Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Energy and Prox Analysis
Uploaded by
freak009Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Energy and Prox Analysis
Uploaded by
freak009Copyright:
Available Formats
Energy
Food
ENERGY
Nutrients Gross E Digestible E Metabolizable E
Energy requirements
David L. Hammond, DVM, DACVIM
Resting energy requirements Daily energy requirements
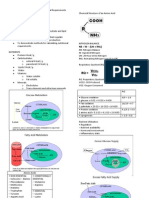
Nutrients - Definitions Any food constituent that helps support life Essential
Basic Nutrient Categories
VITAMINS MINERALS Lipids
indispensable - the body cannot synthesize
Conditionally essential
ENERGY
PROTEINS CARBOHYDRATES WATER
required during certain physiologic or pathologic conditions dispensable - the body can synthesize
Nonessential
Energy density = Kcal/unit of volume
Proximate Analysis
Most
Proximate Analysis
Protein
common analysis done for nutritional testing Crude fat, crude protein, moisture, crude fiber & ash
carbohydrates determined by calculation
16 + 2% nitrogen Nitrogen 6.25 = Crude Protein Non-protein nitrogen (e.g. urea or ammonia) = error
NFE
(nitrogen free extract)
Carbohydrate content 100% - % H2O - % CP - % fat - % CF % ash = NFE
Nutrients - Proximate Analysis
Average Nutrient Analysis
More
accurate than proximate analysis Petfood manufacturers information
Product guides Company websites Customer service (telephone)
SACN 4th Edition
Energy Content of Food
Nutrients - Proximate Analysis
Energy
density
Gross E 9.0 kcal/g 4.0 kcal/g 4.0 kcal/g 0 kcal/g Atwater 8.5 kcal/g 3.5 kcal/g 3.5 kcal/g 0 kcal/g
Fat CHO Protein Fiber
SACN 4th Edition
Modified Atwater Formula
Proximate
Energy Needs of the Patient
analysis:
Protein + 1.5% Fat + 1.0% Crude fiber 0.7% Moisture 4% Ash (when not provided)
Calorimetry - measurement of heat Direct
measurement of heat dissipation by physical methods inference of heat production from quantitative measurement of chemical byproducts of metabolism
Indirect
2% for canned foods 6% for dry foods
e.g. O2 consumption, CO2 production
Hill RC et al JAVMA 2009;234:347-351
Energy Needs of the Patient
Energy Needs of the Patient
Daily
Resting energy requirement (RER) 1000 kcal/m2 70 (Wtkg)0.75 30(Wtkg) + 70*
*(> 2 kg and < 45 Kg) Use Ideal Body Weight
energy requirement (DER) in kcal per day
aka: MER, MEE & DEE DER = RER maintenance factor
maintenance factor varies according to species, age, reproductive status, environment and activity level
only represents an estimate
Calculation of DER
Calculation of DER
Canine Maintenance (1.0 to 1.8 x RER) Neutered adult = 1.6 x RER Intact adult = 1.8 x RER Obese-prone = 1.4 x RER Weight loss = 1.0 x RER Weight gain = 1.2-1.4 x RER at ideal weight Light work = 2 x RER Moderate work = 3 x RER Heavy work = 4-8 x RER
Feline Maintenance (0.8 -1.4 x RER) Neutered adult = 1.2 x RER Intact adult = 1.4 x RER Obese-prone = 1.0 x RER Weight loss = 0.8 x RER Weight gain = 1.2-1.4 x RER at ideal weight
Food Dosage Determination
Food Dosage Determination
Example: 20 kg spayed female
red spaniel
Calculate RER: RER = [30(BWtkg) + 70] RER = [30(20 kg) + 70] RER = 670 kcal/day
Calculate DER: DER = RER Factor DER = 670 kcal/day 1.4 DER = 938 kcal/day
Food Dosage Determination
A Measuring Cup
Determine food dose:
Energy Requirement Energy Density of food 938 kcal day cup = 2.68 cups/d 350 kcal
An
8 ounce measuring cup holds 8 fluid ounces (volume) not 8 ounces of weight
938 kcal/day 350 kcal/cup = 2.68 cups/day
You might also like
- MedicineDocument17 pagesMedicineSubhashini R0% (1)
