Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ds74 Sol Review Cells
Uploaded by
api-110789702Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ds74 Sol Review Cells
Uploaded by
api-110789702Copyright:
Available Formats
SOL REVIEW
DAYSHEET 74: SOL Review Part III: Cells Name: _______________________________
Biology I
Date:
____________________________
Catalyst/Bellringer:
Because
of
our
shortened
class
period
today,
please
follow
these
instructions
in
order
to
start
Part
III
of
our
SOL
review:
1.
Take
out
your
tablet
2.
Go
to
www.biomonsters.com
3.
Click
on
Academic
Biology
4.
Click
on
Video
Podcasts
5.
PLAY
the
SOL
Review
Part
3:
Cells
Podcast
Please
remember
you
are
expected
to
use
every
minute
of
class
time
to
prepare
for
the
SOL!!!!
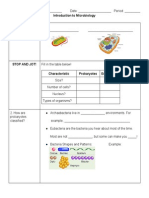
Cells 1. There are two types of cells: __________________ and ____________________ Prokaryotes Kingdoms of Life Size? Simple or Complex? Nucleus? Membrane-bound organelles? Eukaryotes
2. There are two main type of eukaryotic cells: ______________________ and _______________________ Plants Nucleus? Mitochondria? Cell wall? Chloroplast? Large central vacuole? Animals
3. Here are some of the important cell parts: Nucleus = ____________________________________________________________________________ Ribosome = ___________________________________________________________________________ Mitochondria = ________________________________________________________________________ Chloroplast = __________________________________________________________________________ Cell Membrane = ________________________________________________________________________ Cytoplasm = ___________________________________________________________________________ Lysosome = ___________________________________________________________________________ Vacuole = _____________________________________________________________________________
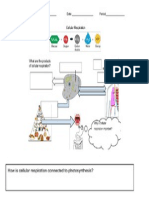
4. Photosynthesis uses energy from the _______ to make _________ energy (food). The equation for photosynthesis is:
5. Aerobic respiration breaks down ___________ to make usable ______________ (_______). The equation for respiration is: 2
6. There are two types of cellular respiration: ___________ and ______________. Aerobic uses __________. Anaerobic does not use ___________. 7. The cell membrane lets some things enter the cell, but keeps other things out. It is ___________________________________________________. It looks like this:
8. There are four types of transport: Diffusion Passive or Active? What is being transported? High Low or Low High? Do proteins help? Does it need energy?
Osmosis
Facilitated Diffusion
Active Transport
9. Where will the water go? Water likes to go from areas of ______ concentration to areas of _____ concentration. Pure or _________________ water has a high concentration.
SOL Top Facts to Know: Cells Activity 1: Organelle Function Directions: Match the organelles on the left with their functions on the right! If you have trouble remembering, MAKE FLASHCARDS!!! 1. Mitochondria 2. Chloroplast 3. Cell Membrane 4. Cytoplasm 5. Lysosome 6. Nucleus 7. Ribosome 8. Cell wall 9. Large central vacuole a. fluid-filling of the cell; mostly water b. breaks down and recycles molecules; only in animal cells c. contains the cells DNA; control center of the cell d. site of protein synthesis e. selectively permeable lipid bilayer; controls what enters and exits f. breaks down glucose into usable energy (ATP); uses oxygen g. converts light energy into chemical energy (food); only in plant cells h. stores nutrients and water; only in plant cells i. provides support and protection in plant cells only
Activity 2: Types of Cells Directions: Using the list of organelles above, answer the following questions 1. Which organelles that are found in BOTH prokaryotes and eukaryotes? (Hint: There are 4)
2. Which organelles are found ONLY in EUKARYOTES? (Hint: There are 4)
3. Which organelles are found in BOTH plant and animal cells? (Hint: There are 5)
4. Which organelles are found ONLY in PLANT cells? (Hint: There are 3)
5. Which organelle is found ONLY in ANIMAL cells? (Hint: There is 1)
