values which satisfy a quadratic equation are known as the roots. o The roots can be determined by (a) factorization method.
(b)
b b 2 4ac using formula, x = . 2a
Conditions for different types of roots
o Given a quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, if (a) b2 4ac > 0, the equation has two real and distinct roots, (b) b2 4ac = 0, the equation has two real and equal roots, (c) b2 4ac < 0, the equation has no roots. (d) b2 4ac 0, the equation has real roots. o The expression b2 4ac is known as the discriminant of a quadratic equation.
Forming a quadratic equation from given roots.
o If and are the roots of a quadratic equation, then b o Sum of the root (SOR) + = a c o Product of the roots (POR) = a
Hence, the quadratic equation is : x2 (SOR)x + POR = 0
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 1JJ
1. Express the quadratic equation x 3 = (2x + 5)(x + 2) in the general form. Ungkapkan persamaan kuadratik x 3 = (2x + 5)(x + 2) dalam bentuk am.
Answer : .. 2. One of the roots of the quadratic equation 2x2 + kx 3 = 0 is 3, find the value of k. Satu daripada punca-punca persamaan kuadratik 2x2 + kx 3 = 0 ialah 3, cari nilai k.
Answer : k = .. 3. Given that the roots of the quadratic equation x2 hx + 8 = 0 are p and 2p, find the values of h. Diberi punca-punca persamaan kuadratik x2 hx + 8 = 0 ialah p dan 2p, cari nilai-nilai h.
Answer : h =
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
10
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
4.
A quadratic equation x2 + kx + 9 = 2x has two equal roots. Find the possible values of k. Persamaan kuadratik x2 + kx + 9 = 2x mempunyai dua punca sama. Cari nilai-nilai k yang mungkin.
Answer : k = .. 5. A quadratic equation px2 3px + 9 = 0 has two equal roots, where p is positive. Determine the value of p. Persamaan kuadratik px2 3px + 9 = 0 mempunyai dua punca sama dengan keadaan p positif. Tentukan nilai p.
Answer : p = .. 6. A quadratic equation x2 + 3x + p + 5 = 0 has two distinct (different) roots. Find the range of values of p. Persamaan kuadratik x2 + 3x + p + 5 = 0 mempunyai dua punca berbeza. Cari julat nilai p.
Answer : ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
11
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
7.
Form a quadratic equation which has roots 2 and 5. Give your answer in general form. Bentukkan persamaan kuadratik yang mempunyai punca-punca 2 dan 5. Berikan jawapan anda dalam bentuk am.
Answer : .. 8. A quadratic equation 2x2 + 3x 2 = k has two equal roots. Find the value of k. Suatu persamaan kuadratik 2x2 + 3x 2 = k mempunyai dua punca sama. Cari nilai k.
Answer : k = .. 9. Given that the quadratic equation 4px2 3kx + p = 0 has two equal roots, find the ratio k : p. Diberi persamaan kuadratik 4px2 3kx + p = 0 mempunyai dua punca sama, cari nisbah k : p.
Answer : ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
12
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
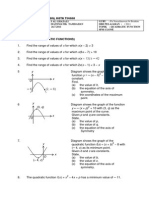
3. QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS
"IMPORTANT NOTES AND FORMULAE
Quadratic functions and their graphs
o A quadratic function in the general form is f (x) = ax2 + bx + c, where a, b and c are constants and a 0. o The graph of a quadratic function is a parabola with an axis of symmetry passing through the maximum or minimum point of the curve. o If a > 0, then the graph is :
If a < 0, then the graph is :
axis of symmetry
axis of symmetry
minimum graph
maximum graph
o The positions of quadratic functions and the types of roots are as follows : Types of roots Discriminant Position of graph
(a) Two different roots
b2 4ac > 0
a>0
x a<0
(b) Two equal roots
b2 4ac = 0
a>0 x a<0
(c) No roots
b2 4ac < 0
a>0 x a<0
13
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
Maximum and minimum values of quadratic functions
o Completing the square (CTS) and sketching graphs of quadratic functions
The quadratic function f (x) = ax2 + bx + c, can be expressed in the form f (x) = a(x + p)2 + q by completing the square.
y
y-intercept x = p y-intercept
x = p
(p, q)
(p, q)
GRAPH A
GRAPH B
For graph A (a > 0)
For graph B (a < 0)
Function : f (x) = a(x + p)2 + q. a is positive. minimum point is (p, q). minimum value of f (x) is q. corresponding value of x is p. axis of symmetry is x = p.
o Methods of Completing the Square
Function : f (x) = a(x + p)2 + q. a is negative. maximum point is (p, q). maximm value of f (x) is q. corresponding value of x is p. axis of symmetry is x = p.
f (x) = ax2 + bx + c (general form) convert to f (x) = a(x + p)2 + q (CTS form) (a) Method 1 (i) Case a = 1
b b f (x) = x + +c 2a 2a
2 2
Example : Convert f (x) = x2 6x + 8 to CTS form. Solution :
2
6 2 f (x) = x ( 3) + 8 2(1)
= (x 3)2 1
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
14
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
(ii) Case a 1 b f (x) = a x 2 + x + c a
b = a x + 2a
2
solve until we get in the form f (x) = a(x + p)2 + q Example : Determine the maximum or minimum point for f (x) = 2x2 4x + 5. Solution : f (x) = 2(x2 2x) + 5 = 2[(x 1)2 (1)2 ] + 5 = 2(x 1)2 2 + 5 = 2(x 1)2 + 3 (b) Method 2 (Using Formula) f (x) = a x + + 2a
b
2
b 2 + c 2a
4ac b 2 4a
OR
f (x) = a x + + c 2a 4a
b2
Example : Determine the maximum or minimum point for f (x) = 3x2 12x + 13. Hence, sketch the graph of f (x). Solution :
b 4ac b2 f (x) = a x + + 2a 4a
(12) 4(3)(13) (12) 2 + = a x + 2(3) 4(3)
2
= 3(x 2)2 + 1 Hence, the minimum value of f (x) is 1 and the corresponding value of x is 2. Hence, the minimum point is (2, 1). The graph of f (x) is :
y
Important facts on sketching the graph : - Minimum parabola shape. - Minimum point is (2, 1). - Minimumvalue of y is 1. - The other 2 points must be shown i.e. (0, 13) and (3, 4). - Axis of symmetry is x = 1.
13 (2, 1) 0
(3, 4)
x
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
15
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
QUADRATIC INEQUALITIES o
The range of the values of x that satisfies quadratic inequalities can be determined by graphical method. Example 1 : Find the range of values of x for x2 4x 12 > 0
Solution : x2 4x 12 > 0 (x + 2)(x 6) > 0 x = 2, 6
Thus, x < 2, x > 6 Example 2 : Solve the inequality x(2x 1) < 3. Solution : x(2x 1) < 3 2x2 x 3 < 0 (2x 3)(x + 1) < 0 3 x = , 1 2
3 2
Thus, 1 < x <
3 2
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
16
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 1JJ
1. Find the range of values of x if 2x2 9x + 4 > 0. Cari julat nilai x jika 2x2 9x + 4 > 0.
Answer : .. 2. Find the range of values of x if x2 7x + 12 < 0. Cari julat nilai x jika x2 7x + 12 < 0.
Answer : .. 3. Find the range of values of x for which x(x 6) < 16. Cari julat nilai x bagi x(x 6) < 16.
Answer : ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
17
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
4.
Find the range of values of x which satisfies the inequality (x 3)2 < 9 8x. Cari julat nilai x yang memuaskan ketaksamaan (x 3)2 < 9 8x.
Answer : .. 5. Find the range of values of k if the quadratic equation (1 + k)x2 + 4kx + 9 = 0 has two real and distinct roots. Cari julat nilai k jika persamaan kuadratik (1 + k)x2 + 4kx + 9 = 0 mempunyai dua punca nyata yang berbeza.
Answer : .. 6. Find the range of values of p if the quadratic equation px2 + 8x + p 6 = 0 does not have real roots. Cari julat nilai p jika persamaan kuadratik px2 + 8x + p 6 = 0 tidak mempunyai punca nyata.
Answer : ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
18
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
7.
Find the range of values of p if the quadratic equation (2 3p)x2 + (p 4)x + 2 = 0 has two distinct roots. Cari julat nilai p jika persamaan kuadratik (2 3p)x2 + (p 4)x + 2 = 0 mempunyai dua punca berbeza.
Answer : .. 8. Find the range of values of x for which (2x + 1)(x + 3) > (x + 3)(x 3). Cari julat nilai x untuk (2x + 1)(x + 3) > (x + 3)(x 3).
Answer : ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
19
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
9.
Find the range of values of m such that x2 + 6x = mx 1 has two different roots. Cari julat nilai m dengan keadaan x2 + 6x = mx 1 mempunyai dua punca berbeza.
Answer : .. 10. Diagram 10 shows a curve y = p(x + q)2 + r where (3, 1) is a turning point. Determine the value of p, q and r. Rajah 10 menunjukkan lengkung y = p(x + q)2 + r dengan keadaan (3, 1) adalah titik pusingan. Tentukan nilai p, q dan r.
y
19
(3, 1)
0
Diagram 10 / Rajah 10
Answer : p = .. q = r =
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
20
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 2JJ
11. Express f (x) = 2x2 4x + 9 in the form a(x + h)2 + k where a, h and k are constants. Ungkapkan f (x) = 2x2 4x + 9 dalam bentuk a(x + h)2 + k dengan keadaan a, h dan k adalah pemalar. (a) State the values of a, h and k. Nyatakan nilai a, h dan k. (b) Determine the maximum or minimum value of f (x) and the corresponding value of x. Tentukan nilai maksimum atau minimum bagi f (x) dan nilai x yang sepadan. (c) Sketch the graph of f (x) = 2x2 4x + 9. Lakarkan graf f (x) = 2x2 4x + 9. (d) Find the range of values of p such that 2x2 4x + 9 = p has two different real roots. Cari julat nilai p dengan keadaan 2x2 4x + 9 = p mempunyai dua punca nyata yang berbeza.
12. The quadratic function f (x) = 3[(x k)2 + h], where h and k are constants, has a minimum point at P(5p, 6p2). Fungsi kuadratik f (x) = 3[(x k)2 + h], dengan keadaan h dan k adalah pemalar, mempunyai titik minimum pada P(5p, 6p2). (a) State the value of h and of k in terms of p. Nyatakan nilai h dan nilai k dalam sebutan p. (b) Given that p = 1, find the range of values of t such that f (x) = t has real roots. Diberi bahawa p = 1, cari julat nilai t supaya f (x) = t mempunyai punca-punca nyata. 13. Given that f (x) = 7 mx x2 = 16 (x + n)2 for all real values of x. If m > 0 and n > 0, find Diberi bahawa f (x) = 7 mx x2 = 16 (x + n)2 untuk semua nilai x yang nyata. Jika m > 0 dan n > 0, cari (a) the value of m and of n, nilai m dan nilai n, (b) the coordinates of the maximum point. koordinat titik maksimum. (c) Hence, sketch the graph f (x) and state the axis of symmetry. Seterusnya, lakar graf f (x) dan nyatakan persamaan paksi simetrinya.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
21
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
4. SIMULTANEOUS EQUATIONS
"IMPORTANT NOTES AND FORMULAE
Linear equation = equation that involves two variables such as x and y where the maximum indices of x and y is one. Non linear equation = equation involves x and y other than linear equation. Basic algebra in this topic :
o Expanding
Example 1 : Expand (2x 1) . Solution : (2x 1)(2x 1) = 4x2 4x + 1
x 3 Example 2 : Expand . 2 x 3 x 3 Solution : 2 2
=
o Changing subject
x2 6 x + 9 4
Example 3.
Given 2x 3y = 6, express x as a subject.
