Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pediatric Drug Dosage - All in One
Uploaded by
BJ TiewOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pediatric Drug Dosage - All in One
Uploaded by
BJ TiewCopyright:
Available Formats
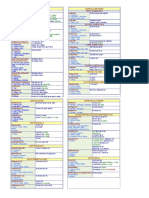
Pediatric drugs info
Acetaminophen
Elixir(oral solution) 10-15 mg/kg/dose
120mg=5cc
drop:100mg/ml 10kg=5cc qid drop;2.5drop/kg
Pain or fever: Oral, rectal Children <12 years: 10-15 mg/kg/dose every 4-6 hours as needed; do not exceed 5 doses (2.6 g) in 24 hours Limit dose to <4 g/day Activated charcoal Antidiarrheal Antidote, Adsorbent Antiflatulent 5-10 [intoxicated drug] 30-100mg/250cc water
Single dose: Charcoal in water (a cathartic such as sorbitol should be added in appropriate doses): Infants <1 year: 1 g/kg Children 1-12 years: 1-2 g/kg or 25-50 g Adolescents and Adults: 30-100 g or 1-2 g/kg Adult cold Acetaminophen 325+Phenylephrine HCL 5mg+Chlorpheniramine 2mg
Amoxiciline
susp 125 & 250=5cc 20-40 mg/kg/24hrs 10 kg =5cc tds
cap 250 & 500 mg
DOSING: PEDIATRIC Susceptible infections: Oral: Children 3 months: 20-30 mg/kg/day divided every 12 hours Children: >3 months and <40 kg: Dosing range: 20-50 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8-12 hours
Ear, nose, throat, genitourinary tract, or skin/skin structure infections: Oral: Children: >3 months and <40 kg: Mild-to-moderate: 25 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours or 20 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours Severe: 45 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours or 40 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours
Acute otitis media: Oral: Children: >3 months and <40 kg: 80-90 mg/kg/day divided every 12 hours
Lower respiratory tract infections: Oral: Children: >3 months and <40 kg: 45 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours or 40 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours
Subacute bacterial endocarditis prophylaxis: Oral: Children: >3 months and <40 kg: 50 mg/kg 1 hour before procedure
Anthrax exposure (unlabeled use): Oral: Note: Postexposure prophylaxis only with documented susceptible organisms: <40 kg: 15 mg/kg every 8 hours 40 kg: 500 mg every 8 hours Co-amoxyclav tab 375mg Susp 312mg : 250mg Amoxy/5cc tds
Ampiciline
susp 125 & 250=5cc 50-100 mg/kg/24 hrs
cap 250 & 500 mg 10kg=5cc qid
DOSING: PEDIATRIC Mild-to-moderate infections: Infants and Children: I.M., I.V.: 100-150 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 6 hours (maximum: 2-4 g/day) Oral: 50-100 mg/kg/day in doses divided every 6 hours (maximum: 2-4 g/day)
Severe infections/meningitis: Infants and Children: I.M., I.V.: 200-400 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 6 hours (maximum: 6-12 g/day)
Endocarditis prophylaxis: Infants and Children: I.M., I.V.: Dental, oral, respiratory tract, or esophageal procedures: 50 mg/kg within 30 minutes prior to procedure in patients unable to take oral amoxicillin Genitourinary and gastrointestinal tract (except esophageal) procedures: High-risk patients: 50 mg/kg (maximum: 2 g) within 30 minutes prior to procedure, followed by ampicillin 25 mg/kg (or amoxicillin 25 mg/kg orally) 6 hours later; must be used in combination with gentamicin. Moderate-risk patients: 50 mg/kg within 30 minutes prior to procedure. AL-MG-S AL(OH)3 225mg/5cc syr 1-2 cc/kg/24hrs
MG(OH)2 200mg/5cc Simethicone(Gas-X) 25mg/5cc Atrovent(ipratropium bromide) DOSING: PEDIATRIC Bronchospasm: Nebulization: Infants and Children 12 years: 125-250 mcg 3 times/day Children >12 years: Refer to adult dosing. Metered dose inhaler: Children 3-12 years: 1-2 inhalations 3 times/day, up to 6 inhalations/24 hours
Children >12 years: Refer to adult dosing.