Directions: Use your answers to the previous section to help you answer the questions below 1. A scientist is examining a cell under the microscope. The cell has ribosomes, a cell wall, and a region of loose DNA not in a nucleus. What type of cell is it? A. Prokaryote B. Eukaryote C. Prokaryote or Eukaryote 2. A student is examining a cell under the microscope. The cell has ribosomes, a cytoplasm, and a cell membrane. What type of cell is it? A. Prokaryote B. Eukaryote C. Prokaryote or Eukaryote 3. A student is examining a cell under the microscope. The cell has mitochondria, chloroplasts, and a cell membrane. What type of cell is it? A. Prokaryote B. Eukaryote C. Prokaryote or Eukaryote 4. A scientist is examining a cell under the microscope. The cell has a cell wall, a nucleus, and several chloroplasts. What type of cell is it? A. Plant B. Animal C. Plant or Animal 5. A scientist is examining a cell under the microscope. The cell has nucleus, several mitochondria and a cell membrane. What type of cell is it? A. Plant B. Animal C. Plant or Animal Activity 3: Photosynthesis and Respiration Directions: Complete the following diagram using the words below showing the relationship between photosynthesis and respiration. Oxygen (O2) Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Glucose Water Light ATP
Chloroplast (Photosynthesis)
Mitochondrion (Respiration
5
Directions: Fill in the chart below by placing a check in the appropriate boxes Photosynthesis Occurs in the chloroplast Occurs in the mitochondrion Uses Oxygen Releases Oxygen Uses Glucose Makes Glucose (Food) Uses Carbon Dioxide Releases Carbon Dioxide Uses Light Energy Makes ATP (Energy) Occurs in plants only Types of Transport Directions: Identify the type of transport being described in each statement. Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis Active Transport Cellular Respiration
Diffusion
1. A molecule of salt moves into the cell from a high concentration to a low concentration without the use of cell energy or proteins _______________________ 2. Water moves into the cell from a high concentration to a low concentration. _________________ 3. There is a higher concentration of potassium inside the cell, but the cell continues to pump more potassium inside with the help of ATP and proteins ___________________ 4. Chloride ions move from an area of high concentration inside the cell to an area of low concentration by flowing through a protein channel. No ATP is necessary. ___________________ Directions: Use the terms below to describe what will happen to the cell in each of the following scenarios. HINT: Remember that water likes to go from HIGH to LOW. Cells will shrivel Cells will expand Cells will stay the same
1. A piece of potato is soaked in very salty water ______________________________ 2. Red blood cells are put in distilled (pure) water ______________________________ 3. 4.
_______________________________
__________________________________
6
You might also like
- Taxonomy FoldableDocument19 pagesTaxonomy FoldableLori Simonson88% (16)
- The Complete Biomonster Vocabulary Reference GuideDocument26 pagesThe Complete Biomonster Vocabulary Reference Guideapi-110789702100% (1)
- Ds65-Summative PCR Quiz Term II ReivewDocument7 pagesDs65-Summative PCR Quiz Term II Reivewapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Bio Sol SheetDocument6 pagesBio Sol Sheetapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Bio - UNIT 1 - Organisms and Life ProcessesDocument18 pagesBio - UNIT 1 - Organisms and Life ProcessesMuhammad Mahi Nurul IslamNo ratings yet
- Cell Division ExerciseDocument3 pagesCell Division ExerciseFauziah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Cellgrow 10 AnsDocument6 pagesCellgrow 10 Ansprofesor_science100% (3)
- Lab Report #1 BiologyDocument3 pagesLab Report #1 BiologyCharles Maclean100% (1)
- Genetics Multiple AllelesDocument2 pagesGenetics Multiple AllelesPonlawit WisomkaNo ratings yet
- ds75 Sol Review BiochemistryDocument7 pagesds75 Sol Review Biochemistryapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Bio 100 A Virtual Labs Unit OneDocument7 pagesBio 100 A Virtual Labs Unit OneTammy SmithNo ratings yet
- Cell DefinitionDocument2 pagesCell DefinitionjudyNo ratings yet
- Organ Systems Cloze ReadDocument1 pageOrgan Systems Cloze Readapi-342334216No ratings yet
- ds84 Unit 7 Assessment Intro To GeneticsDocument9 pagesds84 Unit 7 Assessment Intro To Geneticsapi-1107897020% (1)