Solution : 2x = 3y + 6 3y + 6 x= 2
o Solving quadratic equation
Example 4. Solve 2x2 + 5x 3 = 0. Solution :
Factorization Method
(2x 1)(x + 3) = 0 1 x = , 3 2
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
22
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
Example 5. Solve 2x2 5x 4 = 0. Solution :
Formula Method
(Usually used when the final answer is not an integer or fraction) x= = b b 2 4ac 2a
(5) (5) 2 4(2)(4) 2(2) = 3137, 0637 Final answers can be calculated by using calculator, that is :
MODE/EQN/degree(2)/a?/b?/c?)
All early and final answers should be written in at least 4 significant figures. Then, conclude your final answer according to the question stated. All simultaneous equations should be solved by substitution method.
TO SOLVE SIMULTANEOUS EQUATIONS, FOLLOW THESE STEPS o o o o
From linear equation, express x or y as a subject. Substitute the result into the non-linear equation (notice that only one unknown remains). Solve the quadratic equation formed (by factorization or using formula). Find the second unknown (by substituting in the third equation).
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
23
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 2JJ
1. 2. Solve the simultaneous equation x2 y + y2 = 2y + 2x = 10. Solve the simultaneous equations x + 2 y = 2 and 2 y 2 xy = 7 . Give your answers correct to two decimal places. Selesaikan persamaan serentak x + 2 y = 2 dan 2 y 2 xy = 7 . Berikan jawapan anda betul sehingga dua tempat perpuluhan. Solve the simultaneous equation 3 x y = 2 x 2 6 y 2 = 1 Selesaikan persamaan serentak 3 x y = 2 x 2 6 y 2 = 1 Solve the simultaneous equation x2 + y2 = 3x + y = 5.. Selesaikan persamaan serentak x2 + y2 = 3x + y = 5... Solve the simultaneous equations a b = 3 and a2 + 2b = 10. Give your answers correct to two decimal places. Selesaikan persamaan serentak a b = 3 dan a 2 + 2b = 10 . Berikan jawapan anda betul sehingga dua tempat perpuluhan. Solve the simultaneous equations Selesaikan persamaan serentak 2x 3y + 4 = 0 x 2 5 xy 1 = 0 Solve the following simultaneous equations : Selesaikan persamaan serentak berikut : 3x + 2y + 1 = 0 x2 + 4xy + 4 = 0 Give your answer correct to two decimal place. Berikan jawapan anda betul kepada dua tempat perpuluhan. Solve the simultaneous equations x 5y = 2 and x 2 4 y 2 = 7 xy 6. Give your answers correct to two decimal places. Selesaikan persamaan serentak x 5y = 2 dan x 2 4 y 2 = 7 xy 6. Berikan jawapan anda betul kepada dua tempat perpuluhan.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
24
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
5. INDICES AND LOGARITHMS
"IMPORTANT NOTES AND FORMULAE
Laws of Indices :
a a = a (a ) = a
n
m+n
a a = a
n
mn
m n
mn
(ab) = a b
n n
an a = bn b
a0 = 1 : a
1 an
Zero Index : Negative Index
1 an
m
Fractional Index :
Laws of Logarithms :
and
an =
(n a)
loga mn = loga m + loga n
loga
m = loga m loga n n
loga mn = n loga m
The properties of logarithms :
Since a1 = a , loga a = 1 Since a0 = 1 , loga 1 = 0
Change of base of logarithms :
log a b =
log c b log c a
and
log a b =
1 logb a
Method to change logarithmic form to index form and vice versa :
If loga N = x then, ax = N
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
25
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 1JJ
32 p +3 9 p 2 . 27 p 1 32 p +3 9 p 2 Ringkaskan . 27 p 1
Simplify
1.
Answer : .. 2. Solve the equation 16 = 32
x x
x1
.
x1
Selesaikan persamaan 16 = 32
Answer : ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
26
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
3.
Given that log10 x = m and log10 y = n, express log10 Diberi log10 x = m dan log10 y = n, ungkapkan log10
x3 y in terms of m and n. 100 x3 y dalam sebutan m dan n. 100
Answer : .. 4. Given that log 3 N = x, express each of the following in terms of x, Diberi log 3 N = x, ungkapkan setiap yang berikut dalam sebutan x, (a) log 3 N 2 , (b) log 9 N .
Answer : (a) .. (b) ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
27
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
5.
Solve the equation log 2 2 p log 2 (1 3 p ) = 1. Selesaikan persamaan log 2 2 p log 2 (1 3 p ) = 1.
Answer : .. 6. Solve the equation 3(9 x + 4) = 27x + 1. Selesaikan persamaan 3(9 x + 4) = 27x + 1.
Answer : ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
28
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
7.
1 = 0. 125 1 Selesaikan persamaan 5x = 0. 125
Solve the equation 5x
Answer : .. 8. Solve the equation 4 2 x 1 = 32 x + 2 . Selesaikan persamaan 4 2 x 1 = 32 x + 2 .
Answer : .. 9. Solve
2 2 x +1 = 16 . 2 2 x +1 = 16
Selesaikan
Answer : ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
29
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
10. Solve the equation 43x 1 2x = 16 x 5. Selesaikan persamaan 43x 1 2x = 16 x 5.
Answer : ..
4 2
x5
11. Solve the equations 16 x 1 = Selesaikan persamaan
. 4
x5
16 x 1 =
Answer : ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
30
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
6. COORDINATE GEOMETRY
"IMPORTANT NOTES AND FORMULAE
Distance between two points. Distance AB = ( x2 x1 ) 2 + ( y2 y1 ) 2
Midpoint. x +x y +y (x, y) = 1 2 , 1 2 2 2 A point dividing a segment of a line with ratio m : n.
ny1 + my2 nx + mx2 (x, y) = 1 , m+n m+n
Area of polygon. 1 x1 x2 Area = 2 y1 y2 =
1 2
x3 y3
x1 y1
( x1 y2 + x2 y3 + x3 y1 ) ( x2 y1 + x3 y 2 + x1 y3 )
Gradient of a straight line. y y Gradient, m = 2 1 x2 x1 To form equation of a straight line.
Method 1
y y1 = m(x x1), where m is gradient and (x1, y1) is any point on the straight line.
Method 2
y = mx + c (by finding the value of c)
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
31
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
Forms of equation of a straight line.
o Gradient form y = mx + c
ax + by + k = 0 x y o Intercept form + = 1, where a and b lie on the x-axis and y-axis a b respectively.
o General form
Parallel and perpendicular straight lines.
o For parallel straight lines m1 = m2 o For perpendicular straight lines m1 m2 = 1
Equation of locus involving distance between two points.
o Distance from a moving point P(x, y) to a fixed point, A is a constant.
PA = k
o Distance from a moving point P(x, y) to two fixed points, A and B is equal (equidistant). PA = PB o Distance from a moving point P(x, y) to two fixed points, A and B is in the ratio m : n.
PA = kPB
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
32
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 1JJ
1. A straight line that passes through points A(k + 3, 5k) and B(k 1, 2k + 1) has a gradient of
1 . Find 2
(a) the value of k, (b) the equation of AB.
Answer : (a) k = .. (b) .................................... 2. In Diagram 2, the equation of the straight line AB is 2y = x + k. Given that AB is perpendicular to AC at point A(0, 4). Dalam Rajah 2, persamaan garis lurus AB ialah 2y = x + k. Diberi AB berserenjang dengan AC pada titik A(0, 4). y B 2y = x + k A (0, 4)
Diagram 2 / Rajah 2
Find / Cari (a) the value of k, nilai k, (b) the equation of AC. persamaan AC. Answer : (a) k = .. (b) ....................................
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
33
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
3.
In Diagram 3, PQ and QR are two straight lines which are perpendicular to each other at point Q. Points P and Q are on the x-axis and the y-axis respectively. The equation of PQ is x 2y + 6 = 0. Dalam Rajah 3, PQ dan QR adalah dua garis lurus yang berserenjang antara satu sama lain pada titik Q. Titik P dan titik Q terletak pada paksi-x dan paksi-y masingmasing. y R
x 2y + 6 = 0 Q P O x
Diagram 3 / Rajah 3
Find / Cari (a) the coordinates of P and Q, koordinat P dan Q, (b) the equation of QR. persamaan bagi QR.
Answer : (a) P = .. Q = ............................. (b) ....................................
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
34
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
4.
In Diagram 4, the straight line PQ intercepts the x-axis and the y-axis at the points P and Q respectively. Dalam Rajah 4, garis lurus PQ memintas paksi-x dan paksi-y pada titik P dan titik Q masing-masing. y P(0, 3)
Q(4, 0)
Diagram 4 / Rajah 4
(a) Write down the equation of PQ in the intercept form. Tulis persamaan PQ dalam bentuk pintasan. (b) Find the equation of a straight line which is parallel to the straight line PQ and passes through the point S(8, 3). Cari persamaan garis lurus yang selari dengan garis lurus PQ dan melalui titik S(8, 3).
Answer : (a) ............ (b) ....................................
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
35
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
5.
The points A and B have coordinates (6, 3) and (4, k) respectively. The straight line 3x + 5y 15 = 0 is parallel to the straight line joining the points A and B. Titik A dan titik B mempunyai koordinat (6, 3) dan (4, k) masing-masing. Garis lurus 3x + 5y 15 = 0 adalah selari dengan garis lurus yang menyambungkan titik A dan titik B. Find / Cari (a) the value of k, nilai k, (b) the distance of AB, jarak AB.
Answer : (a) k = .. (b) ....................................
6.
PQR is a straight line where the coordinates of P and Q are (2, 1) and (1, 2) respectively. If Q divides the straight line PR in the ratio 3 : 2, find the coordinates of R. PQR ialah garis lurus dengan koordinat P dan Q masing-masing ialah (2, 1) dan (1, 2). Jika Q membahagi garis lurus PR dengan nisbah 3 : 2, cari koordinat R.
Answer : ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
36
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
7.
Given that the coordinates of A and B are (4, 1) and (1, 2) respectively. Find the equation of the straight line that passes through the point T(1, 3) and parallel with to the straight line AB. Diberi koordinat A dan B masing-masing ialah (4, 1) dan (1, 2). Cari persamaan garis lurus yang melalui titik T(1, 3) dan selari dengan garis lurus AB.
Answer : .. 8. The coordinates of R, S and T are (5, 2), (1, 4) and (3, 6) respectively. If point S divides the straight line RST in the ratio m : 1, find the value of m. Titik-titik R, S dan T masing-masing mempunyai koordinat (5, 2), (1, 4) dan (3, 6). Jika titik S membahagi garis lurus RST dengan nisbah m : 1, cari nilai m.
Answer : m = ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
37
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
9.
Find the equation of the straight line perpendicular to the straight line 6x + 3y 2 = 0 and passes through the point (6, 1). Cari persamaan garis lurus yang berserenjang dengan garis lurus 6x + 3y 2 = 0 dan melalui titik (6, 1).
Answer : .. 10. Given the straight line 4x + 3y 6 = 0 is parallel to the straight line y = ax + b which passes through the point (12, 5), find the value of a and of b. Diberi garis lurus 4x + 3y 6 = 0 adalah selari dengan garis lurus y = ax + b yang melalui titik (12, 5), cari nilai a dan nilai b.
