Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Real Ccheatheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Jun KangCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Real Ccheatheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Jun KangCopyright:
Available Formats
Engineering News Record (ENR): Heavy & highway, nonresidential building (building+ind.const.), multiunit housing. Res. Build. Cons.
Single-family homes, multi-unit townhouses, apartments, condo. Non-res. Build. Cons. Sch. U, hosp, warehouses, theaters. Ind. Cons. Petroleum refineries, steel mills, heavy manufacturing plants. Heavy Eng. Cons. dams, tunnels, bridges, highways, pipelines. 10 Major Infra. Pro. In HK->Local Railway & Highway (South Island MTR Line, Sha Tin to Central Rail Link, Tuen Mun Western Bypass), Cross-Border Development (Guangzhou-Shenzhen-HK Express Rail Link, HK-Zhuhai-Macau Bridge, Chek Lap Kok to Shenzhen Airport Rail Link, HK-Shenzhen Joint Development of Lok Ma Chau), Regional Development (West Kowloon Cultural District, Kai Tak Development, New Territories Northwest Development). Manufacturing>automobile, TV,phones; same products are manufactured multiple times; designed & produced without designated buyers; manufacturers make own decisions for design & production, prior to sale; advertising to attract buyers; at risk of failing to recover $ as products remain unsold (x market)/ sold at $ lower than cost;$=direct design/man. Costs(labor, materials)+indirect cost(marketing)+Gen.& Administrative+profit; man. Risk: market demand & $, buyers risk: product operates as advertised? Sales networks: to indi(mail, web), to wholesalers(bulk) & to retailers.; single item is made n times; mass production, batch production. Payment is made when unit is purchased. Construction>one of a kind nature with unique products; purchase process begins with a client who needs a facility; client (buyer) is known be4 const. starts, designers defines scope of work& details of pro., contractor builds product, start when agreement is reached among participants; high risk of failure to complete pro. In functional/timely manner; large no. of stakeholders & issues that must be dealt with prior to pro. Completion lead to complex level of risk for participants; commitment to purchase facility starts after preliminary design. Cons. Tech.->methods & tech. to place phy. Materials & elements of cons. at job site; evaluation & selection of methods & techn. Cons. management->Resources 4M1T:Manpower, machines, materials, money, time);technical: design of formwork, capacities of excavators;qualitative:motivation of workers, form of contracts, safety on job site, legal liability. CM optimally apply resources to realize a constructed facility of acceptable quality, on time & within budget. (quality, time, $); Key Roles: owner-client, designer/design professional-consultant, constructor/builder-Contractor; subcontractors, material vendors, regulatory bodies, fabricators, special interest groups
Legal
Pro development cycle: need established>conceptual design> approval of conceptual design>preliminary & final design>bid package complete>decision to release for bid> advertise notice to bidders>bid period & receipts of proposals>select contractor>notice to proceed>construction period>inspection & acceptance of pro. Cons. Pro. Development(Owners view)->(Need for facility>initial feasibility & cost projections>decision to proceed with conceptual design, scope of work, approximate estimate of cost>decision to proceed with final design doc. that define pro. for cons.>advertising pro.& request for proposals>>constructor selection & notice to constructor to proceed with work, based on proposal (formation of a contract)>construction>facility testing(as designed & planned)>operation & maintenance of facility over specified service life>facility is disposed/maintained for life). Private commercial entities: Pro. Profitability $->economic basis based on market studies projecting demand for facility; considerations: facility size, site location, availability of labor & supporting resources(energy, water, shipping connections) are investigated in feasibility study report & supporting cost analyses. ; structure of feasibility study is dictated by requirements of financial institutions who lend $ for facility development; feasibility info & supporting $ analyses are submitted to board of directors. Public & community-service-related pro. (not involve profit )->highways, tunnels, dams, museums; public entities (government) are continuously reviewing societal needs; need feasibility study & cost analyses. Pro. Feasibility study:Is it possible to build (Land, technology, construction, finance, public/social/authoritys responses); worthwhile to build? (pro. Justification); project useful? (benefits/reward/revenue) Issue add. in feasibility study: