Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Genetic Conditions For USMLE
Uploaded by
kcxieOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Genetic Conditions For USMLE
Uploaded by
kcxieCopyright:
Available Formats
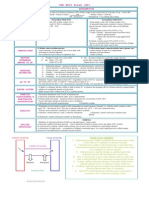
Condition Hereditary breast-ovarian cancer syndrome Breast and ovarian cancer syndromes
Basic Mechanisms
Cowden
Li Fraumeni
Clinical Features Breast cancer, ovarian cancer. AD; BRCA1 and Rx: surgery/chemo, cancer BRCA2 surveillance, prophylactic surgery GI hemartomatous polyposis; AD; PTEN gene (tumor Macrocephaly, Facial/buccal suppressor) papules soft tissue sarcoma, AD; TP53 tumor osteosarcoma, bilateral breast suppressor cancer, CNS tumors AD, STK11 gene hyperpigmented macules lips/mouth, GI hemartomatous polyps NPNCC-related tumors: colorectal, endometrial, ovarian, urinary tract; Rx: Colectomy, Cancer surveillance
Other Cancers BRCA1- prostate and colon; BRCA2laryngeal, colon, stomach, bile duct, hematologic and melanoma Breast cancer, thyroid cancer, endometrial cancers very high cancer risk. Early onset. leukemia, brain, adrenal cortical cancer, melanoma, etc childhood GI hamartomas/cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
nonpolyposis
Lynch syndrome
AD, MLH1 and MSH2 (mismatch repair, caretaker)
colon, endometrium, ovary, stomach, small intestine, hepatobiliary tract, urinary tract, brain, skin Breast cancer, thyroid cancer, endometrial cancers childhood GI hamartomas/cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer extracolonic tumors (upper GI, desmoid, osteoma, thyroid, brain) gardner syndrome: + osteomas and soft tissue tumors; turcot syndrome: +CNS tumors (medulloblastoma); short stature, hyper/hypopig mentation, pancytopenia, urogenital abnormalities
Cowden
AD; PTEN gene (tumor hamartomatous polyps; suppressor) facial/buccal papules AD; TP53 tumor suppressor hamartomatous polyps; hyperpigmented macules adenomatous polyps; attenuated FAP: fewer polyps Rx: surgery/chemo, cancersurveillance, prophylactic surgery
Peutz-Jeghers
Colon Cancer
many polyps
familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP)
AD; APC gene tumor suppressor (gatekeeper)
autosomal recessive
Fanconi's anemia
AR; chromosomal breakage disorder
Radial hypoplasia (absent radii leukemia, myelodysplasic and thumbs), pancytopenia Rx: syndrome, solid tumors, liver bone marrow transplant ataxia, telangiectasias, cancer risk
Ataxia telangiectasia
AR; chromosome breakage disorder
lymphoma, leukemia
Von Hippel-Lindau disease MEN 1
MEN 2
Hemangioblastoma (cerebellum, retina, spinal cord), pheochromocytoma (HTN), renal cell ca PPP (pituitary, parathyroid, pancreas) thyroid-medullary cancer, AD; RET gene, proto- pheochromocytoma, oncogene marfanoid habitus mucosal neuromas AD; VHL gene tumor suppressor (gatekeeper) AD; MEN1 gene tumor suppressor retinoblatoma (bilateral = hereditable, unilateral = nonheritable) heritable: extraocular osteosarcomas, sarcomas, melanomas
Other
Endocrine
Retinoblastoma
AD; RB1 tumor suppressor