Answer : a = b =
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
38
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 2JJ
11. Solution to this question by scale drawing will not be accepted. Penyelesaian secara lukisan berskala tidak diterima. In Diagram 11, the equation of the straight line PQR is 2x y + 4 = 0. Dalam Rajah 11, persamaan garis lurus PQR ialah 2x y + 4 = 0. y R
Q P
Diagram 11 / Rajah 11
Given that PQ : QR = 2 : 3, find Diberi PQ : QR = 2 : 3, cari (a) the coordinates of R, koordinat R, (b) the equation of a straight line perpendicular to PR and passes through R. persamaan garis lurus yang berserenjang dengan PR dan melalui R.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
39
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
12. Solution to this question by scale drawing will not be accepted. Penyelesaian secara lukisan berskala tidak diterima. Diagram 12 shows three points A, B and C on the straight line 2y = x + 4 such that AB : BC = 1 : 4. Rajah 20 menunjukkan tiga titik, A, B dan C yang berada pada garis lurus 2y = x + 4 dengan keadaan AB : BC = 1 : 4.
y
A O
B(2, 3)
x
Diagram 12 / Rajah 12
Find Cari (a) the coordinates of A, koordinat A, (b) the coordinates of C, koordinat C, (c) the area of triangle COA. luas segitiga COA.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
40
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
13. Solution to this question by scale drawing will not be accepted. Penyelesaian secara lukisan berskala tidak diterima. In Diagram 13, PQ and QR are two straight lines which are perpendicular to each other at point Q. Point P and point Q lie on the x-axis and y-axis respectively. Given that the equation of PQ is 3y + 2x 9 = 0. Dalam Rajah 13, PQ dan QR ialah dua garis lurus yang berserenjang di titik Q. Titik P dan titik Q masing-masing terletak di atas paksi-x dan paksi-y. Diberi persamaan garis lurus PQ ialah 3y + 2x 9 = 0.
Q 3y + 2x 9 = 0 O P
Diagram 13 / Rajah 13
(a) Find the equation of QR. Cari persamaan garis lurus QR. (b) The straight line RQ is extended to a point S which lies on the x-axis and RQ = 2QS. Find the coordinates of R. Garis lurus RQ dipanjangkan ke titik S yang terletak di atas paksi-x dan RQ = 2QS. Cari koordinat R. (c) Calculate the area of PQR. Hitung luas PQR.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
41
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
7. STATISTICS
"IMPORTANT NOTES AND FORMULAE
For Ungrouped Data
Mean, x =
Variance, 2 =
x N
x2
( x) 2
Standard deviation, =
x 2 ( x) 2
N
For Grouped Data
Mean, x =
fx f
Variance, 2 =
fx 2 ( x) 2 f fx 2 ( x)2 f
Standard deviation, = Mode
The mode of a data set can be obtained from a histogram : Modal class
Frequency
Mode
Variable
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
42
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
Median
N 2 F m = L+ C , where fm
First Quartile L = lower boundry of the median class N = total frequency C = class size F = cumulative frequency before median class fm = frequency of median class
N 4 F Q1 = LQ1 + C , where f Q 1
LQ1 = lower boundry of the 1st quartile class N = total frequency C = class size F = cumulative frequency before 1st quartile class fQ1 = frequency of 1st quartile class
Third Quartile
3N 4 F Q3 = LQ 3 + C , where fQ 3
LQ3 = lower boundry of the 3rd quartile class N = total frequency C = class size F = cumulative frequency before 3rd quartile class fQ3 = frequency of 3rd quartile class
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
43
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 1JJ
1. Table 1 shows the distribution of the marks acquired by 40 students in a test. Jadual 1 menunjukkan taburan markah yang diperolehi 40 pelajar dalam suatu ujian. Marks/Markah Number of students Bilangan pelajar 30-39 4 40-49 9 50-59 16 60-69 11
Table 1 / Jadual 1
Without drawing an ogive, calculate the median mark. Tanpa melukis ogif, hitung markah median.
Answer : .. 2. Table 2 shows the distribution of age of 100 residents in a particular housing area. Jadual 2 menunjukkan taburan umur 100 penduduk di suatu taman perumahan. Age (in years) 1 15 16 30 31 45 46 60 Umur (dalam tahun) No. of residents 28 52 14 6 Bilangan penduduk
Table 2 / Jadual 2
Without drawing the ogive, find the third quartile age. Tanpa melukis ogif, cari umur kuartil ketiga.
Answer : ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
44
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
3.
The sum of the 10 numbers is 170 and the sum of the squares of the numbers is 2930. Find the variance of the 10 numbers. Hasil tambah 10 nombor ialah 170 dan hasil tambah kuasa dua nombor-nombor itu ialah 2930. Cari varians bagi 10 nombor itu.
Answer : .. 4. Given that the mean of a set of data 5, 3, 5, 10 and x is 6. Find the value of Diberi bahawa min bagi set data 5, 3, 5, 10 dan x ialah 6. Cari nilai (a) x, (b) the variance. varians.
Answer : (a) x = .... (b) .. 5. The mean of the set of data 12 5a, 4a, 3a and a2 is 5. Find the possible values of a. Min bagi set data 12 5a, 4a, 3a dan a2 ialah 5. Cari nilai-nilai a yang mungkin.
Answer : a = ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
45
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
6.
Given that the mean of a set of six numbers, 11, 13, 19, 20, m and 2m is 14, find Diberi min bagi satu set enam nombor, 11, 13, 19, 20, m dan 2m ialah 14, cari (a) the value of m, nilai m, (b) the standard deviation of the set of numbers. sisihan piawai bagi set nombor itu.
Answer : (a) m = .. (b) .. 7. A set of data x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 has mean 7 and standard deviation 3. Find Satu set data x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 mempunyai min 7 dan sisihan piawai 3. Cari (a) the sum of the data, x, hasil tambah bagi data, x, (b) the sum of the squares of the data, x2 hasil tambah bagi kuasa dua data, x2 .
Answer : (a) .. (b) ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
46
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
8.
Table 8 shows the score of a group of students in a quiz, calculate the mean of the score. Jadual 8 menunjukkan skor sekumpulan pelajar dalam suatu pertandingan kuiz, hitung nilai skor min. Score 1 2 3 4 Skor Number of students 3 9 13 5 Bilangan pelajar
Table 8 / Rajah 8
Answer : .. 9. A set of six numbers has a mean of 13 and the sum of squares of these numbers is 1030. Find the variance of the set of data. Satu set enam nombor mempunyai min 13 dan hasil tambah kuasa dua nombor-nombor itu ialah 1030. Cari varians bagi set data itu.
Answer : ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
47
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 2JJ
10. A set of scores, x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 and x6 has a mean of 4 and a standard deviation of 3. Satu set skor, x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 dan x6 mempunyai min 4 dan sisihan piawai 3. (a) Find / Cari (i) x, (ii) x2. (b) Each score is multiplied by 4 and then 3 is added to it. For the new set of scores, find Setiap skor didarab 4 dan kemudian ditambah 3. Untuk set skor yang baru, cari (i) the mean, min, (ii) the standard deviation. sisihan piawai.
11. The mean of a set of numbers 2, 6, x, x + 1, 6, 10, 7, 8 is 6. Min bagi satu set nombor-nombor 2, 6, x, x + 1, 6, 10, 7, 8 ialah 6. Find / Cari (a) the value of x, nilai x, (b) the standard deviation of the numbers above. sisihan piawai bagi nombor-nombor di atas. If each of the numbers above is multiplied by 2 and then 3 is added it, find Jika setiap nombor di atas didarab 2 dan kemudian ditambah 3, cari (c) the mean, min, (d) the variance varians of the new set of numbers. bagi set nombor-nombor baru itu.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
48
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
12. (a) A set of positive integers consists of 1, 4 and p. The variance for this set of integers is 6. Find the value of p. Satu set integer positif terdiri daripada 1, 4 dan p. Nilai varians untuk set ini ialah 6. Cari nilai p. (b) Given that set P = {x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7}. The sum of the numbers is 140 and the sum of the squares of the numbers is 3080. Diberi bahawa set P = {x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7}. Hasil tambah bagi nombornombor itu ialah 140 dan hasil tambah bagi kuasa dua nombor-nombor itu ialah 3080. (i) Find the mean and the variance for the 7 numbers. Cari min dan varians bagi 7 nombor itu. (ii) When k is added to set P, the mean increased by 2. Apabila k ditambah kepada set P, min bertambah sebanyak 2. Find / Cari (a) the value of k, nilai k, (b) the standard deviation of the set of 8 numbers. sisihan piawai bagi set 8 nombor itu.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
49
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
8. CIRCULAR MEASURE
"IMPORTANT NOTES AND FORMULAE
rad = 180
Conversion of radians to degrees and vice versa (a) Convert from radians to degrees. 180o rad =
(b) Convert from degrees to radians = 180o
Length of arc AB, s = r, where must be in radian.
B r
r A
s (Length of arc AB)
Area of a sector of a circle, A =
1 2 r , where must be in radian. 2
P
r O
r Q
minor sector
major sector Area of triangle, A = ab sin C Hence, A = r2 sin , where can be in degrees or radians.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
50
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 1JJ
1. Convert / Tukar (a) 3925 to radians, 3925 ke radian, (b) 0428 radian to degrees and minutes. 0428 radian kepada darjah dan minit. (Use / Guna = 3142)
Answer : (a) .. (b) .. 2. Diagram 2 shows a sector OAB. Rajah 2 menunjukkan sektor OAB.
B
125 cm
O
82
A
Diagram 2 / Rajah 2
(a) Convert BOA to radians. Tukar BOA ke radian. (b) Find the length of arc AB. Cari panjang lengkok AB. (Use / Guna = 3142)
Answer : (a) .. (b) ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
51
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
3.
Diagram 3 shows a sector POQ with centre O. Rajah 3 menunjukkan sektor POQ berpusat O. P
Diagram 3 / Rajah 3
Given the length of arc PQ is 125 cm and the perimeter of sector POQ is 425 cm. Find the value of in radians. Diberi panjang lengkok PQ ialah 125 cm dan perimeter sektor POQ ialah 425 cm. Cari nilai dalam radian.
Answer : = .. 4. Diagram 4 shows a circle with centre O. Rajah 4 menunjukkan bulatan berpusat O.
105 rad.
E F
Diagram 4 / Rajah 4
Given that the length of the major arc EF is 4187 cm, find the length, in cm, of the radius. Diberi bahawa panjang lengkok major EF ialah 4187 cm, cari panjang, dalam cm, bagi jejari. (Use / Guna = 3142)
Answer : ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
52
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
5.
In Diagram 5, AOB = 20 and the length of arc AB is 8 cm. Dalam Rajah 5, AOB = 20 dan panjang lengkok AB ialah 8 cm. A
20
B
Diagram 5 / Rajah 5
Find / Cari (a) the length of OB, panjang OB, (b) the area of the sector OAB. luas sektor OAB. (Use / Guna = 3142) Answer : (a) .. (b) .. 6. In Diagram 6, OPR is a quadrant of a circle with centre O. OQR is a triangle where OQ = 5 cm and QR = 13 cm. Dalam Rajah 6, OPR ialah sukuan bulatan berpusat O. OQR ialah segitiga dengan keadaan OQ = 5 cm dan QR = 13 cm. P
O
Diagram 6 / Rajah 6
Find the perimeter of the shaded region. Cari perimeter kawasan berlorek. (Use / Guna = 3142)
Answer : ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
53
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 2JJ
7. In Diagram 7, ABCD is a semicircle with centre O and diameter 10 cm. Dalam Rajah 7, ABCD ialah semibulatan berpusat O dan diameter 10 cm.
B
Diagram 7 / Rajah 7
Given that BD is an arc with centre A. Diberi bahawa BD ialah lengkok bulatan berpusat A. (a) State BAD in radian. Nyatakan BAD dalam radian. (b) Find Cari (i) the length of arc BD, panjang lengkok BD, (ii) the area of the shaded region. luas kawasan berlorek.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
54
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
8.
In Diagram 8, AB is an arc of a circle, with centre O while BC is an arc of a circle with centre D. Given that D is the mid point of OB where OB = 12 cm and CDB = 18 rad. Dalam Rajah 8, AB adalah lengkok suatu bulatan berpusat di O manakala BC adalah lengkok suatu bulatan berpusat di D. Diberi bahawa D ialah titik tengah OB dengan keadaan OB = 12 cm dan CDB = 18 rad. A C
18 rad
Diagram 8 / Rajah 8
Find / Cari (a) the value of , in radians, nilai , dalam radian, (b) the area of the sector OAB, luas sektor OAB, (c) the perimeter of the shaded region. perimeter bagi rantau berlorek. [Use / Guna = 3142]
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
55
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
9. DIFFERENTIATION
"IMPORTANT NOTES AND FORMULAE
Techniques of differentiation
1.