layout/alignment; land; design approach; const. method; materials; workmanship; maintenance requirements; consultation; programme; estimates(cost/cash flow) >>> carry out site investigation, design info, data collection, working drawings, estimates, programs, consultation & contract doc. Conceptual pro. Stage(be4 preliminary design): prepare graphical representation of pro & a layout diagram, cost/benefit analysis, cost estimate based on conceptual-level info; present to potential funding sources (banks & investors). Cost/Benefit analysis: commercial/profitbased>comparison of estimated cost against projected revenues to be generated; benefit for public/non-profit based>tangible (electricity generated) & intangible (flooding prevention & lake for recreation), gov. authorities establish protocols for converting intangible aspects into eco. Benefits; Evaluate intangible is judgement call & sub. to review & criticism. Impact Assessment Studies: by engineer, need detail study, (DIA, SIA, EIA, TIA, CTIA), identify potential impacts, give mitigation solutions & implementation & monitoring. Cost Estimates: based on conc. drawing & other design info(floor space, roof area); approved pro may not be built for years>project cost to future const. date, cost indexes, use Building Works Tender Price Index (BWTPI) to adjust building cost for estimating, x reflect level of tender prices for build services work. Preliminary design: 40% completion, extension of concept docs; design team leader coordinates design professionals; architect-floor plan& general layout, build. cladding & interior/exterior finish; civil/structural engineer: structural frame, subsurface foundation support; mechanical engineer: heating, ventilating & air conditioning (HVAC), service water systems (pumps). Detail design: completion in plans & specifications for bidding; produce cost estimate at 3% accuracy; owners cost estimate as benchmark to ensure design is within owners financial resources & evaluate bids submitted; owner may reject bids, withdraw pro for redesign/consideration if bids>>estimate. Bid package: doc available to contractor for him to make decision to bid with notice to bidders; general conditions, special conditions, Technical specs, plans & drawings, proposal form; basis for determine bid $ & influence willingness of bidders to bid a contract. Proposal form: offer, x formal contract, indicates contractors intent to enter into contract to complete specified work at specified $; contains project duration (may in SCC) & start date; award contract based on this, contractual r/ship forms; award of contract is sent by Notice to Proceed->legally binding contractual r/ship. Lump sum: the amount of money the client is willing to pay for certain construction item; Unit price: the price of every unit of material/construction price of a particular item. GCC: standard set of stipulations that applies to all contracts on how a contract is to be administered & r/ships between parties established. Rights, privileges & responsibilities that accrue to primary contractual parties are defined; sections pertaining to owner, A/E, contractor, subcontractor; different provisions has own legal implications; wording establishes a fair & equitable balance of protection of all parties concerned, shall not be changed without careful consideration. SCC: unique to given pro (pro duration, additional instructions of commencement of work, ownerprocured materials, mandatory wages of local area, project progress reporting format, mount of liquidated damages; modifications to basic articles of GC in form of +, deletions/substitutions; additional articles of a contractual-legal nature that desirable/necessary for a particular pro; paragraph titles may be similar to those in GC. Plans & drawings: schedule & graph presentation of pro. Tech. Specifications: textual, written description of tech. requirements of pro. Legally precise pic of tech aspects of work to be performed; pertain in large part to establishment of quality levels, standards of workmanship, material standards are defined; specific brand name/model number is cited as desired for installation; quality referred to accepted practice/quality specification (ACI, ASTM AWS); organization follows sequence of construction. Addenda: change in detail, +, correction & contract conditions before bids are opened that are intended to become part of bid package (incorporated into it). Change orders: future changes in scope/details of contract. Once contract is signed, future changes in scope/details of contract may form basis for a new financial r/ship between contracting parties. Notice to Bidders (NTB): owner advertises pro to capable contractors to achieve lowest bid $; doc announcing to prospective bidders that design doc are available for consideration & that owner is ready to receive bids; contains project type & size, availability of plans & spec for review, place date time of bid opening; methods to know: A/E firms have mailing list (qualified bidders), a builders exchange may operate to serve contracting community & keep it appraised of status of design & bid activities by operating plans rooms & publishing newsletters, nationwide(web-based) services; includes: general type, size, plans and specifications, time, place date of bid opening