- Crystal Aromatherapy Lesson 1Document9 pagesCrystal Aromatherapy Lesson 1crystals21No ratings yet
- Recommended Dietary AllowanceDocument24 pagesRecommended Dietary Allowanceuttkarsh100% (4)
- Human Anatomy QsDocument31 pagesHuman Anatomy QsAzhagar Ramesh SNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Weld RadiographsDocument10 pagesInterpretation of Weld RadiographsarianaseriNo ratings yet
- Trees in IndiaDocument43 pagesTrees in IndiaAr Archana PrabakaranNo ratings yet
- Process RecordingDocument12 pagesProcess RecordingIanna J. L. PedrosaNo ratings yet
- DolcetDocument3 pagesDolcetConn_Casipe_8158100% (4)
- Neonatal TPN: Dr. Fahad Al-AqlDocument10 pagesNeonatal TPN: Dr. Fahad Al-AqlAnonymous 9dVZCnTXSNo ratings yet
- Total Parenteral NutritionDocument12 pagesTotal Parenteral NutritionSheikhNo ratings yet
- Retinos PDFDocument83 pagesRetinos PDFPaulo Gan100% (2)
- Metabolism and Energy BalanceDocument45 pagesMetabolism and Energy BalanceNabil Zakin100% (1)
- Pet Nutrition-Zadina 7.11.11Document34 pagesPet Nutrition-Zadina 7.11.11doczadina5428100% (1)
- Phytochemical Screening and Extraction A ReviewDocument9 pagesPhytochemical Screening and Extraction A Reviewsaivasya50% (2)
- Energy Intake and ExpenditureDocument38 pagesEnergy Intake and ExpenditureNichNo ratings yet
- Parenteral NutritionDocument35 pagesParenteral NutritionRhomizal Mazali100% (1)
- High Protein & Low Carb Diet Women - Lose Weight Quickly and Much - Men - Increase Muscle Mass and Become Very Strong -: COOKBOOK, #3From EverandHigh Protein & Low Carb Diet Women - Lose Weight Quickly and Much - Men - Increase Muscle Mass and Become Very Strong -: COOKBOOK, #3No ratings yet
- Calculation of Energy RequirementsDocument2 pagesCalculation of Energy Requirementsfreak009No ratings yet
- Energy Requirements of Ruminants (2012)Document56 pagesEnergy Requirements of Ruminants (2012)Nestor E. ObispoNo ratings yet
- Determination of Feed EnergyDocument19 pagesDetermination of Feed EnergyIonela HoteaNo ratings yet
- 1 Energy 2012Document6 pages1 Energy 2012Luis Matos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Kebutuhan Zat Gizi Untuk Pasien Pada Berbagai Gangguan: Oleh: Dr. Ikbal Gentar Alam, Mkes, SPGK, AifoDocument103 pagesKebutuhan Zat Gizi Untuk Pasien Pada Berbagai Gangguan: Oleh: Dr. Ikbal Gentar Alam, Mkes, SPGK, AifoRafsya JulwandikaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet (Repaired)Document4 pagesNutrition and Diet (Repaired)iamarrhinneNo ratings yet
- Dairy Cattle Nutrition - The Basics: Dr. L. E. Chase Department of Animal Science Cornell UniversityDocument49 pagesDairy Cattle Nutrition - The Basics: Dr. L. E. Chase Department of Animal Science Cornell UniversityEarl Adam LambacoNo ratings yet
- PrelimsDocument7 pagesPrelimstabiNo ratings yet
- Nutritional RequirementDocument4 pagesNutritional RequirementAngela Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Professional Diploma in Sports Nutrition: Lesson 7Document28 pagesProfessional Diploma in Sports Nutrition: Lesson 7Jomari ServanoNo ratings yet
- School of Arts & Sciences Natural Science Department: PED 291 - Physical Fitness Final Exam - Spring 2017Document12 pagesSchool of Arts & Sciences Natural Science Department: PED 291 - Physical Fitness Final Exam - Spring 2017Eliot KhNo ratings yet
- UnitVII-2Nutrition and DietDocument38 pagesUnitVII-2Nutrition and DietYuNa YoshinoyaNo ratings yet
- Diet Planning PDFDocument37 pagesDiet Planning PDFNa NisNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Ped CCM (Picucourse)Document46 pagesNutrition in Ped CCM (Picucourse)surasuarezlopezNo ratings yet
