Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IESO 2012 WR Atmosphere and Hydrosphere
Uploaded by
lelo2k3Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IESO 2012 WR Atmosphere and Hydrosphere
Uploaded by
lelo2k3Copyright:
Available Formats
IESO 2012 Written TEST Atmosphere Name_____________________________ Nationality _________________________
1) . Look at this picture below and indicate the correct answer: (1 pts)
Figure 1. Satellite image of Tropics area
This belt of clouds forms on the equator, where cold air from the northern hemisphere meets warm air from the southern hemisphere. During the summer of the northern hemisphere, the mean position of this belt of clouds is north of the equator. This belt of clouds is associated with high pressures. This belt of clouds forms at the confluence of winds named westerlies. This belt of clouds forms where cold air from the upper atmosphere comes down. 2). What is the INCORRECT statement about the jet stream? (1 pt) A sharp variation of the height of the tropopause gives information about the position of the jet stream The presence of dark stripes visable in a water vapour image gives information about the position of the jet stream The jet stream has a maximum velocity called the jet stream core On a 300 hPa chart the position of the jet stream is not able to be identified
A B C D E A B
C D
Figure 2. Geopotential contours
.3). Figure 2 above illustrates the distribution of the geopotential contour of the 500 hPa isobaric surface over Korea. (1 pt) Select the best answer among the statements that describes the upper air corectly 1. Pressure gradient forces act from point X towards point Y. 2. At point Z the wind blows from the west to the east. 3. The steeper the slope of the 500hPa isobaric surface the greater the pressure gradient force
1 2 3 2 and 3 1 and 2 1 and 3
A B C D E F
1,2, and 3 G
4). The western coast of the southernmost part of South America, to the west of the Andes, is characterized by the presence of a rain forest. As opposed to the area to the east of the mountain chain which is a desert (the Patagonia). Taking into account that winds in the area blow most of the time from west to east, how you could explain this difference in vegetation? (1 pt)
In the Andes there are many A volcanoes that produce a lot of ash that facilitates precipitation. The rainfall mainly resulted B from mountain effect orographic uplift Seasonal Monsoonal rainfall C Increased in water flow due to the melting of glaciers D
5). Choose the correct statement about the atmosphere near the equator (1 pt) : A (A) Cold and warm fronts are the dominant source of rainfall (B) Diurnal variation is not important (C) Typhoons often develop in this area (D) The Tropopause temperature is colder than that of midlatitude regions (E) The pressure gradient is important for weather analysis B C D E
Figure 3a January
Figure 3b July
2 and 3 6). Figures 3a and 3b above illustrates the distribution of annual average atmospheric pressure on the ground in January and July. Select the best response from the following statements to describe the given weather charts correctly. (1 pt)
1 and 2
1 and 3 1. In the northern hemisphere Winter, high pressure develops over the land area. 2. In January, high pressure develops over the land area in the 1,2, and 3 southern hemisphere. 3. There is less average variation in atmospheric pressure between winter and summer in the northern hemisphere, compared with the southern hemisphere.
7). Match the following statements with the right choices (1pt) 1. Which gas has the biggest variation in space and time, and has strong influence on the local weather? 2. Which gas has the highest concentration in the Earths atmosphere? 3. Which gas makes the largest contribution to the greenhouse effect? 4. Which gass anthropogenic concentration change is contributing most to climate change?