Decision to bid: major financial decision to contractor; needs contractors commitment of man-hours for development of estimate costs & resource requirements; predictions are made based on past exp & ability to sense potential trouble spots that affect field costs; quantity takeoff/surveying: process of determining required material quantities on a job; most failure-incorrect & unrealistic estimating & bidding practices; cost of time & effort to develop a total bid price & submit proposal is recover when receives contract; estimating $ is 0.25% of total bid price. Prequalification: interested contractors need submit doc that establish firms expertise & capability in accomplishing similar types of construction; win-win: contractor x prepare bid & x incur cost unless he can qualify; owner x find himself in position of being under pressure to accept a low bid from an incompetent firm. Subcontractor & Vendor Quotations/Contracts: solicits specialty areas (electrical work, interior finish, roofing) & material $ from subcontractors; Quotations via phone/email; integrate quotations into total bid $; electronically transmitted doc & signed quotations eliminate misunderstandings & prevent suppliers/subcont from change quoted $. Construction bonds: role in surety bonds(principal: who may default, obligee: who may be damaged/loss some advantage, surety: who offset damage/loss of advantage, beneficiary); guarantee-surety guarantees contractor (principal) will perform obligation stated in bond. Bid bond: owner requires a bid security to offset damage due to contractors default (failure) to start pro as directed; damage = difference bet winners $ & next low bid; responsibility of surety is indemnified (covered) by principal; if principal unable to pay, surety cover it; as alternative, owner may accept a cashiers check in specified amount, if contractor fails to enter contract, he forfeits his check; penal sum (coverage, liability): gov construction contracts: 20% of bid $, private const agencies:510%. Performance bond: issued to contractor to guarantee owner that contract work wil be completed & comply with pro spec. Payment bond: protect owner against any liens/charges against pro that are unpaid due to contractors default. Surety may elect to negotiate short-term financing for contractor (current liquidity problems); Surety may grant loans/help contractor obtain additional loans; list of troubleshooters, negotiation with 2nd contractor to complete; issed for premium (0.5-3%), increases with penal sum of bond; The Miller Act, 1935: performance bond 100% of contract amount; payment bond: 50% if contract is %1,000,00/less, 40% if $1,000,000 - $5,000,000;max of $2,500,000 if contract > $5,000,000; Surety keep informed of contractors performance & with its changing business & financial status, through contractors reports on costs, payments, & disputes. Net quick assets (cash on hand, demand deposits, accounts receivable): contractors assets available to surety in case of default. Bonding capacity: multiple of net quick assets; new: 5/6, old & reliable, 40/>
Issuance of NTB opens bidding period; Bid opening marks formal end of bidding period; pro duration measured from notice to proceed; late submission is disqualified; prior to bid opening, contractors can withdraw bid without penalty. Acceptance period: No submitted bid may be withdrawn; owner must send written notice of award, if no, contractors can withdraw/adjust bids after period; bid security protects owner from failure by contractor to enter into formal construction agreement; contractor is protected by acceptance period, if not owner could hold bids for unspecified period, affecting financing/approximation for pro; specified in NTB. NTP: completes contractual r/ship from legal viewpoint; site is free of encumbrances & contractor can enter site; reference date for pro start & damage calculation. Letter of Intent: indicate selection & acceptance of proposal, when encumbrances exist on site & owner x issue NTP to authorize contractor to enter site; establish owners intent to enter into contracts as soon as barriers have been removed. Contract Agreement: single doc that binds contractual parties, & by reference describes work to be performed in legal sense; includes drawings, general conditions, supplementary conditions, technical spec, addenda; standard forms of contract agreement are available from various professional