- Feeds, Nutrients, and Animal Requirements: NDSU Feedlot SchoolDocument81 pagesFeeds, Nutrients, and Animal Requirements: NDSU Feedlot SchoolIonela HoteaNo ratings yet
- Energy ChapterDocument13 pagesEnergy Chaptersebastian110504No ratings yet
- Nutr1 F09Document39 pagesNutr1 F09Safeer SiddickyNo ratings yet
- Diet PlanDocument5 pagesDiet PlanUdit MittalNo ratings yet
- 375 Body Comp Changes&Meal Planning 5-21-19Document44 pages375 Body Comp Changes&Meal Planning 5-21-19Justin DoepkerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NutritionDocument30 pagesIntroduction To NutritionAmera GBTNo ratings yet
- Calculation Energy Step by StepDocument6 pagesCalculation Energy Step by StepcchatrumaNo ratings yet
- Metabolism in SurgeryDocument5 pagesMetabolism in Surgeryjc_sibal13No ratings yet
- Goat Nutrition Feeds & Feeding: by Shelby Filley and Amy Peters Oregon State University Extension ServiceDocument54 pagesGoat Nutrition Feeds & Feeding: by Shelby Filley and Amy Peters Oregon State University Extension ServiceVet Dr-BabarNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Making Well-Informed Food ChoicesDocument5 pagesChapter Four: Making Well-Informed Food ChoicesJessa Mae AlgarmeNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts On Parentheral Nutrition by IrfanDocument239 pagesBasic Concepts On Parentheral Nutrition by Irfanzamurd76No ratings yet
- Basic Human Needs - NutritionDocument65 pagesBasic Human Needs - NutritionAfnila AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Class Note NUT 301 - 3 - ENERGY REQUIREMENTSDocument13 pagesClass Note NUT 301 - 3 - ENERGY REQUIREMENTSomonzejele jenniferNo ratings yet
- Nutririon Sec1 NEW FinalDocument40 pagesNutririon Sec1 NEW FinalMOSTAFA HAMDYNo ratings yet
- Diet Design Tools and GuidelinesDocument68 pagesDiet Design Tools and GuidelinescheriemooreNo ratings yet
- Energy MetabolismDocument40 pagesEnergy MetabolismRuby JayaseelanNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: Dra - Esperanza Jean Ferrer-JimenezDocument56 pagesNutrition: Dra - Esperanza Jean Ferrer-JimenezDan FabrosNo ratings yet
- Fish Nutrition and FeedingDocument28 pagesFish Nutrition and FeedingAdi SusantoNo ratings yet
- Feed and FeedingDocument10 pagesFeed and Feedingshinwar benyamenNo ratings yet
- Project Analysis Forms: Weight Management and Physical ActivityDocument13 pagesProject Analysis Forms: Weight Management and Physical ActivityDanny_B_MonterrosoNo ratings yet
- Baaop DikuDocument58 pagesBaaop DikusiscaNo ratings yet
- LAMA-Protein-Energy Malnutrition in AlpacasDocument7 pagesLAMA-Protein-Energy Malnutrition in Alpacastaner_soysuren100% (2)
- Energy BalanceDocument29 pagesEnergy BalanceAlinta AyuningtyasNo ratings yet
- Metabolism and Energy BalanceDocument49 pagesMetabolism and Energy BalanceMadya Pratama100% (1)
- Wildlife Nutrition WSCI 6371: Dr. David HewittDocument52 pagesWildlife Nutrition WSCI 6371: Dr. David HewittJazmín FloresNo ratings yet
- Parenteral Nutrition: DR Mohd Nikman AhmadDocument35 pagesParenteral Nutrition: DR Mohd Nikman AhmadMaryGraceVelascoFuentesNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: A. E B - Energy Is Derived or Obtained From Foods ConsumedDocument11 pagesNutrition: A. E B - Energy Is Derived or Obtained From Foods Consumeddlneisha6167% (6)
- 1 Helios ProductionDocument64 pages1 Helios ProductionGovind GuptaNo ratings yet
- Pakan KudaDocument20 pagesPakan KudaAndini NurfitrieNo ratings yet