Colds (symptomatic relief of rhinorrhea): Intranasal: Safety and efficacy of use beyond 4 days in patients with the common cold have not been established: Children 5-11 years: 0.06%: 2 sprays in each nostril 3 times/day Children 5 years and Adults: 0.06%: 2 sprays in each nostril 3-4 times/day
Allergic/nonallergic rhinitis: Intranasal: Children 6 years: Refer to adult dosing. USE Anticholinergic bronchodilator used in bronchospasm associated with COPD, bronchitis, and emphysema; symptomatic relief of rhinorrhea associated with the common cold and allergic and nonallergic rhinitis Azithromycine (Zithromax) tab 250 mg susp 100,250mg/5cc children2 y-old 12mg/kg/daily
Bacterial sinusitis: Oral: Children 6 months: 10 mg/kg once daily for 3 days (maximum: 500 mg/day) Pharyngitis, tonsillitis: Oral: Children 2 years: 12 mg/kg/day once daily for 5 days (maximum: 500 mg/day) Cardiac glycosides: Macrolides may increase the serum concentrations of cardiac glycosides; monitor. Warfarin: Azithromycin and other macrolides may decrease metabolism, via CYP isoenzymes, of warfarin. Monitor for increased effects.
Belladonna Pb Bisacodyl
Atropine+Hyosine+Hyocyamine+Phenobarbital
0.1 cc/kg
ped Supp 5mg-----------1 +adult supp 10 mg------------------1-2 DOSING: PEDIATRIC Relief of constipation: Oral: Children >6 years: 5-10 mg (0.3 mg/kg) at bedtime or before breakfast Rectal (suppository): Children: <2 years: 5 mg as a single dose >2 years: 10 mg
Bromhexine hcl elixir
Mucolytic Agent
syr 5cc=4mg
Oral: Children <2 years: 1 mg 3 times/day Children 2-6 years: 4 mg(5cc) twice daily or 2 mg 3 times/day Children 6-12 years: 4 mg(5cc) 3 times/day Children >12 years and Adults: 8 mg(10cc) 3 times/day Cefixime tab 200&400 mg susp 100mg/5cc---------------8mg/kg/daily---bd-------------- 0.5cc/kg/daily---bd
USE Treatment of urinary tract infections, otitis media, respiratory infections due to susceptible organisms including S. pneumoniae and S. pyogenes, H. influenzae and many Enterobacteriaceae; uncomplicated cervical/urethral gonorrhea due to N. gonorrhoeae DOSING: ADULTS Susceptible infections: Oral: 400 mg/day divided every 12-24 hours Uncomplicated cervical/urethral gonorrhea due to N. gonorrhoeae: Oral: 400 mg as a single dose Note: For S. pyogenes infections, treat for 10 days DOSING: PEDIATRIC Susceptible infections: Oral: Children 6 months: 8 mg/kg/day divided every 12-24 hours Children >50 kg or >12 years: Refer to adult dosing. Note: For S. pyogenes infections, treat for 10 days
Cotrimoxasole
Susp 40 mgTMP=5cc 8-10 mg/kg/24hrs TMP
pediatric tab=20 mgTMP/Adult tab=80mgTMP 10 kg= 5cc BD
Shigellosis: Oral: 8 mg TMP/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours for 5 days I.V.: 8-10 mg TMP/kg/day in divided doses every 6, 8, or 12 hours for up to 5 days Acute otitis media: Oral: 8 mg TMP/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours for 10 days Urinary tract infection:
Treatment: Oral: 6-12 mg TMP/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours I.V.: 8-10 mg TMP/kg/day in divided doses every 6, 8, or 12 hours for up to 4 days with serious infections Prophylaxis: Oral: 2 mg TMP/kg/dose daily or 5 mg TMP/kg/dose twice weekly CONTRAINDICATIONS Hypersensitivity to any sulfa drug, trimethoprim, or any component of the formulation; porphyria; megaloblastic anemia due to folate deficiency; infants <2 months of age; marked hepatic damage; severe renal disease; pregnancy (at term)
Diazepam DOSING: PEDIATRIC Conscious sedation for procedures: Oral: Children: 0.2-0.3 mg/kg (maximum dose: 10 mg) 45-60 minutes prior to procedure Adolescents: 10 mg I.V.: Adolescents: 5 mg; may repeat with 2.5 mg if needed
Febrile seizure prophylaxis: Oral: Children: 1 mg/kg/day divided every 8 hours; initiate therapy at first sign of fever and continue for 24 hours after fever is gone
Sedation or muscle relaxation or anxiety: Oral: Children: 0.12-0.8 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 6-8 hours I.M., I.V.: Children: 0.04-0.3 mg/kg/dose every 2-4 hours to a maximum of 0.6 mg/kg within an 8-hour period if needed
Status epilepticus: I.V.: Infants >30 days and Children <5 years: 0.05-0.3 mg/kg/dose given over 3-5 minutes, every 15-30 minutes to a maximum total dose of 5 mg or 0.2-0.5 mg/dose every 2-5 minutes to a maximum total dose of 5 mg; repeat in 2-4 hours as needed Children 5 years: 0.05-0.3 mg/kg/dose given over 3-5 minutes, every 15-30 minutes to a maximum total dose of 10 mg or 1 mg/dose every 2-5 minutes to a maximum of 10 mg; repeat in 2-4 hours as needed Rectal: 0.5 mg/kg/dose then 0.25 mg/kg/dose in 10 minutes if needed
Anticonvulsant (acute treatment): Rectal gel: Infants <6 months: Not recommended Children <2 years: Safety and efficacy have not been studied Children 2-5 years: 0.5 mg/kg Children 6-11 years: 0.3 mg/kg Children 12 years: Refer to adult dosing. Note: Dosage should be rounded upward to the next available dose, 2.5, 5, 10, 12.5, 15, 17.5, and 20 mg/dose; dose may be repeated in 4-12 hours if needed; do not use for more than 5 episodes per month or more than one episode every 5 days.