Put the letter of your choice below
A. CO2 B. CO C. H2O D. He E. N2
8). Clouds are classified according to height and form. High cloud Which response best describes Altocumulus Middle cloud lenticularis? (1 pt) Low cloud Stratiform cloud Cirriform cloud
A B C D E
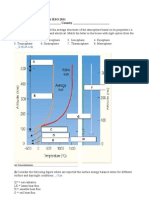
Figure 4
Question number 9 and 10 refers to Figure 4 to the left. Figure 4 shows the vertical profile of mean global air pressure starting from mean sea level and going up to 50 km in altitude. Use the information from Figure 4 to answer the following questions:
9). The term Pressure at the horizontal axis is equivalent to ......... (1 pt)
Weight divided by Volume Mass divided by Area Density multiplied by Temperature Mass multiplied by Temperature Force divided by Area
A B C D E
10). According to Figure 4, The thickest layer is ........ (1 pt)
101-110 hPa 501-510 hPa 701-710 hPa 1001-1010 hPa
A B C D
11). Choose the correct answer (1 pt) 1 and 2 are true 1. Wind above the 1 km elevation generally blows parallel to the pressure contour lines. 2. It always rains when a warm front is approaching. 3. Behind the cold front a northwest wind will blow. A southeast winds will blow behind a warm front. 4. The fronts are expected to move towards the north. 5. The speed of the cold front is nearly the same as the wind speed just behind front. 2 and 4 are true 1 and 3 are true 1 and 4 are true 1 and 5 are true 3 and 5 are true 4 and 5 are true 3 and 4 are true A B C D E F G H
12). The center of mass of the Earths atmosphere is (1pt): A) a little less than halfway between the Earths surface and the outer boundary of the atmosphere. B) near the surface of the Earth. C) near the outer boundary of the atmosphere. D) near the center of Earth. E) none of the above.
13). Look at the picture of the clouds in Figure 5 below Figure 5 Which statement is correct ? (1pt) The clouds are: (A) associated with a vertical wind shear (B) formed due to a passage of a jet plane (jet contrail) (C) thunderstorm clouds (D) a precursor of an earthquake (E) cloud street
Calculation Problems 14). Temperature (0C) 10,0 12,0 14,0 16,0 18,0 20,0 22,0 24,0 26,0 28,0 30,0 The vapor pressure of water decreases as the temperature decreases. If the amount of water vapor in the air is kept constant as the air is cooled, then the temperature would reach the dew point, at which the partial pressure and vapor pressure coincide and the vapor is saturated. If the air is cooled further, vapor condenses to liquid until the partial pressure again equals the vapor pressure at that temperature. In the meteorological laboratory with the room temperature 26.0 oC, a meteorologist cools a metal can by gradually adding cold water. When the can temperature reaches 16.0oC, water droplets form on the cans outside surface.
Vapor Pressure (X 103Pa) 1,23 1,40 1,60 1,81 2,06 2,34 2,65 2,99 3,36 3,78 4,24
What is the relative humidity of the 26.0oC air in the room? (show all your calculations) (3 pts)
Answer. Relative humidity =
partial pressure of water vapor at temperature T x 100 % saturated vapor pressure of water at temperature T
The experiment shows that the dew point is 16.0oC, so the partial pressure of water vapor at 26.0oC is equal to the vapor pressure at 16.0oC, which is 1.81103 Pa. Thus the relative humidity =
1.81 10 3 Pa 100% = 0.539 100% = 53.9% 3.36 10 3 Pa
15). In a static atmosphere, the pressure change with height is governed by the hydrostatic equation p = gz. In this equation: g is the gravitational acceleration in m/s2 (g = 9.81 m/s2) is the air density in kg/m3 p is pressure difference in Pa (pascal) z is the thickness of different height When the mean air density between 1000 hPa to 500 hPa layer is 0.910 kg/m3, calculate the height of 500 hPa level with the assumption that mean sea level pressure is 1000 hPa (show your calculations). (3 pts) Answer: 1 hPa = 100 Pa = 100 kg/m/s2