organizations. Change orders: any alteration of contract doc constitutes alteration of contract; modifications to original doc; legal arrangement; unit price has flexibility; lump sum contract has no leeway for change/interpretation; procedures to implement are specified in GCC; ~mini contracts, implementation similar to bid cycle, just x competition; formal communication of change in scope & supporting technical doc should be sent to contractor; contractor respond with price quotation (offer), owner can accept offer/attempt to negotiate (make counteroffer); contractor is justified in increasing $ to recover costs; poorly scoped & prepared, project turn into change orders-> cause adverse r/ships, increase costs & const duration. Change conditions: engineering designs are based on site conditions as perceived by A/E; conditions of structural, mechanical & electrical items above ground are constant & easily determined; subsurface & topographical portions are difficult to predict; ability of below grade area to support weight is established by a gird of test piles; info from subsurface investigation is contractors basis to estimate excavation& foundation work, to claim a changed condition; some condition (underground river, depth of rock layer) may not be detected during design; failure to reflect conditions cause contractor to claim changed conditions for + costs; owner accept change order; decline, solve through litigation/arbitration. Rework:installed work x comply/meet required spec; major sources of unplanned cost growth on const pro; Const Ind Institute (CII), reduce field work, save 10% cost;not caused solely by cons site activities; prevent improve effectiveness of early project phases, helped by computer-based tools . Suspension, delay/interruption (SDI): GCC-Contracting officer may order Contractor in writing to SDI all/any part of work such period of time as he may determine to be appropriate for convenience of owner; costly to contractor: demobilization-remobilization, inflated labor & materials;compensation provision: an adjustment shall be made for any increase in cost of performance of this contract necessarily caused by such unreasonable SDI & contract modified in writing accordingly; amount of adjustment by owner is contested by contractor & lead to possible lengthy litigation. Time Extensions: pro duration can be specified in working/calendar days; procedures set in GCC; claims based on delays caused by owner, owners agents/acts of Gods design errors, design changes & worksite hindrance-owner-assignable delays, weather delays-act of God type delay; avg percent of time extension granted on typical gov pro. Liquidated damage: assessed when contractor exceeds pro duration(ori duration+time extensions); actual: from NTP to complete; Date of Substantial Completion of Work/designated portion thereof is Date certified by owners representative when const is sufficiently complete, in accordance with Contract Doc, so Owner can occupy/utilize Work/designed portion thereof for use for which it is intended; Completion date-beneficial occupancy date (BOD); complete on time? Tied to Utilization/occupancy date; unavailability-lost (rental) revenues, cost of administration & supervision of contract; amount charged is given is SCC, x arbitrary & reflector actual damage incurred; Unreasonably high charge, owner x justify, court may rule charge is penalty charge for overrun-> penalty-bonus clauses apply, owner must offer bonus in equal amount for every day brings pro early. Progress payment: contractor is reimbursed on periodic basis; at end of month, owners representative & contractor estimate work performed during month; amount by owner to cover contractors expenditures & fee for work. Retainage: retain portion of $, incentive to properly complete pro; if pro is close to completion, receive all bid price, x motivated to do closing-out tasks; provision: in making progress payments, there shall be retained 10% of estimated amount until final completion & acceptance of work; owner may decide to drop retainage requirement if work is progressing satisfactorily at 50% completion point. Progress reporting: contractors required to submit a schedule of activity & periodically update schedule reflecting actual progress stated in GCC;S-curves/bar charts: based on indi activities, $ completion og work categoris (concrete, structural, electrical & mechanical work); basis for progress payments, ensure satisfactory progress by contractor. Final acceptance: joint inspection on part of owners representative (pro/resident eng) & contractor, scheduled on mutually acceptable date; notes deficiencies-punch list-basis for accepting work as final, releasing final payment (+retainage) to contractor. Value management: cost-what an item is; value: what an item does; done during design phase & construction phase; functional analysis: producing lowcost products w/out reducing quality; contractor is more + than designers of field conditions &const. methods; prepare value engineering change proposal (VECP)-improve design, reduce cost, maintain/improve functionality; incentive clause allows contractor to share net savings. Stages of VM: information, analytical, creative, judgment, development phase; multi-criteria evaluation: cost, aesthetics, performance safety; weighted system for final analysis.