- Spaced Learning Session 1 Life ProcessesDocument37 pagesSpaced Learning Session 1 Life Processesapi-210088695No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Macromolecules Guided Notes - 4th BlockDocument6 pagesUnit 2 - Macromolecules Guided Notes - 4th Blockapi-375285021No ratings yet
- 7.1 Life Is CellularDocument5 pages7.1 Life Is Cellularalex rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biochemical Aspects) : Dr. Abid AliDocument49 pagesCell (Biochemical Aspects) : Dr. Abid AliShahzad MazharNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 4 Study Guide AnswersDocument3 pagesBiology Chapter 4 Study Guide AnswersEmma Frasier50% (2)
- Types of Cell PDFDocument20 pagesTypes of Cell PDFDave Billona100% (1)
- Cells WebquestDocument4 pagesCells Webquestapi-347555363No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration NotesDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration Notescsujithan100% (1)
- Digital Unit Plan TemplateDocument5 pagesDigital Unit Plan Templateapi-324405732No ratings yet
- Cell Structures and Functions 02Document22 pagesCell Structures and Functions 02YASMERONo ratings yet
- Rat Dissection Lesson 2Document7 pagesRat Dissection Lesson 2api-209270909No ratings yet
- 03 Genome Chromosome and Dna Webquest 2 1Document4 pages03 Genome Chromosome and Dna Webquest 2 1api-315857844No ratings yet
- Stem Cells in HumansDocument4 pagesStem Cells in HumansSana NainaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cell HyperdocDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Cell Hyperdocapi-458056701No ratings yet
- Rajeem Outlaw Wright - Mitosis Vs Meiosis BiologyDocument2 pagesRajeem Outlaw Wright - Mitosis Vs Meiosis BiologyRajeem Outlaw WrightNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cells PuzzleDocument3 pagesPlant and Animal Cells PuzzleLisa Ellis0% (1)
- The Cell Cycle & Cell DivisionDocument30 pagesThe Cell Cycle & Cell DivisionamitNo ratings yet
- BIO 127 General Microbiology:: Course Description and ObjectivesDocument24 pagesBIO 127 General Microbiology:: Course Description and Objectivescheramae ancesNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Review ActivityDocument5 pagesCell Organelles Review ActivityAngelica PantaleonNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Diffusion Lab-1Document7 pagesOsmosis Diffusion Lab-1api-1658690000% (1)
- Video Recap of Homeostasis and The Cell Membrane King by The Amoeba SistersDocument1 pageVideo Recap of Homeostasis and The Cell Membrane King by The Amoeba Sistersapi-233187566No ratings yet
- 9th Unit 1Document17 pages9th Unit 1[36] IX-B P.Vishnu Vardhan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Identification 10th GradeDocument5 pagesCarbohydrates Identification 10th GradeAndres Felipe MarroquinNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Lecture PDFDocument49 pagesEukaryotic Cell Lecture PDFDaezel Deux100% (1)
- Chromosomes and Heredity ReviewDocument8 pagesChromosomes and Heredity ReviewarurusipNo ratings yet
- In The WOMB-National Geographic ChannelDocument2 pagesIn The WOMB-National Geographic ChannelEmanuel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Ws1-Membrane Transport WorksheetDocument3 pagesWs1-Membrane Transport WorksheetTy BakrNo ratings yet
- SOM 201 Cellular MembranesDocument34 pagesSOM 201 Cellular Membraneskxng crockedNo ratings yet
- Explain Why Phospholipids Are Amphipathic Molecules.: Homework #8: Chapter 7Document7 pagesExplain Why Phospholipids Are Amphipathic Molecules.: Homework #8: Chapter 7haithere123No ratings yet
- AP Biology Unit 2: CellsDocument67 pagesAP Biology Unit 2: Cellsapi-292966101No ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 10 Term 1 Week 5 - 2021Document10 pagesLife Sciences Grade 10 Term 1 Week 5 - 2021Chelain Boucher100% (1)
- Cell MembraneDocument49 pagesCell MembraneKristen KonradNo ratings yet
- Domain Kingdom PhylumDocument74 pagesDomain Kingdom PhylumRia PerezNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER ONE: A View of Life: 1.1 How To Define LifeDocument60 pagesCHAPTER ONE: A View of Life: 1.1 How To Define LifeIngrid Dominique P. SanchezNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Kgis Grade 11Document64 pagesCell Structure Kgis Grade 11Katie Al HodaliNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument10 pagesCell TheoryLuigi Miguel G. Tirana100% (1)