Muscle spasm associated with tetanus: I.V., I.M.: Infants >30 days: 1-2 mg/dose every 3-4 hours as needed Children 5 years: 5-10 mg/dose every 3-4 hours as needed In children, do not exceed 1-2 mg/minute IVP; adults 5 mg/minute
Diphenhydramine
HCL Elixir 12.5mg=5cc 5mg/kg/24hrs 10 kg =5cc tds-qid
tab 25 mg
DOSING: PEDIATRIC Treatment of dystonic reactions and moderate to severe allergic reactions: Oral, I.M., I.V.: 5 mg/kg/day or 150 mg/m2/day in divided doses every 6-8 hours, not to exceed 300 mg/day
Minor allergic rhinitis or motion sickness: Oral, I.M., I.V.: 2 to <6 years: 6.25 mg every 4-6 hours; maximum: 37.5 mg/day 6 to <12 years: 12.5-25 mg every 4-6 hours; maximum: 150 mg/day 12 years: 25-50 mg every 4-6 hours; maximum: 300 mg/day
Night-time sleep aid: 30 minutes before bedtime: Oral, I.M., I.V.: 2 to <12 years: 1 mg/kg/dose; maximum: 50 mg/dose 12 years: 50 mg
Antitussive: Oral, I.M., I.V.: 2 to <6 years: 6.25 mg every 4 hours; maximum 37.5 mg/day 6 to <12 years: 12.5 mg every 4 hours; maximum 75 mg/day 12 years: 25 mg every 4 hours; maximum 150 mg/day Diphenhydramine compound=Diphenhydramine+Sodium citrate+Ammonium chloride+Menthol Dexa methasone Dicyclomine in Croup 0.6 mg/kg/IM/stat
Gastrointestinal motility disorders/irritable bowel Amp 20 mg child=10 mg DOSING: PEDIATRIC Oral: Infants >6 months: 5 mg/dose 3-4 times/day Children: 10 mg/dose 3-4 times/day syr 5cc=10 mg
Dimethicone(activated simethicone)
drop 1cc=40 mg Child max 20 drop tds
inf max=15 drop tds
DOSING: PEDIATRIC Flatulence/bloating: Oral: Infants: 20 mg 4 times/day Children <12 years: 40 mg 4 times/day Children >12 years: Refer to adult dosing.
