Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Term Human Resource Implies Human Capital That Operates An Organization
Uploaded by
kiranaishaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Term Human Resource Implies Human Capital That Operates An Organization
Uploaded by
kiranaishaCopyright:
Available Formats
HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
Question1: WHAT IS HUMAN RESOURCE PLANNING? The term human resource implies human capital that operates an organization. The word planning suggests a course of action. And lastly, process is the method of operation. Thus, the human resource planning process is defined as, 'a course of action that the human capital takes up for a methodical achievement of predetermined goals'. The definition of human resource does not end here. The term includes, its management, which primarily involves issues related to the workforce. Human resource management (HRM) is the strategic and coherent approach to the management of an organization's most valued assets - the people working there who individually and collectively contribute to the achievement of the objectives of the business. A company may have all the financial resources it may need. But what if the manpower employed to manage the finances isn't well trained? Well, nothing more than your finances going down the drain. Improper human capital may gain the output, but not the desired one in terms of quality. As the earlier mentioned definition suggests, the human resource management means managing your valued assets. The term human resource management has replaced personnel management. However, the meaning is still the same. It involves, employing, developing, utilizing, managing and understanding the staff in an organization. Human resources planning refers to classic HR administrative functions, and the evaluation and identification of human resources requirements for meeting organizational goals. It also requires an assessment of the availability of the qualified resources that will be needed. Human resources planning should be a key component of nearly every corporations strategic business planning. To ensure their competitive advantage in the marketplace, organizations must implement innovative strategies that are designed to enhance their employee retention rate and recruit fresh talent into their companies.
Page 1
HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
Effective human resources planning strategies are those that include having sufficient staff, with the right mixture of talent, and who are in the appropriate locations, performing their jobs when needed. It moves beyond the traditional role of human resources as primarily an administrative control function. In todays corporate environment, it is viewed as a valuable component for adding value to an organization. Both employees and the company will often realize many benefits of planning over the long-run. In uncertain business settings, the significance of strategic human resources planning can become obvious very quickly. A company that reacts to circumstances by cutting staff as a measure to reduce short-term overhead can create unwanted repercussions. What initially looked like a smart and necessary move to economize in lean times can end up costing the company much more in the long-run. The resources that will be needed to subsequently recruit, hire, and train new employees may well exceed any short-term cost savings. Forward-looking human resources planning typically anticipate future staffing requirements. It can help organizations avoid cost errors. Strategies are formulated to not only anticipate their needs over time, but to consider optimal solutions for the long term and under challenging economic conditions. This approach minimizes the chance of short-sighted and reactive choices being implemented by decision-makers. Organizations with a plan in place, and a keen understanding of their long-range objectives, may instead decide to weather the economic storm and keep trained, talented, and dedicated staff in place for the inevitable business uptrend
Importance of Human Resource Management Since the industrial revolution, the world has progressed tremendously. Be it the steel industry, IT, fashion houses or housing sectors, development in all of these is evident. However, over the ages man has indiscriminately used and abused the natural resources available to him. It has resulted in a global energy crises and depletion of resources in general. In this backdrop, what remains is an abundance of human resource, or let's say human capital. To achieve any more goals, tapping the right kind of human resource is the key. You may have a business house worth millions of dollars. But what if there isn't the manpower that suits the
Page 2
HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
nature of the business? Hence, developing the manpower is of utmost importance. The Process of Human Resource Management Planning The human resource planning process, demands the HR manager to first understand the business requirement. Only if he comprehends the nature and scope of the business, will he be able to employ those who will deliver the required performance. When it comes to engaging the manpower, the manager should have a keen eye for spotting the talent. It ensures that the workforce is competent enough the meet the targets. Additionally, the existing 'talent pool' in the workplace should be taken into consideration, so that people with complementary skills can be employed. The functions of the HR manager are varied; he has to assess the currently employed workforce and their shortcomings. Identifying these shortcomings goes a long way in choosing an efficient workforce. While recruiting the new employees, the HR manager must calculate the expected workload. This way the HR department can design an accurate job profile and job expectations. Once you have the decided job descriptions, looking for candidates who fit the job will be easy. Don't be fooled by their qualifications, it is only the relevant experience that matters more. A good HR manager is one who has the zeal and passion to motivate his prospective employees to perform to their potential. Human resource planning process, thus, can be considered as one of the strategic steps for building the strong foundation of an efficient workforce in an organization!
