Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Satellite and Planetary Motion
Uploaded by
ExpertsmindEduCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Satellite and Planetary Motion
Uploaded by
ExpertsmindEduCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics Assignment Help | Satellite and Planetary
Motion|www.expertsmind.com
S Sa at te el ll li it te e a an nd d P Pl la an ne et ta ar ry y M Mo ot ti io on n
MOTION OF A SATELLITE IN A CIRCULAR ORBIT
Orbital Velocity of Satellite: Satellites are natural or artificial bodies describing orbit around a
planet under its gravitational attraction. Moon is a universal satellite while INSAT1B is an artificial
satellite of earth. Condition for creation of artificial satellite is that the centre of orbit of satellite
must coincide with centre of earth or satellite must move around great circle of earth.
Orbital speed of a satellite is the velocity required to put the satellite into its orbit around the earth.
For motion of satellite around the earth, the gravitational pull provides the required centripetal
force.
2
2
mv GMm
r r
=
GM
v
r
=
2
gR g
v R
R h R h
= =
+ +
[As GM = gR
2
and r = R + h]
Angular Speed: The corresponding angular speed is,
e = v
0
/r
Putting v
0
=
GM
r
, we obtain,
e =
3
GM
r
=
3
GM
(R h) +
.
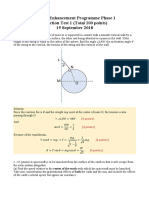
M
R
h
r
Earth F
g
P
m
v
Satellite
Time Period of Revolution: The period of revolution
T = 2t/e
Putting, e =
3
GM
r
, T = 2t
3
r
GM
= 2t
3
(R h)
GM
+
.
Potential Energy: The Gravitational potential energy of the planet satellite system is,
PE =
GMm
r
.
The negative sign shows that the satellite is subjected to planets gravitational field.
Kinetic Energy: KE of a satellite in orbit is given by , KE =
1
2
2
0
mv , where v
0
=
GM
r
,
KE =
GMm
2r
.
Total Energy: The total mechanical energy of the satellite is equal to the sum of its potential and
kinetic energies.
Total energy E =
GMm
r
|
|
' .
+
GMm
2r
|
|
' .
=
GMm
2r
The total energy is negative because the satellite is bound by the planets gravitational field.
Angular Momentum: The angular speed of the satellite is shown by, L = mv
0
r.
Puttingv
0
=
GM
r
, we obtain, L = m( GMr ).
ESCAPE VELOCITY
The minimum velocity with which a body must be projected up so as to enable it to just overcome
the gravitational force, is called as escape velocity
The work done to displace a object from the surface of earth (r = R) to infinity (r = ) is
2
R
GMm 1 1
W dx GMm
R x
(
= =
(
}
GMm
W
R
=
This work needed to project the body so as to escape the gravitational pull is performed on the
body by providing an equal amount of kinetic energy to it at the surface of the earth.
If v
e
is the required escape velocity, then kinetic energy which could be shown to the body is
2
e
1
mv
2
2
e e
1 GMm 2GM
mv v
2 R R
= =
e
v 2gR = [As GM = gR
2
]
or
e
4
v 2 GR R
3
= t
e
8
v R G
3
= t [As
4
g GR
3
= t ]
Velocity of a Planet in Terms of Eccentricity: Applying the law of conservation of angular
momentum at perigee and apogee
Mv
p
r
p
= mv
a
r
a
p
a
a p
v
r a c 1 e
v r a c 1 e
+ +
= = =
[As r
p
= a c, r
a
= a + c and eccentricity
c
e
a
=
]
Applying the relational of mechanical energy at perigee and apogee
2 2 2 2
p a p a
p a p a
1 GMm 1 GMm 1 1
mv mv v v 2GM
2 r 2 r r r
(
= =
(
(
2 2
a p a p 2
a 2
a p p
r r r r
v 2GM
r r r
( (
=
( (
( (
[As
a a
p
p
v r
v
r
= ]
p 2 2
a a
a p a
r
2GM 2GM a c 2GM 1 e
v v
r r r a a c a 1 e
( | |
= = =
(
| |
+ + + ' . ' .
Thus the speeds of planet at apogee and perigee are,
a
2GM 1 e
v
a 1 e
|
=
|
+ ' .
,
p
2GM 1 e
v
a 1 e
| +
=
|
' .