The first derivative of y = ax n using formula. Given that y = ax n where a is a constant and n is an integer.
dy = nax n 1 dx
If y = k , where k is constant dy = 0 dx 2. The first derivative of a product of two polynomials. Given that y = uv
dv du dy =u +v dx dx dx
3.
The first derivative of a quotient of two polynomials. Given that
y=
u v
dy = dx
du dx
dv dx
v2
4.
The first derivative of the composite function. Given that y = k(ax + b)
n
dy dx
= nka ( ax + b )
n 1
the value of a is the differentiation of the expression in the brackett
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
56
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 1JJ
1. Given y = 4(1 2x)3, find
Diberi y = 4(1 2x)3, cari
dy dx dy
dx
. .
Answer :
2.
Differentiate x2(2x 5)4 with respect to x.
Bezakan x2(2x 5)4 terhadap x.
Answer :
3.
Differentiate
Bezakan
1 (3 x 5) 2 1
with respect to x.
(3 x 5) 2
terhadap x.
Answer :
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
57
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
4.
Given a curve with an equation y = (2x + 1)5, find the gradient of the curve at the point
x = 1. Diberi suatu lengkung dengan persamaan y = (2x + 1)5, cari kecerunan lengkung itu pada titik di mana x = 1.
Answer :
5.
Given that y = 3x2
Diberi y = 3x2
4 dy + 4, find the value of when x = 2. x dx
4 dy + 4, cari nilai apabila x = 2. x dx
Answer : .. 6. Given y =
Diberi y =
5 x3 1 d2y , evaluate 2 when x = 3. dx 6 5 x3 1 d2y , nilaikan 2 apabila x = 3. dx 6
Answer :
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
58
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
7.
Find the equation of the tangent to the curve y = 3x 2 + 5 at the point (1, 2).
Cari persamaan tangen kepada lengkung y = 3 x 2 + 5 pada titik (1, 2).
Answer :
8.
Find the equation of the normal to the curve y = 3 x 2 8 x + 1 at the point (1, 4).
Cari persamaan normal kepada lengkung y = 3 x 2 8 x + 1 pada titik (1, 4).
Answer : .. 9. Given y =
Diberi y =
3 dy , find the value of when x = 1. 2 (2 x 3) dx 3 dy , cari nilai bagi apabila x = 1. 2 (2 x 3) dx
Answer :
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
59
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 2JJ
10. The gradient of the curve y = 4 x
k 1 at the point (2, 7) is 4 , 2 x k 1 Kecerunan lengkung y = 4 x pada titik (2, 7) ialah 4 , 2 x Find / Cari
(a) value of k, nilai k, (b) the equation of the normal at the point (2, 7), persamaan normal pada titik (2, 7), (c) small change in y when x increases from 2 to 202. perubahan kecil bagi y bila x menokok dari 2 kepada 202.
11. Given that y =
Diberi y =
4 and h = 2 x 5 , find h2
4 dan h = 2 x 5 , cari h2
(a)
dy in terms of x, dx dy dalam sebutan x, dx
(b) the rate of change of x when h changes at a rate of 4 units s 1 ,
kadar perubahan bagi x apabila kadar perubahan bagi h ialah 4 unit s 1,
(c) the small change in y when x decreases from 2 to 198.
perubahan kecil dalam y apabila x menyusut dari 2 kepada 198.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
60
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
10. SOLUTIONS OF TRIANGLES
"IMPORTANT NOTES AND FORMULAE
SINE RULE
For any triangle ABC, the sine rule is applicable.
B
Sine Rule
c A a
a sin A
=
b sin B
c sin C
C b The sine rule can be applied in the following cases : (a) Two angles and the length of a side are given. (b) Two sides and a non-included angle are given.
COSINE RULE
For any triangle ABC, the cosine rule is applicable.
B
2
Cosine Rule
a C
a = b2 + c2 2bc cos A b2 = a2 + c2 2ac cos B c2 = a2 + b2 2ab cos C
c A
The cosine rule can be applied in the following cases : (a) Two sides and an included angle are given. (b) Three sides are given.
AMBIGUOUS CASE
Ambiguous case arises when : (a) two sides and a non-included angle are given and (b) the non-included angle is an acute angle that is opposite the shorter side given.
A b
B c a C a C
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
61
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
AREA OF A TRIANGLE
For any triangle ABC, the area can be calculated by the formula : B c A a C Area of ABC = or or
1
2 1
ab sin C ac sin B bc sin A
2 1 2
HHPAPER 2JJ
SECTION C
1. Diagram 1 shows a triangle ABC where ADC is a straight line and BDC is obtuse. Rajah 1 menunjukkan segi tiga ABC dengan keadaan ADC adalah garis lurus dan BDC cakah.
B
5 cm 54
x cm 6 cm C
D
Diagram 1 / Rajah 1
2 cm
Find Cari (a) BDA, (b) the value of x. nilai x.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
62
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
2.
In Diagram 2, ADB is a straight line. Dalam Rajah 2, ADB ialah garis lurus.
C 62 cm A
38 cm 44 D B
34 cm
Diagram 2 / Rajah 2
Calculate the length of DB. Hitung panjang DB.
3.
In Diagram 3, SUT is a straight line where RU = 5 cm, SU = 3 cm and UT = 7 cm. Dalam Rajah 3, SUT ialah garis lurus dengan keadaan RU = 5 cm, SU = 3 cm dan UT = 7 cm.
R
5 cm 65 3 cm U 7 cm T
Diagram 3 / Rajah 3
Given that RUS = 65, calculate Diberi bahawa RUS = 65, hitung (a) the length of RS, panjang RS, (b) the area of the triangle RTU. luas segitiga RTU.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
63
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
4.
Diagram 4 shows a quadrilateral PQRS. Rajah 4 menunjukkan sebuah sisiempat PQRS.
P
58 cm
Q
106
167 cm
48
R
62 cm
Diagram 4 / Rajah 4
(a) Calculate Hitung (i) the length, in cm, of PR, panjang, dalam cm, bagi PR, (ii) PRQ. (b) Calculate the area, in cm2, of PQR. Hitung luas, dalam cm2, bagi PQR.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
64
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
11. INDEX NUMBERS
"IMPORTANT NOTES AND FORMULAE
Index number or price index.
I=
Q1 100 Q0
Q0 = Quality or price of the item at base time Q 1 = Quality or price of the item at the specific time
Composite index.
I =
W I W
i
i i
W = weightage I = index number or price index
To find corresponding price.
Index Number I
Year A Price = Q0
Since,
Year B Price = Q1
I=
Q1 100 Q0
I Q0 100
Corresponding price, Q 1 =
To find composite index involving three years. Index or Index or Composite Index Composite Index Q P Year A Year B
Index or Composite Index R
Formula R = PQ 100
65
Year C
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 2JJ
SECTION C
1. Table 1 shows the prices and the price indices of four types of food items in the year 2006 based on the year 2004. Diagram 1 shows the pie chart that reflects the proportion of expenditure of Puan Aminah in the year 2004. Jadual 1 menunjukkan harga dan indeks harga bagi empat jenis makanan dalam tahun 2006 berasaskan tahun 2004. Rajah 1 menunjukkan carta pai bagi perbandingan sebahagian perbelanjaan Puan Aminah pada tahun 2004. Price per kg Harga se kg Year 2004 Tahun 2004
x
Food item Makanan
P Q R S
Year 2006 Tahun 2006 RM 720
y
Price index in 2006 based on 2004 Indeks harga tahun 2006 berasaskan tahun 2004 120 110 130
z
RM 500 RM 400 RM 700
RM 520 RM 910
Table 1 / Jadual 1
S P 120 70 R 80 Q
Diagram 1 / Rajah 1
(a) Find the values of x, y and z. Cari nilai-nilai x, y dan z. (b) Calculate the price index of P in the year 2004 based on the year 2002 if the price of P in the year 2002 is RM 545. Hitung indeks harga bagi P pada tahun 2004 berasaskan tahun 2002 jika harganya pada tahun 2002 ialah RM 545. (c) Find the composite index for the four types of food in the year 2006 based on the year 2004. Cari nombor indeks gubahan bagi empat jenis makanan itu pada tahun 2006 berasaskan tahun 2004.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
66
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
2.
Diagram 2 is a bar chart indicating the weekly cost of the items P, Q, R, S and T for the year 1990. Table 2 shows the prices and the price indices for the items. Rajah 2 menunjukkan carta bar bagi kos mingguan bagi item P, Q, R, S dan T pada tahun 1990. Jadual 2 menunjukkan harga dan indeks harga bagi barangan-barangan itu.
33 30 Weekly cost (RM) 24 Kos mingguan 15 12
Items Barangan
Diagram 2 / Rajah 2
Items Barangan
P Q R S T
Price in year 1990 Harga pada tahun 1990 x RM 200 RM 400 RM 600 RM 250
Price in year 1995 Harga pada tahun 1995 RM 070 RM 250 RM 550 RM 900 z
Table 2 / Jadual 2
Price index in 1995 based on 1990 Indeks harga tahun 1995 beasaskan tahun 1990 175 125 y 150 120
(a) Find the value of / Cari nilai (i) x (ii) y (iii) z (b) Calculate the composite index for items in the year 1995 based on the year 1990. Hitung indeks komposit bagi item-item ini pada tahun 1995 berasaskan tahun 1990. (c) The total weekly cost of the items in the year 1990 is RM456. Calculate the corresponding total weekly cost for the year 1995.
Jumlah kos mingguan bagi item-item ini pada tahun 1990 ialah RM456. Hitung jumlah kos mingguan yang sepadan bagi tahun 1995.
(d) The cost of the items increases by 20% from the year 1995 to the year 2000. Find the composite index for the year 2000 based on the year 1990.
Kos bagi item-item meningkat sebanyak 20% dari tahun 1995 kepada tahun 2000. Cari indeks komposit bagi tahun 2000 berasaskan tahun 1990.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
67
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
3.
A particular kind of cake is made by using four ingredients, P, Q, R and S. Table 3 shows the prices of the ingredients.
Sejenis kek dibuat dengan menggunakan empat jenis bahan, P, Q, R dan S. Jadual 3 menunjukkan harga bagi bahan-bahan tersebut.
Ingredient Bahan
P Q R S
Price per kilogram Harga sekilogram (RM) Year 2004 Year 2005 Tahun 2004 Tahun 2005 x 500 250 400 y 1000 400 440
Table 3 / Jadual 3
(a) Given that the index number of ingredient P in the year 2005 based on the year 2004 is 120, calculate the value of x. Diberi bahawa nombor indeks bagi bahan P dalam tahun 2005 berasaskan tahun 2004 ialah 120, hitung nilai x. (b) The index number of ingredient R in the year 2005 based on the year 2004 is 125. Nombor indeks bagi bahan R dalam tahun 2005 berasaskan tahun 2004 ialah 125. Calculate the value of y. Hitung nilai y. (c) The composite index for the cost of making the cake in the year 2005 based on the year 2004 is 1275. Indeks komposit bagi kos untuk membuat kek dalam tahun 2005 berasaskan tahun 2004 ialah 1275. Calculate / Hitung (i) the price of a cake in the year 2004 if its corresponding price in the year 2005 is RM3060, harga kek bagi tahun 2004 jika harganya yang sepadan dalam tahun 2005 ialah RM3060, (ii) the value of m if the quantities of ingredients P, Q, R and S used are in the ratio of 7 : 3 : m : 2. nilai m jika kuantiti bahan-bahan P, Q, R dan S yang digunakan adalah mengikut nisbah 7 : 3 : m : 2.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
68
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
12. PROGRESSIONS
"IMPORTANT NOTES AND FORMULAE
ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS (AP)
Is a sequence of the terms in which each term is obtained by adding a constant to the previous term. The difference between two consecutive terms is known as the common difference, d. o d = Tn Tn 1 The n-th term of the AP o Tn = a + (n 1)d where a is the first term d is the common difference. n is the number of terms. Sum of the first n terms of AP n o S n = [2a + (n 1) d ] where a is the first term 2 d is the common difference n is the number of terms.