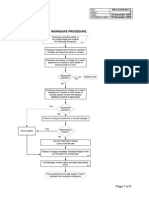
Steps in the Human Resource Planning Process 1. Designing the Management System
o
A crosscutting issue in human resource planning is to ensure that a proper system is in place to handle the process. The overall aim of this system is to manage human resources in line with organizational goals. The system is in charge of human resource
Page 3
HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
plans, policies, procedures and best practices. For example, the system should track emerging human resource management trends, such as outsourcing certain non-core functions, adopting flexible work practices and the increased use of information technology, and, if appropriate, implement them.
2. Environmental Analysis
o
The first step in the human resource planning process is to understand the context of human resource management. Human resource managers should understand both internal and external environments. Data on external environments includes the following: the general status of the economy, industry, technology and competition; labor market regulations and trends; unemployment rate; skills available; and the age and sex distribution of the labor force. Internal data required include short- and long-term organizational plans and strategies and the current status of the organization's human resources.
3. Forecasting Human Resource Demand
o
The aim of forecasting is to determine the number and type of employees needed in the future. Forecasting should consider the past and the present requirements as well as future organizational directions. Bottom-up forecasting is one of the methods used to estimate future human resource needs by gathering human resource needs of various organizational units.
4. Analyzing Supply
o
Organizations can hire personnel from internal and external sources. The skill inventories method is one of the techniques used to keep track of internal supply. Skill inventories are manual or computerized systems that keep records of employee experience, education and special skills. A forecast of the supply of employees projected
Page 4
HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
to join the organization from outside sources, given current recruitment activities, is also necessary.
5. Reconciliation and Planning
o
The final step in human resource planning is developing action plans based on the gathered data, analysis and available alternatives. The key issue is that the plans should be acceptable to both top management and employees. Plans should be prioritized and their key players and barriers to success identified. Some of these plans include employee utilization plan, appraisal plan, training and management development plan and human resource supply plan.
Objectives for Human Resources Planning 1) Consider Future Workforce:
Organizations use strategic planning to achieve goals. This relates to the organization's vision, mission and strategic objectives. An organization must analyze its future employment needs. If an organization decides it must increase productivity by 25 percent, it may need to grow its workforce by 2 percent. If an organization wants to increase market share by moving offices into new locations, it must consider the human resource requirements.
2) Analyze Current Workforce:
With future workforce needs considered, human resource planning must analyze the competency of the present workforce. Comparing future needs with current workforce strengths and abilities will identify gaps or surpluses.
3) Future Preparation:
Considering workforce surpluses and deficits, human resources must prepare action plans for the workforce. This includes identifying the type and number of employees needed,
Page 5
HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
employee competency, budget considerations, recruiting and retaining measures, and the development and training of employees. 4) Evaluation Process:
Ensuring objectives are being met by the future workforce requires an evaluation process. This will determine if the workforce is adequate to satisfy strategic goals. Planning for this process now will more easily and quickly identify future workforce gaps or surpluses.
What Is the Most Important Step for Human Resource Planning? The first step in human resources planning is projecting workforce needs and determining the resources necessary to meet those needs. This stage in human resources planning includes establishing workforce goals, such as creating staffing models, performance management standards, compensation and benefits, and training and development. Within those steps are several activities designed to enhance employee satisfaction, motivation and productivity. Human resource metrics is another aspect essential to the planning stages. Of the common five to six steps in the human resources planning process, projecting workforce needs is the most important. A. Staffing Needs:
o
Human resources planning requires careful attention to staffing needs. Determining your staffing needs can mean the difference between a company that struggles to meet payroll and a profitable, successful organization. Startup companies experience difficulties in developing staffing models that work the first time around -they are subject to incur expenses related to recruiting, training and employee turnover. The best way to prevent unnecessary staffing expenses is to create a model that aligns your business goals with the types of skill sets required to accomplish your objectives.
