Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MOSFET Operation: Step by Step MOSFET Operation: Step-by-Step
Uploaded by
John EppsOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MOSFET Operation: Step by Step MOSFET Operation: Step-by-Step
Uploaded by
John EppsCopyright:
Available Formats
MOSFET Operation: Step by Step MOSFET Operation: Step-by-Step
1
MOSFET Operation: Step by Step MOSFET Operation: Step-by-Step
The channel current is carried by inversion charge at the
semiconductor/oxide interface. This charge is controlled
b th t lt by the gate voltage
The threshold voltage V
T
defines the onset of strong
inversion in the channel
The channel current saturates at a sufficiently high drain-
source voltage.
2
MOSFET Operation: Step by Step MOSFET Operation: Step-by-Step
Inthesub threshold regime thedraincurrent isasmall In the sub-threshold regime, the drain current is a small
leakage current since only a small number of electrons can
pass over the potential barrier separating the drain and the
source. This regime is called the sub-threshold regime of
operation. An increase in a gate voltage in this regime leads
to a reduction of the barrier height and, hence, to an g , ,
exponential increase of this small sub-threshold current. At
larger gate voltages, the barrier is reduced so much that
electronscanenter thechannel fromthesourceand electrons can enter the channel from the source and
effectively from the second conducting plate of the MIS
capacitor. At that point, a further increase in the gate voltage
l d i l i f h l i h
3
leads to a proportional increase of the electronic charge, q
ns
,
in the channel.
MOSFET Example MOSFET Example
Example
The electron concentration in the drain and source contact
regions of a Si MOSFET is 10
18
cm
-3
. The electron
concentration in the MOSFET channel at zero drain-to-source
biasinthesub-thresholdregimeof operationis10
9
cm
-3
4
bias in the sub threshold regime of operation is 10 cm .
Estimate the barrier height between the source and the drain.
MOSFET Example MOSFET Example
5
MOSFET Sub threshold MOSFET Sub-threshold
Sub threshold characteristics of a MOSFET: Sub-threshold characteristics of a MOSFET:
exponential dependence I
D
~ exp (V
G
/kT).
Vsub.slope < 30 mV.
2
2
exp
log log
ap
S
B
V
I
nk T
I
V
I
(
| |
|
(
\ .
= = (
| |
( 1
2
2 1
g g
exp
1; 1
ap
S
B
ap ap
V
I
I
nk T
V V
for n
k T
| |
(
|
(
\ .
= =
2 1
26
B
ap ap
nk T
V V V mV A = =
V
6
I-V in Sub-threshold and Above
Threshold Regimes
7
MOSFET I V Curves MOSFET I-V Curves
Idealized drain Idealized drain
characteristics of a
MOSFET. For V
D
~ V
Dsat
,
the drain current remains
constant.
8
Four types of MOSFETs Four types of MOSFETs
9
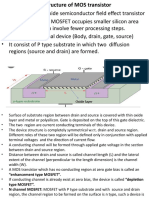
MOSFET Physics MOSFET Physics
10
Threshold voltage
MOSFET Physics MOSFET Physics
11 Threshold voltage
MOSFET Physics MOSFET Physics
12
Current-Voltage Characteristics
MOSFET Physics MOSFET Physics
13
Current-Voltage Characteristics, Linear Regime
MOSFET Physics MOSFET Physics
14
Current-Voltage Characteristics, Saturation
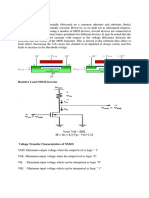
MOSFET I Vs MOSFET I-Vs
Current-Voltage Current-Voltage
Characteristics
15
MOSFET PSPICE Circuits MOSFET PSPICE Circuits
4.225uA -1.000V
R1
1
-1.000V
-1.000V
I
-1.000V
V1
1Vdc
4.225uA
M4
0A
-4.225uA
0A
MbreakP 4.225uA 1.010pA -650.0mV
0
0V
V2
-0.650Vdc
0
0
0
16
Current-Voltage Characteristics - PSPICE
You might also like
- VLSI Design BasicsDocument39 pagesVLSI Design BasicsNuniwal JyotiNo ratings yet
- Cmos Sessional 1Document5 pagesCmos Sessional 1Ashish KumarNo ratings yet
- DC-DC MOSFET Chopper Design and TestingDocument25 pagesDC-DC MOSFET Chopper Design and Testingcharan524No ratings yet
- Unit 4Document45 pagesUnit 4321910402038 gitamNo ratings yet