p = 1000 hPa 500 hPa = 500 hPa = 50000 Pa z = p/(g) p = gz = 50000 Pa / (0.910 kg/m3 x 9.81 m/s2) = 50000 Pa/(8.9271 kg/m2/ s2) = 5600,9 m Thus the hight of 500 hPa level is 5601 m
IESO 2012 Written TEST Hydrosphere Name_____________________________ Nationality _________________________
Figure 1(a) vertical temperature profiles
Figure 1(b) time series of isothermal contours. 1). Figures 1(a) and 1(b) show growth and decay of the seasonal thermocline at 50N, 145W in the eastern North Pacific. The upper mixed layer, as seen in the upper part of Figure 1(a) is a vertically mixed layer with nearly homogeneous water temperature. Referring the above figures 1(a) and 1(b), choose two right answers (2pts). A. Variation of the mixed layer depth depends on the strength of the warm and cold water currents. B. Decreasing of the mixed layer thickness from winter to summer is due to the heat increase from solar radiation and the decrease of mixing by weakening winds. C. The main processes that cause the highest water temperature to occur in August are due to the cold water runoff from the land and the decrease of mixed layer thickness. D. The depth of the mixed layer in November is deeper than in May. One of the factors causing an increase in depth of the mixed layer in November is thermal convection due to the surface cooling by heat loss. All the right answers are: B, D
2). Methane hydrates, also called fire ice, trap methane molecules, and are found in enormous quantities in the near subsurface of marine sediments in many places. If the warming of water melts the fire ice, and liberates the methane molecules into the ocean water and eventually into the atmosphere, what will the effect on the global weather be: (2 pts) 3). Tide is the most periodic phenomena in the sea but the tidal range varies every day. Choose the two INCORRECT answers describing the tidal phenomena (2 pts).
Decreasing the global warming Increasing the global warming It will not affect the global warming Increasing only the local warming
A B C D
Lunar tide is generated by the difference of forces between the gravitational attraction force A of the Moon and the centrifugal force by the Earths rotation. Tide generating forces (TGF) by the Sun is about B 46% of TGF by the Moon. Tidal range is greater in the new and full moon C phases than in quarter moon phases. Spring and neap tides are produced by the D superposition of diurnal and semi-diurnal tides. High and low tides occur once or twice a day E depending on the geographical locations on the Earth.
4). Figure 2 below indicates the general pattern of ocean currents in the Pacific Ocean. Figure 2
4.1) From Figure 2, what wind is responsible for the current at location A? (2pts) (A) Polar Westerly Wind (B) Southeasterly Trade Wind (C) Westerly Wind (D) Northeasterly Trade Wind
4.2) From Figure 2, what is the name of current at location B? (2pts) (A) South Equatorial Current (B) Equatorial Counter Current (C) North Equatorial Current (D) North Pacific Current
4.3) Currents at locations A, B, C all belong to the geostrophic current. What are the two major opposing forces that create the geostrophic currents? (2 pts) (A) Wind stress (B) Coriolis force (C) Pressure gradient force (D) Bottom friction
5) . (3 pts) Figure 3
The alpine river Isre, in France flows through the city of Grenoble. Its drainage basin, as measured at this location, has an area of 6x109 m2. The mean density of the rocks in this drainage basin is 2.5g/cm3. During the year 2004, the Isre at Grenoble removed 3x109 kg of material (dissolved and solid). For the drainage basin, calculate the mean rate of erosion in depth per year for 2004. Choose the correct answer.