Page 6
HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
B. Labor Market:
o
Once you determine the qualifications and skill sets your company needs to achieve its business goals, your next step is to identify the availability of workers in the labor market who possess those skills. For some occupations, there is an abundance of talent in the labor market. For other jobs, finding employees can be quite a task, especially with shortages of qualified and available workers in fields such as health care and computer science. Attracting, recruiting and interviewing applicants are components of the overall employment process. Effective recruitment and selection processes save time and money. Turnover is costly for both startups and established businesses. Therefore, the ultimate goal is to make wise hiring decisions that result in higher levels of employee retention.
C. Employee Satisfaction:
o
Assigning job duties, tasks and responsibilities according to qualifications and criteria is to putting the right people in the right jobs. Employees whose skills are underutilized become dissatisfied when their job duties are not challenging. For many employees, mundane and uninteresting work causes their motivation and engagement levels to drop. You accomplish high levels of employee satisfaction through acknowledging employee talents and, if at all possible, modifying job responsibilities to match the employee's talents. For future roles within the company, recognize aptitude and offer training opportunities for employees who demonstrate the ability to accept more responsible positions.
D. Performance Management:
o
In addition to judging your staffing needs, assigning challenging duties and maintaining employee satisfaction, another aspect of meeting workforce needs is providing the means for employees to continually improve their performance. Performance management goals and standards support the workforce through constructive feedback, mentoring and establishing employee goals. Performance management systems -- including performance appraisals -- improve productivity and job competencies and must, therefore, become integral parts of human resources planning.
Page 7
HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
Question2: WHAT IS THE IMPORTANCE OF HUMAN RESOURCE PLANNING?
Human Resources, or HR, may be the most important department in a company. It is the only department that affects every single employee from top to bottom, and is responsible for managing what is almost always the single greatest expenditure for a company---employee costs.
As Workforce.com puts it, "A comprehensive Human Resource Strategy plays a vital role in the achievement of an organizations overall strategic objectives." An HR department that is well-versed and experienced in planning can make a company much more productive and cost-efficient. It can also make a real difference in the employees morale if workers know that decisions affecting their careers are being made in accordance with thoughtful, proactive analysis instead of last-minute reactive actions. The importances are as follows: i.
o
Minimizing wasted dollars on excess personnel. A small company that can get by with nine people but has 10 on staff wastes nearly 10 percent of personnel costs that could be used elsewhere. While this may only be $30,000 to a small company, the costs, following the 10 percent model, may waste of millions of dollars for larger companies. Conversely, having too many tasks for too few personnel can cause stress to build up to a critical level as people struggle to get the job done. Matching the number of people needed to complete the tasks is critical for any company's profit.
ii.
o
Forecasting future needs and expenses. Situations change and so do human resource needs. Long-term forecasting allows a company to make tactical plans to meet those needs. For instance, an expansion of the
Page 8
HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
company in three years might provide a need for 300 additional employees. If the community doesn't have the needed demographics, though, those new employees may have to be brought in from elsewhere, which raises expenses and takes much longer to accomplish. For seasonal businesses, every six months may make a significant difference in the amount of personnel needed. This may become a reoccurring problem if the HR department isn't responsible for the planning. iii.
o
Scheduling productivity---meeting workflow. Some companies schedule more than one work shifts, though staffing levels may differ between each. It's this type of planning when the production department and HR have to work together. If a big bump in orders is coming in 60 days, the need for overtime may be apparent to production but not to HR, which may consider that period prime time for allowing vacations.
iv.
o
Hiring HR plans for workers being replaced because of personnel losses, what personnel resources are available in the community, how to best reach those resources, and what they need in the way of salaries and benefits to become part of the company. Interviewing and selecting new hires is, at best, an inexact science. It's never known until weeks, and perhaps months, go by whether someone will work out. But the better the HR department has planned the company's needs, the better it works out. Constant communications between management, HR and other departments creates an environment where planning becomes an everyday part of the hiring process.
v.
o
Training HR may be heavily involved in the training process for the employees. Effective training can't be done without a plan that details what knowledge needs to be communicated, who will provide the training and how the training will be done. The HR department that ensures employees are thoroughly trained and competent makes the difference in productivity, reliability and employee safety.
Page 9
HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
CONCLUSION An HR department that is well-versed and experienced in planning can make a company much more productive and cost-efficient. It can also make a real difference in the employees morale if workers know that decisions affecting their careers are being made in accordance with thoughtful, proactive analysis instead of last-minute reactive actions.HR planning is very important in an organisation,for the owners and the employees also. It deals with the protocols of the particular organization.
