Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thevenin's Theorem
Uploaded by
Yzza Veah EsquivelOriginal Title
Copyright
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Thevenin's Theorem
Uploaded by
Yzza Veah EsquivelCopyright:
THEVENINS THEOREM
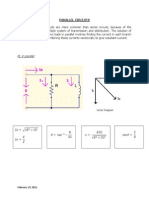
THEVENINS THEOREM A circuit analysis method that allows us to convert any linear circuit, or a portion of a circuit into a single equivalent circuit. The resulting simplified circuit consists of a constant voltage source (Thevenins Voltage, VTH) and a single series resistor (Thevenins Resistance, RTH). Used to simplify one part of a circuit (consisting of components that will not vary) in order to simplify the analysis of a second part of the circuit (consisting of components whose values change). The point in circuit that separates these two circuit sections is called THE POINT OF SIMPLIFICATION. Steps in Thevenizing a circuit: 1. Short all voltage sources then open all current sources. Also, open the circuit at the point of simplification. 2. Calculate the value of Thevenins resistance as seen from the point of simplification. 3. Replace voltage and current sources with their original values and open the circuit at the point of simplification. 4. Calculate Thevenins voltage at the point of simplification. 5. Replace the original circuit with the Thevenin equivalent for subsequent analysis of the circuit beyond point of simplification.
Example 1 Given:
Solution:
Example 2 Given:
REQUIRED: VX
Solution: Solve for RTH
Solve for VTH
For VX:
You might also like
- RA 6713 - Code of Conduct and Ethical Standard For Public Officials and EmployeesDocument12 pagesRA 6713 - Code of Conduct and Ethical Standard For Public Officials and EmployeesCrislene Cruz83% (12)
- Lecture 5 Thevenin and Norton EquivalentsDocument18 pagesLecture 5 Thevenin and Norton Equivalentsjazila140No ratings yet
- Thevenin's TheoremDocument6 pagesThevenin's TheoremShriprasad ChorgheNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 TransformersDocument70 pagesCHAPTER 2 TransformersTom100% (1)
- Philippine Constitution - Civil Service Exam ReviewerDocument41 pagesPhilippine Constitution - Civil Service Exam ReviewerYzza Veah Esquivel50% (2)
- Book 4: Alternating Current Electric CircuitDocument566 pagesBook 4: Alternating Current Electric CircuitMAT JIBRUD100% (3)
- Modulation (Am/fm)Document15 pagesModulation (Am/fm)Yzza Veah Esquivel94% (17)
- MSA Civil Service Reviewer PDFDocument79 pagesMSA Civil Service Reviewer PDFAhMy Endaya82% (77)
- Series-Parallel RC CircuitDocument29 pagesSeries-Parallel RC CircuitYzza Veah Esquivel80% (5)
- English Reviewer (Reading Comprehension, Vocabulary)Document6 pagesEnglish Reviewer (Reading Comprehension, Vocabulary)Yzza Veah Esquivel92% (36)
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- QXGQ7QX9 Lab3Document4 pagesQXGQ7QX9 Lab3Emre SelviliNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theorems Major Advantage Kirchhoff's Law: For A Large Complex Circuit, Tedious Computation Is InvolvedDocument21 pagesCircuit Theorems Major Advantage Kirchhoff's Law: For A Large Complex Circuit, Tedious Computation Is Involveddaniel gelawNo ratings yet
- Simplify Any Circuit with Thevenin's TheoremDocument20 pagesSimplify Any Circuit with Thevenin's Theoremamina MuneerNo ratings yet
- DC Circuit Analysis Simplification Using Thevenin's TheoremDocument8 pagesDC Circuit Analysis Simplification Using Thevenin's TheoremTeslim BalogunNo ratings yet
- What Will Cover in This Lab?: Thevenin TheoremDocument5 pagesWhat Will Cover in This Lab?: Thevenin TheoremMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- NortonDocument3 pagesNortonDhaivat PandyaNo ratings yet
- ), I) - Values Calculated Were Observed To Be Approximately EqualDocument4 pages), I) - Values Calculated Were Observed To Be Approximately EqualAngel MallariNo ratings yet