WEIGHTLESSNESS
The weight of a body is the force with which it is attracted towards the centre of earth. When an
object is stationary with respect to the planet, its weight equals the gravity. This weight of the
object is called as its static or true weight.
We become conscious of our weight, in that case when our weight is opposed by some other
object. Usually, the operation of measuring the weight of a body with a weighing machine lies in
the fact that as we place the body on the machine, the weighing machine repulses the weight of
the object. The reaction of the weighing machine to the body gives the measure of the weight of
the body.
The phase of weightlessness may be observed in the following situations:
(i) When objects fall freely under gravity : For example, a lift goes down freely, or an airship
showing a feat in which it falls freely for a few seconds in the mean while its flight, are in
state of weightlessness.
(ii) When a satellite revolves in its orbit around the earth : Weightlessness poses many serious
problems to the astronauts. It seems quite difficult for them to control their positions.
Everything in the moon has to be saved tied down. Creation of duplicate gravity is the answer
to this problem.
(iii) When bodies are at null points in outer space : On a body shown up, the force of the earth
goes on decreasing, but at the similar time the gravitational force of the moon on the body
goes on increasing. At one point, the two gravitational forces may be equal and opposite
and the net pull on the body converts to zero. This is zero gravity fields or the null point
and the body in question is said to appear weightless.
Weightlessness in a Satellite: A satellite, which does not give its own gravity, moves around the earth
in a circular orbit under the action of gravity. The acceleration of satellite is
2
GM
r
towards the centre of
earth.
If a body of mass m placed on a surface inside a satellite moving around the earth. Then forces on the
body are
(i) The gravitational pull of earth
2
GMm
r
=
(ii) The reaction by the surface = R
By Newtons law
2
GMm
R ma
r
= ;
2 2
GMm GM
R m
r r
|
=
|
' .
R = 0
2
G M m
r
Thus the field does not exert any force on the body and hence its apparent weight is zero.
A body needs no support to stay at rest in the satellite and hence all position are equally
comfortable. Such a state is called weightlessness.
GEO STATIONARY SATELLITES
The satellites which seemat rest relative to earth or which has similar angular velocity as that of
earths rotation i.e. with a time phase of 24 hours, such satellite must be operating in an orbit of
specific radius. That orbit is known as parking orbit. If a stationary satellite is at a length h above
the earths field, then its orbiting speed is shown by,
e
gs
e
GM
V
R h
=
+
The time period of its revolution can be given as,
,
2
3
2
e
e
4
T R h
GM
t
= +
or
1/ 3
2 2
e
e 2
gR T
h R
4
|
=
|
t ' .
; h 36000 Km ~
You might also like
- Disappearance of Madeleine McCannDocument36 pagesDisappearance of Madeleine McCannCopernicNo ratings yet
- 2019 IL and Federal Pharmacy Law Review PDFDocument176 pages2019 IL and Federal Pharmacy Law Review PDFAnonymous 3YNJfYNQ100% (5)
- Physics Notes by Derek LauDocument110 pagesPhysics Notes by Derek LauLynn BlackNo ratings yet
- Modesto Mabunga Vs PP (GR 142039)Document3 pagesModesto Mabunga Vs PP (GR 142039)Ericha Joy GonadanNo ratings yet
- My Son The Fanatic, Short StoryDocument4 pagesMy Son The Fanatic, Short StoryScribdAddict100% (2)
- Ucl - ac.Uk-See Practical ExerciseDocument29 pagesUcl - ac.Uk-See Practical Exerciseriponkumar100% (1)
- C++ NotesDocument129 pagesC++ NotesNikhil Kant Saxena100% (4)
- PE and Health 12 - Module 7Document19 pagesPE and Health 12 - Module 7Stephen Lorenzo A. DoriaNo ratings yet
- Organizing and Delivering A Memorized SpeechDocument9 pagesOrganizing and Delivering A Memorized SpeechJanice L. Langit100% (4)
- TelanganaDocument16 pagesTelanganaRamu Palvai0% (1)
- Revision Notes On Gravitation - Gravitation For IITJEEDocument13 pagesRevision Notes On Gravitation - Gravitation For IITJEEKushagra RathiNo ratings yet