DOSING: ADULTS Flatulence/bloating: Oral: 40-120 mg after meals and at bedtime as needed, not to exceed 500 mg/day
Domperidone Motilium PHARMACOLOGIC CATEGORY Dopamine Antagonist Gastrointestinal Agent, Prokinetic
DOSING: ADULTS GI motility disorders: Oral: 10 mg 3-4 times/day, 15-30 minutes before meals Severe/resistant cases: 20 mg 3-4 times/day, 15-30 minutes before meals Nausea/vomiting associated with dopamine-agonist anti-Parkinson agents: Oral: 20 mg 3-4 times/day
Erythromycine
susp 200 mg=5cc
tab 200 & 400 mg
30-50 mg /kg/24 hrs------ qid
DOSING: ADULTS Usual dosage range: Oral: (Note: Due to differences in absorption, 400 mg erythromycin ethylsuccinate produces the same serum levels as 250 mg erythromycin base, sterate or estolate) Base: 30-50 mg/kg/day in 2-4 divided doses; do not exceed 2 g/day Estolate: 30-50 mg/kg/day in 2-4 divided doses; do not exceed 2 g/day Ethylsuccinate: 30-50 mg/kg/day in 2-4 divided doses; do not exceed 3.2 g/day Stearate: 30-50 mg/kg/day in 2-4 divided doses; do not exceed 2 g/day I.V.: Lactobionate: 15-20 mg/kg/day divided every 6 hours or 500 mg to 1 g every 6 hours, or given as a continuous infusion over 24 hours (maximum: 4 g/24 hours)
Ophthalmic infection: Ophthalmic: Instill 1/2" (1.25 cm) 2-6 times/day depending on the severity of the infection
Dermatologic infection: Topical: Apply over the affected area twice daily after the skin has been thoroughly washed and patted dry
Indication-specific dosing: Cervicitis: Oral: 500 mg 4 times/day for 7 days Chancroid (unlabeled use; not a preferred agent): Oral: 500 mg 4 times/day for 7 days Community-acquired pneumonia, bronchitis: Oral, I.V.: 500-1000 mg 4 times/day for 10-14 days. If Legionella is suspected/confirmed, 750-1000 mg 4 times/day for 21 days or more may be recommended. Note: Other macrolides and/or fluoroquinolones may be preferred and better tolerated. Lymphogranuloma venereum: Oral: 500 mg 4 times/day for 21 days Nongonococcal urethritis (recurrent): Oral: CDC Guidelines for the Treatment of Sexually Transmitted Diseases recommendation: Metronidazole (2 g as a single dose) plus 7 days of erythromycin base (500 mg 4 times/day) or erythromycin ethylsuccinate (800 mg 4 times/day) Pertussis: Oral: 250-500 mg every 6 hour; standard treatment course is 14 days, but there is evidence to support a shorter (7-day) course Preop bowel preparation (unlabeled use): Oral: 1 g erythromycin base at 1, 2, and 11 PM on the day before surgery combined with mechanical cleansing of the large intestine and oral neomycin Gastrointestinal prokinetic (unlabeled use): Oral: Erythromycin has been used as a prokinetic agent to improve gastric emptying time and intestinal motility. In adults, 200 mg was infused I.V. initially followed by 250 mg orally 3 times/day 30 minutes before meals. Lower dosages have been used in some trials. DOSING: PEDIATRIC Prophylaxis of neonatal gonococcal or chlamydial conjunctivitis: Neonates: Ophthalmic: 0.5-1 cm ribbon of ointment should be instilled into each conjunctival sac
Usual dosage range: Infants and Children: Oral:Note: Due to differences in absorption, 400 mg erythromycin ethylsuccinate produces the same serum levels as 250 mg erythromycin base, stearate or estolate). Base: 30-50 mg/kg/day in 2-4 divided doses; do not exceed 2 g/day Estolate: 30-50 mg/kg/day in 2-4 divided doses; do not exceed 2 g/day Ethylsuccinate: 30-50 mg/kg/day in 2-4 divided doses; do not exceed 3.2 g/day Stearate: 30-50 mg/kg/day in 2-4 divided doses; do not exceed 2 g/day I.V. (as lactobionate): 15-50 mg/kg/day divided every 6 hours, not to exceed 4 g/day
Indication-specific dosing: Acne vulgaris (unlabeled use): Adolescents: Oral: 250-1500 mg/day in 2 divided doses; therapy may be continued for 4-6 weeks at lowest possible dose Pharyngitis: Oral: 40 mg/kg/day in 2 doses; maximum: 1600 mg/day; short-course therapy for 5 days may be considered Pertussis: Oral: 40-50 mg/kg/day in divided doses; standard treatment course is 14 days, but there is evidence to support a shorter (7-day) course Preop bowel preparation: Oral: 20 mg/kg erythromycin base at 1, 2, and 11 PM on the day before surgery combined with mechanical cleansing of the large intestine and oral neomycin Ophthalmic infection: Ophthalmic: Refer to adult dosing. Topical: Refer to adult dosing.
Guaifenesine(Expectorant )
syr 100 mg =5cc Cough (expectorant): Oral: Children: 6 months to 2 years: 25-50 mg every 4 hours, not to exceed 300 mg/day 2-5 years: 50-100 mg every 4 hours, not to exceed 600 mg/day 6-11 years: 100-200 mg every 4 hours, not to exceed 1.2 g/day >12 years: Refer to adult dosing. WARNINGS / PRECAUTIONS Not for persistent cough such as occurs with smoking, asthma, chronic bronchitis, or emphysema or cough accompanied by excessive secretions. When used for self-medication (OTC), contact healthcare provider if needed for >7 days or for a cough with a fever, rash, or persistent headache.