REFERENCES: http://www.ehow.com/how-does_5135285_steps-human-resource-planning-process.html http://www.bing.com/search?q=Human+Resource+Planning+Objectives&FORM=R5FD3 http://www.google.com http://www.msn.com
Page 10
You might also like
- MaslowDocument10 pagesMaslowkiranaishaNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Property RightsDocument11 pagesIntellectual Property RightskiranaishaNo ratings yet
- Adv& DisadvDocument6 pagesAdv& DisadvkiranaishaNo ratings yet
- RecruitmentDocument20 pagesRecruitmentkiranaisha100% (1)
- Performance ManagementDocument9 pagesPerformance ManagementkiranaishaNo ratings yet
- Topic: What Is The Purpose of Planning? Analyse The Key Factors That Influence The HRP Processes?Document11 pagesTopic: What Is The Purpose of Planning? Analyse The Key Factors That Influence The HRP Processes?kiranaishaNo ratings yet
- Performance ManagementDocument9 pagesPerformance ManagementkiranaishaNo ratings yet
- Competitive AdvantageDocument27 pagesCompetitive Advantagekiranaisha100% (1)
- COMPENSATIONDocument4 pagesCOMPENSATIONkiranaishaNo ratings yet
- Global MarketingDocument7 pagesGlobal MarketingkiranaishaNo ratings yet
- Competitor AnalysisDocument12 pagesCompetitor AnalysiskiranaishaNo ratings yet
- Optimum Appointees ProcessDocument25 pagesOptimum Appointees ProcesskiranaishaNo ratings yet
- Lewin's Three-Stage Model of Change ExplainedDocument7 pagesLewin's Three-Stage Model of Change ExplainedkiranaishaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Alliances: The Right Way To Compete in The 21St CenturyDocument5 pagesStrategic Alliances: The Right Way To Compete in The 21St Centuryjeet_singh_deepNo ratings yet
- People ManagementDocument18 pagesPeople ManagementkiranaishaNo ratings yet
- NewDocument1 pageNewkiranaishaNo ratings yet
- A Systematic Approach in Achieving A High Level of Effectiveness and Efficiency Would Be Through A Selection and Recruitment ProcessDocument46 pagesA Systematic Approach in Achieving A High Level of Effectiveness and Efficiency Would Be Through A Selection and Recruitment ProcesskiranaishaNo ratings yet
- Employee 1Document100 pagesEmployee 1sulthan1987No ratings yet
- Managing Information SystemDocument19 pagesManaging Information SystemkiranaishaNo ratings yet
- Assumptions Underlying The Concept of Comparative AdvantageDocument7 pagesAssumptions Underlying The Concept of Comparative AdvantagekiranaishaNo ratings yet
- Job Evaluation and Job RotationDocument3 pagesJob Evaluation and Job RotationMinal WahurwaghNo ratings yet
- CorporateDocument23 pagesCorporatekiranaishaNo ratings yet
- Burning PlatformDocument4 pagesBurning PlatformkiranaishaNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument25 pagesCloud ComputingkiranaishaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Human Resource ManagementDocument120 pagesStrategic Human Resource ManagementMostafijurRahmanNahid100% (4)
- Marketing Planning Is A Very Essential Tool For Business and The First Step TowardsDocument11 pagesMarketing Planning Is A Very Essential Tool For Business and The First Step TowardskiranaishaNo ratings yet
- Review of The HeckscherDocument6 pagesReview of The HeckscherkiranaishaNo ratings yet
- Rewmansymprpt 0705Document22 pagesRewmansymprpt 0705kiranaishaNo ratings yet
- Models of Change ManagementDocument12 pagesModels of Change ManagementkiranaishaNo ratings yet
- CorporateDocument23 pagesCorporatekiranaishaNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- 1610747465.1724823 Clb Investments d b a Mcdonald s Hourly Employee General Handbook 102017Document37 pages1610747465.1724823 Clb Investments d b a Mcdonald s Hourly Employee General Handbook 102017Lucia SortoNo ratings yet