2 meters per year
1 meter per year 20 millimeters per year 2 millimeters per year 0.2 millimeter per year
B C D E
You might also like
- IESO Question Paper 2009Document78 pagesIESO Question Paper 2009Science Olympiad BlogNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Elements of Ecology 9Th Edition by Msmith and Leo Smith Isbn 9780321934185 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Elements of Ecology 9Th Edition by Msmith and Leo Smith Isbn 9780321934185 Full Chapter PDFearl.lakey528100% (18)
- IESO 2012 PT AtmosphereDocument5 pagesIESO 2012 PT Atmospherelelo2k3No ratings yet
- Research Program: Entrance Paper Atmospheric CodeDocument10 pagesResearch Program: Entrance Paper Atmospheric Codegeorgescribd33No ratings yet
- Dessler Et Al-2008-Geophysical Research LettersDocument4 pagesDessler Et Al-2008-Geophysical Research LettersMajidNo ratings yet
- SE-151 ENVI POLN (Air Polln - Units, Meteorology) Lecture 4Document11 pagesSE-151 ENVI POLN (Air Polln - Units, Meteorology) Lecture 4Princess Jean L. GalabinNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Meteorology II - 020210Document42 pagesAir Pollution Meteorology II - 020210Alon MandelNo ratings yet
- Air Pollutants and Global ClimateDocument83 pagesAir Pollutants and Global ClimateJohnrick LaquintaNo ratings yet
- IESO 2016 Written Test No 2Document12 pagesIESO 2016 Written Test No 2YUSUPNo ratings yet
- UD 2 The Atmosphere 1º ESODocument10 pagesUD 2 The Atmosphere 1º ESONoelia Francisco PastorNo ratings yet
- Earths Climate Past and Future 3rd Edition by Ruddiman ISBN Test BankDocument7 pagesEarths Climate Past and Future 3rd Edition by Ruddiman ISBN Test Banksteven100% (28)
- Meterology QuestionDocument15 pagesMeterology QuestionAMIRNo ratings yet
- ES 1C03 Quiz 3Document26 pagesES 1C03 Quiz 3NTRisforthinkersNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere - KeyDocument4 pagesAtmosphere - KeyMária NemesNo ratings yet
- The Ocean The Ocean: Idi O Indian OceanDocument51 pagesThe Ocean The Ocean: Idi O Indian OceanHelmleyNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere: CyanobacteriaDocument11 pagesAtmosphere: CyanobacteriaNaser MahmudNo ratings yet
- Tananyag Fejlesztés Idegen Nyelven: Prevention of The AtmosphereDocument39 pagesTananyag Fejlesztés Idegen Nyelven: Prevention of The AtmospheremoxlindeNo ratings yet
- Surr Ka FileDocument3 pagesSurr Ka Filemv7602456No ratings yet
- 01 Hartmann Global Physical Climatology 2nd - Ed Páginas 7 29Document23 pages01 Hartmann Global Physical Climatology 2nd - Ed Páginas 7 29ElizabethCastañedaHernandez100% (2)
- Design Exercise No 1Document6 pagesDesign Exercise No 1Ubair Javaid 16 (Game Play)No ratings yet
- 1.4 The AtmosphereDocument11 pages1.4 The AtmosphereJoefel BessatNo ratings yet
- Lindzen, 1994, On The Scientific Basis For Global Warming Scenarios - #GlobalwarmingDocument10 pagesLindzen, 1994, On The Scientific Basis For Global Warming Scenarios - #GlobalwarmingYovanMenkevickNo ratings yet
- Meteorology 001Document193 pagesMeteorology 001Andrin JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Climate Tipping PointsDocument36 pagesClimate Tipping PointsKopal AroraNo ratings yet
- Es Unit 4 Exam ClimateDocument6 pagesEs Unit 4 Exam Climateapi-287186223No ratings yet
- Lectures On Meteorology-ThaerO - RoomiDocument54 pagesLectures On Meteorology-ThaerO - RoomiNtokozo MtshaliNo ratings yet