- Module 2-18EE53Document59 pagesModule 2-18EE53AshwiniNo ratings yet
- CMOSDocument15 pagesCMOSVinesh JayaramanNo ratings yet
- What Is LatchupDocument15 pagesWhat Is LatchupNagendra BoyellaNo ratings yet
- MOSFET SEMICONDUCTOR FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORDocument38 pagesMOSFET SEMICONDUCTOR FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORVimal KunwarNo ratings yet
- Ministry Of Higher Education Northern Technical University Technical College /Mosul Department Of Computer Engineering MOSFET CharacterizationDocument11 pagesMinistry Of Higher Education Northern Technical University Technical College /Mosul Department Of Computer Engineering MOSFET Characterizationالزهور لخدمات الانترنيتNo ratings yet
- 8.1 S06L05-FieldEffectTransistors-MOSFETs - PDF - (FreeCourseWeb - Com)Document19 pages8.1 S06L05-FieldEffectTransistors-MOSFETs - PDF - (FreeCourseWeb - Com)yotopia horoor gameNo ratings yet
- Microwave PresentationDocument49 pagesMicrowave PresentationPawan YadavNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2022-23 BEEE102L TH VL2022230105984 Reference Material I 19-01-2023 003 MOSFETDocument22 pagesFALLSEM2022-23 BEEE102L TH VL2022230105984 Reference Material I 19-01-2023 003 MOSFETvishwadeepNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Properties of MosDocument10 pagesBasic Electrical Properties of Mosmayamohan725No ratings yet
- Electrical Properties of Mos DeviceDocument28 pagesElectrical Properties of Mos Devicemayamohan7250% (1)
- Unit 5Document6 pagesUnit 5Tarun SinghalNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Group-B Q&aDocument13 pagesVlsi Group-B Q&aROHAN CHOWDHURYNo ratings yet
- BEng FETDocument13 pagesBEng FETJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- Lect 4,5,6,7 MOSFET Construction, Working Principle SND ChsrscteridticsDocument26 pagesLect 4,5,6,7 MOSFET Construction, Working Principle SND Chsrscteridticsshashikala kotiNo ratings yet
- ETI 2203 Lesson 7Document10 pagesETI 2203 Lesson 7amash.emillyNo ratings yet
- ECE221 MOSFETs-I SRMAP PDFDocument30 pagesECE221 MOSFETs-I SRMAP PDFRajeshNo ratings yet
- Mosfet BasicsDocument51 pagesMosfet BasicsRaghava KatreepalliNo ratings yet
- MOSFETs 2015 02 23Document197 pagesMOSFETs 2015 02 23楊易儒No ratings yet
- Trasistor BasicsDocument50 pagesTrasistor BasicsMuhammad SaadNo ratings yet
- Leakage CurrentDocument5 pagesLeakage CurrentImam WijayaNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument22 pagesElectronicsVARSHITH REDDY JNo ratings yet
- Overview of the two first chapters: Instructor: Dr.Nguyễn Vũ ThắngDocument32 pagesOverview of the two first chapters: Instructor: Dr.Nguyễn Vũ ThắngAlo HaNo ratings yet
- MOSFET BasicsDocument23 pagesMOSFET Basicsgopikrishna yarlagaddaNo ratings yet
- Implementation and Simulation of Half Bridge Series Resonant Inverter in Zero Voltage SwitchingDocument5 pagesImplementation and Simulation of Half Bridge Series Resonant Inverter in Zero Voltage Switchingwhite_lonelinessNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Rew 2Document58 pagesVlsi Rew 2Smilling AssassineNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicDocument17 pagesPower ElectronicHAMID SULIAMANNo ratings yet
- Poer ElectronicDocument17 pagesPoer ElectronicHAMID SULIAMANNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices & Circuits: Khurram Bughio Lecturer Electrical Engineering, MUETDocument29 pagesElectronic Devices & Circuits: Khurram Bughio Lecturer Electrical Engineering, MUETNoor SabaNo ratings yet
- Mofet - IGBT - SCR - Traic - Snubber CKTDocument17 pagesMofet - IGBT - SCR - Traic - Snubber CKTTejas krishnakanthNo ratings yet
- Unit 01Document21 pagesUnit 01mathanstar77No ratings yet
