Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Milling Operations
Uploaded by
inboxsweetsOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Milling Operations
Uploaded by
inboxsweetsCopyright:
Available Formats
http://vlabs.iiitdmj.ac.in/Manufacturing/Exp5/Milling Operations.
htm
Objective:
To perform milling operations, Profile milling, Pocket milling and Slot milling through basic operational differences
Equipment:
Milling Machine, Milling Cutters, Surface Roughness Gauge, Work piece
Theory and Background:
Milling:
Milling is a production process which is based on material removal. Most of the cutting tools used are multipoint cutting tools, as a result higher material removal rates can be achieved along with high surface finish. The common operations performed on milling machine are: facing, shaping, slot cutting, drilling, T-slot cutting etc.
Types of Milling Machines:
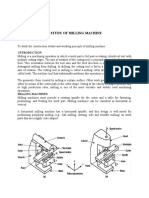
Milling machines are broadly classified as: Horizontal Milling Machine The horizontal milling machine can be recognized by its horizontal spindle. The cutter is mounted on a horizontal arbor and is rotated by supplying power. The work table can be fed in a longitudinal, cross or vertical directions. This type of machine is generally used for surface milling, profile milling, gear cutting etc. The profile cutters, plain milling cutters, gear cutters are the tools commonly used with this machine. Fig. 1 Horizontal Milling Machine Vertical Milling Machine The vertical milling machine can be recognized by the position of its spindle which is vertical (normal to the work table). The table can be moved in all the axes (X, Y and Z). The spindle head which is clamped to the vertical column can be swiveled at an angle, permitting the milling cutter mounted on the spindle to work on angular surfaces. In some machines spindle can also be adjusted up or down relative to work piece. The machine is adapted for machining grooves, slots and flat surfaces. The end mills and face milling cutters are the usual tools mounted on the spindle. Fig. 2 Vertical milling Machine
Milling Processes:
Milling Process can take place in two ways Up Milling In Up-milling process (also known as Conventional Milling) the direction of rotation of milling cutter and the direction of work piece feed are opposite to each other. As a result, the thickness of chip at the start is nil and is maximum when the cutting teeth leave the surface of the work piece. During this process the cutting teeth tend to uproot and lift up the work piece from the machine table. Fig. 3 Up-Milling Process
1 of 4
5/11/2013 3:33 PM
http://vlabs.iiitdmj.ac.in/Manufacturing/Exp5/Milling Operations.htm
Down Milling In Down-Milling process (also known as Climb Milling) the direction of rotation of milling cutter and the direction of work piece feed are same. As a result, the thickness of the chip at the start is the maximum and gradually becomes nil when the cutting teeth leave the surface of the work piece. During the process, the cutting teeth tend to push the work-piece into the table.
Milling Cutters:
Milling cutters can be classified mainly on the following bases: According to direction of rotation of the cutter: a) Right hand rotational cutter b) Left hand rotational cutter According to the helix of cutter teeth: a) Parallel or Straight teeth cutter b) Right hand Helical Cutter c) Left hand Helical Cutter d) Alternate Helical teeth Cutter Standard Milling Cutters: 1) Plain Milling Cutter a) Light duty plain milling cutter b) Heavy duty plain milling cutter
c) Helical plain milling cutter 2) Side milling cutter a) Plain side milling cutter b) Staggered teeth side milling cutter
c) Half side milling cutter d) Interlocking side milling cutter 3) Metal slitting saw a) Plain metal slitting saw b) 4) Staggered teeth metal slitting saw
Angle milling cutter a) Single angle milling cutter b) Double angle milling cutter
5)
End mill cutter a) Taper shank end mill b) Straight shank end mill
c) Shell end mill 6) 7) T-slot milling cutter Woodruff key slot milling cutter
2 of 4
5/11/2013 3:33 PM
http://vlabs.iiitdmj.ac.in/Manufacturing/Exp5/Milling Operations.htm
8) 9)
Fly cutter Formed cutter a) Convex milling cutter b) Concave milling cutter
c) Corner rounding milling cutter d) Gear cutter e) Thread milling cutter 10) Tap and reamer cutter
Milling Operations:
Profile Milling: Profile milling is the process of transferring a specific profile onto the work-piece. The formed cutters are used for this process. The cutter of required profile cuts out material from the work piece, transferring the profile onto it in multiple steps. Steps to perform Pro ile Milling
1. Install the Cutter on the arbor of horizontal milling machine a. Align the slot on the cutter with the slot on the arbor b. Insert key into the slot Fix the work-piece on the vice mounted on the work table Align the work-piece with the cutter Start the machine at low RPM Give a small depth of cut along the z-axis, and feed rate along x-axis and perform one run of cutting Return to the initial position by giving feed in the negative x-direction and repeat the process by incrementing the table position along the z-axis Continue till the desired profile is achieved
2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.