Ferrous sulfate DOSING: ADULTS Dose expressed in terms of ferrous sulfate: Treatment of iron deficiency anemia: Oral: 300 mg twice daily up to 300 mg 4 times/day or 250 mg (extended release) 1-2 times/day Prophylaxis of iron deficiency: Oral: 300 mg/day
DOSING: PEDIATRIC Dosage expressed in terms of elemental iron: Treatment of severe iron-deficiency anemia: Oral: 4-6 mg Fe/kg/day in 3 divided doses
Treatment of mild-to-moderate iron-deficiency anemia: Oral: 3 mg Fe/kg/day in 1-2 divided doses
Prophylaxis: Oral: 1-2 mg Fe/kg/day up to a maximum of 15 mg/day ADMINISTRATION Administer ferrous sulfate 2 hours prior to, or 4 hours after antacids ADVERSE REACTIONS SIGNIFICANT >10%: Gastrointestinal: GI irritation, epigastric pain, nausea, dark stools, vomiting, stomach cramping, constipation
1% to 10%: Gastrointestinal: Heartburn, diarrhea Genitourinary: Discoloration of urine Miscellaneous: Liquid preparations may temporarily stain the teeth
<1% (Limited to important or life-threatening): Contact irritation
CONTRAINDICATIONS Hypersensitivity to iron salts or any component of the formulation; hemochromatosis, hemolytic anemia
Furazolidone
susp 50mg=15cc
tab 100 mg
max 8mg/kg/24hrs
DOSING: PEDIATRIC Diarrhea/enteritis: Oral: Children >1 month: 5-8 mg/kg/day in 4 divided doses for 7 days, not to exceed 400 mg/day or 8.8 mg/kg/day
ADVERSE REACTIONS SIGNIFICANT >10%: Genitourinary: Discoloration of urine (dark yellow to brown)
1% to 10%: Central nervous system: Headache Gastrointestinal: Abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting
<1% (Limited to important or life-threatening): Agranulocytosis, disulfiramlike reaction after ethanol ingestion, hemolysis in patients with G6PD deficiency, hypoglycemia, leukopenia, orthostatic hypotension
CONTRAINDICATIONS Hypersensitivity to furazolidone or any component of the formulation; concurrent use of ethanol; infants <1 month of age because of the possibility of producing hemolytic anemia; foods high in tyramine content
WARNINGS / PRECAUTIONS Use caution in patients with G6PD deficiency when administering large doses for prolonged periods; furazolidone inhibits monoamine oxidase
Hydroxyzine
syr 10 mg=5cc 2mg/kg/24hrs
tab 10,25 mg 10kg=2.5cc tds-qid
amp 100 mg=2cc
Metronidasole
susp 125 mg=5cc
tab 250mg 10kg=5cc 10 kg=2cc Drop 0.6 cc daily
Amebiasis 35-50 mg/kg/24hrs Giardiasis 15 mg/kg/24hrs Multivitamine MOM (mg(oh)2) Metoclopramide Syr 5cc daily 0.5-1 cc/kg +200cc water
drop 60mg=15cc 1cc=15 drop=4mg 0.1 mg/kg/dose
amp 10mg=2cc
5kg=2drop qid tab500000 iu
Nystatine
term more than 2500gr = 30drops Less than 2500 gr = 15 drops Children 400000-600000 iu or tab/qid
Mebandasole Promethasine
chewable tab 100 mg syr 5.65 mg=5cc tab 25mg amp 25,50 mg
1mg/kg/24hrs Phenobarbital tab 15,30,60,100
10kg=2.5cc amp 100, 200 mg amp 5mg/kg/24hrs/bd/Im 4-8 mg/kg24hrs/bd
Amp 10 mg/kg/IM/stat Phenytoine Pyrantel pamoate
amp 15/mg/kg/stat slowly IV tab 125 mg 11mg/kg/dose
syr 250mg=5cc single dose syr 2mg=5cc 20kg=5cc 0.15 mg/kg/dose 0.375cc/kg
Salbutamole (ventoline)
You might also like
- Drugs For Paediatric UseDocument14 pagesDrugs For Paediatric Usefouza100% (1)
- Pediatric Doses For Commonly Used OTCsDocument7 pagesPediatric Doses For Commonly Used OTCsCharles Xavier KimNo ratings yet
- Rle Neonate DrugsDocument13 pagesRle Neonate DrugsLhara Vhaneza CuetoNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Drug Dosage - All in One PDFDocument15 pagesPediatric Drug Dosage - All in One PDFHuang Hasjim33% (9)
- RHU Blue Book 6 - 070852 1Document14 pagesRHU Blue Book 6 - 070852 1Jm Jm100% (1)
- Useful Medications For Oral Conditions: AnalgesicsDocument7 pagesUseful Medications For Oral Conditions: AnalgesicsAswathyNo ratings yet
- IVF Dosage Guide for Common Pediatric MedicationsDocument5 pagesIVF Dosage Guide for Common Pediatric MedicationsEloiseBalasbasNo ratings yet