- Thevenin's TheoremDocument2 pagesThevenin's TheoremanupsorenNo ratings yet
- DC NETWORK ANALYSIS TECHNIQUESDocument30 pagesDC NETWORK ANALYSIS TECHNIQUESKrishanu NaskarNo ratings yet
- Circuit TheoremsDocument9 pagesCircuit TheoremsEllen Kay CacatianNo ratings yet
- ID-20193007011 Presentation About Thevenin's Theorem........Document7 pagesID-20193007011 Presentation About Thevenin's Theorem........abid raihanNo ratings yet
- Norton PDFDocument23 pagesNorton PDFlvsaruNo ratings yet
- ThéveninDocument1 pageThéveninRakesh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- ALFA PHYSICS NETWORK ANALYSISDocument24 pagesALFA PHYSICS NETWORK ANALYSISRishi KalaNo ratings yet
- Objective:: Practical No. 1Document7 pagesObjective:: Practical No. 1Anonymous I13s99No ratings yet
- Amrita Virtual Labs WordDocument6 pagesAmrita Virtual Labs WordAlima AaliyaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theorem and Thevenin'STheoremDocument6 pagesCircuit Theorem and Thevenin'STheoremThakur Varun Singh JadounNo ratings yet
- Thevenin - Norton Equivalents and Maximum Power TransferDocument32 pagesThevenin - Norton Equivalents and Maximum Power TransferMahmoud AlaaNo ratings yet
- Lab #3Document10 pagesLab #3Najmul Puda PappadamNo ratings yet
- Number System 1Document4 pagesNumber System 13qinoor.aaNo ratings yet
- Thvee Lab 8 PDFDocument4 pagesThvee Lab 8 PDFTayyab SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Superposition Theorem, Thevenin's Theorem, Nortons's Theorem, Maximum Power Transfer TheoremDocument28 pagesSuperposition Theorem, Thevenin's Theorem, Nortons's Theorem, Maximum Power Transfer Theoremkali hembramNo ratings yet
- BEE Module 1 Lec 8 - 10Document28 pagesBEE Module 1 Lec 8 - 10Jasmine HansdaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Resistive Circuit CalculationsDocument10 pagesLesson 3 Resistive Circuit CalculationsBlueprint MihNo ratings yet
- Lect 7Document19 pagesLect 7ABNo ratings yet
- Understanding Thevenin's TheoremDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Thevenin's Theoremakhil nigamNo ratings yet
- ECElecture 4Document42 pagesECElecture 4rupesh3655No ratings yet
- EEE1001 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Verification of NETWORK THEOREMS (Thevenin's Theorem)Document8 pagesEEE1001 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Verification of NETWORK THEOREMS (Thevenin's Theorem)RohilNo ratings yet
- Module 1 DC Circuits (Part - 2)Document14 pagesModule 1 DC Circuits (Part - 2)Sattwik MannaNo ratings yet
- Network TheoremDocument3 pagesNetwork Theoremsantosh_jbp5391No ratings yet
- Thevenins and NortonsDocument15 pagesThevenins and Nortonsdallisrinivas14No ratings yet
- Laboratory Work 3Document5 pagesLaboratory Work 3Makhmud AssentayNo ratings yet
- Superposition Theorem (BTEE-211) (U-1, P-1)Document10 pagesSuperposition Theorem (BTEE-211) (U-1, P-1)Bernard BraingixNo ratings yet
- Thevenin and Norton EquivalentsDocument36 pagesThevenin and Norton EquivalentsJosé Guillermo De Chomón AranguenaNo ratings yet
- Presented By, P.Sai Sarath ChandraDocument20 pagesPresented By, P.Sai Sarath ChandraSai SarathNo ratings yet
- Question AnswersDocument4 pagesQuestion Answershamza akhtarNo ratings yet
- Lab Report -03 Verification of Thevenin's TheoremDocument6 pagesLab Report -03 Verification of Thevenin's TheoremMst.Sharmin Akter SuchiNo ratings yet
- Superposition and Norton Theorems PresentationDocument24 pagesSuperposition and Norton Theorems PresentationMahmudul AlamNo ratings yet
- Exp. 07 Lab ManualDocument4 pagesExp. 07 Lab Manualdurjoyghosh00186No ratings yet
- Experiment 3:toverify Thevenin Theorem and Find Out Thevenin'S Equivalent Circuit Using DC Sources AimDocument4 pagesExperiment 3:toverify Thevenin Theorem and Find Out Thevenin'S Equivalent Circuit Using DC Sources Aimnational printersNo ratings yet