Videos: Pocket Milling: Pocket milling is the process of removing material inside some arbitrary closed boundary on a flat surface of work-piece up to a certain fixed depth. The end mill cutters are used for this process. Steps to perform pocket milling
1. 2. 3. 4. Install end mill cutter on the Vertical Milling Machine Fix the work-piece on the vice mounted on the work table Setup the spindle speed according to the work-piece and tool materials. Start the machine, with a small depth of cut, perform facing operation (machine the entire surface by giving feed along the x and y axis alternately) 5. Give a small depth of cut along the z-axis, and by giving appropriate feed along the x-axis and the y-axis, perform pocket milling operation. 6. Increment the table position along the z-axis and repeat the process till the desired depth of profile is achieved
Slot Milling: Slot milling is the process of cutting slots through a work-piece surface. These slots can be plain slots using the end mill cutter, or the T-slots, using the T-slot cutter. Steps to perform Slot Milling
1. 2. 3. Install the end mill cutter on the vertical milling machine Fix the work piece on the vice mounted on the work table Setup the spindle speed according to the work-piece and tool materials
3 of 4
5/11/2013 3:33 PM
http://vlabs.iiitdmj.ac.in/Manufacturing/Exp5/Milling Operations.htm
Start the machine, with a small depth of cut, perform facing operation (machine the entire surface by giving feed along the x and y axis alternately) 5. Align the center of the cutter with the center line of the desired slot 6. Give a small depth of cut along the z-axis and by giving appropriate feed along the x-axis perform cutting operation 7. Increment the table position along the z-axis and repeat the process till the desired depth of slot is achieved
4.
Videos: For TSlot Cutting (continue from above)
8. 9. 10. 11. Replace the end mill cutter with T-Slot cutter Align the center of the cutter with the center line of the slot (already cut) Move the table along the z-axis in order to align the plane of the cutter with the plane of desired T-slot Give a small depth of cut along the y-axis and by giving appropriate feed along the x-axis perform cutting operation 12. Increment the table position along the y-axis and repeat the process till the desired depth of T-slot (along y-axis) is achieved 13. Repeat the process for the negative y-direction
Videos:
4 of 4
5/11/2013 3:33 PM
You might also like
- Milling: Group 2 (Manufacturing Process)Document30 pagesMilling: Group 2 (Manufacturing Process)Taufiq Byomantoro100% (1)
- Benchtop Table Saw Stand PlanDocument7 pagesBenchtop Table Saw Stand Plansenthil karthikNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing of GearsDocument47 pagesManufacturing of GearsMuhammad UmarNo ratings yet
- Drilling MachineDocument30 pagesDrilling MachineNitinManjeraNo ratings yet
- Drilling MachineDocument9 pagesDrilling MachineAqib ZamanNo ratings yet
- Finishing Operations Lec 4Document27 pagesFinishing Operations Lec 4AnnieMalik100% (1)
- Grinding MachinesDocument11 pagesGrinding MachinesVikash Kumar Vimal100% (1)
- Production Technology Lab FileDocument45 pagesProduction Technology Lab FileSakshi RoyNo ratings yet
- Grinding MachinesDocument44 pagesGrinding MachinesPrashant Rao MeshramNo ratings yet