INTOXICATION General characteristics of intoxication pathways: normal delivery, symptom-free before crash. Poor feeds, weak suck, weight loss, vomit, weak cry, hypertonia/hypotonia/seizures/coma Condition Basic Mechanisms Clinical Features Other Dx DDx Galactosemia intoxication phenotypes AR; Galactose-1-phosphate cataract, hepatomegaly, E. coli uridyltransferase (GALT) sepsis. Rx: dietary intervention, enzyme lactose restriction AR; branched-chain alphalethargy - coma, seizures, maple ketoacid dehydrogenase syrup odor; Rx: dietary enzyme complex (BCKAD); intervention, BCAA restriction aminoacidopathy AR; organic acidemia X-linked recessive; urea cycle disorder AR, phenylalanine hydroxylase enzyme, aminoacidopathy AR, cystathionine beta synthase enzyme (CBS) severe ketoacidosis, seizures, encephalopathy Coma, seizures, hyperammonemia; Rx: hemodialysis MR, blue eyes/fair skin, eczematous rash. Rx: dietary phenylalanine restriction ectopic lentis, thromboembolism, MR/DD, marfanoid. Rx: dietary protein restriction Urea Cycle disorder OTC deficiency galactosuria, FTT, vomiting/diarrhea, hepatomegaly, e coli sepsis poor feeding, maple syrup odor elevated BCAAs, enzyme analysis ketosis, no acidosis, no hyperammonemia
Maple Syrup Urine Disease
Methylmalonic acidemia Ornithine Transcarbamyl-ase deficiency (OTC)
severe ketoacidosis, hyperammonemia, neutropenia, vomiting hyperammonemia, respiratory expressed in females due alkalosis, protein avoidance, to lyonization FTT, vomiting musty body odor, hyperactivity, seizures newborn screen, plasma phenylalanine newborn screen; urine homocystine, plasma Aas, enzyme analysis, DNA analysis
ketosis, acidosis, hyperammonemia hyperammonemia, no ketosis, no acidosis
nonintoxication phenotypes
PKU
homocystinuria
Amino Acidopathy PKU MSUD homocystinuria
Organic Acidemia methylmalonic acidemia
ENERGY DEFICIENCY prenatal abnormalities (absent corpus callosum), no symptom-free interval, flaccid birth, poor respiratory effort, several hypotonia, dysmorphology, usually craniofacial, true seizures from birth Condition Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON) Basic Mechanisms mtDNA point mutations Clinical Features bilateral vision loss- young adult Other bilndness, neuropathy, myopathy cardiomyopathy, arrhythmia, encephalomyopathy, stroke like episodes, seizures, hearing loss, lactic acidosis, vomiting Facial dysmorphism: high forehead, large fontanels, hypotonia, seizures, poor feeding liver dysfunction Dx opthalmology exam, mtDNA analysis lactate, brain imaging, muscle biopsy, mtDNA analysis biochem testing including VLCFA levels, DNA analysis DDx
mitochondrial
MELAS
mtDNA pt mutation: m3243A>G MT-TL1 gene (tRNA) AR; peroxisomal disease (no peroxisomes are formed)
mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, stroke-like episodes
Fatty-acid oxidation peroxisom defect al
Zellweger syndrome
hypotonia, facial dysmorphism, elevated VLCFA
Medium-Chain AcylAR; MCAD enzyme, fatty Coenzyme A (MCAD) acid oxidation defect deficiency
hypoketotic hypoglycemia, myopathy, cardiomyopathy. Rx: avoid fasting, frequent feedings, carbs
normal at birthy, vomiting, sudden infant death
newborn screen, plasma acylcarnitines, enzyme and/or DNA analysis