- Power MosfetsDocument11 pagesPower MosfetsSoudip KUNDUNo ratings yet
- Lecture10 MOS Field Effect Transistors v1Document33 pagesLecture10 MOS Field Effect Transistors v1Dr-Suraj Kumar SawNo ratings yet
- Mosfet PowerPoint PresentationDocument71 pagesMosfet PowerPoint PresentationMohammad Rameez100% (7)
- High Voltage MOSFETsDocument31 pagesHigh Voltage MOSFETsharendraNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lecture 4: The MOSFET and The IGBTDocument16 pagesPower Electronics Lecture 4: The MOSFET and The IGBTSolayman Salindato MasoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Introduction To Mos TechnologyDocument57 pagesUnit 2 Introduction To Mos Technologykshitiz vNo ratings yet
- Technical Examination LEVEL -7 Electronics and CircuitsDocument37 pagesTechnical Examination LEVEL -7 Electronics and CircuitsMadhunath YadavNo ratings yet
- Course Name: Basic Electronics Engineering Course Code: EC101 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)Document37 pagesCourse Name: Basic Electronics Engineering Course Code: EC101 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)Dr Sunipa RoyNo ratings yet
- L2 Ivlsi 11012019Document31 pagesL2 Ivlsi 11012019naman mathurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Mosfet Transistor)Document22 pagesChapter 4 (Mosfet Transistor)Muriel MeyouNo ratings yet
- 7.1 The MOSFET - Introduction: 7.1.1 Basic Structure and Principle of OperationDocument4 pages7.1 The MOSFET - Introduction: 7.1.1 Basic Structure and Principle of OperationManoj VatsNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument61 pages1 Introductionfiraol temesgenNo ratings yet
- Mos Transistor TheoryDocument144 pagesMos Transistor TheorymailtolokiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS (FET) EditDocument58 pagesCHAPTER 5 FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS (FET) Editruhiyahnazihah_15106No ratings yet
- Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transisitor AssignmentDocument20 pagesMetal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transisitor AssignmentSokoine Hamad DenisNo ratings yet
- Philip - MOSFET-1Document12 pagesPhilip - MOSFET-1Philip AustinNo ratings yet
- Debre Markos University Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Computer Engineering (PG)Document10 pagesDebre Markos University Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Computer Engineering (PG)enidegNo ratings yet
- AEC Lab ManualDocument75 pagesAEC Lab Manualphalanetra100% (1)
- FETs 11Document55 pagesFETs 11بلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design Important Questions On MOSFET For Exams: VoltageDocument5 pagesVLSI Design Important Questions On MOSFET For Exams: VoltageTarun SinghalNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii: MOSFET Device Physics and ModelingDocument32 pagesUnit Ii: MOSFET Device Physics and ModelingMd. Sadique SheikhNo ratings yet
- Second-Order Effects On MOSFET Small-Signal ModelDocument22 pagesSecond-Order Effects On MOSFET Small-Signal Modelsasi kiranNo ratings yet
- Power Mosfets: Introduction To Fet'SDocument21 pagesPower Mosfets: Introduction To Fet'SSharth KumarNo ratings yet
- Lpvlsi - V Unit Q & ADocument17 pagesLpvlsi - V Unit Q & ANarasimhulu MaddireddyNo ratings yet
- Borderlessworld 130217125325 Phpapp02Document38 pagesBorderlessworld 130217125325 Phpapp02John EppsNo ratings yet
- GlobalizationDocument53 pagesGlobalizationMario NguyenNo ratings yet
- Night Owl Business Plan EvaluationDocument3 pagesNight Owl Business Plan EvaluationJohn EppsNo ratings yet
- Case Study Sony CorporationDocument5 pagesCase Study Sony Corporationbahrian09100% (2)
- I JM BR 17851356985n800Document20 pagesI JM BR 17851356985n800mome057144No ratings yet