- Technology of Machine Tools: Universal Cutter and Tool GrinderDocument64 pagesTechnology of Machine Tools: Universal Cutter and Tool GrinderAnibal Daza100% (1)
- Lathe Accessories and Attachments Lathe Accessories:: 1. Face PlateDocument7 pagesLathe Accessories and Attachments Lathe Accessories:: 1. Face PlateRohan SahaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Mounting of Jobs and Cutting ToolsDocument19 pagesMethods of Mounting of Jobs and Cutting ToolsRaghav L NaikNo ratings yet
- Milling Process02Document83 pagesMilling Process02Ben AhmedNo ratings yet
- Drilling ProcessDocument15 pagesDrilling ProcessAl Fredo95% (21)
- Abrasive Jet and Water Jet Machining Mp2Document50 pagesAbrasive Jet and Water Jet Machining Mp2Drew LadlowNo ratings yet
- Drilling SRM UniviersityDocument27 pagesDrilling SRM UniviersityBhavin Desai100% (2)
- Rsdc-Skill - Gap - Study-Rubber Technology and Manufacturing Process of Rubber Products PDFDocument119 pagesRsdc-Skill - Gap - Study-Rubber Technology and Manufacturing Process of Rubber Products PDFVijay YajivNo ratings yet
- Types of Angles in Drill BitsDocument2 pagesTypes of Angles in Drill BitsAbdul AhadNo ratings yet
- LatheDocument63 pagesLatheRandom100% (1)
- BS 4825-5 - 2009 - Stainless Steel Tubes and Fittings For The Food Industry - Recessed Ring JointsDocument24 pagesBS 4825-5 - 2009 - Stainless Steel Tubes and Fittings For The Food Industry - Recessed Ring JointsroburtrNo ratings yet
- Machine Tools NotesDocument16 pagesMachine Tools NotesKarNo ratings yet
- Construction and Details of GearsDocument19 pagesConstruction and Details of GearsAkhil Nair0% (1)
- Unit IV - Abrasive Process and Broaching PDFDocument80 pagesUnit IV - Abrasive Process and Broaching PDFKanda SamyNo ratings yet
- Tail Stock of LatheDocument7 pagesTail Stock of LatheKIÊN HOÀNG TRUNG100% (1)
- LatheDocument74 pagesLatheChandrakantha K100% (1)
- Method Statement For Installation of PVC PipesDocument23 pagesMethod Statement For Installation of PVC Pipeschathura dharmasenaNo ratings yet
- JJ104 Workshop Technology Chapter6 Milling MachineDocument27 pagesJJ104 Workshop Technology Chapter6 Milling MachineAh Tiang100% (3)
- Introduction To Fitting Shop.Document11 pagesIntroduction To Fitting Shop.Mahmood AliNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Hydraulic Systems of Machine ToolsDocument56 pagesLecture 5 - Hydraulic Systems of Machine ToolsAli FaycalNo ratings yet
- LatheDocument14 pagesLatheHimanshu ModiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Drilling 29Document41 pagesUnit 2 - Drilling 29normanjames966No ratings yet
- Machining of MetalsDocument23 pagesMachining of MetalsFiq IskandarNo ratings yet
- IS 14246-1995 Galvalume SheetDocument10 pagesIS 14246-1995 Galvalume SheetkumarchemNo ratings yet
- Norsok M 121 AluminiumDocument17 pagesNorsok M 121 Aluminiumale_f_79No ratings yet
- Lab Report 3Document7 pagesLab Report 3mamoona noreen100% (1)
- Milling Report SampleDocument3 pagesMilling Report SampleAmanda LamNo ratings yet
- Name of The Experiment:: Study and Operation Bench Drilling MachineDocument5 pagesName of The Experiment:: Study and Operation Bench Drilling MachinemadNo ratings yet
- Shaping MachineDocument25 pagesShaping Machinekatakamharish100% (1)
- Drilling Machines and Its TypesDocument26 pagesDrilling Machines and Its TypesRana MohsinNo ratings yet
