Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CCNA Resumen Sinoptico
Uploaded by
Heather MillerCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CCNA Resumen Sinoptico
Uploaded by
Heather MillerCopyright:
Available Formats
PDUs
Frames are also referred to as Protocol Data Units
destination and source MAC addresses Preamble for sequencing and timing Start of frame delimiter Length and type of frame Frame check sequence to detect transmission errors
The size of Ethernet frames is limited to a maximum of 1518 bytes and a minimum size of 64 bytes.
Ethernet Frame
Preamble SFD Start Frame Delimiter MAC Address Destination MAC Address Source Length/Type Data Encapsulation FCS Frame Check Sequence
6
The destination MAC can be unicast, multicast or broadcast.
46 - 1500
4
FCS is created by the device that sends data and recalculated by the destination device to check for damaged frames.
Define pattern of Marks the end of alternating 1 and 0 the timing bits used to information and synchronize timing. start of the frame.
The lenght indicate the number of bytes of data that The source MAC is follows this field. unicast. A Type value indicates which protocol will receive the data.
The broadcast MAC address is actually a 48-bit address made up of all ones.
The broadcast MAC address in hexadecimal notation is FFFF.FFFF.FFFF. Each F in the hexadecimal notation represents four ones in the binary address.
ARP
address resolution protocol
The sending host can use an IP protocol called ARP to discover the MAC address of any host on the same local network.
baseline or document network performance.
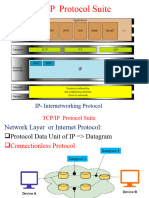
The IP packet is sometimes referred to as a datagram.
ISPs obtain blocks of IP addresses from a local, national or regional Internet registry (RIR).
Every ISP has a control facility for their network, known as the Network Operations Center (NOC).
A POP is the connection point between the ISP's network and the particular geographical region that the POP is servicing.
using DSL technology to connect, the ISP must have a DSL Access Multiplexer (DSLAM) 4.3.2
cable modems to connect, the ISP must have a Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS).
The TIA/EIA organization defines two different patterns, or wiring schemes, called T568A and T568B. 4.5.2
Two devices directly connected and using different pins for transmit and receive are known as unlike devices.
Devices that are directly connected and use the same pins for transmit and receive, are known as like devices.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
is the transport protocol that manages the individual conversations between web servers and web clients. TCP formats the HTTP messages into segments to be sent to the destination host. It also provides flow control and acknowledgement of packets exchanged between hosts.
Multicast Experimental
224.0.0.0 239.255.255.255 240.0.0.0 255.255.255.255
APIPA allocates IP addresses in the private range 169.254.0.1 to 169.254.255.254. Also Link-Local Addresses
In APIPA, all devices use the default network mask 255.255.0.0
Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) assigns the system an address from the 169.254.0.0 address range and configures the subnet mask (255.255.0.0). However, it doesnt configure the system with a default gateway address. As a result, communication is limited to the local network. Loopback Although only the single 127.0.0.1 address is used, One such reserved addresses 127.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255 are reserved. address is the IPv4 Any address within this block will loop back within the loopback address local host. 127.0.0.1.
Default Route
IPv4 default route is 0.0.0.0. The default route is used as a "catch all" route when a more specific route is not available. The use of this address also reserves all addresses in the 0.0.0.0 - 0.255.255.255 (0.0.0.0 /8) address block.
Port Numbers
Ports are broken into three categories and range in number from 1 to 65,535. Ports are assigned and managed by an organization known as the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN).
The address block 192.0.2.0 to 192.0.2.255 (192.0.2.0 /24) is set aside for teaching and learning purposes. TEST-NET Addresses You may often find these addresses used with the domain names example.com or example.net in RFCs, vendor, and protocol documentation. Ping uses a Layer 3 protocol that is a part on the TCP/IP suite called Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP). Ping uses an ICMP Echo Request datagram. Round Trip Time (RTT) is the time a packet takes to reach the remote host and for the response from the host to return with tracer command. An asterisk (*) is used to indicate a lost packet.
Well-Known Ports
Registered Ports
Dynamic, Private or Ephymeral Ports
Destination ports that are associated with Ports 1024 through 49151 can be used as Ports 49152 through 65535, often used as common network applications are either source or destination ports. These source ports. These ports can be used by identified as well-known ports. These can be used by organizations to register any application. ports are in the range of 1 to 1023. specific applications such as IM applications.
The TCP/IP model is a protocol model because it describes the functions that occur at each layer of protocols within the TCP/IP suite.