GEOMETRIC PROGRESSIONS (GP)
Is a sequence of terms in which each term is obtained by multiplying the preceding term by a constant. This constant is known as common ratio, r. T o r= n Tn 1 The n-th term of the GP, Tn = ar n 1
Sum of the first n terms of GP
Sn = a(1 r n ) , r <1 1 r a(r n 1) , r >1 r 1
69
or
Sn =
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
The sum to infinity of the GP, where 1< r < 1
S = a 1 r
T1 = S 1 T2 = S2 S1 T3 = S3 S2 and so on
Relation between Tn and Sn Tn = Sn Sn 1
HHPAPER 1JJ
1. The first three terms of an arithmetic progression are 2k 3, 4k + 1 and 5k + 6. Tiga sebutan pertama suatu janjang aritmetik adalah 2k 3, 4k + 1 dan 5k + 6. Find / Cari (a) the value of k, nilai k, (b) the eighth term. sebutan kelapan.
Answer : (a) k = .... (b) .. 2. The first three terms of an arithmetic progression are m 3, m + 3, 2m + 2. Tiga sebutan pertama suatu janjang aritmetik adalah m 3, m + 3, 2m + 2. Find / Cari (a) the value of m, nilai m, (b) the sum of the first 9 terms of the progression. hasil tambah 9 sebutan pertama janjang ini.
Answer : (a) m = .. (b) ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
70
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
3.
Given that 25, 22, 19,. are the first three terms in an arithmetic progression, find the sixteenth term. Diberi 25, 22, 19,. adalah tiga sebutan pertama bagi suatu janjang aritmetik, cari sebutan keenam belas.
Answer : 4. The first three terms of an arithmetic progression are 3, 7, 11. Find Tiga sebutan pertama suatu janjang arithmetik adalah 3, 7, 11. Cari (a) the common difference of the progression, beza sepunya janjang itu, (b) the sum of the first 10 terms after the third term. hasil tambah sebutan sebutan pertama selepas sebutan ketiga.
Answer : (a) .. (b) .. 5. Given a geometric progression k, 3,
Diberi janjang geometri k, 3,
9 , m,. express m in terms of k. k
9 , m, ungkapkan m dalam sebutan k. k
Answer :
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
71
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
13. LINEAR LAW
"IMPORTANT NOTES AND FORMULAE
Reducing non-linear relations to linear form.
Y Y = mX + c
y = f(x)
O Diagram A Non-linear graphs refer to any graph which is not linear such as quadratic, cubic, reciprocal etc. Diagram A shows a quadratic graph. x
c X
O Diagram B
Linear graph refers to a straight line graph with gradient, m and y-intercept, c. Diagram B shows a linear graph.
o A non-linear function which has variables x and y can be reduced to the linear function :
Y = mX + c
y only or both x and y but without constant
a constant only
x and a constant but without y
IMPORTANT STEPS IN PAPER 2
Construct a table value. Plot all points on the correct axis. Draw a line of best fit. Reduce the equation to linear form. From the graph obtained, (a) read the value of c, that is y-intercept y y (b) find the gradient, m by using m = 2 1 x2 x1 (c) find the values of constants. (d) find the value of variables.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
72
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 1JJ
1. Diagram 1 shows the linear graph of y against
1 1 . x
Rajah 1 menunjukkan graf linear y melawan . x y
(0, 6)
(3, 0)
Diagram 1 / Rajah 1
1 x
Express y in terms of x Ungkapkan y dalam sebutan x. Answer : 2. Diagram 2 shows the linear graph of
y x
y x
against x 2. The variables x and y are related by
the equation y = ax3 bx, where a and b are constants.
Rajah 2 menunjukkan graf linear
y x
melawan x2.Pembolehubah x dan y dihubungkan
oleh persamaan y = ax3 bx, dengan keadaan a dan b adalah pemalar.
(12, 2)
O x2
4
Diagram 2 / Rajah 2
Determine the value of a and of b. Tentukan nilai a dan nilai b.
Answer : a = b =
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
73
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
3. The variables x and y are related by the equation y =
k ,where k is a constant. 5x Diagram 3 shows the line graph obtained by plotting log10 y against x. k Pembolehubah x dan y dihubungkan oleh persamaan y = x , dengan keadaan k 5 adalah pemalar. Rajah 3 menunjukkan graf yang diperoleh dengan memplot log10 y melawan x.
log10 y
O (0, 2)
Diagram 3 / Rajah 3
(a) Express the equation y = shown in Diagram 5.
k in its linear form used to obtain the straight line graph 5x
k dalam bentuk linear yang digunakan untuk 5x memperoleh graf garis lurus seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam Rajah 5.
Ungkapkan persamaan y =
(b) Find the value of k. Cari nilai k.
Answer : (a) .. (b) k = ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
74
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 2JJ
4. Table 4 shows the values of two variables, x and y, obtained from an experiment. k Variables x and y are related by the equation y = hx + , where h and k are constants. hx Jadual 4 menunjukkan nilai-nilai bagi dua pembolehubah, x dan y, yang diperoleh daripada satu eksperimen. Pembolehubah x dan y dihubungkan oleh persamaan k y = hx + , dengan keadaan h dan k adalah pemalar. hx
x y
10 55
20 47
30 50
40 65
50 77
55 84
Table 4 / Jadual 4
(a) Plot xy against x2, by using a scale of 2 cm to 5 units on both axes. Hence, draw the line of best fit.
Plotkan x y melawan x2, dengan menggunakan skala 2 cm kepada 5 unit pada kedua-dua paksi. Seterusnya, lukiskan garis lurus penyuaian terbaik.
(b) Use the graph in (a) to find the value of Gunakan graf anda dari (a) untuk mencari nilai (i) h, (ii) k.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
75
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
5.
Table 5 shows the values of two variables, x and y, obtained from an experiment. px Variables x and y are related by the equation y = 2kx2 + , where p and k are k constants. Jadual 5 menunjukkan nilai-nilai bagi dua pembolehubah, x dan y, yang diperoleh daripada satu eksperimen. Pembolehubah x dan y dihubungkan oleh persamaan px y = 2kx2 + , dengan keadaan p dan k adalah pemalar. k
x y
2 8
3 132
4 20
5 275
6 366
7 455
Table 5 / Jadual 5
(a) Plot
y against x, by using a scale of 2 cm to 1 unit on both axes. x Hence, draw the line of best fit. y melawan x, dengan menggunakan skala 2 cm kepada 1 unit pada x kedua-dua paksi.
Plotkan
Seterusnya, lukiskan garis lurus penyuaian terbaik.
(b) Use the graph in (a) to find the value of Gunakan graf anda dari (a) untuk mencari nilai (i) p, (ii) k, (iii) y when x = 12. y apabila x = 12.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
76
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
14. INTEGRATION
"IMPORTANT NOTES AND FORMULAE
INDEFINITE INTEGRAL
Integration is the reverse process of differentiation. If
dy = f (x), then y = dx
f ( x) dx
Integration of algebraic functions.
o o o o
n ax dx =
n x dx =
xn + 1 + c , where c is a constant. n +1 k dx = kx + c, where k and c are constants.
n
ax n + 1 + c , where a and c are constants. n +1
(ax + b) n + 1 (ax + b) dx = (n + 1)(a) + c , where a, b and c are constants.
differentiation in the brackett
To obtain equation of a curve from given gradient function. dy If the gradient function is = f (x), then its equation is y = dx be found)
f ( x) dx (where c must
DEFINITE INTEGRAL
f ( x) dx =
[ g ( x) ] a
b
2
= g(b) g(a).
Example : Evaluate 3 x 2 dx .
1
Solution :
2 x3 1
= 23 13 = 7
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
77
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
Characteristics of Integral o
k f ( x) dx = k f ( x) dx , where k is a constant.
a a
o o o
a
b a b
f ( x) dx = f ( x) dx .
b
[ f ( x) g ( x)] dx =
c
f ( x)dx g ( x) dx .
a
f ( x)dx + f ( x) dx = a a b
f ( x) dx .
AREA UNDER A CURVE
y y = f (x) y
b a
y = f (x)
(a) The area under a curve which is enclosed by x = a, x = b and x-axis is
Ax =
(b) The area under a curve which is enclosed by y = a, y = b and y-axis is
Ay =
y dx
a
x dy
a
The limits are on x-axis and write y in terms of x.
The limits are on y-axis and write x in terms of y.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
78
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
VOLUMES OF REVOLUTIONS
y y = f (x) y
b
y = f (x)
a 0
(a) The volume generated when the region bounded by the curve y = f (x) , x = a and x = b is rotated through 360 about the x-axis is
(b) The volume generated when the region bounded by the curve y = f (x) , y = a and y = b is rotated through 360 about the y-axis is
Vx = y dx
2 a
Vy = x 2 dy
a
The limits are on x-axis and write y2 in terms of x.
The limits are on y-axis and write x2 in terms of y.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
79
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 1JJ
1. Find
Cari
2(1 4 x) 2(1 4 x)
3 3
dx . dx
Answer : 2. Find
Cari
(4 x 1)2 dx.
(4 x 1)2 dx.
16
16
Answer :
3x 2 2
3.
with respect to x. x2 3x 2 2 Kamirkan terhadap x. x2
Integrate
Answer : 4. Evaluate
(2 x)(2 + x ) dx. x2
80
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
Nilaikan
(2 x)(2 + x ) dx. x2
Answer :
4
4
5.
Given that
f ( x) + 2 dx . f ( x) dx = 12, evaluate 0 2
0
Diberi bahawa
f ( x) + 2 dx . f ( x) dx = 12, nilaikan 0 2
0
Answer : 6. Given that
f ( x) dx = 6, evaluate
[2 f ( x) 5] dx . 1
81
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
Diberi bahawa
f ( x) dx = 6, nilaikan [2 f ( x) 5] dx .
1
Answer :
4
7.
Given that
f ( x) dx = 5 and
4
f ( x) dx = 2, find the value of 4
5
Diberi bahawa
4
f ( x) dx = 5 dan f ( x) dx = 2, cari nilai bagi 0 4
(a) (b)
2 f ( x) dx , 5 3 f ( x) dx . 0
5
Answer : (a) .. (b) ..
HHPAPER 2JJ
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
82
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
8.
Given that kx2 x is a gradient function of a curve where k is a constant. y 5x + 7 = 0 is the equation of tangent to the curve at the point (1, 2). Find Diberi kx2 x adalah fungsi kecerunan bagi suatu lengkung di mana k ialah pemalar. y 5x + 7 = 0 ialah persamaan tangen kepada lengkung itu pada titik (1, 2). Cari (a) the value of k, nilai k, (b) the equation of the curve. persamaan lengkung itu.
x2 + 1 at A(2, 3). 2
x2 + 1 pada titik 2
9.
In Diagram 9, the straight line PQ is normal to the curve y = The straight line AR is parallel to the y-axis.
Dalam Rajah 9, garis lurus PQ adalah normal kepada lengkung y = A(2, 3). garis lurus AR adalah selari dengan paksi-y.
y P y= x2 +1 2
A(2, 3)
Q(k, 0)
Diagram 9 / Rajah 9
Find / Cari (a) the value of k, nilai k, (b) the area of the shaded region, luas rantau berlorek, (c) the volume generated, in terms of , when the region bounded by the curve, the y-axis and the straight line y = 3 is revolved through 360 about the y-axis. isipadu yang dijanakan, dalam sebutan , apabila rantau yang dibatasi oleh lengkung, paksi-y dan garis lurus y = 3 diputarkan melalui 360 pada paksi-y.