- Super Finishing ProcessDocument14 pagesSuper Finishing ProcessKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Experiment Name: Study and Operation of Bench Drilling MachineDocument13 pagesExperiment Name: Study and Operation of Bench Drilling MachineHashim Al-mahdliNo ratings yet
- 2 Lab - Report - MillingDocument1 page2 Lab - Report - MillingAbu Rectify100% (1)
- Lathe MachineDocument22 pagesLathe MachineRaghavMaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Non Chip FormingDocument33 pagesNon Chip FormingNur AmirahNo ratings yet
- Shot Blasting Is A Rapid, Environment Friendly, CostDocument10 pagesShot Blasting Is A Rapid, Environment Friendly, CostSulfikar SalimNo ratings yet
- ShaperDocument20 pagesShaperMilan SainiNo ratings yet
- Drilling MachineDocument30 pagesDrilling MachinePuneeth KumarNo ratings yet
- Drilling, Tapping & ReamingDocument5 pagesDrilling, Tapping & ReamingAayush AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Milling Machine PresentationDocument30 pagesMilling Machine PresentationYash Jain100% (1)
- Machining Science Sybtech Prod by DV ShirbhateDocument121 pagesMachining Science Sybtech Prod by DV ShirbhateDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENo ratings yet
- DrillingDocument61 pagesDrillingAjay RanaNo ratings yet
- Rolling ProcessDocument17 pagesRolling ProcessRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- Cutting ToolsDocument25 pagesCutting ToolsjaiswalsiddharthNo ratings yet
- Milling OperationDocument22 pagesMilling Operationnuraini ab rahimNo ratings yet
- Basic of GrindingDocument19 pagesBasic of GrindingKaushik SreenivasNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iv: Milling MachineDocument74 pagesUnit - Iv: Milling MachineDevarakonda KondayyaNo ratings yet
- Press Working TerminologyDocument16 pagesPress Working TerminologyAadrika UmashankarNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Classification, Applications and Operations of MachinesDocument19 pagesModule 4 - Classification, Applications and Operations of MachinesIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- MP I - 3rd SEM - DMEDocument17 pagesMP I - 3rd SEM - DMEBARUN BIKASH DENo ratings yet
- BME Milling and GrindingDocument16 pagesBME Milling and GrindingalysonmicheaalaNo ratings yet
- MilingDocument18 pagesMilingKasar nagib 2002No ratings yet
- Milling MachineDocument8 pagesMilling Machinegirma workuNo ratings yet
- Machine Shop Theory and Practi Ce: Mechanical EngineeringDocument14 pagesMachine Shop Theory and Practi Ce: Mechanical EngineeringJohn BorjaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 03Document5 pagesExperiment 03Ritik agarwalNo ratings yet
- MillingDocument54 pagesMillingNelsan PatelNo ratings yet
- Machine Tools - Milling MachineDocument11 pagesMachine Tools - Milling Machinejineesha p jNo ratings yet
- Adama Science and Technology University: Department of Thermal and Aerospace EngineeringDocument13 pagesAdama Science and Technology University: Department of Thermal and Aerospace Engineeringregassa rajiNo ratings yet
- How To Fix A Cyclic Redundancy Check Error - 9 Steps PDFDocument6 pagesHow To Fix A Cyclic Redundancy Check Error - 9 Steps PDFinboxsweetsNo ratings yet
- Browning Fricke Negele (2006) - Process Modeling ConceptsDocument25 pagesBrowning Fricke Negele (2006) - Process Modeling ConceptsinboxsweetsNo ratings yet