STORAGE DISEASE Glycogen storage: metabolic symptoms - hypoglycemia, hepatomegaly and no splenomegaly Lysosome storage: hepatosplenomegaly, CNS, bone, skin. Symptoms are progressive Condition Glycogen von Gierke's disease (GSD I) Basic Mechanisms Clinical Features Other hypoglycemia, massive AR; glucose 6-phosphatase; hepatomegaly, lactic acidosis; Rx: growth failure, hypoglycemic glycogen storage disease avoid fasting, frequent feedings, seizures carbs AR; acid alpha glucosidase cardiomegaly/HCM, macroglossia, (GAA) enzyme; glycogen muscle weakness. Rx: Enzyme storage and lysosome replacement therapy storage X-linked; alpha galactosidase enzyme, lysosomal storage disease corneal opacities, angiokeratomas, acroparesthesias. Rx: enzyme replacement therapy Dx clinical features, liver enzyme analysis and/orDNA analysis von gierke's symptomes + cardiomegaly DDx
Glycoge + lysosome
Pompe disease
cardiomegaly, macroglossia, blood enzyme activity hypotonia, poor feeding, and/or DNA analysis failure to thrive, elevated creatinine kinase cardiomyopathy, transient ischemic attacks, stroke, neuropathy, angiokeratoma, proteinuria, kidney failure, irritable bowel syndrome clinical features. Male: enzyme analysis and/or DNA analysis. Females: DNA analysis
Fabry
Gaucher Lysosome
absence of primary CNS AR; glucosylceramidase clinical features, enzyme anemia, hepatosplenomegaly, no disease, bone disease/pain, enzyme, lysosomal storage analysis and/or DNA lipid-laden macrophages with cherry red spot disease analysis wrinkled paper inclusions AR; hexoasminidase A infant, cherry red spot, enzyme; lysosomal storage progressive neurodegeneration disease hypotonia, loss of motor skills, hyperacusis neurodeneration: seizures, spasticity; normal sized liver and spleen macrocephaly, corneal opacities, enlarged tongue, valvular heart disease, hearing loss, joint stiffness, dwarfism, Urine: dermatan sulfate and heparin sulfate clinical features, enzyme analysis and/or DNA analysis
no cherry red spot
Tay Sachs
cherry red spot
Hurler syndrome, AR, [all MPS =AR except coarse features, MR, Mucopolysaccharidos Hunter (MPS II) is X-linked]; hepatosplenomegaly. Rx: ERT, es type I (MPS I) lysosomal storage disease. bone marrow transplant
blood enzyme activity and/or DNA analysis
You might also like
- Uw Step 2 CK Im H ODocument67 pagesUw Step 2 CK Im H OAilyn MNo ratings yet
- Medical Student Amnesia USMLE Step 1 - Flash Cards by CueFlashDocument13 pagesMedical Student Amnesia USMLE Step 1 - Flash Cards by CueFlashMuhammad Farhan KhaliqNo ratings yet
- HY USMLE Review Part IIIDocument17 pagesHY USMLE Review Part IIIKamel SamaraNo ratings yet
- HistCellBioUSMLEDocument25 pagesHistCellBioUSMLERushi ShahNo ratings yet
- High Yield EmbryologyDocument5 pagesHigh Yield EmbryologyKyle Derouen100% (1)
- Pediatric Clerkship NotesDocument4 pagesPediatric Clerkship Notesxx_caligurl_93xxNo ratings yet
- Lippin NotesDocument8 pagesLippin Noteswalt65100% (1)
- Skin and MSK EverythingDocument31 pagesSkin and MSK EverythingBernard HernandezNo ratings yet
- 2011-09 - Ob-GynDocument24 pages2011-09 - Ob-Gynsahilius100% (1)
- Diseases - BiochemDocument4 pagesDiseases - BiochemJay FeldmanNo ratings yet
- Second Aid - USMLE MnemonicsDocument21 pagesSecond Aid - USMLE MnemonicsKgerbNo ratings yet
- 7-Week Usmle Step 1 Sample ScheduleDocument2 pages7-Week Usmle Step 1 Sample ScheduleHannah ChanNo ratings yet
- Pathology Test I Diseases GuideDocument6 pagesPathology Test I Diseases GuideBahaa Ibrahim HelmiNo ratings yet
- USMLE First Aid Classic Findings - Flash CardsDocument56 pagesUSMLE First Aid Classic Findings - Flash CardsSaeed Hasan100% (1)
- Rashes and FeversDocument36 pagesRashes and FeversLucykeshNo ratings yet
- Uworld CK Questions NotesDocument2 pagesUworld CK Questions NotesPierreNo ratings yet