- جرعات الاطفالDocument50 pagesجرعات الاطفالWael Hamdy100% (1)
- Normal Values HR RR BPDocument28 pagesNormal Values HR RR BPKthrine CrronNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Dosage of Some Drugs-1Document45 pagesPaediatric Dosage of Some Drugs-1JaneNo ratings yet
- Common TreatmentsDocument5 pagesCommon TreatmentsRaj MandumulaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Dosing For OTCsDocument5 pagesPediatric Dosing For OTCsCareyTranNo ratings yet
- Pedia NotesDocument2 pagesPedia NotesPaolo EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosing in PediatricDocument1 pageDrug Dosing in Pediatricnattawat100% (1)
- Essenc I Al TherapyDocument9 pagesEssenc I Al TherapyFabian Ramirez HincapiéNo ratings yet
- AMOXICILLIN TO ZINC GLUCONATE GUIDELINES FOR COMMON CONDITIONSDocument4 pagesAMOXICILLIN TO ZINC GLUCONATE GUIDELINES FOR COMMON CONDITIONSRenette Uy100% (1)
- Tickler Print PediaDocument8 pagesTickler Print PediaCarlos H. AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Drugs & DosagesDocument29 pagesDrugs & DosagesCristina VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Drug ND DosesDocument5 pagesPaediatric Drug ND Dosesanon_842593420No ratings yet
- Drug HandBookDocument10 pagesDrug HandBookAhmed FekryNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics Drug Doses - DocToon PDFDocument49 pagesPediatrics Drug Doses - DocToon PDFBharat Jamod100% (1)
- Pediatric Drug DosagesDocument4 pagesPediatric Drug DosagesNandita BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- ImportantPractical Notes PediaDocument11 pagesImportantPractical Notes PediaJun JunNo ratings yet
- Acute MedicineDocument54 pagesAcute MedicineTipuNo ratings yet
- GP Notes-1Document126 pagesGP Notes-1Fida AnjumNo ratings yet
- Paediatrics Drug DosesDocument9 pagesPaediatrics Drug DosesRayhan 'sNo ratings yet
- AtropineDocument13 pagesAtropineMostafa HassanNo ratings yet
- Pedia EZ Notes PDFDocument102 pagesPedia EZ Notes PDFLuisa Paula LioanagNo ratings yet
- Ok Ok Notes PediaDocument14 pagesOk Ok Notes PediaChristian PasicolanNo ratings yet
- Paediatric DoseDocument12 pagesPaediatric DoseYohanes AdiputraNo ratings yet
- Pedia DosesDocument7 pagesPedia DosesSai Krishna MaddiralaNo ratings yet
- Neonate: TPR of Newborns BW 1500gDocument9 pagesNeonate: TPR of Newborns BW 1500gAnne Lorraine BringasNo ratings yet
- Pedia MedicationsDocument9 pagesPedia MedicationsMichael Villavert100% (1)
- Common OPD DrugsDocument22 pagesCommon OPD DrugsAira Jhamaica DimacaleNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Dosage of Some DrugsDocument46 pagesPaediatric Dosage of Some DrugsS S LNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Notes Draft 12 1Document98 pagesPediatric Notes Draft 12 1Aljon S. TemploNo ratings yet
- The GP Book KeralaDocument44 pagesThe GP Book KeralaMuhammed Abrar100% (1)
- Paediatric DosesDocument2 pagesPaediatric DosesEdio PathicNo ratings yet
- Cefalexin and other common antibioticsDocument3 pagesCefalexin and other common antibioticsmikayNo ratings yet
- Beta-Lactams Cephalosporins: Phenoxymethyl PenicillinDocument3 pagesBeta-Lactams Cephalosporins: Phenoxymethyl PenicillinBobet ReñaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs: Drug Action Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Management Atropine SulfateDocument15 pagesEmergency Drugs: Drug Action Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Management Atropine Sulfate092109No ratings yet
- Pediatric cough/cold medicine dosing chartDocument1 pagePediatric cough/cold medicine dosing chartShahid KhanNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs: Cardiac Drugs Atropine SulfateDocument14 pagesEmergency Drugs: Cardiac Drugs Atropine SulfateJayvee Montoya-Pujante100% (1)