- Win GravitationDocument4 pagesWin GravitationChittaranjan Pani100% (1)
- Chapter 13 GravitationDocument7 pagesChapter 13 GravitationSuraj KushwahaNo ratings yet
- JEE Physics Gravitation NotesDocument13 pagesJEE Physics Gravitation NotesShubham AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Me 20111108 On SiteDocument54 pagesMe 20111108 On SiteyashuNo ratings yet
- Newton's First Law States That, If A Body Is at Rest or Moving at A Constant Speed in ADocument5 pagesNewton's First Law States That, If A Body Is at Rest or Moving at A Constant Speed in Atwitch tv caibingweiNo ratings yet
- 7 Gravitation PHY11Document20 pages7 Gravitation PHY11mysixthidisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06Document1 pageChapter 06AmeetNo ratings yet
- Module 5 HSC Physics NotesDocument8 pagesModule 5 HSC Physics NotesLiam KorngoldNo ratings yet
- SS3 Physics GRAVITATIONAL FIELD AND LAW - PassnownowDocument9 pagesSS3 Physics GRAVITATIONAL FIELD AND LAW - Passnownowsunlias0% (1)
- Chapter 6 GravitationDocument7 pagesChapter 6 GravitationJonathan Teng100% (1)
- GravitationDocument4 pagesGravitationdr.pujap935No ratings yet
- 11 Physics Notes 06 GravitationDocument17 pages11 Physics Notes 06 Gravitationutsav161No ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument9 pagesPhysics ProjectIshan AggarwalNo ratings yet
- GravDocument11 pagesGravapi-231880547No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Physics - Gravitation NotesDocument9 pagesCBSE Class 11 Physics - Gravitation NotesAyush GoelNo ratings yet
- 7 GravitationDocument22 pages7 GravitationNejiNo ratings yet
- Gravitation: Important PointsDocument19 pagesGravitation: Important PointsSrinivasu ChintalaNo ratings yet
- Gravitation: F MM 1 F D MM F D MM F G DDocument6 pagesGravitation: F MM 1 F D MM F D MM F G DVenu GopalNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 8 GRAVITATION PDFDocument12 pagesPhysics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 8 GRAVITATION PDFBilal Ahmed25% (4)
- 13) Gravitation and Magnetism_1551343725Document12 pages13) Gravitation and Magnetism_1551343725ungaranigundla sachivalayamNo ratings yet
- Physics 11th GravitationDocument15 pagesPhysics 11th Gravitationkunalsolankicool2007No ratings yet
- Earth's gravity field explorationDocument23 pagesEarth's gravity field explorationNishant MishraNo ratings yet
- Physics Gravitation PDFDocument6 pagesPhysics Gravitation PDFHardik Dobariya100% (1)
- PHYS 0100: DR Xsitaaz Chadee Ms. Nalini DookieDocument27 pagesPHYS 0100: DR Xsitaaz Chadee Ms. Nalini DookieJohn McNellNo ratings yet
- TLS - XI - Physics - Gravitation - Week2Document10 pagesTLS - XI - Physics - Gravitation - Week2aniruddha deshpandeNo ratings yet
- Gravitation (XII) Eng WADocument16 pagesGravitation (XII) Eng WAPrashantcool1999No ratings yet
- Gravity PresentationDocument10 pagesGravity PresentationjdlawlisNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument25 pagesGravitationrezaewewqewqeNo ratings yet
- CH 8 GravitationDocument27 pagesCH 8 GravitationPUNISHER ARPANNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Physics GravitationDocument13 pagesCBSE Class 9 Physics GravitationTinkercad SifatNo ratings yet
- Lec 17Document24 pagesLec 17David ChenNo ratings yet
- Solid Earth Geophysics (ES655) (ES655) : Earth's Gravity and Isostasy - 1Document15 pagesSolid Earth Geophysics (ES655) (ES655) : Earth's Gravity and Isostasy - 1Praveen AKNo ratings yet
- 9 (1) (1) 2spaceDocument31 pages9 (1) (1) 2spacedasdaNo ratings yet
- Gravity Conceptual ProblemsDocument96 pagesGravity Conceptual ProblemsElvis100% (1)
- Gravity, The Shape of The Earth, Isostasy, Moment of InertiaDocument14 pagesGravity, The Shape of The Earth, Isostasy, Moment of InertiaMark KaplanNo ratings yet
- SPM PHYSICS SHORT NOTES CHAPTER 2 Forces and MotionDocument14 pagesSPM PHYSICS SHORT NOTES CHAPTER 2 Forces and MotionJay BeeNo ratings yet
- Gravitational Fields - AllDocument27 pagesGravitational Fields - AlleugeniawijonoNo ratings yet
- Satellite Communication - Orbital MechanicsDocument6 pagesSatellite Communication - Orbital Mechanicsarif8932869039No ratings yet