- Nutrition - Practicals: DR Vinod M Asst Prof Dept of Pediatrics BgsgimsDocument51 pagesNutrition - Practicals: DR Vinod M Asst Prof Dept of Pediatrics BgsgimsJeevanNo ratings yet
- Diet and NutritionDocument25 pagesDiet and NutritionRainy seasonNo ratings yet
- AS 252 DR Chris - ARCDocument105 pagesAS 252 DR Chris - ARCSuhuyineNo ratings yet
- Nutrition1: Outline: Biochemistry Julie & ZyrhcDocument11 pagesNutrition1: Outline: Biochemistry Julie & ZyrhcZei RuhanoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Oral HealthDocument109 pagesNutrition and Oral Healthmangesh andhareNo ratings yet
- Case 4Document139 pagesCase 4KurlNo ratings yet
- Nutrition 1Document51 pagesNutrition 1hpxyf2zh7nNo ratings yet
- Diet ComputationDocument19 pagesDiet ComputationgraciaNo ratings yet
- Food ComponentsDocument34 pagesFood Componentsghlaogh8No ratings yet
- 2006 Drought StrategiesDocument3 pages2006 Drought Strategiesfreak009No ratings yet
- Parasite Control Guidelines FinalDocument24 pagesParasite Control Guidelines Finalfreak009No ratings yet
- Ischeminc Myelopathy in 52 DogsDocument9 pagesIscheminc Myelopathy in 52 Dogsfreak009No ratings yet
- AVMA Background Sheep Tail DockingDocument3 pagesAVMA Background Sheep Tail Dockingfreak009No ratings yet
- Ethical and Professional Guidelines: Position Statement Protocol (2010)Document29 pagesEthical and Professional Guidelines: Position Statement Protocol (2010)freak009No ratings yet
- Bio Guidelines Cont of Ven Trans DisDocument22 pagesBio Guidelines Cont of Ven Trans Disfreak009No ratings yet
- Animal Welfare AVMA Policy - Animals Used in Entertainment, Shows, and For ExhibitionDocument1 pageAnimal Welfare AVMA Policy - Animals Used in Entertainment, Shows, and For Exhibitionfreak009No ratings yet
- A A Ep Care Guidelines RR 2012Document36 pagesA A Ep Care Guidelines RR 2012freak009No ratings yet
- Bio Security Guidelines Final 030113Document5 pagesBio Security Guidelines Final 030113freak009No ratings yet
- Adult Vaccination Chart Final 022412Document5 pagesAdult Vaccination Chart Final 022412freak009No ratings yet
- Foal Vaccination Chart Updated 090612Document5 pagesFoal Vaccination Chart Updated 090612freak009No ratings yet
- Equine Physical Exam and Restraint ReviewDocument6 pagesEquine Physical Exam and Restraint Reviewfreak009No ratings yet
- Herd Health Protocols For Heifers: Clostridium Type A SeleniumDocument1 pageHerd Health Protocols For Heifers: Clostridium Type A Seleniumfreak009No ratings yet
- Equine Herpesvirus Myeloencephalopathy (EHM) & EHV-1: Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument2 pagesEquine Herpesvirus Myeloencephalopathy (EHM) & EHV-1: Frequently Asked Questionsfreak009No ratings yet
- Biosecurity On Dairies: A BAMN PublicationDocument4 pagesBiosecurity On Dairies: A BAMN Publicationfreak009No ratings yet
- Cow Calf Vax ProtocolDocument4 pagesCow Calf Vax Protocolfreak009No ratings yet
- Clinical MastitisDocument1 pageClinical Mastitisfreak009No ratings yet
- Dry Cow Protocol: Internal Teat SealantDocument1 pageDry Cow Protocol: Internal Teat Sealantfreak009No ratings yet
- Herd Health Protocols For The Cowherd: MLV VaccineDocument1 pageHerd Health Protocols For The Cowherd: MLV Vaccinefreak009No ratings yet
- Biosecurity On Dairy FarmsDocument2 pagesBiosecurity On Dairy Farmsfreak009No ratings yet
- Management Cycles in Beef Production: F. Glen HembryDocument14 pagesManagement Cycles in Beef Production: F. Glen Hembryfreak009No ratings yet
- Hmlesson 4 Biosecurity Antibiotic Use and Beef Quality AssuranceDocument12 pagesHmlesson 4 Biosecurity Antibiotic Use and Beef Quality Assurancefreak009No ratings yet