- Experiment Name ObjectiveDocument3 pagesExperiment Name ObjectiveImam Mehedi HasanNo ratings yet
- 9Document20 pages9Pradnya Surwade0% (1)
- Chapter 04 PDFDocument30 pagesChapter 04 PDFRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- ECSE 200 - Electric CircuitsDocument5 pagesECSE 200 - Electric CircuitsAlainNo ratings yet
- Shuvajit Paul (Ec 304)Document13 pagesShuvajit Paul (Ec 304)Candy CrUshNo ratings yet
- Thevenin's Theorem: S. No. Apparatus Range Type QuantityDocument10 pagesThevenin's Theorem: S. No. Apparatus Range Type QuantityUpender Rao SunkishalaNo ratings yet
- AC Thevenin's Theorem LabDocument5 pagesAC Thevenin's Theorem Labyasir aliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Circuit TheoremsDocument21 pagesChapter 4-Circuit TheoremsISLAM & scienceNo ratings yet
- Thevenin and Norton Theorems ExplainedDocument17 pagesThevenin and Norton Theorems ExplainedSunmbal JaveriaNo ratings yet
- Thevenin's Theorem Circuit AnalysisDocument7 pagesThevenin's Theorem Circuit AnalysismarionNo ratings yet
- Thevenin S TheoremDocument3 pagesThevenin S TheoremAldren RebaLdeNo ratings yet
- Learning Element 3Document17 pagesLearning Element 3niel lunaNo ratings yet
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Civil Service Exam ReviewerDocument103 pagesCivil Service Exam ReviewerPatrick Hel O. Laurito78% (18)
- Experiment No.4 Nodal AnalysisDocument2 pagesExperiment No.4 Nodal AnalysisYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
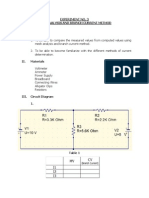
- Experiment No.1 Series-Parallel Resistive CircuitsDocument4 pagesExperiment No.1 Series-Parallel Resistive CircuitsYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- COMMUNICATIONDocument6 pagesCOMMUNICATIONYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Noise FigureDocument4 pagesNoise FigureYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
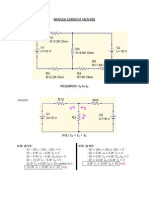
- Branch Current Method 1Document2 pagesBranch Current Method 1Yzza Veah Esquivel0% (1)
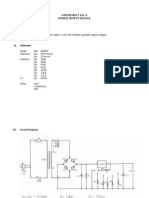
- Experiment No. 6 - Power Supply DesignDocument7 pagesExperiment No. 6 - Power Supply DesignYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Noise and CommunicationDocument5 pagesNoise and CommunicationYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Superposition TheoremDocument4 pagesSuperposition TheoremYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Nodal AnalysisDocument2 pagesNodal AnalysisYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Sine Wave 1Document2 pagesSine Wave 1Yzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Branch Current Method2Document2 pagesBranch Current Method2Yzza Veah Esquivel0% (1)
- Sine Wave 2Document2 pagesSine Wave 2Yzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.3 Mesh Analysis and Branch Current MethodDocument3 pagesExperiment No.3 Mesh Analysis and Branch Current MethodYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Sine Wave 3Document5 pagesSine Wave 3Yzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- R-C Parallel CircuitsDocument5 pagesR-C Parallel CircuitsYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Power in RC and RL CircuitsDocument4 pagesPower in RC and RL CircuitsYzza Veah Esquivel100% (1)
- Polyphase SystemDocument2 pagesPolyphase SystemYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Phasor AlgebraDocument5 pagesPhasor AlgebraYzza Veah Esquivel100% (1)
- Experiment No. 4 - The RC-RL Lead-Lag NetworksDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 4 - The RC-RL Lead-Lag NetworksYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 2 - Ac Voltage MeasurementsDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 2 - Ac Voltage MeasurementsYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet