Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Instruct Motor Basico
Uploaded by
kom376376Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Instruct Motor Basico
Uploaded by
kom376376Copyright:
Available Formats
Service Training MALAGA
3600 Engines - Basic
STUDENT BOOK
Thorben MARCH 1998
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Description
COURSE OBJECTIVES
DESCRIPTION This book is designed to provide necessary information to the instructor to prepare for class and to conduct the training course. The material in this book identifies components, covers the basic operation of the engine systems and goes through disassembly, assembly and adjusting procedures for the major areas of the engine. The practical part of the class will be held on a 3612 engine (nonrunning). CONTENTS The Student book contents 5 chapters and is covering: - Introduction to 3600 engines - Lubrication system - Air intake & exhaust system - Fuel system - Cooling system This course is designed for dealer and customer personnel who will be servicing 3600 engines. Good theoretical and practical understanding of diesel engines and correct mechanical procedures. Safety glasses and safety shoes (or hard leather shoes) are required. Work clothing is suggested because of hands-on exercises on the engine. During the course the students will participate following tasks: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Locate all engine components. Utilize hydraulic assembly and disassembly tooling. Remove and install a cylinder head. Remove and install a piston, connecting rod and cylinder liner. Remove and install a main bearing. Remove and install a camshaft segment and time the camshaft(s) to the crankshaft.
AUDIENCE
PREREQUISITE
EQUIPMENT
COURSE ACTIVITIES
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Description
COURSE OBJECTIVES
7. Adjust the valves and valve bridges. 8. Synchronize and time the unit injectors, set the fuel limit. 10. Service the main and centrifugal oil filters.
LITERATURE
SENR3593-01 SENR3594-03
SYSTEM OPERATION TESTING & ADJUSTING (3612 & 3616) DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY (3612 & 3616)
Service manual and other literature are for course use only.
NOTE: The course is designed for a 4.5 days at 6 hours a day plus half day 3 hours.
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Description
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION ........................................................................................................ 3600 engine specifications.......................................................................................... Engine components .................................................................................................... Lab exercises .............................................................................................................. LUBRICATION SYSTEM............................................................................................ Lubrication system schematic ..................................................................................... Lubrication flow ........................................................................................................... Priority valve ............................................................................................................... Centrifugal oil filters .................................................................................................... Lab exercises .............................................................................................................. AIR INTAKE & EXHAUST SYSTEM .......................................................................... Engine air flow ............................................................................................................ Cam segment trim....................................................................................................... Lab exercises .............................................................................................................. FUEL SYSTEM ........................................................................................................... Fuel system schematic ............................................................................................... Fuel flow...................................................................................................................... Unit injector ................................................................................................................. Injector control linkage ................................................................................................ Injector synchronization .............................................................................................. Lab exercises .............................................................................................................. COOLING SYSTEM ................................................................................................... Combined circuit cooling system ................................................................................ Coolant flow schematic ............................................................................................... Separate circuit cooling system .................................................................................. Coolant flow schematic ............................................................................................... Lab exercises ..............................................................................................................
Page:
Service Training MALAGA
3600 Engines - Basic
I. INTRODUCTION
Thorben MARCH 1998
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Introduction
3600 engine specifications
The 3600 engine family contains 4 models: - 6 & 8 cylinder engines (in-line engines) - 12 & 16 cylinder engines (vee engines)
At the end of 1997 Caterpillar will bring out an 18 cylinder engine (3618), which will be produced in Spain.
Bore x stroke Rated speed Low idle speed Output
280 x 300 mm (11.0 x 11.8 in) 720 to 1000 rpm 280 to 400 rpm 280 kW/cyl (375 hp/cyl) @ 1000 rpm
Compression ratio Combustion system Peak cylinder pressure
13:1 Direct Injection New 2350 psi (16190 kPa) Former 2200 psi (15160 kPa)
Rotation
CCW standard Cw optional
Mean piston velocity BMEP Displacement/cyl.
10 m/s (33 ft/s) @ 1000 rpm 18.2 bar (264 psi) @ 1000rpm 18.5 L
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Introduction
3600 engine specifications
Weight of serviceable parts (kg)
Cylinder head assembly Liner Piston assembly Piston pin Connecting rod Turbocharger Unit injector Front housing Camshaft segment Camshaft journal
196 101 35 19 57 400 11.3 258 29.5 10.4
3606 Block & bearing caps Crankshaft Flywheel assembly Damper Rear housing Aftercooler core 4638 1782 491 190 222 42
3608 6476 2288 491 249 222 42
3612 6810 2091 474 496 350 94
3616 9625 3630 463 496 350 125
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Introduction
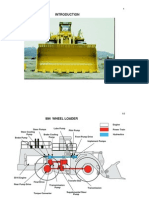
Engine components
The picture above shows a 3616 engine.
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Introduction
Engine components
The picture above shows a 3616 marine engine. On the following page write down the names of the components referring to the numbers on the picture. It is allowed to use the Caterpillar service literature. On this picture there are shown some additional components, which not have been shown on page 4.