The primary purpose of a reference model is to aid in clearer understanding of the functions and process involved.
A DNS server provides the name resolution using the name daemon, which is often called named, (pronounced namedee).
Requests for Comments (RFCs). Publicly-available set of documents contain technical and organizational documents about the Internet, including the technical specifications and policy documents produced by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). The form that a piece of data takes at any layer is called a Protocol Data Unit (PDU). Data Segment Packet Frame Bits The general term for the PDU used at the Application layer. Transport Layer PDU. Internetwork Layer PDU. Network Access Layer PDU. A PDU used when physically transmitting data over the medium.
The DNS server stores different types of resource records used to resolve names. These records contain the name, address, and type of record.
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) Domain Name Service Protocol (DNS). Port TCP/UDP 53, Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). Port TCP 80, Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP). Port TCP 25, Telnet, a terminal emulation protocol. Port TCP 23, File Transfer Protocol (FTP). Port TCP 20, 21, DHCP Port UDP 56.
Some of these Record Types are: A an end device address NS an authoritative name server CNAME the canonical name (or Fully Qualified Domain Name) for an alias; used when multiple services have the single network address but each service has its own entry in DNS. MX mail exchange record; maps a domain name to a list of mail exchange servers for that domain
If a given server has resource records that correspond to its level in the domain hierarchy, it is said to be authoritative for those records.
The Application layer, is the layer that provides the interface between the applications and the underlying network over which our messages are transmitted.
GET is a client request for data. A web browser sends the GET message to request pages from a web server.
E-mail Server Processes - MTA and MDA 3.3.3
Application Layers
The Presentation Layer Coding and conversion of Application layer data. Compression of the data. Encryption of the data.
The Session Layer, create and maintain dialogs between source and destination applications. Handles the exchange of information to initiate dialogs, keep them active, and to restart sessions that are disrupted or idle for a long period of time.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
POST and PUT are used to send messages that upload data to the web server.
The Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) process is used to forward email.
If the mail is addressed to When people compose ea user whose mailbox is mail messages, they use a on the local server, the Mail User Agent (MUA), mail is passed to the or e-mail client. MDA.
PUT uploads resources or content to the web server.
The Server Message El protocolo SMB describe el establish a long term Block (SMB) is a acceso al sistema de archivos y connection to client/server file la manera en que los clientes servers. sharing protocol. hacen solicitudes de archivos.
connection using Telnet is called a Virtual Terminal (VTY) session, or connection.
For secure communication across the Internet, the HTTP Secure (HTTPS) protocol is used for accessing or posting web server information.
The LINUX and UNIX operating systems also provide a method of sharing resources with Microsoft networks using a version of SMB called SAMBA.
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
UDP is a simple, connectionless protocol, described in RFC 768. The pieces of communication in UDP are called datagrams. UDP segment only has 8 bytes of overhead.
The UDP PDU is referred to as a datagram, although the terms segment and datagram are sometimes used interchangeably to describe a Transport layer PDU.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
TCP is a connection-oriented protocol, described in RFC 793. TCP segment has 20 bytes of overhead.
La combinacin del nmero de puerto de la Por ejemplo, una solicitud de pgina Web capa de Transporte y de la direccin IP de la HTTP que se enva a un servidor Web capa de Red asignada al host identifica de (puerto 80) y que se ejecuta en un host manera exclusiva un proceso en particular que con una direccin IPv4 de Capa 3 se ejecuta en un dispositivo host especfico. Esta 192.168.1.20 ser destinada al socket 192.168.1.20:80. combinacin se denomina socket. Fields within the TCP segment header, there are six 1-bit fields that contain control information used to manage the TCP processes. URG - Urgent pointer field significant ACK - Acknowledgement field significant PSH - Push function RST - Reset the connection SYN - Synchronize sequence numbers FIN - No more data from sender
IPv4 basic characteristics: Connectionless - No connection is established before sending data packets. Best Effort (unreliable) - No overhead is used to guarantee packet delivery. Media Independent - Operates independently of the medium carrying the data.
The maximum size of PDU that each medium can transport. This characteristic is referred to as the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU).
In some cases, an intermediary device - usually a router will need to split up a packet when forwarding it from one media to a media with a smaller MTU. This process is called fragmenting the packet or fragmentation.