15. VECTOR
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
83
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
"IMPORTANT NOTES AND FORMULAE
A vector quantity is a quantity that has magnitude and direction. A vector in the direction from A to B can be denoted as AB or a or u or any other % B suitable letters. u a
%
The magnitude of a vector AB is denoted as | AB | or | a |. A vector can be multiplied by a scalar, k AB .
A AB = BA
Triangle Law of Vector Q
Parallelogram Law of Vector b a a+b b a
PQ + QR = PR
Vectors in a Cartesian Plane
In a Cartesian plane, a vector can be expressed in the form : x o xi + yj or where i is a unit vector which is parallel to x-axis and j is a % % % % y unit vector parallel to y-axis. 3 o In the diagram, PQ = 3i + 4 j or PQ = . % % Q 4 o The magnitude of PQ , | PQ | = x 2 + y 2 | PQ | = 32 + 42 P = 5 unit
o
For a vector r = xi + yj , the unit vector in the direction of r is % % % %
84
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
r = % r % |r| % xi + yj % % = x2 + y 2
To prove collinear and parallel vector
P A A Q B
(a) To prove that A, P and B are collinear, you have to show that AB = AP or AB = PB (must find the value of ). (b) To prove that AB is parallel to QR, you have to show that AB = QR (must find the value of ).
Problems on non-parallel vector
y %
x % o If x and y are non-parallel vectors where h x + k y = m x + n y , then % % % % % % (a) h = m and k = n (by comparing the coefficient of each vector). then solve the simultaneous equations.
OR (b) rearrange : h x m x = n y k y (such that x and y are separated) % % % % % % then factorize : (h m) x = (n k) y % % and then solve the simultaneous equations : h m = 0 nk=0
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
85
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 1JJ
Diagram 1 shows vector OP drawn on a Cartesian plane. Rajah 1 menunjukkan vektor OP yang dilukis pada satah Cartesan.
y
1.
Diagram 1 / Rajah 1
x (a) Express OP in the form . y
x Ungkapkan OP dalam sebutan . (b) Find | OP |. Cari | OP |.
y
Answer : (a) OP = ..
(b) | OP | = ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
86
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
2.
Diagram 2 shows two vectors, OP and QO . Rajah 2 menunjukkan dua vektor, OP dan QO .
y Q(3, 4) P(7, 5)
O
Diagram 2 / Rajah 2
Express Ungkapkan
x (a) OP in the form . y
x OP dalam bentuk . y
(b) QP in the form xi + yj. QP dalam bentuk xi + yj. Answer : (a) .. (b) .. 3. Given that O(0, 0), P(3, 3) and Q(2, 12), find in terms of the unit vectors, i and j, Diberi O(0, 0), P(3, 3) dan Q(2, 12), cari dalam sebutan vektor unit, i dan j, (a) PQ , (b) the unit vector in the direction of PQ . vektor unit dalam arah PQ .
Answer : (a) PQ = .. (b) ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
87
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
4.
Rajah 4 menunjukkan vektor AB .
B
Diagram 4 shows vector AB .
Diagram 4 / Rajah 4
(a) Express AB in the form xi + yj. Ungkapkan AB dalam bentuk xi + yj.
(b) Find the unit vector in the direction of AB . Cari vektor unit dalam arah AB . Answer : (a) AB = .. (b) ..
5.
Diagram 5 shows a rectangle OPQR and the point T lies on the straight line OQ. Rajah 5 menunjukkan sebuah segiempat tepat OPQR dan titik T terletak pada garis lurus OQ. Q R
T
9y %
12 x % Diagram 5 / Rajah 5
It is given that OT = 2TQ. Express OT in terms of x and y . % % Diberi bahawa OT = 2TQ. Ungkapkan OT dalam sebutan x dan y . % %
Answer : OT =
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
88
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 2JJ
6. Diagram 6 shows a trapezium ABCD. Rajah 6 menunjukkan sebuah trapezium ABCD.
S
A
Diagram 6 / Rajah 6
3 2 1 It is given that DA = 4 x , DC = 12 y , DT = DC , DC = AB and TS = DA . 4 3 2 % % 3 2 1 Diberi bahawa DA = 4 x , DC = 12 y , DT = DC , DC = AB dan TS = DA . 4 3 2 % % (a) Express in terms of x and y % % Ungkapkan dalam sebutan x dan y % % (i) DB , (ii) DS . *(b) Hence, prove that D, S and B are collinear
Seterusnya, buktikan bahawa D, S dan B adalah segaris.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
89
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
7.
In Diagram 7, PQ = 4a, PS = 2b and SR = a. Dalam Rajah 7, PQ = 4a, PS = 2b dan SR = a.
P
T S R
Diagram 7 / Rajah 7
(a) Express in terms of a and b, Ungkapkan dalam sebutan a dan b, (i) PR (ii) QS
(b) Given that PT = h PR and QT = k QS , express PT Diberi bahawa PT = h PR dan QT = k QS , ungkapkan PT (i) in terms of h, a and b, dalam sebutan h, a dan b, (ii) in terms of k, a and b. dalam sebutan k, a dan b, *(c) Hence, find the value of h and k. Seterusnya, cari nilai h dan nilai k.
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
90
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
16. TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
"IMPORTANT NOTES AND FORMULAE
Six Trigonometric Functions
P(x, y) r
y r x cos = r y . tan = x
sin =
tan =
sin cos
1 sin 1 sec = cos 1 cot = tan
cosec =
cot =
cos sin
Relation between complementary angles
90
y x
y and cos (90 ) = r x cos = and sin (90 ) = r y r x r
sin =
sin = cos (90 ) sin = cos (90 )
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
91
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
Negative angle
sin all (positive)
(clockwise)
tan cos
sin () = sin cos () = cos tan () = tan
GRAPHS OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
Sine graph
y
1
y = sin x
O
90 180 270 360
-1
Cosine graph
y
1
y = cos x
O
90 180 270 360
-1
Tangent graph
y = tan x
90
180
270
360
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
92
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
Steps to sketch graph
Using : y = a sin px or
y = a cos px or y = a tan px Period/cycle Shape
Amplitude
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.
Shape of graph : look at basic sin, cos and tan graph Constant of angle : periodic/cycle (repeat) in 360 or 2 Constant of trigonometric equation : amplitude (maximum/minimum) Negative shape : upside down/reverse shape Shifting upward and downward. Modulus/absolute sign : reflection at x-axis Find a suitable straight line by solving simultaneous equations using substitution method. Draw the straight line. State the number of solutions.
If drawing graph o we need accuracy. o construct a table of coordinates (x, y) at least 5 points. o use regular/uniform scale on graph paper.
SET OF FORMULAE Basic Identities
sin + cos = 1 1 + cot = cosec tan + 1 = sec
Addition Formulae
sin (A B) = sin A cos B cos A sin B cos (A B) = cos A cos B m sin A sin B tan A tan B tan (A B) = 1 m tan A tan B
Double Angle formulae
sin 2A = 2 sin A cos A cos 2A = cos2 A sin2 A = 2 cos2 A 1 = 1 2 sin2 A 2 tan A tan 2A = 1 tan 2 A
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
93
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 1JJ
3 5 and cos B = where A is an acute angle and B is an obtuse angle. 5 13 3 5 Diberi sin A = dan kos B = dengan keadaan A adalah tirus dan B adalah 5 13 cakah.
1.
Given sin A =
Find the value of Cari nilai (a) sin (A + B), (b) cos 2A. kos 2A.
Answer : (a) .. (b) .. 2. Given that cos = k for 0 90, express in terms of k Diberi kos = k bagi 0 90, ungkapkan dalam sebutan k (a) sec , sek , (b) sin 2.
Answer : (a) .. (b) ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
94
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
3.
Solve the equation cot x + 2 cos x = 0 for 0 x 360. Selesaikan persamaan kot x + 2 kos x = 0 bagi 0 x 360.
Answer :
7 3 and cos y = with x and y are in the same quadrant. 24 5
4.
Given that tan x =
Find the value of 7 3 Diberi tan x = dan kos y = dengan x dan y terletak pada sukuan yang sama. 24 5 Cari nilai (a) sin (x y), (b) cosec 2y. kosek 2y.
Answer : (a) .. (b) ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
95
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 2JJ
5. Sketch the graph y = 4 sin 2 x for 0 x 2. Lakar graf bagi y = 4 sin 2 x untuk 0 x 2. Find the equation of a suitable straight line for solving the equation 4 sin 2 x + x = 4 . Cari persamaan garis lurus yang sesuai untuk menyelesaikan persamaan 4 sin 2 x + x = 4 . Hence, using the same axes, sketch the straight line and state the number of solutions to the equation 4 sin 2 x + x = 4 for 0 x 2. Seterusnya, menggunakan paksi yang sama, lakarkan garis lurus itu dan nyatakan bilangan penyelesaian bagi persamaan 4 sin 2 x + x = 4 untuk 0 x 2.
6.
3 Sketch the graph y = 2 cos x for 0 x 2. 2 3 Lakar graf bagi y = 2 kos x untuk 0 x 2. 2
Find the equation of a suitable straight line for solving the equation 3 3 cos x = x 1 . 2 4 Cari persamaan garis lurus yang sesuai untuk menyelesaikan persamaan 3 3 kos x = x 1 . 2 4 Hence, using the same axes, sketch the straight line and state the number of 3 3 solutions to the equation cos x = x 1 for 0 x 2. 2 4
Seterusnya, menggunakan paksi yang sama, lakarkan garis lurus itu dan nyatakan 3 3 bilangan penyelesaian bagi persamaan kos x = x 1 untuk 0 x 2. 2 4
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
96
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
17. PERMUTATIONS AND COMBINATIONS
"IMPORTANT NOTES AND FORMULAE
PERMUTATIONS
If event A occurs in r ways and event B occurs in s ways The number of way is r s The number of permutation of n different objects is n! where n! = n(n 1)(n 2)(n 3) 3 2 1 0!=1 The number of permutations of objects taken from n different objects is given by
n
Pr =
n! (n r ) !
Pn
=n!
COMBINATIONS
The number of combination of r objects taken from n different objects is given by
n
n n! Cr = = r (n r ) ! r !
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
97
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
HHPAPER 1JJ
1. The word COMPUTER are to be arranged in a row. Find Perkataan COMPUTER hendak disusun dalam satu baris. Cari (a) the number of arrangements, bilangan cara menyusun, (b) the number of arrangements if the wowels are next to each other. bilangan cara menyusun jika huruf vokal berada sebelah menyebelah.
Answer : (a) .. (b) .. 2. Four of the letters in the word SQUARE are arranged with the condition that the first letter is a vocal. Find the number of different arrangements possible. Empat huruf daripada perkataan SQUARE hendak disusun dengan syarat huruf pertama adalah vowel. Cari bilangan susunan berlainan yang mungkin.
Answer : 3. Three letters were chosen from the word CYBER and then arranged in a row. Tiga huruf dipilih daripada perkataan CYBER dan kemudian disusun dalam sebaris. Find / Cari (a) the different number of arrangement, bilangan susunan yang berlainan, (b) the number of arrangements that begin with a consonant. bilangan susunan berlainan yang bermula dengan huruf konsonan.
Answer : (a) .. (b) ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
98
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
4.
Given five digits as shown in Diagram 4. Diberi lima digit seperti dalam Rajah 4.
2, 4, 5, 7, 9
Diagram 4 / Rajah 4
Calculate / Hitung (a) the number of four-digit numbers that can be formed without repetitions. bilangan nombor empat digit dapat dibentuk tanpa ulangan, (b) the number of four-digit numbers which is greater than 5000 that can be formed without repetitions. bilangan nombor empat digit yang lebih besar daripada 5000 dapat dibentuk tanpa ulangan.