- Engineering Bill of MaterialsDocument2 pagesEngineering Bill of MaterialsinboxsweetsNo ratings yet
- Sample ResumesDocument3 pagesSample ResumesinboxsweetsNo ratings yet
- Astrid Baumgardner - How To Set Priorities - 3 Steps For Taking Control of Your TimeDocument5 pagesAstrid Baumgardner - How To Set Priorities - 3 Steps For Taking Control of Your TimeinboxsweetsNo ratings yet
- Weld SymbolsDocument2 pagesWeld SymbolsinboxsweetsNo ratings yet
- 3 Introduction To Engineering DrawingDocument14 pages3 Introduction To Engineering DrawinginboxsweetsNo ratings yet
- 1 Cadcaecam ReviewDocument59 pages1 Cadcaecam ReviewAtsis PapadopoulosNo ratings yet
- Metal Casting ProcessesDocument39 pagesMetal Casting ProcessesAthith DNo ratings yet
- Cosmos Products: Technical Service Data SheetDocument1 pageCosmos Products: Technical Service Data Sheetgowtham_venkat_4No ratings yet
- Technical PresentationDocument66 pagesTechnical Presentationsamualessa80No ratings yet
- What Is WeldingDocument5 pagesWhat Is WeldingJennie VicentaNo ratings yet
- Programme AFC 13 The 13th Asian Foundry Congress Hanoi PDFDocument9 pagesProgramme AFC 13 The 13th Asian Foundry Congress Hanoi PDFPhung Tuan AnhNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Pedal Powered HacksawDocument22 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Pedal Powered HacksawAshish Jindal100% (3)
- Surface Preparation: Paint Guide: Standards, Glossary, Surface Preparation and NotesDocument24 pagesSurface Preparation: Paint Guide: Standards, Glossary, Surface Preparation and NotesMd Shuzaur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Hi Solid PolyurethaneDocument4 pagesHi Solid PolyurethaneafvasquezNo ratings yet
- 01 Adhesive and Selant Product Catalog10Document2 pages01 Adhesive and Selant Product Catalog10abdul muslimNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Tile CAD - Detail Document2Document46 pagesCeramic Tile CAD - Detail Document2داروین پرزNo ratings yet
- Rolleri Catalogue 2016 INT PDFDocument292 pagesRolleri Catalogue 2016 INT PDFAdrian Vargas SanchezNo ratings yet
- MCP First PagesDocument16 pagesMCP First PagessureshkumarNo ratings yet
- Heat TintDocument4 pagesHeat Tintvratsista agoritsaNo ratings yet
- 0852 Sigma Acrylic Primer SealerDocument2 pages0852 Sigma Acrylic Primer SealerIbrahim MahranNo ratings yet
- VCR Face Seal (Ms-01-24) r4Document18 pagesVCR Face Seal (Ms-01-24) r4herysyam1980No ratings yet
- Pulp & PaperDocument14 pagesPulp & PaperhiuNo ratings yet
- Unconventional Machining Processes - Introduction and ClassificationDocument3 pagesUnconventional Machining Processes - Introduction and ClassificationVishal KumarNo ratings yet
- Quick Selection Guide: Filter Grade Air Filter SelectionDocument1 pageQuick Selection Guide: Filter Grade Air Filter SelectionNguyen DuyNo ratings yet
- CarTech® Custom 455® StainlessDocument11 pagesCarTech® Custom 455® StainlessElkin ColoradoNo ratings yet
- Renold SSDocument6 pagesRenold SSmichael KetselaNo ratings yet
- Shaper Machine (Lab)Document2 pagesShaper Machine (Lab)AbdulNo ratings yet
- Bearings Data SheetDocument3 pagesBearings Data SheetZin Maung Maung ThantNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument35 pagesPowder Metallurgyjohn powerNo ratings yet