- SonyDocument31 pagesSonyYu Jun TanNo ratings yet
- Linguistics: Chapter 1 - 10Document41 pagesLinguistics: Chapter 1 - 10Ahmad A. JawadNo ratings yet
- Fiery Training 1Document346 pagesFiery Training 1shamilbasayevNo ratings yet
- C11 RacloprideDocument5 pagesC11 RacloprideAvina 123No ratings yet
- Presentation On Ich Topics & Guidelines With A Special Reference ToDocument79 pagesPresentation On Ich Topics & Guidelines With A Special Reference ToVidyaNo ratings yet
- Malaysia Year 2011 Calendar: Translate This PageDocument3 pagesMalaysia Year 2011 Calendar: Translate This PageStorgas FendiNo ratings yet
- Java MCQ QuestionsDocument11 pagesJava MCQ QuestionsPineappleNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast High School and College EssayDocument6 pagesCompare and Contrast High School and College Essayafibkyielxfbab100% (1)
- Startups Helping - India Go GreenDocument13 pagesStartups Helping - India Go Greensimran kNo ratings yet
- Levels of Attainment.Document6 pagesLevels of Attainment.rajeshbarasaraNo ratings yet
- Aquafine Optivenn Series Data SheetDocument8 pagesAquafine Optivenn Series Data SheetKenz ZhouNo ratings yet
- EMMS SpecificationsDocument18 pagesEMMS SpecificationsAnonymous dJtVwACc100% (2)
- Future Design of Accessibility in Games - A Design Vocabulary - ScienceDirectDocument16 pagesFuture Design of Accessibility in Games - A Design Vocabulary - ScienceDirectsulaNo ratings yet
- Global 6000 SystemsDocument157 pagesGlobal 6000 SystemsJosé Rezende100% (1)
- 40 Multiple Choice Questions in Basic StatisticsDocument8 pages40 Multiple Choice Questions in Basic StatisticsLevi CorralNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument18 pagesElectrocardiography - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediapayments8543No ratings yet
- Hydrotest CalculationDocument1 pageHydrotest CalculationkiranNo ratings yet
- Color Codes and Irregular Marking-SampleDocument23 pagesColor Codes and Irregular Marking-Samplemahrez laabidiNo ratings yet
- Addition and Subtraction of PolynomialsDocument8 pagesAddition and Subtraction of PolynomialsPearl AdamosNo ratings yet
- Guidelines 2.0Document4 pagesGuidelines 2.0Hansel TayongNo ratings yet
- 99 181471 - Sailor System 6000b 150w Gmdss MFHF - Ec Type Examination Module B - Uk TuvsudDocument6 pages99 181471 - Sailor System 6000b 150w Gmdss MFHF - Ec Type Examination Module B - Uk TuvsudPavankumar PuvvalaNo ratings yet
- Believer - Imagine Dragons - CIFRA CLUBDocument9 pagesBeliever - Imagine Dragons - CIFRA CLUBSilvio Augusto Comercial 01No ratings yet
- Overview for Report Designers in 40 CharactersDocument21 pagesOverview for Report Designers in 40 CharacterskashishNo ratings yet
- Trove Research Carbon Credit Demand Supply and Prices 1 June 2021Document51 pagesTrove Research Carbon Credit Demand Supply and Prices 1 June 2021Ceren ArkancanNo ratings yet
- Caribbean Examinations Council Caribbean Secondary Certificate of Education Guidelines For On-Site Moderation SciencesDocument9 pagesCaribbean Examinations Council Caribbean Secondary Certificate of Education Guidelines For On-Site Moderation SciencesjokerNo ratings yet
- Long Run Average Cost (LRAC) : Economies of ScaleDocument3 pagesLong Run Average Cost (LRAC) : Economies of ScaleA PNo ratings yet
- 153C Final Exam Study Guide-2Document6 pages153C Final Exam Study Guide-2Soji AdimulaNo ratings yet
- Seminar #22 Vocabury For Speaking PracticeDocument7 pagesSeminar #22 Vocabury For Speaking PracticeOyun-erdene ErdenebilegNo ratings yet
- Module 4-Answer KeyDocument100 pagesModule 4-Answer KeyAna Marie Suganob82% (22)
- Euro4 vehicle diesel engines 199 - 397 kW (270 - 540 hpDocument6 pagesEuro4 vehicle diesel engines 199 - 397 kW (270 - 540 hpBranislava Savic63% (16)