- Therapeutic Dosages22Document11 pagesTherapeutic Dosages22Rishikesh AsthanaNo ratings yet
- Drugs and DosagesDocument4 pagesDrugs and DosagesDin-Din Que33% (3)
- UbatopdDocument4 pagesUbatopdKhai RyNo ratings yet
- Guideline for Managing Eclampsia and Severe Pre-EclampsiaDocument15 pagesGuideline for Managing Eclampsia and Severe Pre-EclampsiaMegane YuliNo ratings yet
- Fluid and electrolyte management guidelinesDocument12 pagesFluid and electrolyte management guidelinesDavid JonesNo ratings yet
- Idiot NotesDocument53 pagesIdiot NotesRay PerezNo ratings yet
- A Drug For IntDocument58 pagesA Drug For IntVajirawit PetchsriNo ratings yet
- Malaria Treatment IndiaDocument1 pageMalaria Treatment IndiaSubzer OmerNo ratings yet
- Common Drug Use in Adult For ExternDocument5 pagesCommon Drug Use in Adult For ExternVajirawit PetchsriNo ratings yet
- Pyridoxine 50mg Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SMPC)Document3 pagesPyridoxine 50mg Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SMPC)OdunlamiNo ratings yet
- AntibioticGuidelines PrimaryDocument12 pagesAntibioticGuidelines PrimaryHandriyato SukmaNo ratings yet
- Pre Eclampsia Eclampsia Guideline For The Management of SevereDocument15 pagesPre Eclampsia Eclampsia Guideline For The Management of SevereMelanie JuntakNo ratings yet
- Drug Infusion ChartDocument2 pagesDrug Infusion ChartNisbet SamuelNo ratings yet
- Pedia TicklerDocument71 pagesPedia TicklermikayNo ratings yet
- Common DrugDocument2 pagesCommon DrughengpanhatashiNo ratings yet
- Nepal Essential MedicationsDocument103 pagesNepal Essential MedicationsPriya SahNo ratings yet
- Useful Medications For Oral Conditions: AnalgesicsDocument8 pagesUseful Medications For Oral Conditions: AnalgesicsKaren SandovalNo ratings yet
- Understanding, Evaluating and Implementing Effective HIRARC at WorkplaceDocument4 pagesUnderstanding, Evaluating and Implementing Effective HIRARC at WorkplaceBJ TiewNo ratings yet
- Efficiency Opportunities For Cement IndustryDocument13 pagesEfficiency Opportunities For Cement IndustryBJ TiewNo ratings yet
- Tubular TYK Fabrication and Inspection: It Is Important To Plan Ahead For These Complex WeldsDocument5 pagesTubular TYK Fabrication and Inspection: It Is Important To Plan Ahead For These Complex Weldsluz82No ratings yet
- Socso Contribution TableDocument2 pagesSocso Contribution Tablestudytillvomit57% (7)
- Cement Review PaperDocument24 pagesCement Review Paperleojay24100% (1)
- Brent Spar - DossierDocument130 pagesBrent Spar - DossiereddythedolphinNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma For SmallbusinessDocument224 pagesSix Sigma For SmallbusinessBJ TiewNo ratings yet
- Note 1.1 For Computational NeuroscienceDocument10 pagesNote 1.1 For Computational NeuroscienceBJ TiewNo ratings yet
- Offshore Safe Work Practices HandbookDocument132 pagesOffshore Safe Work Practices HandbookBJ Tiew100% (1)
- Statistics 1Document97 pagesStatistics 1BJ TiewNo ratings yet
- Matlab - A Brief Intro To Financial EngineeringDocument11 pagesMatlab - A Brief Intro To Financial EngineeringHemendra TiwariNo ratings yet
- Vegetable Gardening EncyclopediaDocument261 pagesVegetable Gardening EncyclopediaTezza13100% (26)
- Idea Group Neural Networks in Business ForecastingDocument311 pagesIdea Group Neural Networks in Business ForecastingBJ TiewNo ratings yet
- Finance EngineeringDocument73 pagesFinance EngineeringBJ TiewNo ratings yet
- Brochure Sensor Ex Process AnalyticDocument4 pagesBrochure Sensor Ex Process AnalyticBJ TiewNo ratings yet
- L-BV5 Vacuum Pump Data SheetDocument4 pagesL-BV5 Vacuum Pump Data SheetBJ TiewNo ratings yet
- CacalF - Concept Analysis of Compassion Fatigue - NR 501Document10 pagesCacalF - Concept Analysis of Compassion Fatigue - NR 501Nenette Tolentino Cacal100% (1)