Contract: agreement btw 2/> parties, a promise for breach of which law recognizes duty, legally enforceable. R/ships: owner-contractor/design professional; contractor-subcontractor/surety; (sub)contractorworkers/suppliers. Pro delivery method: comprehensive process of assigning contractual responsibilities for designing & constructing a pro; address 2 critical issue: responsibility to owner for pro design & construction tie to single/multiple entities? Criteria for award based on lowest cost/other?; type: DBB, DB, CM contract;competitively bid, negotiated contract. DB contract: turn-key contract, DB contractor-design builder/ EPC(engineer, procure, construct) contractor; advantageous from clients view point to have single contractor provide entire pro as a single contract package; design & construction can be done concurrently; coordination btw design & construction is enhanced: low life cycle cost, efficient construction process, constructability/maintainability; large & complex projects for firms with large design & construction capabilities. DB in Consortium Format: builders with x in0hse design capability can form consortium; each member at risk & motivated to work with other to minimize delays & disputes; give owner a final lump-sum $ at end of preliminary design phase(30-40% of design); reducing need for contingency as final $ is locked in; competition-major factor, non-selected consortia incur losses.CM Contract: owner contracts separately, but simultaneously, with A/E & with a firm whose primary expertise is construction (CM); CM is hired during design phase, work directly with A/E & avoid potential design issues before completion of construction doc. Agency CM(CMa): agent of, advisor to owner; owner has trade contracts with multiple trade contractors & suppliers, CM receives fee for service basis, manages, supervises & coordinates trade contracts on behalf of owner in best interests of owner; construction coordinator & assists in obtaining bids & managing construction; links owner, contractor & A/E; provides single point of coordination to owners; contracts btw design & construction firms are signed by owner. CM At-Risk: coordinates pro, assumeresponsibility for construction phase (like construction contractor in DBB); sign all contracts related to construction phase of work, take direct responsibility for construction means & methods; design & other pre-construction contracts signed by/remain with owner; hired during design phase to act as pro coordinator & general contractor (CM/GC); Construction Management as Constructor (CMc) contract. Fast track construction: stages of design & construction overlap, shortening time need ed to complete pro; allowed in DB & CM contracts. Competitively Bid Contracts: NTB-advertise, invite quote for work, award to lowest $ & responsible bidder; contractor qualifications reviewed in $-ascending order: technical competence & experience, current financial position, bonding capacity, current amount of work under way, past history of calims litigation, defaults on previous contracts; advan: ensures lowest responsible $, essential for public work to ensure all bidders are treated equally; disadvan: change orders tend to offset competitive advan, purposely low bid(0/- profit), plans & spec 100% completed prior bid advertisement; long pro duration (x parallel). Lump-Sum Contracts: quotes one price for work & services; direct costs: labor, materials, machines; indirect costs: field/front office supervision, equipment, maintenance costs; profit: 10, 15%, suitable for building construction, x for earthwork; advan: guarantee $ for work specified, owner w/out worrying abt contingency, reduced work of field measurement for contractor; disadvan: lack flexibility to change design/modify contract, any deviation to ori plan must handled as change order, potential litigation, adversary contractual r/ships. Unit-price contracts: payments based on precise measurement of field quantities, work is broken down into work items characterized by units; larger quantities allow economies of scale; flexibility for variations in amount of work; price renegotiation if actual field quantity deviates from guide quantity; advan: flexibility in accommodating in variation in field quantities, precision of quantity takeoff need not be as exact as lump-sum contract, reduce no. of change orders, used in heavy & highway contracts (earthwork, foundation work); disadvan: owner x precise final $, contingency allowances must bemade.
