Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Toxicology Table
Uploaded by
kcxieCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Toxicology Table
Uploaded by
kcxieCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug
Toxidrome
Acetaminophen
Phase 1 (0-6 hrs): nausea/vomiting Phase 2 (4-24 hrs): clinically silent, LFTs, PT rise Phase 3 (18-72 hrs): toxic hepatitis, peaks in 2-3d in pts that recover; otherwise fulminant liver failure Phase 4: full recovery of liver function
Anticholinergics (antimuscarinic)
Mydriasis, dry mouth, dry skin, tachycardia, slows GI and GU tracts (urinary retention), altered mental status (staring, mumbling, "picking" at clothes/sheets) pts look like zombies MAO inhibitors: HTN rxn with some foods Tricyclic antidepressants: - anticholinergic toxidrome + abnormal EKG (due to Na channel blockade) SSRIs, SNRIs: serotonin syndrome - neuromuscular: myoclonus, rigidity (legs>arms) - autonomic: tachycardia, hyperthermia, hyper/hypotension, diaphoresis - altered mental status: agitation, sz, coma Overdose effects: - CNS depression, sz, decr BP - QT prolongation Adverse effects: - movement disrder, distonia, parkinsonian-life effects neuroleptic malignant syndrome - muscle rigidity, hyperthermia, autonomic instability, altered MS/delirium, rhabdo
Antidepressants - MAO inhibitors - Tricyclic antidepressents
Antipsychotics
Aspirin
Primary respiratory alkalosis - stimulates brainsteam resp ctr --> breathe fast Primary anion gap metabolic acidosis Tinnitus
Beta blockers
Bradycardia and hypotension
Calcium channel blockers
Bradycardia and hypotension - hyperglycemia common
Symptoms of hypoxia Carbon monoxide "cherry red" discoloration: usually preterminal finding
Cholinesterase SLUDGE/DUMBBELS inhibitors - diaphoresis, urination, miosis, broncho - organophosphate/ - produce a lot of fluid carbamates
Cyanide
Turns off aerobic metabolism - anion gap metabolic acidosis - elevated serum lactate - coma: brain needs ATP - hypotension
Digoxin
Ethanol and sedative-hypnotics
Opioids
Miosis, CNS depression, respiratory depression
Rattlesnake envenomation
3 "flavors" of effects: 1) local tissue injury: progressive pain and swelling, extends proximally up limb 2) hematologic: decr platelets, fibrinogen, coagulopathy (incr PT/INR) - looks like DIC 3) Neurologic: paresthesias, metallic taste, muscle twitching - usually a minor issue in US snakes Tachycardia, tremor, vomiting Severe: seizures
Theophylline
Toxicokinetics/dynamics Activated by liver into toxic metabolite Small amount oxidized by CYP450 to N-acetyl-parabenzoquinoneimine (NAPQI) very reactive, short half life - results in centrilobular hepatic necrosis Toxicity occurs when glutathione stores are depleted
Antidote
N-acetylcysteine (NAC) - repletes glutathione - PO or IV, both are effective; IV shorter time, but higher incidence of anaphylactoid rxns
Supprotive: IV fluid, sedation Physostigmine: inhibits AchE - raises synaptic Ach levels to overcome blockade
Serotonin syndrome: bzd, ?cyproheptadine
NMS: alpha adrenergic block --> decr ?dantrolene, bromocriptin, BP amantadine
Overdose: 1st order elimination --> zero order - half life increases - primarily renal elimination
1. GI decontamination (activated charcoal) 2. Maintain urine output: - IV fluid bolus + infusion - urine alkalinization (ion trapping with NaHCO3) Severe cases: hemodialysis Supportive, IV fluids, atropine, vasopressors glucagon: uses Gs/cAMP, bypassing blocked beta receptors IV fluids/atropine/vasopressors, Ca salts
Hyperglycemia: need Ca to release insulin vesicles
both b-blocker and CCB toxicity: high dose insulin/ glucose, mechanical adjuncts, IABP, bypass hyperbaric O2 (controversial)
CO poisoning prevents O2 delivery
atropine - fixes muscarinic effects only pralidoxime - regenerates active AChE - muscarinic and nicotinic