- MCQs on skin flaps, burns, trauma and thyroid disordersDocument9 pagesMCQs on skin flaps, burns, trauma and thyroid disordersFarrukh Ali Khan0% (1)
- Top 10 DDx in family medicine: FatigueDocument1 pageTop 10 DDx in family medicine: FatigueAnonymous HNTNhspNo ratings yet
- Professional Adjustment and Nursing Care Management Practice Exam Answer KeyDocument20 pagesProfessional Adjustment and Nursing Care Management Practice Exam Answer Keystuffednurse93% (41)
- Manoj DissertationDocument82 pagesManoj DissertationSheela ShahNo ratings yet
- Dental Implant Awareness Among Patients in Our Institution in Chennai-Cross-Sectional SurveyDocument4 pagesDental Implant Awareness Among Patients in Our Institution in Chennai-Cross-Sectional SurveyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Arrhythmia - VT: Braghmandaru A.BDocument113 pagesVentricular Arrhythmia - VT: Braghmandaru A.BFaisol SiddiqNo ratings yet
- Septum Drill Kit: User Manual Ver.01Document12 pagesSeptum Drill Kit: User Manual Ver.01Ashok ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- PROSTHODONTICS SEMINAR II Topics 1Document1 pagePROSTHODONTICS SEMINAR II Topics 1Jalil Enock0% (1)
- NEUROPrelims - History Taking in NeurologyDocument4 pagesNEUROPrelims - History Taking in NeurologyRenatoCosmeGalvanJuniorNo ratings yet
- CBTDocument2 pagesCBTSHAH JAHAN BANONo ratings yet
- Acute Flaccid ParalysisDocument4 pagesAcute Flaccid ParalysisZharah RuzNo ratings yet
- SURVEILANS HEALTH CARE ASSOCIATED INFECTIONSDocument49 pagesSURVEILANS HEALTH CARE ASSOCIATED INFECTIONSfebri12No ratings yet
- Elizabeth Wettlaufer - Agreed Statement of FactsDocument57 pagesElizabeth Wettlaufer - Agreed Statement of FactsNick Westoll100% (3)
- H&P TemplateDocument6 pagesH&P TemplateRicardoMelendezNo ratings yet
- GastroenterologyDocument297 pagesGastroenterologyphotopem100% (1)
- Fluid Volume Assessment for Amoebiasis PatientDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Assessment for Amoebiasis PatientRellie CastroNo ratings yet
- Accupuncture Trigger Points and Musculoskeletal PainDocument744 pagesAccupuncture Trigger Points and Musculoskeletal PainTeaganFalakNo ratings yet
- Nursing Ethics DilemmasDocument3 pagesNursing Ethics DilemmasDeng Navarro PasionNo ratings yet
- Patient History & Physical Exam RPTDocument2 pagesPatient History & Physical Exam RPTcptjimmy15No ratings yet
- Bisphenol A Epoxy ResinDocument1 pageBisphenol A Epoxy ResincnhathoangNo ratings yet
- AP Psych Midterm Study Guide 09-10 ObjDocument4 pagesAP Psych Midterm Study Guide 09-10 Objmrsaborges0% (1)
- Hospital Outdoor Spaces - Therapeutic Benefits and Design ConsiderationsDocument15 pagesHospital Outdoor Spaces - Therapeutic Benefits and Design Considerationsmimk2014No ratings yet
- MSQH SURVEY FINDINGS & RECOMMENDATIONSDocument2 pagesMSQH SURVEY FINDINGS & RECOMMENDATIONSChristine TanNo ratings yet
- Knee Injury Seminar GroupDocument96 pagesKnee Injury Seminar GroupAqilah Ab RahmanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics Compartment ModelingDocument94 pagesPharmacokinetics Compartment ModelingPinkishBlue100% (1)
- ICS Factsheet 6 (JW) July 2016Document3 pagesICS Factsheet 6 (JW) July 2016José Ignacio YánezNo ratings yet
- BLS MCQ For Final Exam PDFDocument33 pagesBLS MCQ For Final Exam PDFMoaz Albaba86% (14)
- PT IDS Medical Systems Indonesia Price List E-CatalogueDocument28 pagesPT IDS Medical Systems Indonesia Price List E-Cataloguekoes marNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of StereotaxyDocument45 pagesFundamentals of StereotaxyBenazir BegamNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- The Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossFrom EverandThe Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)