Management organization: areas & levels of responsibility of members of firm; communication of members. Legal organization: influencing/dictating governing laws & taxes; liability distribution if firm fails; ability to raise capital. Organizational: legal & business structure, functional areas of management, interaction btw head office & field managers. Pro level: pro breakdown; time, cost, quality control of pro. Process & operation: construction tech & processes; at field lvl. Task: identification & assignment of work to field units & work crews. Proprietorship: simplest form; indi retains ownership & sole control of firm; all revenue to firm is personal cash revenue to proprietor; all losses/expenses incurred are personal expenses to proprietor; taxed as indi, x separate taxation of firm; Before-tax Profit=Revenue/Income-Cost/Expenses; Tax=(Before-tax Profit-Deductions)x(Tax Rate); credit that firm can obtain & its ability to generate new capital are limited by personal assets; x limitation of liability, x suitable for high-risk business; bankruptcy of firm is personal bankruptcy; life corresponds to owner, die, proprietorship ceases to exist; assets divided among heirs to proprietors estate. Partnership: 2/> ppl start a firm together; division of ownership based on monetary/ non-monetary assets, specified in Charter of Ownership, equal ownership if based on verbal mutual agreement only; to division risk & pool resources; partners share profits & losses according to their degree of ownership; x limitation of liability, directly transmitted to partners; 1 partner may carry more liability as liability of each is not limited. Limited partnership: carry a limited liability, liable only to his investments; x voice in management of firm; allow general partners to attract capitals resources to firm; more difficult to establish; contribution made by limited partner must be tangible (cash, shares of stock, x patent, x copyright); partnership is terminated if 1 partner dies; agreement can be made for continuation; general partners actively involved in management may decide to pay themselves a salary (taxable), action of 1partner is binding on all partners; marriage Corporation: company is a separate legal entity; initial issuance of shares of stock to establish level of ownership of initial stockholders; protection of stockholders personal assets; most complicated: lawyer to prepare legal doc, fees to cover actions by chartering body, printed stock, formal meetings by principals; advan: limitation of liability-good for businesses with high risks, only assets belonging to it are subject to claims settlement & losses; get capital by sell stock instead of borrow $, not subject to repayment/not a liability on balance sheet, corporations continuity is independent of stockholders, unless firm is bankrupt/ corporate charter lapses/all stockholders agree to dissolve; disadvan: reduced lvl of control in management decision making, larger company more decentralized ownership, difficult to reach agreement of all stockholders; certain restrictions when operating outside of its place of incorporation-foreign corporation, legal restrictions; double taxation- same profit that is taxed within corporation is taxed again when it is distributed to stockholders as a dividend
You might also like
- Stop SignboardDocument1 pageStop SignboardJun KangNo ratings yet
- Stockwell TransformDocument5 pagesStockwell TransformJun KangNo ratings yet
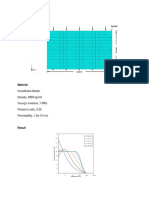
- Effect of Change in Permeability On Clay PropertiesDocument18 pagesEffect of Change in Permeability On Clay PropertiesJun KangNo ratings yet
- Draft - CNNDocument3 pagesDraft - CNNJun KangNo ratings yet
- Cheat SheetDocument1 pageCheat SheetJun KangNo ratings yet
- Project CIVL5110Document2 pagesProject CIVL5110Jun KangNo ratings yet
- Project CIVL 5720Document12 pagesProject CIVL 5720Jun KangNo ratings yet
- Summary - ConsolidationDocument3 pagesSummary - ConsolidationJun KangNo ratings yet
- Stat515 Midterm II Fall 2010Document1 pageStat515 Midterm II Fall 2010Rishabh VaishNo ratings yet
- FEM2Document1 pageFEM2Jun KangNo ratings yet
- Summary - SensorDocument1 pageSummary - SensorJun KangNo ratings yet
- Multifractal AnalysisDocument1 pageMultifractal AnalysisJun KangNo ratings yet
- Stop SignboardDocument1 pageStop SignboardJun KangNo ratings yet
- Journal ReviewDocument3 pagesJournal ReviewJun KangNo ratings yet
- Summary - Gibson (1963)Document1 pageSummary - Gibson (1963)Jun KangNo ratings yet
- Hs SeriesDocument3 pagesHs SeriesJun KangNo ratings yet
- 1 1 1 + 2 3 sin 2 π 3 sin θ sin 2 π 3: K - G modelDocument2 pages1 1 1 + 2 3 sin 2 π 3 sin θ sin 2 π 3: K - G modelJun KangNo ratings yet