IP Destination Address 32-bit binary value. IP Source Address 32-bit binary value. Time-to-Live (TTL) is an 8-bit binary value that indicates the remaining "life" of the packet. Protocol 8-bit binary value indicates the data payload type that the packet is carrying and enables to pass the data to the appropriate upper-layer protocol. Type-of-Service 8-bit binary value that is used to determine the priority of each packet. Fragment Offset and the MF flag is used to reconstruct the packet when it arrives at the destination host. The fragment offset field identifies the order in which to place the packet fragment in the reconstruction. Don't Fragment (DF) flag is a single bit in the Flag field that indicates that fragmentation of the packet is not allowed. CH 1, 5.1.7 CCNA
Protocolos de enrutamiento comunes se incluyen: protocolo de informacin de enrutamiento (RIP), protocolo de enrutamiento de gateway interior mejorado (EIGRP) Open Shortest Path First (OSPF).
Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) (http://www.iana.net)
LACNIC (Regional AfriNIC (African APNIC (Asia Pacific ARIN (American Latin-American and Network Network Registry for Internet Caribbean IP Information Centre) Information Centre) Numbers) Address Registry)
RIPE NCC (Reseaux IP Europeans)
ICMP is the messaging protocol for the TCP/IP suite. ICMP provides control and error messages and is used by the ping and traceroute utilities. Ch1-6.6.5
ICMP messages that may be sent include: Host confirmation Unreachable Destination or Service Time exceeded Route redirection Source quench
Among the Destination Unreachable codes are: 0 = net unreachable 1 = host unreachable 2 = protocol unreachable 3 = port unreachable
Logical Link Control (LLC)
places information in the frame that identifies which Network layer protocol is being used for the frame.
Engineering Task Force (IETF)
Media Access Control (MAC)
Addresses the frame and marks the beginning and the end of the frame
Request for Comments (RFCs)
Physical layer technologies are defined by organizations such as: The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) The Electronics Industry Alliance/Telecommunications Industry Association (EIA/TIA) National telecommunications authorities such as the Federal Communication Commission (FCC) in the USA.
Flow control field (FCS) Used to start and stop traffic over the media
comprobacin de redundancia cclica (CRC)
MDI (interfaz dependiente del medio) utiliza un diagrama de pines normal de Ethernet. Los pins 1 y 2 se utilizan como transmisores y los pins 3 y 6 como receptores. Dispositivos como computadoras, servidores o routers tendrn conexiones MDI.
MDIX (Interfaz cruzada dependiente del medio). Los cables MDIX intercambian los pares transmisores internamente.
channel service unit/data service unit (CSU/DSU) Types of WAN connections EIA TIA 232 EIA TIA 449 V.35 X.21 EIA 530
Data Communications Equipment (DCE) - A device that supplies the clocking services to another device. Typically, this device is at the WAN access provider end of the link. (Femail Connector) Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) - A device that receives clocking services from another device and adjusts accordingly. Typically, this device is at the WAN customer or user end of the link. (Male Connector)
The Ping Command Ping uses the ICMP protocol to check for connectivity. Ping command moves from Layer 3 of the OSI model to Layer 2 and then Layer 1.
Testing the Loopback The ping command is used to verify the internal IP configuration on the local host by using the ping command on a reserved address called the loopback (127.0.0.1). This verifies the proper operation of the protocol stack from the Network layer to the Physical layer - and back - without actually putting a signal on the media. Testing Router Connectivity As with an end device, we can verify the Layer 3 connectivity with the ping and traceroute commands. In the Router 1 figure, you can see sample outputs from a ping to a host in the local LAN and a trace to a remote host across the WAN. Testing the Interface Assignement In this case ping the address asigned to the NIC in the network. This test verifies that the NIC driver and most of the NIC hardware are working properly. It also verifies that the IP address is properly bound to the NIC. ch1_11.3.2.2