- Goljan Transcripts - Nts MODIFIED With SLIDES 5Document91 pagesGoljan Transcripts - Nts MODIFIED With SLIDES 5Divya KondaveetiNo ratings yet
- Pestana VignettesDocument41 pagesPestana VignettesDane BrodkeNo ratings yet
- 'Aliah's Physio NotesDocument30 pages'Aliah's Physio NotesLuqman Al-Bashir FauziNo ratings yet
- Pancreas, Liver, and Biliary DiseasesDocument6 pagesPancreas, Liver, and Biliary DiseasesBang QuachNo ratings yet
- Brenner and Stevens, Pharmacology 3 © 2010Document5 pagesBrenner and Stevens, Pharmacology 3 © 2010PharAwayNo ratings yet
- Step 2 CKDocument2 pagesStep 2 CKSundeepSigh4sapNo ratings yet
- Ebr Hy CluesDocument16 pagesEbr Hy CluesStaporn KasemsripitakNo ratings yet
- Bio Chem 1Document5 pagesBio Chem 1Reynaldo RiveraNo ratings yet
- Divine Intervention Episode 17 Diseases of The Pediatric Population Part 1Document14 pagesDivine Intervention Episode 17 Diseases of The Pediatric Population Part 1Swisskelly1No ratings yet
- Lac operon regulation and polyol pathway in diabetesDocument38 pagesLac operon regulation and polyol pathway in diabetesAnonymous lLiWgjFiNo ratings yet
- Renal SystemDocument76 pagesRenal SystemDaNy ChiriacNo ratings yet
- Immuno Micro VirologyDocument15 pagesImmuno Micro VirologyReynaldo RiveraNo ratings yet
- Step1 Journey-To 271Document7 pagesStep1 Journey-To 271Nilay BhattNo ratings yet
- UW (Step 1) Renal - Educational Objectives PDFDocument50 pagesUW (Step 1) Renal - Educational Objectives PDFDrbee10No ratings yet
- Pediatric Pathology: Disease Cause/Risk Factors SymptomsDocument12 pagesPediatric Pathology: Disease Cause/Risk Factors SymptomsherethemindNo ratings yet
- Dermatology and skin conditionsDocument36 pagesDermatology and skin conditionsise7No ratings yet
- Uworld - PEDIATRICSDocument50 pagesUworld - PEDIATRICSNikxy100% (1)
- 100 Concepts - MCBDocument316 pages100 Concepts - MCBNisreen SalameNo ratings yet
- Shelf IM Video SlidesDocument69 pagesShelf IM Video SlidesRuth SanmooganNo ratings yet
- KHALIL High Yeild Usmle Step 2 CS Mnemonic PDFDocument19 pagesKHALIL High Yeild Usmle Step 2 CS Mnemonic PDFPok LyhongNo ratings yet
- Uwise HYDocument3 pagesUwise HYJack GuccioneNo ratings yet
- MSK Pathology For USMLE Step OneDocument6 pagesMSK Pathology For USMLE Step OneGrilled CroweNo ratings yet
- Amboss Hemolytic AnemiaDocument16 pagesAmboss Hemolytic AnemiaAhmed Ali100% (2)
- Dr. Ali's Uworld Notes For Step 2 CKDocument29 pagesDr. Ali's Uworld Notes For Step 2 CKmarina shawkyNo ratings yet
- Divine Intervention Episode 69 Usmle Anatomy Series Part 2Document9 pagesDivine Intervention Episode 69 Usmle Anatomy Series Part 2Swisskelly1No ratings yet
- EMMaA - IMDocument100 pagesEMMaA - IMR IghtzedNo ratings yet
- USMLE WORLD QUESTIONS QuizletDocument87 pagesUSMLE WORLD QUESTIONS QuizletPatricio AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics Step 1Document4 pagesMnemonics Step 1Raji NaamaniNo ratings yet
- Goljan Lecture OrderDocument2 pagesGoljan Lecture OrderKweku Grant-AcquahNo ratings yet
- Immunology FirecrackerDocument45 pagesImmunology FirecrackerMariam A. KarimNo ratings yet
- High Yield Pediatrics: Shelf Exam Review Emma Holliday RamahiDocument78 pagesHigh Yield Pediatrics: Shelf Exam Review Emma Holliday Ramahiskeebs230% (1)