- 123sdfkh Sample QuestionsDocument6 pages123sdfkh Sample Questionsjoebobinson3No ratings yet
- Leighton & Murray 1966Document9 pagesLeighton & Murray 1966maurobioNo ratings yet
- Artigo InpaDocument18 pagesArtigo InpaApotecários da FlorestaNo ratings yet
- APhO Theory Question 1 Question PaperDocument4 pagesAPhO Theory Question 1 Question PaperCretu NicolaeNo ratings yet
- Lecture04 AtmosphereDocument29 pagesLecture04 AtmosphereJason HyunNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document4 pagesLecture 3Shanzay KhanNo ratings yet
- Q. 1 - Q. 9 Carry One Mark Each & Q. 10 - Q. 22 Carry Two Marks EachDocument5 pagesQ. 1 - Q. 9 Carry One Mark Each & Q. 10 - Q. 22 Carry Two Marks Eachambika senNo ratings yet
- TestBookletDocument12 pagesTestBookletOLIVIA CIRILLONo ratings yet
- Met Worksheet 1 - The AtmosphereDocument4 pagesMet Worksheet 1 - The AtmosphereSujan IyerNo ratings yet
- K Ch10 SolutionsDocument6 pagesK Ch10 SolutionsselamitspNo ratings yet
- CE 394K.2 Hydrology: Atmospheric Water and Precipitation - Literary Quote For TodayDocument72 pagesCE 394K.2 Hydrology: Atmospheric Water and Precipitation - Literary Quote For TodayHida CahyaniNo ratings yet
- Meteorology QuizDocument2 pagesMeteorology Quiznali.No ratings yet
- ClimatologyDocument6 pagesClimatologyEyeVanNo ratings yet
- Answer KeyDocument7 pagesAnswer KeyMarilyn Castro LaquindanumNo ratings yet
- Design 1 HydrologyDocument4 pagesDesign 1 HydrologyMuhammad Waseem YaseenNo ratings yet
- P1.7 Measurements of The Radiative Surface Forcing of ClimateDocument8 pagesP1.7 Measurements of The Radiative Surface Forcing of Climatemalfet1066No ratings yet
- Geoglogy Activity 9Document4 pagesGeoglogy Activity 9Cejay SarzNo ratings yet
- Furevik - (Exercise) Atmosphere Ocean DynamicDocument69 pagesFurevik - (Exercise) Atmosphere Ocean Dynamicraiz123No ratings yet
- Actividades 1º ESO Bilingüe T5Document6 pagesActividades 1º ESO Bilingüe T5davidbio_nrNo ratings yet
- Government Engineering College, Valsad: Hydrology & Water Resources ENGINEERING (2150602)Document113 pagesGovernment Engineering College, Valsad: Hydrology & Water Resources ENGINEERING (2150602)Yashika Bhathiya JayasingheNo ratings yet
- Laboratory or Field - Lysimeters: Different Methods To Measure ETDocument24 pagesLaboratory or Field - Lysimeters: Different Methods To Measure ETlance carterNo ratings yet
- GR 10 Geography (English) Controlled Test 1 2023 Question PaperDocument139 pagesGR 10 Geography (English) Controlled Test 1 2023 Question Papermmncube975No ratings yet
- Wa0136.Document5 pagesWa0136.FarhanakhirrmdhnNo ratings yet
- Energy Balance Climate ModelsDocument4 pagesEnergy Balance Climate ModelsLuis Esteban Gómez CadavidNo ratings yet
- Ian Folkins Et Al - Seasonal Cycles of O3, CO, and Convective Outflow at The Tropical TropopauseDocument5 pagesIan Folkins Et Al - Seasonal Cycles of O3, CO, and Convective Outflow at The Tropical TropopauseRemazzzNo ratings yet
- OC 450 Climatic Extremes Problem #1 Due: Friday, Jan 16Document5 pagesOC 450 Climatic Extremes Problem #1 Due: Friday, Jan 16ይቴ ስንሻዉNo ratings yet
- HYDROLOGY AND WATER QUALITY CONTROL FirstDocument7 pagesHYDROLOGY AND WATER QUALITY CONTROL FirstAljon LanguingNo ratings yet
- Geog101 S1 2017Document9 pagesGeog101 S1 2017Cheng FuNo ratings yet
- GWCC UpdatedDocument89 pagesGWCC Updateddurga sharmaNo ratings yet
- Slope EvolutionDocument28 pagesSlope EvolutionkudaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Climatology Short QuestionsDocument12 pagesGrade 10 Climatology Short QuestionsIbraheem KassamNo ratings yet