Answer : (a) .. (b) .. 5. Diagram 5 shows five pieces of different cards. Rajah 5 menunjukkan lima keping kad yang berlainan.
Diagram 5 / Rajah 5
(a) Find the number of possible arrangements, in a row, of all the cards. Cari bilangan susunan yang mungkin, dalam sebaris, bagi semua kad itu. (b) Find the number of arrangements such that the letter E and the letter U are side by side. Cari bilangan susunan, dengan keadaan huruf E dan huruf U adalah sebelah menyebelah..
Answer : (a) .. (b) ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
99
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
6.
Diagram 6 shows six numbered cards. Rajah 6 menunjukkan enam keping kad yang bernombor. 1 3 4 5 6 7
Diagram 6 / Rajah 6
A four-digit number is to be formed by using four of these cards. Suatu nombor empat digit hendak dibentuk menggunakan empat daripada kad-kad tersebut. (a) How many different numbers can be formed? Berapa bilangan nombor berlainan yang dapat dibentuk? (b) How many different odd numbers can be formed? Berapa bilangan nombor ganjil yang berlainan dapat dibentuk?
Answer : (a) .. (b) .. 7. A group of 6 dancers are to be chosen from 7 Malay, 5 Chinese and 4 Indian students to perform a dance during a school cultural night. Sekumpulan 6 penari hendak dipilih daripada 7 pelajar Melayu, 5 China dan 4 India untuk mempersembahkan tarian pada malam kebudayaan peringkat sekolah. Calculate the number of different ways the group of dancers can be formed if Hitung bilangan cara yang berlainan kumpulan penari itu dapat dibentuk jika (a) there is no restriction, tiada syarat, (b) the group of dancers must consist of equal number of Malay, Chinese and Indian students. kumpulan penari itu mesti terdiri daripada bilangan Melayu, China dan India yang sama ramai.
Answer : (a) .. (b) ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
100
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
18. PROBABILITY
"IMPORTANT NOTES AND FORMULAE
n( A) . n( S ) The complement of the event A, P(A) = 1 P(A)
Probability of an event is P(A) =
P(events A or B or both) is given by P(A B) = P(A) + P(B) P(A B) P(two events A and B that are mutually exclusive) is P(A B) = P(A) + P(B), where A B= P(two or three independent events), P(A B) = P(A) P(B) P(A B) = P(A) P(B) P(C)
HHPAPER 1JJ
1. A box contains 8 cards where each card is marked with an alphabet from the word PRACTICE. If a card is chosen at random, calculate the probability that Sebuah kotak mengandungi 8 kad di mana setiap kad ditanda dengan satu huruf daripada perkataan PRACTICE. Jika sekeping kad dipilih secara rawak, hitung kebarangkalian bahawa (a) the card with the alphabet C is chosen. sekeping kad yang bertanda huruf C dipilih, (b) a card with vowel is chosen. sekeping kad yang bertanda huruf C dipilih.
Answer : (a) .. (b) ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
101
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
2.
A marble is drawn at random from a box containing 3 black marbles, 4 green marbles and 5 white marbles. Find the probability of drawing Sebiji guli dicabut secara rawak dari sebuah kotak yang mengandungi 3 guli hitam, 4 guli hijau dan 5 guli putih. Cari kebarangkalian mencabut (a) a black or a green marble. sebiji guli hitam atau sebiji guli hijau. (b) neither a black nor a white marble. bukan guli hitam atau bukan guli putih.
Answer : (a) .. (b) .. 3. Two unbiased dice are thrown together. Calculate the probability that Dua biji dadu adil dilempar serentak. Hitung kebarangkalian bahawa (a) the sum of two numbers is 8, hasil tambah dua nombor ialah 8, (b) the difference of two numbers is 5, beza dua nombor ialah 5, (c) the sum of two numbers is 8 or the difference of two numbers is 5. hasil tambah dua nombor ialah 8 atau beza dua nombor ialah 5.
Answer : (a) .. (b) .. (c) ..
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
102
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
ANSWERS
1. FUNCTIONS (PAPER 1)
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. (a) {q, r} (a) m = 6 (a) 3 (b) many-to-one (b) a = 17 (b) 2 (c) 2 (b) 4, 8
(a) {2, 3, 4} (b) 2, 4 (a) many-to-many (a) k = 5 (a) 15 (a) k = 1 (b)
f : x x2 + 1 1 (b) 2 (b) a = 2
2. QUADRATIC EQUATIONS (PAPER 1)
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 2x2 + 8x + 13 = 0
k = 5 h = 6, 6 k = 4, 8 p=4
11 4 x2 3x 10 = 0 25 k= 8 4:3
p<
3. QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS (PAPER 1)
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
1 ,x>4 2 3<x<4
x<
2 < x < 8 2 < x < 0 3 k< ,k>3 4
103
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
6. 7. 8. 9.
p < 2, p > 8 p < 16, p > 0 x < 4, x > 3 m < 4, m > 8
10. p = 2, q = 3, r = 1
QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS (PAPER 2)
11. f (x) = 2(x 1)2 + 7 (a) a = 2, h = 1, k = 7 (c) (b) min. value = 7, value of x is 1
9 (1, 7)
(2, 9)
(d) p > 7
12. (a) h = 2p2, k = 5p (b) t 6
13. (a) m = 6, n = 3
(c)
(3, 16) (4, 15)
(b) (3, 16)
Axis of symmetry is x = 3
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
104
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
4. SIMULTANEOUS EQUATIONS
1.
2.
5 2 5 y = 3, 2 x = 119, 419,
x = 2, y = 160, 110 1 5 x= , 2 26 1 11 y= , 2 26 x = 1, 2 y = 2, 1 a = 312, 512 b = 012, 812 x = 2698, 01588 y = 04653, 1227 x = 072, 112 y = 157, 118 x = 743 , 129 y = 109 , 066
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
5. INDICES AND LOGARITHMS (PAPER 1)
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 3p + 2 5 1 (3m + n 2) 2 (a) 2x (b)
1 x 2
1 4 x=6
x = 3 x = 12 x=4
10. x = 6 11. x = 3
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
105
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
6. COORDINATE GEOMETRY (PAPER 1)
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. (a) k = 1 (a) k = 8
1 x+3 2 (b) y = 2x + 4
(b) y = (b) y =
(a) P(6, 0), Q(0, 3) (a)
1 x+3 2
x y + =1 4 3
3 (b) y = + 9 4
(a) k = 3
(b) 1166 unit
R(3, 4) y=x4
m=3 1 9. y = x 4 2 4 10. a = , b = 11 3
COORDINATE GEOMETRY (PAPER 2)
11. (a) R(3, 10) 12. (a) A (0, 2) 3 13. (a) y = x + 3 2 (b) x + 2y = 23 (b) C (10, 7) (b) R(4, 9) (c) 10 unit2 (c) 195 unit2
7. STATISTICS (PAPER 1)
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 5388 2906 4 (a) 7 (b) 56 (b) 4472 (b) 290
8 3
a = 4, 2
(a) 7 (a) 35 2223 2667 or
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
106
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
STATISTICS (PAPER 2)
10. (a) (i) (b) (i) 24 19 (ii) 150 (ii) 12 (b) 2291 (c) 15 (d) 21
11. (a) x = 4 12. (a) p = 7
(b) (i) 40
(ii) (a) k = 36 (b) = 7937
8. CIRCULAR MEASURE (PAPER 1)
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. (a) 06851 rad (a) 2576 rad (b) 24 31 (b) 322 cm
5 rad. or 08333 rad. 6
8 cm (a) 2292 cm 3885 cm (b) 917 cm2
CIRCULAR MEASURE (PAPER 2)
7. 8. (a) 07854 rad (a) 09 rad. (b) (i) 5554 cm (ii) 125 cm2 2 (b) 648 cm (c) 2614
9. DIFFERENTIATION (PAPER 1)
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 24 (1 2x)2 2x (6x 5)(2x 5)3 6 (3x 5)3 10 13 15 6x + y = 8 2y = x 9 12
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
107
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
DIFFERENTIATION (PAPER 2)
10. (a) k = 2 (b) 2x + 9y = 67 (c) 009 16 (b) 2 unit s1 (c) 032 11. (a) (2 x 5)3
10.
SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES (PAPER 2 SECTION C)
(b) 7598 cm (b) 1586 cm2 (ii) 2465 (b) 2942 cm2
1. 2. 3. 4.
(a) 4239 5278 cm (a) 4617 or 4618 (a) (i) 1337 cm
11.
INDEX NUMBER (PAPER 2 SECTION C)
z = 130
1.
(a) x = RM600 y = RM550 (b) 1101 (c) 1217
2.
(a) (i)
x = 040
(ii) y = 1375
(iii) z = 300
(b) 1409 (c) RM64250 (d) 1691 3. (a) x = 600 (b) y = 800 (c) (i) RM24 (ii) m = 4
12.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
PROGRESSIONS (PAPER 1)
(b) 41 (b) 252 (b) 330
(a) k = 1 (a) 20 (a) 4
27 k2
m=
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
108
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
13.
1. 2. 3.
LINEAR LAW (PAPER 1)
2 y = +6 x 1 a= , b=4 2 (a) log10 y = x log10 5 + log10 k
(b) 001
LINEAR LAW (PAPER 2)
4. (a)
x2 xy
1 55
4 94
9 150
16 260
25 385
3025 462
(b) (i) 5. (a)
h = 1373
2 4 3 44
(ii) k = 5492 4 5 5 55 6 61 7 65
x y/x
(b) (i)
p = 0754
(ii) k = 026
(iii) y = 42
14.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.
INTEGRATION (PAPER 1)
(1 4 x) 4 +c 8 4 +c 4x 1 2 x
3x +
4
+c
x +c
30 2 (a) 4 (b) 21
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
109
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
INTEGRATION (PAPER 2)
8. 9. (a) k = 6 (a) k = 8 (b) y = 2x3 (b) 12 unit2
7 x2 2 2
(c)
19 3
15.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
VECTOR (PAPER 1)
(b) 10 (b) 10i + j (b) (5i + 12j) 13 1 (10i + 4j) (b) 116
1
8 (a) 6 7 (a) 5
(a) 5i + 12j (a) 10i + 4j 8x +6y
VECTOR (PAPER 2)
6 7. (a) (i) (a) (i) (b) (i) 4 x + 18 y
a + 2b
(ii) 2 x + 9 y % %
(ii) 2b 4a (ii) (4 4k)a + 2kb
(b) Show that DB = 2 DS .
ha + 2hb 4 4 (c) h = , k = 5 5
16.
TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS (PAPER 1)
33 65 1 k
(b)
1. 2. 3. 4.
(a) (a)
7 25
(b) 2k 1 k 2
90, 210, 270, 330 3 24 (a) (b) 5 25
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
110
MINIMUM ADEQUATE PRACTICE (MAP)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS SPM
TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS (PAPER 2)
5.
y
4 y = 4 sin 2x
y = 4 x
6.
y
2
1
y=
2 3
3x 2
3 2
4 3
x
3 2
-4
-2
y = 2 cos
Number of solutions = 4
Number of solutions = 3
17.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.
PERMUTATIONS AND COMBINATIONS
(b) 4320 (b) 48 (b) 72 (b) 48 (b) 240 (b) 1260
(a) 40320 180 (a) 60 (a) 120 (a) 120 (a) 360 (a) 8008
18.
1. 2. (a) (a) (a)
PROBABILITY (PAPER 1)
1 4 7
(b) (b) (b)
3 8 2
3.