- Insurance Need AnalysisDocument8 pagesInsurance Need AnalysisRajesh Chowdary ChintamaneniNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics With Good Governace Amp Social Responsibility Midterm Exam PDF FreeDocument20 pagesBusiness Ethics With Good Governace Amp Social Responsibility Midterm Exam PDF Freepaolo suaresNo ratings yet
- Computerisation of Personnel RecordsDocument3 pagesComputerisation of Personnel RecordsSuraj Luwangcha100% (1)
- Sons, Et Al. vs. UST GR No. 211273 Full TextDocument18 pagesSons, Et Al. vs. UST GR No. 211273 Full TextJasper Magbanua BergantinosNo ratings yet
- Mine Project Director Job PostingsDocument2 pagesMine Project Director Job PostingsScott O'BrienNo ratings yet
- ANC Manifesto 2019Document68 pagesANC Manifesto 2019Mail and GuardianNo ratings yet
- Digital Labour and Karl Marx.: 1st Edition. by Christian Fuchs (Author)Document11 pagesDigital Labour and Karl Marx.: 1st Edition. by Christian Fuchs (Author)Mel Ward100% (1)
- Globalization S4Document10 pagesGlobalization S4Emilien MercenierNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions 2021-22 Term I Class X Social Science - Code 087Document23 pagesPractice Questions 2021-22 Term I Class X Social Science - Code 087Mr TanishNo ratings yet
- Job Offer 1184273338Document21 pagesJob Offer 1184273338dodiyaashishNo ratings yet
- Jia Li (2022) History of Feminism and Gender Equality in Modern PhilippinesDocument12 pagesJia Li (2022) History of Feminism and Gender Equality in Modern PhilippinesFRANCESCA LUISA GEMOTANo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document31 pagesChapter 1Param TrivediNo ratings yet
- Nursing Education in Denmark, Finland, Norway and Sweden - From Bachelor's Degree To PHDDocument13 pagesNursing Education in Denmark, Finland, Norway and Sweden - From Bachelor's Degree To PHDCarmela Lacsa DomocmatNo ratings yet
- Band 6 Nurse Interview Guide: 5 Common Questions AnsweredDocument6 pagesBand 6 Nurse Interview Guide: 5 Common Questions AnsweredGianina Avasiloaie0% (1)
- Worksafe Instructions and Documentation From NR - L2 - OHS - 00112Document3 pagesWorksafe Instructions and Documentation From NR - L2 - OHS - 00112Andre Mendes100% (1)
- Women, Gender, and Labour MigrationDocument36 pagesWomen, Gender, and Labour MigrationMarco J. Martínez Moreno100% (2)
- Volunteer Handbook Kerry LGBT Festival of PrideDocument44 pagesVolunteer Handbook Kerry LGBT Festival of PrideKerryFestivalofPrideNo ratings yet
- Application Format For Individual ApplicantsDocument3 pagesApplication Format For Individual ApplicantsjackproewildNo ratings yet
- Clinical Education - Planning, Conducting, and Evaluating OrientationDocument4 pagesClinical Education - Planning, Conducting, and Evaluating OrientationNisey CruzNo ratings yet
- Resume With Cover LetterDocument3 pagesResume With Cover LetterChristina LuiNo ratings yet
- BALASSA, B. (1961), Towards A Theory of Economic IntegrationDocument17 pagesBALASSA, B. (1961), Towards A Theory of Economic Integrationmonica SouzaNo ratings yet
- HDMFDocument5 pagesHDMFJett LabillesNo ratings yet
- Main ProjectDocument84 pagesMain ProjectMani PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Aratan Et Al Womens Perceptions of Selected Aviation Workplaces in Pasay City Amidst The COVID 19 PandemicDocument292 pagesAratan Et Al Womens Perceptions of Selected Aviation Workplaces in Pasay City Amidst The COVID 19 PandemicRalph A. PastranaNo ratings yet
- Labor CasesDocument91 pagesLabor CasesKim ZayatNo ratings yet
- Royal Bank of Scotland: by Group 9Document8 pagesRoyal Bank of Scotland: by Group 9sheersha kkNo ratings yet
- Local Socio - Economic Profile (LSEP) - Barangay Panamaon, Loreto, Dinagat IslandsDocument11 pagesLocal Socio - Economic Profile (LSEP) - Barangay Panamaon, Loreto, Dinagat IslandsMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Private Tutors and Teachers NecDocument4 pagesPrivate Tutors and Teachers NechimanshuNo ratings yet