- Mesri & Choi (1980)Document1 pageMesri & Choi (1980)Jun KangNo ratings yet
- Bishop (1976)Document2 pagesBishop (1976)Jun KangNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument2 pages1 IntroductionJun KangNo ratings yet
- Summary - Helenelund (1972)Document2 pagesSummary - Helenelund (1972)Jun KangNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument2 pagesSummaryJun KangNo ratings yet
- CIVL5720 Group Assignment 2015Document1 pageCIVL5720 Group Assignment 2015Jun KangNo ratings yet
- 1 1 1 + 2 3 sin 2 π 3 sin θ sin 2 π 3: K - G modelDocument2 pages1 1 1 + 2 3 sin 2 π 3 sin θ sin 2 π 3: K - G modelJun KangNo ratings yet
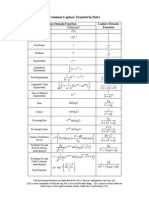
- Common Laplace Transform PairsDocument2 pagesCommon Laplace Transform Pairsf0xnNo ratings yet
- SA520Document18 pagesSA520Jun KangNo ratings yet
- Dual PorosityDocument1 pageDual PorosityJun KangNo ratings yet
- Chronology of Development of Transparent SoilDocument6 pagesChronology of Development of Transparent SoilJun KangNo ratings yet
- Lit. Rev. - Cetin & Soylemez (2004) - Soil-Particle and Pore Orientations During Drained and Undrained Shear of A Cohesive Sandy Silt-Clay SoilDocument2 pagesLit. Rev. - Cetin & Soylemez (2004) - Soil-Particle and Pore Orientations During Drained and Undrained Shear of A Cohesive Sandy Silt-Clay SoilJun KangNo ratings yet
- W Mass of Water Mass of Soil Solids M M: PN PP SN Ns S TC BC FP RM CH TsDocument2 pagesW Mass of Water Mass of Soil Solids M M: PN PP SN Ns S TC BC FP RM CH TsJun KangNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- RT-161 A1 PDFDocument8 pagesRT-161 A1 PDFRaul Diaz100% (1)
- Settling Tank DecantDocument23 pagesSettling Tank Decantjvan migvelNo ratings yet
- Kiln Performance - Efficiency FormulasDocument12 pagesKiln Performance - Efficiency FormulasMohamed ZayedNo ratings yet
- Interurban RMC Rail Bus ManualDocument4 pagesInterurban RMC Rail Bus ManualSteven GardnerNo ratings yet
- VECU - Manual de Producción 70312913Document33 pagesVECU - Manual de Producción 70312913RainorSS100% (2)
- 11 - Hashing PDFDocument24 pages11 - Hashing PDFKealeboga Duece ThoboloNo ratings yet
- OGC-FIC-004-I-Cable Insulation Resistance-Field Installation ChecklistDocument2 pagesOGC-FIC-004-I-Cable Insulation Resistance-Field Installation ChecklistTaylorNo ratings yet
- 008 Cat-6060 Attachment Functions FSDocument37 pages008 Cat-6060 Attachment Functions FSenrico100% (3)
- PC Smart Ptsgob8wDocument11 pagesPC Smart Ptsgob8wJose LopezNo ratings yet
- Boeing Fire AERO - 2011 - Q2 - Article3Document10 pagesBoeing Fire AERO - 2011 - Q2 - Article3Braulio GomesNo ratings yet
- Va Mri Design Plan Drawings and LayoutDocument19 pagesVa Mri Design Plan Drawings and Layoutkusnanto erinNo ratings yet
- Position - List - Tank 17 11 2023Document8 pagesPosition - List - Tank 17 11 2023simionalex1987No ratings yet
- 002 Danfoss PICV Energy Valve Ver 090821 r0Document2 pages002 Danfoss PICV Energy Valve Ver 090821 r0Pattana MekkhumNo ratings yet
- Lab-Java Programming Intro IDocument83 pagesLab-Java Programming Intro IHeavenlyPlanetEarth80% (5)
- Report of Elevator ControllerDocument36 pagesReport of Elevator ControllerSagar G Reddy100% (1)
- MHI NZ Room Sizing Chart 2021Document1 pageMHI NZ Room Sizing Chart 2021fsdfsdfsdNo ratings yet
- SEPG and Consulting ProcessDocument20 pagesSEPG and Consulting ProcesszafzNo ratings yet
- C Aj 1609Document2 pagesC Aj 1609vhin84No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Waveform Coding Techniques PDFDocument33 pagesChapter 3 Waveform Coding Techniques PDFEunielyn SecretoNo ratings yet
- DevOps For VMware Administrators (VMware Press Technology) - 1-321Document321 pagesDevOps For VMware Administrators (VMware Press Technology) - 1-321mailboxrohitsharma100% (1)
- GP2500S/GP2501S - STN Color: Pro-Face Graphic Operator InterfacesDocument2 pagesGP2500S/GP2501S - STN Color: Pro-Face Graphic Operator Interfacesthanh_cdt01No ratings yet
- 30 StabilizersDocument29 pages30 StabilizersnjileoNo ratings yet
- Drying Kinetics and Characteristic Drying Curve of Lightly Salted Sardine (Sardinella Aurita)Document8 pagesDrying Kinetics and Characteristic Drying Curve of Lightly Salted Sardine (Sardinella Aurita)Nguyen Thu HaNo ratings yet
- Google Gender Pay LawsuitDocument31 pagesGoogle Gender Pay LawsuitUSA TODAYNo ratings yet
- ADPDocument165 pagesADPmohhizbarNo ratings yet
- Fletcher Expanding Tables 2013 v7Document59 pagesFletcher Expanding Tables 2013 v7Silviu Prise100% (1)
- DuPont Sontara Wipes Technical SpecsDocument2 pagesDuPont Sontara Wipes Technical SpecsSkySupplyUSANo ratings yet
- Sbi Clerk MainsDocument4 pagesSbi Clerk MainspurushothamNo ratings yet
- Surtec 680: Protection UpgradedDocument7 pagesSurtec 680: Protection Upgradedyudhien4443No ratings yet
- 6 Energy Calculation: UDEC Version 4.0Document28 pages6 Energy Calculation: UDEC Version 4.0Rakshit MishraNo ratings yet