12 5
36
3 1
18
(c)
7 36
THE END
Hak Cipta Cayzec Montoya SMK Sultan Sulaiman Kuala Terengganu
111
You might also like
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Add MTH f4 Binder PDF October 11 2007-6-18 Am 376kDocument49 pagesAdd MTH f4 Binder PDF October 11 2007-6-18 Am 376kTifeny Seng100% (1)
- 07 JPNT Addhm f4 Modul1 Edit BaruDocument9 pages07 JPNT Addhm f4 Modul1 Edit BaruSivaneswary Premendran HometuitionNo ratings yet
- Addmath IsDocument37 pagesAddmath IsYusuf WahabNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics Form 4: Modul Kecemerlangan AkademikDocument49 pagesAdditional Mathematics Form 4: Modul Kecemerlangan AkademikSelvarani NasaratnamNo ratings yet
- 1st Mid-Term Test (Add Maths f4)Document5 pages1st Mid-Term Test (Add Maths f4)Jarnice Ling Yee ChingNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Chapter 1 To 3Document20 pagesForm 4 Chapter 1 To 3Ke Ke SawNo ratings yet
- TRG EmasDocument49 pagesTRG EmasSaya MenangNo ratings yet
- Holiday Homework Penggal 1 2013Document9 pagesHoliday Homework Penggal 1 2013adik5967No ratings yet
- Enrich Add. Maths F4Document72 pagesEnrich Add. Maths F4KHKwongNo ratings yet
- Only 5 Minutes - ONE QUESTION A DAYDocument13 pagesOnly 5 Minutes - ONE QUESTION A DAYmutramNo ratings yet
- The Following Formulae May Be Helpful in Answering The Questions. The Symbols Given Are The Ones Commonly UsedDocument15 pagesThe Following Formulae May Be Helpful in Answering The Questions. The Symbols Given Are The Ones Commonly UsedBenjamin HiNo ratings yet
- 0 BK3 Item Draf PDFDocument31 pages0 BK3 Item Draf PDFShasha WiniNo ratings yet
- Drilling Exercise 2 - f4Document2 pagesDrilling Exercise 2 - f4Muhammad Zaid SabriNo ratings yet
- Kertas 1Document41 pagesKertas 1whuiseanNo ratings yet
- Assignment Pelajar Add Math f4Document6 pagesAssignment Pelajar Add Math f4Zulhanif IdrisNo ratings yet
- Koleksi Soalan SPM Add Maths Form 4 p1Document15 pagesKoleksi Soalan SPM Add Maths Form 4 p1John NgooNo ratings yet
- Add Math SPM 2014 Modul Melaka GemilangDocument65 pagesAdd Math SPM 2014 Modul Melaka GemilangCikgu Faizal71% (7)
- AM Paper 1 Set 1Document10 pagesAM Paper 1 Set 1Amelia ShahrudinNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Study NotesDocument61 pagesAdd Maths Study NotesElisha James100% (1)
- Mid Term 2015 Add 1 f4Document14 pagesMid Term 2015 Add 1 f4HadibahHarunNo ratings yet
- Cgnash Pencetus Bijak Matematik: X X X X HDocument1 pageCgnash Pencetus Bijak Matematik: X X X X HcgnashNo ratings yet
- Perfect Score 2008 ModuleaddDocument50 pagesPerfect Score 2008 ModuleaddbaskieNo ratings yet
- Soalan SPM Paper 1Document34 pagesSoalan SPM Paper 1Anandraj GovindarajNo ratings yet
- Koleksi Soalan SPM Paper 1Document34 pagesKoleksi Soalan SPM Paper 1Basri JaafarNo ratings yet
- Add Math SPM 2013Document36 pagesAdd Math SPM 2013tuntejaputeriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Quadratc Functions (Pearl™)Document11 pagesChapter 3 - Quadratc Functions (Pearl™)Umair HishamNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument30 pagesFunctionsRuby WalshNo ratings yet
- Core Mathematics C4: GCE Examinations Advanced SubsidiaryDocument4 pagesCore Mathematics C4: GCE Examinations Advanced Subsidiarysyedhelal_ahmedNo ratings yet
- QB (Add Math F4)Document15 pagesQB (Add Math F4)Iman ShirazNo ratings yet
- 07 JPNT Addhm f4 Modul1Document9 pages07 JPNT Addhm f4 Modul1Nabila OthmanNo ratings yet
- Session IDocument18 pagesSession ISureendran Gopala KrishnanNo ratings yet
- AM Paper 1 Set 2Document12 pagesAM Paper 1 Set 2Nurallia AjeeraNo ratings yet
- Modul Perefect Score Matematik Tambahan Melaka 2014Document65 pagesModul Perefect Score Matematik Tambahan Melaka 2014Muhammad Hazwan RahmanNo ratings yet
- Core Mathematics C3: GCE Examinations Advanced SubsidiaryDocument4 pagesCore Mathematics C3: GCE Examinations Advanced SubsidiaryJosh ZngrNo ratings yet
- AM Paper 1 Set 3Document11 pagesAM Paper 1 Set 3Nurallia AjeeraNo ratings yet
- Ch10 The Quadratic FunctionDocument36 pagesCh10 The Quadratic Functiontrantuanan123No ratings yet
- SPM Add Maths Paper 1 Practice QuestionsDocument11 pagesSPM Add Maths Paper 1 Practice QuestionsManisha Sekaran MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Soalan Ulangkaji SPM AddMaths TIMES 2011Document10 pagesSoalan Ulangkaji SPM AddMaths TIMES 2011waichunkoNo ratings yet
- Answer: (A) - 3: For Examiner's Use OnlyDocument8 pagesAnswer: (A) - 3: For Examiner's Use OnlyAqbar RafiqNo ratings yet
- SPM Clone (Quadratic Functions)Document2 pagesSPM Clone (Quadratic Functions)Saif IfNo ratings yet
- Spm-Trial-2010-Addmath-Qa-Perak (Gerak Gempur) (Set2)Document36 pagesSpm-Trial-2010-Addmath-Qa-Perak (Gerak Gempur) (Set2)Nur Ashikin IsmahunNo ratings yet
- F4 Mid Year 09Document18 pagesF4 Mid Year 09khooyapronNo ratings yet
- Spm-Trial-2010-Addmath-Qa-Perak (Gerak Gempur) (Set3)Document36 pagesSpm-Trial-2010-Addmath-Qa-Perak (Gerak Gempur) (Set3)tommytan1021No ratings yet
- 2009-PERCUBAAN Matematik Tambahan+Skema (SABAH) PDFDocument50 pages2009-PERCUBAAN Matematik Tambahan+Skema (SABAH) PDFDelima AdanNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Monthly Test March 2016Document10 pagesAdd Maths Monthly Test March 2016Armadaramor ShiNo ratings yet
- Maths in Focus - Margaret Grove - ch9Document34 pagesMaths in Focus - Margaret Grove - ch9Sam Scheding0% (1)
- Add Maths Form 4 Paper 1 2012 2Document15 pagesAdd Maths Form 4 Paper 1 2012 2Thiyaku Marutha100% (2)
- SPM Add Maths Pass Year QuestionDocument62 pagesSPM Add Maths Pass Year QuestionJanice Yizing91% (23)
- Quad FN Worksheet 4Document7 pagesQuad FN Worksheet 4jan12th2004No ratings yet
- Mathematics SPM 2011.powerpointDocument55 pagesMathematics SPM 2011.powerpointuzai88No ratings yet
- 2.01) Add Math Module 01 (Functions)Document15 pages2.01) Add Math Module 01 (Functions)cikguruzanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Quadratic FunctionsDocument8 pagesChapter 3: Quadratic FunctionsHayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Materials and Approaches For On Body Energy HarvestingDocument8 pagesMaterials and Approaches For On Body Energy HarvestingShotech EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Experiences of ISFOC On Concentration Photovoltaic: Francisca RubioDocument49 pagesExperiences of ISFOC On Concentration Photovoltaic: Francisca RubioHikary AcevesNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Chemistry Yearly Plan 2019Document2 pagesForm 4 Chemistry Yearly Plan 2019Jenny WeeNo ratings yet
- Disturbance-Rejection vs. SetpointDocument5 pagesDisturbance-Rejection vs. SetpointravaraeNo ratings yet
- EEE141 Course OutlineDocument5 pagesEEE141 Course OutlineLittle WizardNo ratings yet
- (19MT18302) Modeling and Analysis of Electrical Machines (Theory)Document3 pages(19MT18302) Modeling and Analysis of Electrical Machines (Theory)Prabhu MoorthyNo ratings yet
- Unit-I: Fundamentals of Gas DynamicsDocument45 pagesUnit-I: Fundamentals of Gas DynamicsMuthuvel MNo ratings yet
- Int Endodontic J - 2022 - Terauchi - Present Status and Future Directions Removal of Fractured InstrumentsDocument25 pagesInt Endodontic J - 2022 - Terauchi - Present Status and Future Directions Removal of Fractured Instruments吳國豪No ratings yet
- Space Time Continuum - Terence McKennaDocument6 pagesSpace Time Continuum - Terence McKennaKali23YugaNo ratings yet
- D and F Block Elements-1Document12 pagesD and F Block Elements-1ilias1973No ratings yet
- Engineering Syllabus of First Year EE, ECE, PWE, AEIE, EEE, IC, Apparel 2007Document37 pagesEngineering Syllabus of First Year EE, ECE, PWE, AEIE, EEE, IC, Apparel 2007Anish LahiriNo ratings yet
- A25mhigh: Wall For Stabilization of inDocument8 pagesA25mhigh: Wall For Stabilization of inThaiane RebêloNo ratings yet
- Lab 8 Ee ReportDocument10 pagesLab 8 Ee Reportshikazi ziki100% (1)
- Work Energy Practice Quiz AnswersDocument3 pagesWork Energy Practice Quiz AnswersJohn Mark CabicunganNo ratings yet
- The Andromedan Compendium - 7bDocument10 pagesThe Andromedan Compendium - 7bAnonymous XSNBQQ4yNo ratings yet
- SCS Quad Beams SeriesDocument4 pagesSCS Quad Beams SeriesJeffrey BaldwinNo ratings yet
- INFO-Sheet Fumis ALPHADocument2 pagesINFO-Sheet Fumis ALPHAAnthony GilmoreNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab 12 IndicatorsDocument2 pagesChem Lab 12 IndicatorsZaleNo ratings yet
- Is 2974 Part 4 1979 Indian Standard Code of Practice For Design and Construction of Machine Foundations - Part 4 Foundations For Rotary Type Machines of Low Frequency PDFDocument23 pagesIs 2974 Part 4 1979 Indian Standard Code of Practice For Design and Construction of Machine Foundations - Part 4 Foundations For Rotary Type Machines of Low Frequency PDFBibhu DattaNo ratings yet
- Cve3008 Mid-Term Test (27.10.2022)Document4 pagesCve3008 Mid-Term Test (27.10.2022)damell scottNo ratings yet
- Division 2 - Site WorkDocument14 pagesDivision 2 - Site WorkWincelet CelestinoNo ratings yet
- Ee 1002Document108 pagesEe 1002Akhilesh Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- Bio Well InformationDocument5 pagesBio Well InformationPradyuman PatelNo ratings yet
- Msa Ace Inv 1Document11 pagesMsa Ace Inv 1api-413796204No ratings yet
- The Multiple Directions of Antiferromagnetic Spintronics Nature Physics PDFDocument4 pagesThe Multiple Directions of Antiferromagnetic Spintronics Nature Physics PDFLog LouNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Practice Problems, Module 3: Engineering MechanicsDocument13 pagesSolutions To Practice Problems, Module 3: Engineering MechanicsShaun Patrick AlbaoNo ratings yet
- Insta Grid Products PamphletDocument2 pagesInsta Grid Products PamphletShawn Paul BoikeNo ratings yet
- Hypocycloid - AnimatedDocument29 pagesHypocycloid - AnimatedJairus SamuelNo ratings yet
- User Guide: Elcometer 147Document4 pagesUser Guide: Elcometer 147sergioNo ratings yet