- Mechanics Formula SheetDocument20 pagesMechanics Formula SheetScott FennellNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument6 pagesGravitationSoham NagNo ratings yet
- Orbital Mechanics and LaunchersDocument53 pagesOrbital Mechanics and Launchersali70ymailNo ratings yet
- Universal GravitationDocument6 pagesUniversal GravitationKimmola K SmallNo ratings yet
- Gravitation, Work and Energy - SelectedDocument42 pagesGravitation, Work and Energy - Selectedaavia1928374655No ratings yet
- Rotational Kinetic Energy: Learning OutcomeDocument10 pagesRotational Kinetic Energy: Learning OutcomeBouatake HedstromNo ratings yet
- Gravitationppt 180122143106Document42 pagesGravitationppt 180122143106Saket KesarNo ratings yet
- GSK 2Document6 pagesGSK 2gskNo ratings yet
- Gravitational Field StrengthDocument21 pagesGravitational Field Strengthmallikammu12No ratings yet
- Test1 MarkingDocument6 pagesTest1 MarkingMarcus PoonNo ratings yet
- Gravitation CH8Document25 pagesGravitation CH8Rishab SharmaNo ratings yet
- Pusat Tuition Makrifat Chapter 3.4 F.4.PhyDocument5 pagesPusat Tuition Makrifat Chapter 3.4 F.4.PhyBazil BoliaNo ratings yet
- Physics Gravitation ProjectDocument21 pagesPhysics Gravitation ProjectAdityaNo ratings yet
- Space: Physics Core Topic 9.2Document14 pagesSpace: Physics Core Topic 9.2pussyslayer2770No ratings yet
- 4 Gravitaional Constant GDocument64 pages4 Gravitaional Constant Ggomathi_nellaiNo ratings yet
- GRAVITATION AssignmentDocument7 pagesGRAVITATION AssignmentTHUNDER CHILD 75No ratings yet
- Dynamic Deformation of Earth and Motion Effects Caused by Universe's Gravitational FieldFrom EverandDynamic Deformation of Earth and Motion Effects Caused by Universe's Gravitational FieldNo ratings yet
- Work Done Against GravityDocument3 pagesWork Done Against GravityExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- PowerDocument2 pagesPowerExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Physics Assignment Help - Work Done in Displacement of A Body inDocument1 pagePhysics Assignment Help - Work Done in Displacement of A Body inExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Work Done by A ForceDocument2 pagesWork Done by A ForceExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Oblique CollisionDocument1 pageOblique CollisionExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Rotational Work and EnergyDocument1 pageRotational Work and EnergyExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Types of PendulumDocument5 pagesTypes of PendulumExpertsmindEdu100% (2)
- Variable MassDocument3 pagesVariable MassExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Uniform and Non - Uniform Circular MotionDocument4 pagesUniform and Non - Uniform Circular MotionExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Physics Assignment Help - Relation Between Linear and AngularDocument1 pagePhysics Assignment Help - Relation Between Linear and AngularExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic MotionDocument6 pagesSimple Harmonic MotionExpertsmindEdu100% (1)
- Newton's Law of Universal GravitationDocument2 pagesNewton's Law of Universal GravitationExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- TorqueDocument1 pageTorqueExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Physics Assignment Help - Simple Harmonic Motion in Spring-MassDocument1 pagePhysics Assignment Help - Simple Harmonic Motion in Spring-MassExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Relation Between G and GDocument3 pagesRelation Between G and GExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument2 pagesProjectile MotionExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Vertical CircleDocument2 pagesMotion in A Vertical CircleExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument2 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Motion in Two DimensionsDocument2 pagesMotion in Two DimensionsExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Moment of InertiaDocument2 pagesMoment of InertiaExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Physics Assignment Help - Oscillation of Liquid Column in A UDocument1 pagePhysics Assignment Help - Oscillation of Liquid Column in A UExpertsmindEdu100% (2)