- CH 08Document81 pagesCH 08Divine Grace InovejasNo ratings yet
- Virtual Microscope 3Document6 pagesVirtual Microscope 3Mark Pugong100% (1)
- Introduction To RespirationDocument14 pagesIntroduction To RespirationAzneezal Ar-RashidNo ratings yet
- 08 Lion Elephant Energy From MacromoleculesDocument8 pages08 Lion Elephant Energy From MacromoleculesJonghyun (Justin) YangNo ratings yet
- BIO130 Sec2 - Lec1and2 - 1pptDocument38 pagesBIO130 Sec2 - Lec1and2 - 1pptlemonpartymanNo ratings yet
- Names: Section: Date:: Animal Cell ColoringDocument2 pagesNames: Section: Date:: Animal Cell ColoringKimoi1986No ratings yet
- Cell Structures FinalDocument16 pagesCell Structures Finalapi-269480689No ratings yet
- The Human Body SystemsDocument104 pagesThe Human Body Systemsapi-126624159No ratings yet
- Bio Lysosome NotesDocument11 pagesBio Lysosome NotesCHAN QIAN NI MoeNo ratings yet
- Cell Bio Assignment - Plasma Membrane and Basement MembraneDocument2 pagesCell Bio Assignment - Plasma Membrane and Basement Membranerahul mauryaNo ratings yet
- OsmosisDocument2 pagesOsmosisapi-3420108090% (1)
- Icecores 2015Document2 pagesIcecores 2015api-110789702No ratings yet
- BolincreekmealplanningDocument2 pagesBolincreekmealplanningapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Picture Put Events (Letters / Numbers) in Order From Oldest To YoungestDocument2 pagesPicture Put Events (Letters / Numbers) in Order From Oldest To Youngestapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Symbiosis Practice QuizDocument11 pagesSymbiosis Practice Quizapi-110789702No ratings yet
- MmiummealDocument1 pageMmiummealapi-110789702No ratings yet
- FossilstationsDocument3 pagesFossilstationsapi-110789702No ratings yet
- AnswerkeyofwaterqualitynotesstudentsDocument2 pagesAnswerkeyofwaterqualitynotesstudentsapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Bolin Creek - September 24, 2015Document4 pagesBolin Creek - September 24, 2015api-110789702No ratings yet
- Waterqualityreadings 2015Document17 pagesWaterqualityreadings 2015api-110789702No ratings yet
- ConvergentboundariesDocument1 pageConvergentboundariesapi-110789702No ratings yet
- SpecificheatdataDocument1 pageSpecificheatdataapi-110789702No ratings yet
- EnergyflowpodcastnotesDocument8 pagesEnergyflowpodcastnotesapi-110789702No ratings yet
- HydrologylearningmapDocument3 pagesHydrologylearningmapapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Food / Energy & Disease Eog Review!!! Countdown To Success: 3 Days!!!Document4 pagesFood / Energy & Disease Eog Review!!! Countdown To Success: 3 Days!!!api-110789702No ratings yet
- Hydrologyeogreviewnotes 2014Document5 pagesHydrologyeogreviewnotes 2014api-110789702No ratings yet
- Station #1: Evaporation and TranspirationDocument6 pagesStation #1: Evaporation and Transpirationapi-110789702No ratings yet
- TakealookgraphtablesheetDocument1 pageTakealookgraphtablesheetapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Coral Reef Adventure Quiz: NameDocument2 pagesCoral Reef Adventure Quiz: Nameapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Eogchemistryreviewnotes 2014Document4 pagesEogchemistryreviewnotes 2014api-110789702No ratings yet
- Quest To Grow Human Organs Inside Pigs in JapanDocument2 pagesQuest To Grow Human Organs Inside Pigs in Japanapi-110789702No ratings yet
- SymbiosispodcastnotesDocument2 pagesSymbiosispodcastnotesapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Symbiosis QuizDocument18 pagesSymbiosis Quizapi-110789702No ratings yet
- BBC Bitesize: IllustrateDocument2 pagesBBC Bitesize: Illustrateapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Three ParentbabiesDocument3 pagesThree Parentbabiesapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Viruses Essential Questions NotesDocument3 pagesViruses Essential Questions Notesapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Directions For Graphing Your Bacteria Data: Day Percent Bacteria Cover 0 0 1 2 3 6 7Document1 pageDirections For Graphing Your Bacteria Data: Day Percent Bacteria Cover 0 0 1 2 3 6 7api-110789702No ratings yet
- Name: - Date: - PeriodDocument1 pageName: - Date: - Periodapi-110789702No ratings yet
- ElodealabmealparagraphDocument2 pagesElodealabmealparagraphapi-110789702No ratings yet