Traditional antidote kit: - Amyl nitrite perles (induce methemoglobinemia) - sodium nitrite IV CN- ion binds Fe3+ in iron(induce methemoglobinemia) sulfur complex in mitochondria - sodium thiosulfate (helps normal detox) Hydroxocobalamin: - provitamin B12a binds CN -> Vit B12 Supportive: cardiac monitoring, IV access, atropine for bradycardia digoxin immune Fab: - ovine Fab antibody fragments: digifab and digibind For benzodiazepines: - flumazenil: BZD like structure that competes for GABAa Cl channel - not used empirically because it may precipitate seizures/withdrawal - primary indication: iatrogenic toxicity (when the physician overdoses the pt) Naloxone: IV/IM/ETT/neb - short acting Also naltrexone (PO), nalmefene
Antivenom: CroFab - ovine produced immune fab - very expensive!! Other antivenoms: coral snake, black widow (IgG antivenom), bark scorpion (arizona) Supportive, charcoal beta-blockers, hemodialysis
Notes
Rumack Matthew Nomogram: predicts who is at risk of liver toxicity - serum APAP level and time elapsed since ingestion - derived from acute, single ingestion
Common side effects of many medications: antihistamines, psych drugs (antidepressants, antipsychotics), urinary incontinence drugs
serotonin syndrome: more common as a drug interation, but can also occur in overdose
smoke inhalation/fires, automobile exhaust CO binds heme 250x stronger than O2
Venomous snakes through continental US; 6 in california, 3 in OC Rattlesnakes: Pit vipers - lensshaped pupil, heat sensing pit organ nearly obsolete therapy for asthma/COPD, closely related to caffeine
Drug Heavy metals
Uses
Toxidrome Mutisystem toxic effects via multiple mechanisms of action Developing CNS more susceptible: fetus/children at highest risk
Lead
>30ug/dl: neuro-cognitive - irritability, fatigue, anorexia, sleep disturbance, ataxia, tremor >100ug/dl: encephalopathy - ataxia, stupor, coma, seizure, death Batteries, ammunition (bullets), - peripheral: wrist-drop allyows, glass, paint, Hematotoxicity: gasoline - increased RBC fragility - basophilic stippling Renal: (decr uric acid excretion) "saturnine gout" Reproductive toxicity CV: HTN GI: "Lead colic", gingival lead lines toxic level: 10 ug/dL Rapid-onset gastroenteritis Rare therapeutic use Cardiopulmonary and hemotoxicity as abx, Neuro effects: ascending sensory/motor promyelocytic peripheral neuropathy, encephalopathy leukemia Delay: Mees lines (transverse white nail lines) indicated period of decr growth Semi-conductor industry, wood Chronic: preservatives, constutional symptoms, anemia, pesticides, lewisite neuropathy, skin lesions, skin/kidney/lung (CW agent) cancer
Arsenic
dental amalgam, fish/shellfish 3 flavors: 1) elemental: liquid = least toxic, vapor is well absorbed and dangerous 2) salts: corrosive, cause hemorrhagic gastritis, ATN, renal failure 3) organomercuries: neurotoxicity 10% soln in peanut oil - IM injections Erethism: neuropsychiatric effects (shyness, social withdrawal, depression, explosive anger, blushing) Classic triad: tremore, neuropsychiatric disturbance, gingivostomatitis Acrodynia: painful extremity erythema, mostly in children
Mercury
Chelation Dimercaprol
Toxicokinetics/dynamics
Antidote
Inhaled, absorbed in GI tract (children absorb more than adults, 50% vs 10-15%) - incr absorption with low dietary calcium, iron deficiency, empty stomach Binds RBCs and distributed throughout body Clearance: blood/soft tissue (1-2 months), bone (yrs-decades) Interferes with heme synthesis at multiple steps: elevated protoporphyrin levels can be detected
Terminate further exposure (determine source), supportive care (hydration) Chelation Encephalopathy: treat cerebral edema/seizures steroids/mannitol/ anticonvulsants - IV CaNaEDTA, IM dimercaprol Not encephalopathic: - succimer: primary agent (DMSA, chemet)
Notes
Retained bullets in soft tissues are generally benign - may cause more damage to remove bullet - joints near bone in CSF are more commonly associated with lead poisoning
Avoid some fish in pregnant/lactating women shark, swordfish, king mackerel, tilefish
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Chicken or The Egg? Periodontal-Endodontic Lesions : GHT EssDocument8 pagesThe Chicken or The Egg? Periodontal-Endodontic Lesions : GHT EssFernando CordovaNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Pediatrics NotesDocument25 pagesPediatrics Noteskcxie100% (12)
- Genetic Conditions For USMLEDocument2 pagesGenetic Conditions For USMLEkcxieNo ratings yet