- WWW - Natures.Ir: More Free Usmle, Mccee, Mcqe and Amq FlashcardsDocument54 pagesWWW - Natures.Ir: More Free Usmle, Mccee, Mcqe and Amq FlashcardsNixon GoyalNo ratings yet
- USMLE STEP 1: Microbiology Bug List With Drugs Bugs Drugs: Bacteriology BacteriologyDocument4 pagesUSMLE STEP 1: Microbiology Bug List With Drugs Bugs Drugs: Bacteriology BacteriologymkhararahNo ratings yet
- HY SystemsDocument720 pagesHY SystemsYassandra CalderónNo ratings yet
- QuizletDocument104 pagesQuizletS.No ratings yet
- International Medical Graduate and the United States Medical Residency Application: A Guide to Achieving SuccessFrom EverandInternational Medical Graduate and the United States Medical Residency Application: A Guide to Achieving SuccessRaghav GovindarajanNo ratings yet
- SURVIVOR’S GUIDE Quick Reviews and Test Taking Skills for USMLE STEP 1From EverandSURVIVOR’S GUIDE Quick Reviews and Test Taking Skills for USMLE STEP 1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Drug Summary Table: Chapter 37 Pharmacology of Cancer: Genome Synthesis, Stability, and MaintenanceDocument6 pagesDrug Summary Table: Chapter 37 Pharmacology of Cancer: Genome Synthesis, Stability, and MaintenanceRita GameiroNo ratings yet
- AswinkuDocument3 pagesAswinku451763No ratings yet
- Trigger Topics For FMG Exams by MistDocument3 pagesTrigger Topics For FMG Exams by Mistvijay resuNo ratings yet
- Amenorrhea, Hirsutism & Polycystic Ovary SyndromeDocument15 pagesAmenorrhea, Hirsutism & Polycystic Ovary SyndromeSecret ManNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics NotesDocument25 pagesPediatrics Noteskcxie100% (12)
- Fever of unknown origin evaluation and differentialsDocument3 pagesFever of unknown origin evaluation and differentialskcxieNo ratings yet
- Toxicology TableDocument20 pagesToxicology TablekcxieNo ratings yet
- Posterior TriangleDocument4 pagesPosterior TrianglekcxieNo ratings yet
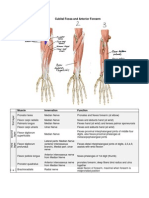
- Cubital Fossa and Anterior ForearmDocument4 pagesCubital Fossa and Anterior ForearmkcxieNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Cavity TableDocument2 pagesPelvic Cavity TablekcxieNo ratings yet
- ShoulderDocument4 pagesShoulderkcxieNo ratings yet
- Lower LimbDocument1 pageLower LimbkcxieNo ratings yet
- Palmar HandDocument3 pagesPalmar HandkcxieNo ratings yet
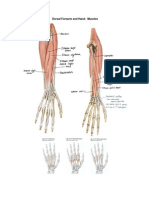
- Dorsal Forearm and HandDocument2 pagesDorsal Forearm and HandkcxieNo ratings yet
- Ankle and Sole of FootDocument4 pagesAnkle and Sole of FootkcxieNo ratings yet
- Communication and Support in Palliative CareDocument30 pagesCommunication and Support in Palliative CareCharles Avevrahamme M. AmlogNo ratings yet
- Cancer Is DEAD: Cancer Cured From A To Z: Brazilian Berry Destroys Cancer Cells in Lab, UF Study ShowsDocument72 pagesCancer Is DEAD: Cancer Cured From A To Z: Brazilian Berry Destroys Cancer Cells in Lab, UF Study Showsseanf1985No ratings yet
- Normal Cell & Cancer CellDocument9 pagesNormal Cell & Cancer Cellal_desNo ratings yet
- Healing RosaryDocument10 pagesHealing RosaryClever Kudzai NyakupindaNo ratings yet
- Physics Behind MammographyDocument52 pagesPhysics Behind MammographyAsterios NtaisNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument24 pagesCancerPavitam ChucksNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Cell LineDocument34 pagesBreast Cancer Cell LineCatherine RajanNo ratings yet