- Bio SecurityDocument2 pagesBio Securityfreak009No ratings yet
- Beef Herd Health CalanderDocument4 pagesBeef Herd Health Calanderfreak009No ratings yet
- A Guide To Calf Milk Replacers Types, Use and QualityDocument4 pagesA Guide To Calf Milk Replacers Types, Use and Qualityfreak009No ratings yet
- Beef Vax ProtocolDocument3 pagesBeef Vax Protocolfreak009No ratings yet
- Beef Cattle Vax ProtocolDocument2 pagesBeef Cattle Vax Protocolfreak009No ratings yet
- Beef Cattle Vax Protocol2Document4 pagesBeef Cattle Vax Protocol2freak009No ratings yet
- Biosec Ip Dairy HerdsDocument4 pagesBiosec Ip Dairy Herdsfreak009No ratings yet
- Beef0708 Is BiosecurityDocument4 pagesBeef0708 Is Biosecurityfreak009No ratings yet
- No Kode SAP Lokasi Rak Nama ProdukDocument117 pagesNo Kode SAP Lokasi Rak Nama ProdukKimia ByPass TabananNo ratings yet
- IOL Masuk Keluar BM SDA NO Nama Obat Awal: Laporan BHP + Iol Ok Smec MojokertoDocument6 pagesIOL Masuk Keluar BM SDA NO Nama Obat Awal: Laporan BHP + Iol Ok Smec MojokertoNaira Calya basagitaNo ratings yet
- Parenteral NutritionDocument8 pagesParenteral NutritionivanNo ratings yet
- Skin Care Plan: Nu Derm Protocol ForDocument7 pagesSkin Care Plan: Nu Derm Protocol ForsheilaNo ratings yet
- Information Technology in SurgeryDocument38 pagesInformation Technology in Surgerydooshy50% (4)
- Chapter 7: Emotional and Behavioural Problems: DR Jessie EarleDocument28 pagesChapter 7: Emotional and Behavioural Problems: DR Jessie EarlejajmajNo ratings yet
- Neurotology Fellowship MilestonesDocument18 pagesNeurotology Fellowship MilestonesAnonymous AuJncFVWvNo ratings yet
- Reiki 1Document19 pagesReiki 1api-246890707No ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Dr. Avinash K. Jangde - . - ., - . (A)Document5 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Dr. Avinash K. Jangde - . - ., - . (A)Mohammad TariqNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of A Comprehensive Hand Hygiene Program ForDocument11 pagesEffectiveness of A Comprehensive Hand Hygiene Program Form1k0eNo ratings yet
- Windy WigaDocument2 pagesWindy WigaWindy wigaNo ratings yet
- Procalcitonin Testing To Guide Antibiotic Therapy in Acute Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument2 pagesProcalcitonin Testing To Guide Antibiotic Therapy in Acute Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract InfectionsMr. LNo ratings yet
- E-Exercise Book: Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS)Document10 pagesE-Exercise Book: Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS)Zia Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Can Oral Sex Cause Throat CancerDocument4 pagesCan Oral Sex Cause Throat CancerjyuldipNo ratings yet
- (2012) - Psychosis and GenderDocument2 pages(2012) - Psychosis and GenderChoko DelgadoNo ratings yet
- EndometriosisDocument153 pagesEndometriosisoannny8661No ratings yet
- SDS - Balloxy HB Light - Comp. B - Marine - Protective - English (Uk) - AustraliaDocument7 pagesSDS - Balloxy HB Light - Comp. B - Marine - Protective - English (Uk) - AustraliaDonNo ratings yet
- D. Motola Et Al 2017Document8 pagesD. Motola Et Al 2017reclinpharmaNo ratings yet
- OB Gyne HistoryDocument2 pagesOB Gyne HistoryNeil Victor Ongco PajugotNo ratings yet
- 2015 Case 6 MBUDocument12 pages2015 Case 6 MBUDinesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- 2023 Aaha Senior Care Guidelines For Dogs and CatsDocument21 pages2023 Aaha Senior Care Guidelines For Dogs and CatsisvpNo ratings yet