- Earths Climate Past and Future 3rd Edition Ruddiman Test BankDocument8 pagesEarths Climate Past and Future 3rd Edition Ruddiman Test BankThomasClinewpsix100% (21)
- Whether the Weather: Aviation Meteorology from A to ZFrom EverandWhether the Weather: Aviation Meteorology from A to ZNo ratings yet
- Science Illustrated July-August 2008Document79 pagesScience Illustrated July-August 2008lelo2k30% (1)
- 15643Document12 pages15643lelo2k3No ratings yet
- Our Fragile Planet - Hydrosphere - Freshwater Sytems and PollutionDocument209 pagesOur Fragile Planet - Hydrosphere - Freshwater Sytems and Pollutionlelo2k3No ratings yet
- 50 Years of The Turbidite Paradigm (Shanmugam, 2000)Document58 pages50 Years of The Turbidite Paradigm (Shanmugam, 2000)hilman_satriaNo ratings yet
- Our Fragile Planet - Geosphere - The Land and Its UsesDocument217 pagesOur Fragile Planet - Geosphere - The Land and Its Useslelo2k3100% (1)
- Soria 2007 Symposium CrustaceansDocument5 pagesSoria 2007 Symposium Crustaceanslelo2k3No ratings yet
- IESO 2012 AstronomyDocument4 pagesIESO 2012 AstronomyAdides Gidson SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- IESO 2012 WR GeosphereDocument8 pagesIESO 2012 WR Geospherelelo2k3No ratings yet
- Year of Planet Earth: EssayDocument1 pageYear of Planet Earth: Essaylelo2k3No ratings yet
- IESO 2012 PT GeosphereDocument3 pagesIESO 2012 PT Geospherelelo2k3No ratings yet
- IESO 2012 WR AstronomyDocument4 pagesIESO 2012 WR Astronomylelo2k3No ratings yet
- Practical Test For Ieso 2010: Dlingo Area, Bantul Regency, Yogyakarta, IndonesiaDocument9 pagesPractical Test For Ieso 2010: Dlingo Area, Bantul Regency, Yogyakarta, Indonesialelo2k3No ratings yet
- Science ConveyorBelt 12Document2 pagesScience ConveyorBelt 12lelo2k3No ratings yet
- IESO 2010 Atmosphere PracticalDocument6 pagesIESO 2010 Atmosphere Practicallelo2k3No ratings yet
- IESO 2011 Hydrosphere Written Test QuestionsDocument5 pagesIESO 2011 Hydrosphere Written Test Questionslelo2k3No ratings yet
- IESO 2011 Written InstructionsDocument1 pageIESO 2011 Written Instructionslelo2k3No ratings yet
- IESO 2010 Meteorology WrittenDocument9 pagesIESO 2010 Meteorology Writtenlelo2k3No ratings yet
- IESO 2010 Oceanography WrittenDocument3 pagesIESO 2010 Oceanography Writtenlelo2k3No ratings yet
- IESO 2011 Atmosphere Written Test QuestionsDocument7 pagesIESO 2011 Atmosphere Written Test Questionslelo2k3No ratings yet
- IESO 2010 Astronomy WrittenDocument5 pagesIESO 2010 Astronomy Writtenlelo2k3No ratings yet
- IESO 2010 Astronomy Practical Answer SheetDocument2 pagesIESO 2010 Astronomy Practical Answer Sheetlelo2k3No ratings yet
- IESO 2010 Geosphere Practical Laboratory Test1Document6 pagesIESO 2010 Geosphere Practical Laboratory Test1GeocienciasUnicampNo ratings yet
- IESO 2011 Geosphere Written QuestionsDocument25 pagesIESO 2011 Geosphere Written Questionslelo2k3No ratings yet
- IESO 2010 Geology WrittenDocument4 pagesIESO 2010 Geology Writtenlelo2k3No ratings yet
- IESO 2010 Geophysics WrittenDocument6 pagesIESO 2010 Geophysics Writtenlelo2k3No ratings yet
- IESO 2010 Astronomy PracticalDocument3 pagesIESO 2010 Astronomy Practicallelo2k3No ratings yet
- Ieso2009 PT AstDocument11 pagesIeso2009 PT Astlelo2k3No ratings yet
- IESO 2010 Astronomy PracticalDocument3 pagesIESO 2010 Astronomy Practicallelo2k3No ratings yet