IOS Ping Indicators A ping from the IOS will yield to one of several indications for each ICMP echo that was sent. The most common indicators are: ! - indicates receipt of an ICMP echo reply . - indicates a timed out while waiting for a reply U - an ICMP unreachable message was received
Testing Sequence Test 1: Local Loopback - Successful Test 2: Local NIC - Successful Test 3: Ping Local Gateway - Successful Test 4: Ping Remote Host - Failure Test 5: Traceroute to Remote Host - Failure at First Hop Test 6: Examine Host Configuration for Proper Local Gateway - Incorrect PC ping, tracert CLI ping, traceroute Next HOP find with #sh ip route
You might also like
- Hacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisFrom EverandHacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Free Comptia Network+ Study Guide by MC McseDocument48 pagesFree Comptia Network+ Study Guide by MC McseMalluNo ratings yet
- N+ Study MaterailDocument59 pagesN+ Study MaterailasimalampNo ratings yet
- Network+ Exam Cram Study SheetDocument3 pagesNetwork+ Exam Cram Study SheetDan Sheets86% (21)
- Port (Computer Networking)Document5 pagesPort (Computer Networking)Andres R. BucheliNo ratings yet
- Comptia-Network Study GuideDocument36 pagesComptia-Network Study GuideJonathan Velez Velazquez100% (3)
- Network CompTIADocument38 pagesNetwork CompTIApedrazini18100% (1)
- F5-101-Master-Cheat-Sheet YoDocument13 pagesF5-101-Master-Cheat-Sheet YoAmandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- ISO/OSI Network ModelDocument19 pagesISO/OSI Network ModelRaazia MirNo ratings yet
- Technical Interview Questions and AnswerDocument9 pagesTechnical Interview Questions and AnswerBadrinath KadamNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument33 pagesUnit VErwin VunguNo ratings yet
- CN Lab Manual 2018Document121 pagesCN Lab Manual 2018Suresh RamanujamNo ratings yet
- Link Layer of TCP/IP ProtocolDocument6 pagesLink Layer of TCP/IP Protocolgani525No ratings yet
- TCP IP ModelDocument31 pagesTCP IP ModelJaveed AhamedNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv-1Document33 pagesUnit Iv-1InnocentNo ratings yet
- ChapterDocument57 pagesChapterYomif NiguseNo ratings yet
- Network Viva Questions and AnswersDocument29 pagesNetwork Viva Questions and AnswersAditya HebbarNo ratings yet
- Notes e CommerceDocument83 pagesNotes e CommerceSawmya ShanmuganathanNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP Protocol SuiteDocument2 pagesTCP/IP Protocol SuiteAtheistNo ratings yet
- Basic Networking ConceptsDocument30 pagesBasic Networking ConceptsQamar KhanNo ratings yet
- Network+ Study GuideDocument51 pagesNetwork+ Study Guiderseara1127No ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument71 pagesChapter TwoyaNo ratings yet
- Imp For InterviewDocument16 pagesImp For InterviewPravin PuriNo ratings yet
- N+ Short Notes Free CompTIA Network+ Study Guide by MC MCSE)Document23 pagesN+ Short Notes Free CompTIA Network+ Study Guide by MC MCSE)Ye Zeiya SheinNo ratings yet
- TCP IP & AddressesDocument18 pagesTCP IP & Addresses366VEDANTI BACHCHUWARNo ratings yet
- NC Mod 4Document40 pagesNC Mod 4Haritha BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Ccna Chap3Document23 pagesCcna Chap3Spirit MyanmarNo ratings yet
- Tcpi IpDocument97 pagesTcpi Ipcborn99100% (1)
- Introduction To TC PipDocument20 pagesIntroduction To TC PipJESUS JHOJANSON BERMEJO LLANOSNo ratings yet
- Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Is A Mechanism in High-PerformanceDocument6 pagesMultiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Is A Mechanism in High-Performancetasnim tamannaNo ratings yet
- Tcp/Ip: How The TCP/IP Protocol Stack Maps To The OSI Model OSI Layers TCP/IP ProtocolsDocument5 pagesTcp/Ip: How The TCP/IP Protocol Stack Maps To The OSI Model OSI Layers TCP/IP Protocolsajithcoumar351No ratings yet
- Network Basics: A Road To Understanding Network SecurityDocument55 pagesNetwork Basics: A Road To Understanding Network SecurityhafeezNo ratings yet
- CN-Unit-1 - Part2 NotesDocument9 pagesCN-Unit-1 - Part2 NotesMeghnadhNo ratings yet