- Nail PsoriasisDocument13 pagesNail PsoriasisAira KellyNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome - A Case StudyDocument11 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome - A Case StudyRocel Devilles100% (2)
- Fever of unknown origin evaluation and differentialsDocument3 pagesFever of unknown origin evaluation and differentialskcxieNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Cavity TableDocument2 pagesPelvic Cavity TablekcxieNo ratings yet
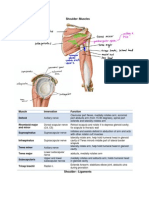
- ShoulderDocument4 pagesShoulderkcxieNo ratings yet
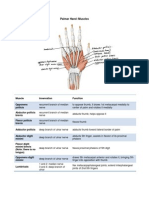
- Palmar HandDocument3 pagesPalmar HandkcxieNo ratings yet
- Posterior TriangleDocument4 pagesPosterior TrianglekcxieNo ratings yet
- Cubital Fossa and Anterior ForearmDocument4 pagesCubital Fossa and Anterior ForearmkcxieNo ratings yet
- Dorsal Forearm and HandDocument2 pagesDorsal Forearm and HandkcxieNo ratings yet
- Lower LimbDocument1 pageLower LimbkcxieNo ratings yet
- Ankle and Sole of FootDocument4 pagesAnkle and Sole of FootkcxieNo ratings yet
- Compendium of XV Annual Convention-09 of ISVIB, India by NeeleshDocument74 pagesCompendium of XV Annual Convention-09 of ISVIB, India by Neeleshneeleshsindhu100% (1)
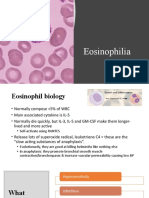
- EosinophiliaDocument8 pagesEosinophiliajohnNo ratings yet
- Cdi Reviewer MidtermDocument8 pagesCdi Reviewer MidtermKIMBERLY MARGARETTE REDNo ratings yet
- List of Books Box # 35: S.No. Author Title Year Edition Vol Call #Document10 pagesList of Books Box # 35: S.No. Author Title Year Edition Vol Call #lubs123No ratings yet
- Sign Up For Our Enews: Chronic Wasting DiseaseDocument4 pagesSign Up For Our Enews: Chronic Wasting DiseasesakuraleeshaoranNo ratings yet
- Responding To The Epidemic: Strengthening Youth Sector InvolvementDocument26 pagesResponding To The Epidemic: Strengthening Youth Sector InvolvementBeverly DatuNo ratings yet
- Bleeding DisorderDocument3 pagesBleeding DisorderyanzwinerNo ratings yet
- Freud'S Analysis of Horace Frink, M.D.: A Previously Unexplained Therapeutic DisasterDocument16 pagesFreud'S Analysis of Horace Frink, M.D.: A Previously Unexplained Therapeutic DisasterIVAN ANDREE VICTORIA VARGASNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument64 pagesProjectPradip DindaNo ratings yet
- PNP RequirementsDocument22 pagesPNP RequirementsJEREMY WILLIAM COZENS-HARDYNo ratings yet
- 1926, August 12 New JerseyDocument2 pages1926, August 12 New JerseyKiara Catelyn RetretaNo ratings yet
- Rizky Asta Pramesti Rini - ID 139Document10 pagesRizky Asta Pramesti Rini - ID 139Rizky KykyNo ratings yet
- Mandibulasr Truma ManagementDocument18 pagesMandibulasr Truma Managementjoal510No ratings yet
- Brain Tissue Oxygen MonitoringDocument11 pagesBrain Tissue Oxygen MonitoringangiolikkiaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Guide GIP VersionDocument22 pagesClinical Guide GIP Versionsireesha gandrotuNo ratings yet
- Referat - Trauma OculiDocument22 pagesReferat - Trauma OculiBesseMarwah AgusHusainNo ratings yet
- Laser Hair RemovalDocument28 pagesLaser Hair RemovalHania KhanNo ratings yet
- Hiv-Aids: Gladys Ziregbe (MRS.)Document25 pagesHiv-Aids: Gladys Ziregbe (MRS.)Esther Anabu EzimaNo ratings yet
- OMCDocument37 pagesOMCyurie_ameliaNo ratings yet
- HealthinDubai 3Document325 pagesHealthinDubai 3GaladariNo ratings yet
- Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorders CRSDDocument11 pagesCircadian Rhythm Sleep Disorders CRSDjaime manciaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 4 Introduction To MicrobiologyDocument36 pagesLECTURE 4 Introduction To MicrobiologyArcee Feb Dela PazNo ratings yet
- Indomethacin - Drug InformationDocument16 pagesIndomethacin - Drug InformationAbraham SarabiaNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka-Wps OfficeDocument2 pagesDaftar Pustaka-Wps OfficeRezha July prakosoNo ratings yet
- Circulating SerotoninDocument17 pagesCirculating Serotoninnihilx27374No ratings yet
- Journal InternasionalDocument6 pagesJournal InternasionalRizka ZahroNo ratings yet
- Naranjo AlgorithmDocument3 pagesNaranjo AlgorithmmilkymilkyNo ratings yet