- Cfcschlorofluorocarbons Ea14Document2 pagesCfcschlorofluorocarbons Ea14api-313086327No ratings yet
- Engleski Jezik - Zbirka Tekstova Sa Vežbanjima - Svetlana VelimiracDocument50 pagesEngleski Jezik - Zbirka Tekstova Sa Vežbanjima - Svetlana VelimiracKatarina Vrhovac100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Tropical Climate Dynamics: Printed BookDocument1 pageFundamentals of Tropical Climate Dynamics: Printed Bookastroboy700No ratings yet
- Reading Activity - PDFDocument1 pageReading Activity - PDFKNACNo ratings yet
- ELS Q1 Week-1aDocument6 pagesELS Q1 Week-1aJocet GeneralaoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Climate Week - 1: Climatology (Rar - 309)Document21 pagesIntroduction To Climate Week - 1: Climatology (Rar - 309)jashndeepNo ratings yet
- Thermalling PDFDocument68 pagesThermalling PDFPara Club MilazzoNo ratings yet
- First Summative TestDocument3 pagesFirst Summative TestNini VillezaNo ratings yet
- Ideas of Ancient Greek: ElementsDocument31 pagesIdeas of Ancient Greek: ElementsJean Carmel Novelo100% (1)
- Plant Selection CriteriaDocument24 pagesPlant Selection CriteriahimaniNo ratings yet
- Gharo Wind FarmDocument35 pagesGharo Wind FarmAbbas AliNo ratings yet
- MPE 571 Chapter 2Document18 pagesMPE 571 Chapter 2Wilbon KibetNo ratings yet
- PictionaryDocument27 pagesPictionarySally PocamasNo ratings yet
- Ventilated Facades INT PDFDocument42 pagesVentilated Facades INT PDFMayre Rachel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 11-12Document16 pagesPractice Test 11-12Thu HiềnNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument25 pagesClimate ChangeHershey MagsayoNo ratings yet
- Science High School Entrance Questions 1 (2018) AKDocument5 pagesScience High School Entrance Questions 1 (2018) AKNeptune Lopez90% (10)
- The Inner Planets: Cross-Curricular Focus: Earth ScienceDocument2 pagesThe Inner Planets: Cross-Curricular Focus: Earth ScienceElisif TitaniaNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower ManualDocument80 pagesCooling Tower ManualBikas Saha100% (3)
- Basic Principles and Systems of Grain DryingDocument13 pagesBasic Principles and Systems of Grain DryingMary - Ann AndalNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange ColumnsDocument13 pagesIon Exchange Columnsjdiosbernal10No ratings yet
- Sains SPM Chapter 3 Form 5Document10 pagesSains SPM Chapter 3 Form 5秀珍100% (1)
- NearSpace Balloon LaunchDocument687 pagesNearSpace Balloon Launchfranco.didio1945No ratings yet
- Action Guide For Climate Champions 2022-2023Document24 pagesAction Guide For Climate Champions 2022-2023kaziba stephenNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 2: Origin and Structure of The Earth (The Subsystem)Document18 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 2: Origin and Structure of The Earth (The Subsystem)Maureen BalanonNo ratings yet
- Ancient Greeks Had Great Understanding of Weather and ClimateDocument6 pagesAncient Greeks Had Great Understanding of Weather and ClimateliezlNo ratings yet
- 117 Jaa Principles of Flight Demo PDFDocument7 pages117 Jaa Principles of Flight Demo PDFLay AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- 7 PDFDocument258 pages7 PDFRobbyo Ardiles PNo ratings yet
- 1st Summative Test in Earth and Life ScienceDocument2 pages1st Summative Test in Earth and Life ScienceAngela Marie Diwa79% (14)
- Sea BreezeDocument2 pagesSea Breezevee propagandaNo ratings yet