- Cisco AssignmentDocument22 pagesCisco AssignmentJiawei TanNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument14 pagesSummaryAbdullah MohammadNo ratings yet
- ECE541 Data Networks 1: Application Layer Functionality and ProtocolsDocument27 pagesECE541 Data Networks 1: Application Layer Functionality and ProtocolsUnicorn54No ratings yet
- Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) / Internet Protocol (Ip)Document24 pagesTransmission Control Protocol (TCP) / Internet Protocol (Ip)Harshitha BaranikaNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks (CS425) : Unix Socket ProgrammingDocument4 pagesComputer Networks (CS425) : Unix Socket ProgrammingAnish VeettiyankalNo ratings yet
- Communication ProtocolsTCPDocument11 pagesCommunication ProtocolsTCPDhiviyansh Punamiya OT3 - 433No ratings yet
- D. The Tcp/Ip Reference Model: ProtocolDocument7 pagesD. The Tcp/Ip Reference Model: ProtocolEcho greenNo ratings yet
- CN Assignment PDFDocument9 pagesCN Assignment PDFVaishnavi VenkatNo ratings yet
- COMP519: Web Programming Autumn 2013: The Slides Are Derivatives of Ones byDocument30 pagesCOMP519: Web Programming Autumn 2013: The Slides Are Derivatives of Ones byrejincjNo ratings yet
- COMP519: Web Programming Autumn 2013: The Slides Are Derivatives of Ones byDocument30 pagesCOMP519: Web Programming Autumn 2013: The Slides Are Derivatives of Ones byrejincjNo ratings yet
- Name: Mbalenhle Ndaba Unique No: 640309: Describe The Functionality Provided by The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)Document3 pagesName: Mbalenhle Ndaba Unique No: 640309: Describe The Functionality Provided by The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)Mbali NdabaNo ratings yet
- Name: Mbalenhle Ndaba Unique No: 640309: Describe The Functionality Provided by The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)Document3 pagesName: Mbalenhle Ndaba Unique No: 640309: Describe The Functionality Provided by The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)Mbali NdabaNo ratings yet
- OSI (Open System Interconnect)Document33 pagesOSI (Open System Interconnect)fishNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions Network Engineer 1632199729Document33 pagesInterview Questions Network Engineer 1632199729Gsk SkNo ratings yet
- Jason Zandri : TCP/IP Protocol Within Windows XP ProfessionalDocument29 pagesJason Zandri : TCP/IP Protocol Within Windows XP ProfessionalruvinduNo ratings yet
- FAQ'sDocument24 pagesFAQ'sduvvuruvitNo ratings yet
- LABSHEET-2 Introduction To Network Programming and Writing A Simple Daytime Client-ServerDocument15 pagesLABSHEET-2 Introduction To Network Programming and Writing A Simple Daytime Client-ServerAnupama InturiNo ratings yet
- OSI Model ConceptsDocument2 pagesOSI Model ConceptsAbhishek kapoorNo ratings yet
- WIA1005 Network Technology Foundation: Application Layer and Build A Small NetworkDocument33 pagesWIA1005 Network Technology Foundation: Application Layer and Build A Small NetworkAina NajihahNo ratings yet
- Physical Layer Data Link Layer: Logical Link Control (LLC) Media Access Control (MAC)Document44 pagesPhysical Layer Data Link Layer: Logical Link Control (LLC) Media Access Control (MAC)GauravNo ratings yet
- Protocols in Application Layer 17.01.2024Document4 pagesProtocols in Application Layer 17.01.2024Aloysius DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Interview Questions With AnswersDocument10 pagesComputer Networks Interview Questions With AnswersDheerja DhawanNo ratings yet
- Ccna 1Document40 pagesCcna 1Dragos CraciunNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 v7.0 Final ExamDocument62 pagesCCNA 1 v7.0 Final ExamDonald TientcheuNo ratings yet
- Internet Protocol SuiteDocument854 pagesInternet Protocol SuiteDilys CheungNo ratings yet
- Network PROTOCOLSDocument11 pagesNetwork PROTOCOLSRose of sharonNo ratings yet
- Tibco Hawk ImplemenrationDocument36 pagesTibco Hawk ImplemenrationAbhishek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sap Pi TutorialDocument86 pagesSap Pi TutorialGirish75% (4)
- mcq-1 - Servlet JSPDocument3 pagesmcq-1 - Servlet JSPrguptamtech100% (1)
- Cookies and SessionsDocument16 pagesCookies and SessionsUzair AhmadNo ratings yet
- OPCServerforAC800M PDFDocument80 pagesOPCServerforAC800M PDFmail_adam_kNo ratings yet