- Ancient Remedy Pau D'Arco Treats Cancer, Fungal InfectionsDocument11 pagesAncient Remedy Pau D'Arco Treats Cancer, Fungal InfectionsJuzzaine Zerrudo100% (2)
- ESMO 2012 Cancer Chemotherapy HandbookDocument226 pagesESMO 2012 Cancer Chemotherapy HandbookHeTranDuc100% (2)
- Anticancer Hormones & AntagonistsDocument27 pagesAnticancer Hormones & AntagonistsBob MuneneNo ratings yet
- Benefits and Risks of Herbal Medicine for Cancer PatientsDocument22 pagesBenefits and Risks of Herbal Medicine for Cancer PatientsMohamed AttiaNo ratings yet
- Prostate Cancer PDFDocument3 pagesProstate Cancer PDFmarkNo ratings yet
- Homoeopathy for Breast CancerDocument5 pagesHomoeopathy for Breast Cancerkathir_cNo ratings yet
- Asymptomatic Microscopic Hematuria in WomenDocument4 pagesAsymptomatic Microscopic Hematuria in WomenAldito GlasgowNo ratings yet
- Neutering in Dogs and CatsDocument11 pagesNeutering in Dogs and CatsEdgar MorenoNo ratings yet
- DR Neil Cherry - Evidence That Electromagnetic Radiation Is Genotoxic - 2002Document69 pagesDR Neil Cherry - Evidence That Electromagnetic Radiation Is Genotoxic - 2002MA-Doc100% (1)
- Combined Inhibition of Invasive Behavior of Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells by Ganoderma Lucidum and Green Tea.Document1 pageCombined Inhibition of Invasive Behavior of Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells by Ganoderma Lucidum and Green Tea.nsagelocspaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Radiobiology - Previous Examination Papers Updated 270709Document20 pagesClinical Radiobiology - Previous Examination Papers Updated 270709Arthi ElangoNo ratings yet
- (Fitness Sutra Book 1) Chopra, Dr. Monika - Workout For Desk Bounds - Quick Stretches & Exercises To Keep Your Neck, Shoulders, Back & Legs Pain-Free and Mind Active-Fitsutra Wellness PVT LTD (2020)Document138 pages(Fitness Sutra Book 1) Chopra, Dr. Monika - Workout For Desk Bounds - Quick Stretches & Exercises To Keep Your Neck, Shoulders, Back & Legs Pain-Free and Mind Active-Fitsutra Wellness PVT LTD (2020)Anh Le100% (2)
- Qualitative Studies On Working Students 2Document75 pagesQualitative Studies On Working Students 2Angelica MatullanoNo ratings yet
- Oral Cancer WordDocument18 pagesOral Cancer WordAdeesh saraf100% (1)
- GENITOGRAPHY (English Version)Document8 pagesGENITOGRAPHY (English Version)Ryesti RahmadheniNo ratings yet
- Construction Health and Safety ManualDocument354 pagesConstruction Health and Safety ManualMahmoud Abdallah100% (6)
- 03.04 - Intraventricular TumoursDocument185 pages03.04 - Intraventricular TumoursBivolaru AlinNo ratings yet
- Theories and Models of Disease CausationDocument62 pagesTheories and Models of Disease CausationsunielgowdaNo ratings yet
- Tumor StagingDocument9 pagesTumor Stagingmalaran.deboraheloisaNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Nclex Questions 5Document18 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Nclex Questions 5dee_day_8No ratings yet
- The Endometriosis Health & Diet Program: Get Your Life BackDocument1 pageThe Endometriosis Health & Diet Program: Get Your Life Backbeluanamaria0% (1)
- Approach To The Adult With Fever of Unknown OriginDocument9 pagesApproach To The Adult With Fever of Unknown OriginsezenitNo ratings yet
- TNM History Updated June2017Document2 pagesTNM History Updated June2017Lucas AndreoNo ratings yet