- CellularrespirationandphotosynthesislabDocument7 pagesCellularrespirationandphotosynthesislabapi-110789702No ratings yet
- BacteriapodcastnotesDocument7 pagesBacteriapodcastnotesapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Ninth Class Biology MCQs (Virus, Bacteria and Cyanobacteria)Document6 pagesNinth Class Biology MCQs (Virus, Bacteria and Cyanobacteria)Dr. Sajid Ali Talpur100% (3)
- Cell SynchronizationDocument21 pagesCell SynchronizationDeep Choudhary100% (3)
- Genetic Codes With No Dedicated Stop Codon Context Dependent Translation TerminationDocument13 pagesGenetic Codes With No Dedicated Stop Codon Context Dependent Translation TerminationAarcamNo ratings yet
- Bgm, A Newly Synthesized Boron Compound, Induces Apoptosis And Reduces Oxidative Stress By Inhibiting Lipogenesis In 3T3-L1 Adipocytes Via Pparγ And Ctrp3Document20 pagesBgm, A Newly Synthesized Boron Compound, Induces Apoptosis And Reduces Oxidative Stress By Inhibiting Lipogenesis In 3T3-L1 Adipocytes Via Pparγ And Ctrp3eric smidtNo ratings yet
- EVOLUTIONDocument18 pagesEVOLUTIONjohn richard amarantoNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Cell Biology 3rd Edition Thomas Pollard William Earnshaw Jennifer Lippincott Schwartz Graham JohnsonDocument3 pagesTest Bank For Cell Biology 3rd Edition Thomas Pollard William Earnshaw Jennifer Lippincott Schwartz Graham Johnsonjennaramosdpczojgkey100% (30)
- Pathogenesis of Dental Fluorosis: Biochemical and Cellular MechanismsDocument15 pagesPathogenesis of Dental Fluorosis: Biochemical and Cellular MechanismsAiluul AlmaaNo ratings yet
- Macrogen Sample Preparation GuideDocument6 pagesMacrogen Sample Preparation Guidekhalid WattoNo ratings yet
- PortfolioDocument2 pagesPortfolioapi-664951280No ratings yet
- Be Uke Boom 2012rty54yDocument5 pagesBe Uke Boom 2012rty54ySyahroniNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work PR2 1st QTRDocument4 pagesBudget of Work PR2 1st QTRAngela Francisca Bajamundi-VelosoNo ratings yet
- Pdrugs and P TreatmentDocument64 pagesPdrugs and P TreatmentWendz BouvierNo ratings yet
- Leaf Structure and FunctionDocument18 pagesLeaf Structure and FunctionShameel PervezNo ratings yet
- Early Life Events and Their Consequences For Later Disease A Life History and Evolutionary PerspectiveDocument19 pagesEarly Life Events and Their Consequences For Later Disease A Life History and Evolutionary PerspectivepomahskyNo ratings yet
- What Are The Key Differences Between DNA and RNADocument5 pagesWhat Are The Key Differences Between DNA and RNAGloriel PateñoNo ratings yet
- Policresulen, A Novel NS2BNS3 Protease Inhibitor, PDFDocument11 pagesPolicresulen, A Novel NS2BNS3 Protease Inhibitor, PDFFernando cisneros prietoNo ratings yet
- Antisense NotesDocument20 pagesAntisense NotesRASHINo ratings yet
- Bryant Et Al - 2021 - Deep Diversification of An AAV Capsid Protein by Machine LearningDocument13 pagesBryant Et Al - 2021 - Deep Diversification of An AAV Capsid Protein by Machine LearningdalicuseNo ratings yet
- Case Files and at A Glance BooksDocument6 pagesCase Files and at A Glance BookszuhudanNo ratings yet
- Book of Apstracts 6th Congress SGSDocument160 pagesBook of Apstracts 6th Congress SGSmilica cucuzNo ratings yet
- CRISPR Cas MethodsDocument399 pagesCRISPR Cas Methodsfusheng zhang100% (1)
- Astrazeneca FinalDocument19 pagesAstrazeneca FinalSayyed FaizNo ratings yet
- Protein Engineering-Methods and ProtocolsDocument347 pagesProtein Engineering-Methods and Protocolslzy100% (1)
- Undergraduate Research Opportunities Program 2012 ApplicationDocument10 pagesUndergraduate Research Opportunities Program 2012 ApplicationColin WilhelmNo ratings yet
- Environmental Factors Influencing Physical DevelopmentDocument2 pagesEnvironmental Factors Influencing Physical DevelopmentArianne Rose FangonNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptDocument17 pagesNIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptSwe Swe LynnNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) : Key PointsDocument17 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) : Key PointsMaryem SafdarNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five Protein Purification and Characterization TechniquesDocument23 pagesChapter Five Protein Purification and Characterization TechniquesReizelle Joy BillonesNo ratings yet