- Motion of Centre of MassDocument2 pagesMotion of Centre of MassExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Law of Conservation of Mechanical EnergyDocument1 pageLaw of Conservation of Mechanical EnergyExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Physics Assignment Help - Kinetic Energy of A Rigid Body: K I N e T I C E N e R G y o F A R I G I D B o D yDocument1 pagePhysics Assignment Help - Kinetic Energy of A Rigid Body: K I N e T I C E N e R G y o F A R I G I D B o D yExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Kinematics and DynamicsDocument2 pagesKinematics and DynamicsExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Kepler's LawsDocument1 pageKepler's LawsExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Gravitational PotentialDocument2 pagesGravitational PotentialExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Gravitational Field IntensityDocument2 pagesGravitational Field IntensityExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Gravitational Potential EnergyDocument3 pagesGravitational Potential EnergyExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Historical Source Author Date of The Event Objective of The Event Persons Involved Main ArgumentDocument5 pagesHistorical Source Author Date of The Event Objective of The Event Persons Involved Main ArgumentMark Saldie RoncesvallesNo ratings yet
- Asian Studies For Filipinos The Philippines in The Asian CenturyDocument15 pagesAsian Studies For Filipinos The Philippines in The Asian CenturyGlaizza QuintonNo ratings yet
- Salford Care Organisation Job Description & Person SpecificationDocument14 pagesSalford Care Organisation Job Description & Person SpecificationAyesha EhsanNo ratings yet
- FeatureSelectionAccepted IEEE Review PDFDocument20 pagesFeatureSelectionAccepted IEEE Review PDFrvsamy80No ratings yet
- Magnets Catalog 2001Document20 pagesMagnets Catalog 2001geckx100% (2)
- Active Disturbance Rejection Control For Nonlinear SystemsDocument8 pagesActive Disturbance Rejection Control For Nonlinear SystemsTrần Việt CườngNo ratings yet
- History shapes Philippine societyDocument4 pagesHistory shapes Philippine societyMarvin GwapoNo ratings yet
- Complete Approval List by FSSAIDocument16 pagesComplete Approval List by FSSAIAnkush Pandey100% (1)
- STS Syllabus 2020Document27 pagesSTS Syllabus 2020AndreaDimaculangan100% (1)
- How To Install Windows XP From Pen Drive Step by Step GuideDocument3 pagesHow To Install Windows XP From Pen Drive Step by Step GuideJithendra Kumar MNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument48 pagesConsumer BehaviourdooncollegeNo ratings yet
- Process of Producting High Carbon Ferro ChromeDocument5 pagesProcess of Producting High Carbon Ferro ChromeSantosh Kumar MahtoNo ratings yet
- ANAPHYDocument23 pagesANAPHYYu, Denise Kyla BernadetteNo ratings yet
- Test Fibrain RespuestasDocument2 pagesTest Fibrain Respuestasth3moltresNo ratings yet
- Food Science, Technology & Nutitions - Woodhead - FoodDocument64 pagesFood Science, Technology & Nutitions - Woodhead - FoodEduardo EstradaNo ratings yet
- MF-QA-001 PDIR ReportDocument2 pagesMF-QA-001 PDIR ReportBHUSHAN BAGULNo ratings yet
- Dryers in Word FileDocument5 pagesDryers in Word FileHaroon RahimNo ratings yet
- Parking Garage LED Retrofit - 1 - Lighting-Guide - Rev.082015 PDFDocument2 pagesParking Garage LED Retrofit - 1 - Lighting-Guide - Rev.082015 PDFmonsNo ratings yet
- GEHC DICOM Conformance CentricityRadiologyRA600 V6 1 DCM 1030 001 Rev6 1 1Document73 pagesGEHC DICOM Conformance CentricityRadiologyRA600 V6 1 DCM 1030 001 Rev6 1 1mrzdravko15No ratings yet
- Silicone Bonding BrochureDocument4 pagesSilicone Bonding BrochureAmir ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Rock Laboratory PricelistDocument1 pageRock Laboratory PricelistHerbakti Dimas PerdanaNo ratings yet
- Security Testing MatDocument9 pagesSecurity Testing MatLias JassiNo ratings yet