- VB Unit4&5Document86 pagesVB Unit4&5Ravi KumarNo ratings yet
- 0113 Little-Known CRM Service Interaction Center Features and Functionality That Offer Big ReturnsDocument48 pages0113 Little-Known CRM Service Interaction Center Features and Functionality That Offer Big ReturnsShivani GuptaNo ratings yet
- New Final Report of Distance Education System Virtual Classroom (With Coding)Document53 pagesNew Final Report of Distance Education System Virtual Classroom (With Coding)Nitesh LachakeNo ratings yet
- Load Balancing Techniques For Release 11I and Release 12 E-Business EnvironmentsDocument8 pagesLoad Balancing Techniques For Release 11I and Release 12 E-Business EnvironmentsrramsNo ratings yet
- Computeracronyms A4 DuplexDocument179 pagesComputeracronyms A4 DuplexAyyasamy SriramNo ratings yet
- By Ken Huang and James Hewitt, CGI NYS Cyber Security Conference 2010Document41 pagesBy Ken Huang and James Hewitt, CGI NYS Cyber Security Conference 2010Ken HuangNo ratings yet
- VMAS Remote Training Module 0Document14 pagesVMAS Remote Training Module 0Rajeev KumarNo ratings yet
- WCFVFPDocument26 pagesWCFVFPMauro Ricardo ChavesNo ratings yet
- Consume NetWeaver Gateway Services Via SAPUI5Document10 pagesConsume NetWeaver Gateway Services Via SAPUI5Balbino SoaresNo ratings yet
- CEIVA V AmazonDocument17 pagesCEIVA V AmazonBen WodeckiNo ratings yet
- QRadar 7.2 Troubleshooting GuideDocument20 pagesQRadar 7.2 Troubleshooting Guidergarcp2348100% (1)
- LoRaWAN 101 PDFDocument39 pagesLoRaWAN 101 PDFRoberto AmbrozioNo ratings yet
- Exploding Java - Simple Synchronizer Token With Spring MVCDocument5 pagesExploding Java - Simple Synchronizer Token With Spring MVCseeni45No ratings yet
- HP E2620 and 8212 Basic Operation ManualDocument8 pagesHP E2620 and 8212 Basic Operation ManualmeistermeowNo ratings yet
- Print IeuDocument13 pagesPrint Ieuroyroberto50% (2)
- SAP ABAP Question and AnswerDocument49 pagesSAP ABAP Question and Answerkalicharan13No ratings yet
- Prctice Final Exam Ccna1Document24 pagesPrctice Final Exam Ccna1Kristo RadionNo ratings yet
- Der Web Agent Guide 6QMR5Document275 pagesDer Web Agent Guide 6QMR5harshad27No ratings yet
- PrintMate Op GuideDocument67 pagesPrintMate Op GuidenebiyouNo ratings yet
- Ejb PPTDocument53 pagesEjb PPTMaha JuneNo ratings yet
- CEH v8 Labs Module 05 System HackingDocument117 pagesCEH v8 Labs Module 05 System HackingDeris Bogdan Ionut100% (1)
- 180+ Sample Test Cases For Testing Web and Desktop Applications - Comprehensive Testing ChecklistDocument10 pages180+ Sample Test Cases For Testing Web and Desktop Applications - Comprehensive Testing ChecklistVuong Anh Mai100% (1)
- Day2 Introduction OBIEE Physical LayerDocument14 pagesDay2 Introduction OBIEE Physical LayermtannaNo ratings yet
- A Novel Approach For Measuring Security in Software Systems - CIAAANDocument11 pagesA Novel Approach For Measuring Security in Software Systems - CIAAANJournal of ComputingNo ratings yet
- Application Layer: Computer Networking: A Top Down ApproachDocument106 pagesApplication Layer: Computer Networking: A Top Down ApproachasdsNo ratings yet
- Arizona, Utah & New Mexico: A Guide to the State & National ParksFrom EverandArizona, Utah & New Mexico: A Guide to the State & National ParksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Japanese Gardens Revealed and Explained: Things To Know About The Worlds Most Beautiful GardensFrom EverandJapanese Gardens Revealed and Explained: Things To Know About The Worlds Most Beautiful GardensNo ratings yet
- The Bahamas a Taste of the Islands ExcerptFrom EverandThe Bahamas a Taste of the Islands ExcerptRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Naples, Sorrento & the Amalfi Coast Adventure Guide: Capri, Ischia, Pompeii & PositanoFrom EverandNaples, Sorrento & the Amalfi Coast Adventure Guide: Capri, Ischia, Pompeii & PositanoRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- New York & New Jersey: A Guide to the State & National ParksFrom EverandNew York & New Jersey: A Guide to the State & National ParksNo ratings yet
- South Central Alaska a Guide to the Hiking & Canoeing Trails ExcerptFrom EverandSouth Central Alaska a Guide to the Hiking & Canoeing Trails ExcerptRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)