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Introduction
Engine components
1._________________________ 2._________________________ 3._________________________ 4._________________________ 5._________________________ 6._________________________ 7._________________________ 8._________________________ 9._________________________ 10.________________________ 11.________________________ 12.________________________ 13.________________________ 14.________________________ 15.________________________ 16.________________________ 17.________________________ 18.________________________ 19.________________________ 20.________________________ 21.________________________ 22.________________________ 23.________________________ 24.________________________ 25.________________________ 26.________________________ 27.________________________ 28.________________________ 29.________________________ 30.________________________ 31.________________________ 32.________________________ 33.________________________ 34.________________________ 35.________________________ 36.________________________
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Introduction
Engine components
1. Jacket water emergency circuit outlet 2. Jacket water emergency circuit inlet 3. Lifting eye 4. Crankcase breather outlet 5. Governor 6. Exhaust 7. Air inlet 8. Thermostat housing 9. Air intake shutoff 10. AC/OC emergency circuit inlet 11. Air starter inlet 12. Jacket water heater connection 13. AC/OC emergency circuit outlet 14. Solenoid shutoff 15. Emergency oil circuit inlet 16. Emergency oil circuit outlet 17. Oil sump drain 18. Fuel transfer pump
19. Mounting foot 20. Explosion relief valves 21. Combined circuit outlet 22. Jacket water circuit outlet 23. Oil circuit thermostat housing 24. JAcket water pump inlet 25. AC/OC water pump inlet 26. Flywheel 27. Optional water pump inlet 28. Optional water pump outlet 29. Fuel filters 30. Oil coolers 31. Oil filters 32. Manual barring device 33. Centrifugal oil filters 34. Oil filler 35. Dipstick 36. Manual fuel priming pump
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Introduction
Instructor notes
Show overhead of page 2-4 and talk about them. Show slides: LEGV0928 - #11 (engine left side) LEGV0928 - #12(engine right side) LEGV0928 - #04 (engine rigth side) LEGV0928 - #13 (engine top view) LEGV0928 - #14 (engine rear view) LEGV0928 - #15 (engine front view)
Take students down to the engine and let them locate the different components and fill out page 7.
Page:
Service Training MALAGA
3600 Engines - Basic
II. LUBRICATION SYSTEM
IL
Thorben MARCH 1998
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Lubrication system
Oil coolers
Inlet water
Oil temp. reg.
Oil flow
Return water Oil coolers Vent
3 Filter elements Vent 3 Filter elements Filter change valve
Priority valve By-pass valve 63 psi
Relief valve 145 psi
Coolin jet flow 20 psi Main oil manifold & bearings
Oil pan
Oil pan Unfiltered oil
Check valve Centrifugal filter No flow under 15 psi Prelube pump Main oil pump
Breather Oil pan Strainer
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Lubrication system
Instructor notes
Let students make the qiuz (see transparency section). Give them about 5 min. and then show them how the system should look like. Explain lube system and the function of the different components. Oil system Oil system provides a constant supply of 85 C (185 F) filtered oil at 430 kPa (62.4 psi) pressure. An oil priority valve regulates oil preesure at the cylinder block oil manifold rather than at the oil pump. This makes the oil manifold pressure independent of oil filter and oil cooler pressure drops. Oil to the oil pump passes through a 650 micron (0.025 in.) screen located between the suction bell and the suction tube. Oil temperature regulators direct the oil to coolers at oil temperatures above 85 C ( 185 F). From the 20 microns (0.78 mils) final filters the oil flows through the priority valve to drilled oil passages in the cylinder block. Prelubrication is required for all 3600 engines before each start. Two methods are available: intermittent and continuous. Continuous prelubrication occurs in stand-by situations. Intermittent prelubrication occurs for a short interval preceding engine start and provides oil to all the engine bearings. A pressure switch and starter interlock prevent starter operation with less than 10 kPa (1.5 psi) lube system pressure.
Page: 3
Priority valve
Suction screen
Temperature regulators
Oil filters
Prelubrication
Two methods of prelubing Continuous
Intermittent
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Lubrication system
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Lubrication system
Priority valve
The priority valve senses filtered oil pressure and bypasses or dumps unfiltered oil back to the oil sump to control the engine oil pressure.
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Lubrication system
Centrifugal filters
The centrifugal oil filters extend the life of the oil filter elements and remove some particles smaller than the oil filters will normally take out. The centrifugal filters receive 3-4 % of the oil pump flow. The flow of oil through the jets causes the rotor assembly to rotate at about 4000 rpm. Oil flow through each filter is 17 L/min. (5.5 gpm) and the dirt capacity is 3.6 kg (8 lbs.). The centrifugal filters should normally be cleaned every 1000 hours.
Page: 6
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Lubrication system
Slides
Show slides and explain the functions of the different components of the lube system. LEGV0928 - #19 Oil pump - the oil pump is driven approximately 1.5 times engine speed. The components of the pump are the same for both standard and reverse rotation. An oil pump can not be removed from a standard rotation engine and installed directly to a reverse rotation engine or visa versa. A single dowel pin in the mounting flange prevents the pump from being rotated 1800 degrees and installed. Oil pump - standrad rotation. Oil pump - reverse rotation. Air operated prelube pump. Electric prelube pump - pumps can be provided with 115/230 VAC, 50/60 Hz single phase motor. They also can be equipped with 24 VDC or 60/70 VDC motors. Higher voltage 3 phase motors are available for continuous prelubrication systems. Oil temperature regulators. Oil filters - (Duplex filters) There are two oil filter housings on all 3600 engines with three replaceable filter elements in each housing. An oil filter change valve allows the filter elements for each filter housing to be changed separatly while the engine is operating. The maximum change period is 1000 hours or when the oil filter pressure drop reaches 104 kPa (15 psi). Oil filter elements. Priority valve.
Page: 7
LEGV3823 - #90 LEGV3823 - #91 LEGV0928 - #20 LEGV0928 - #20
LEGV0928 - #22 LEGV0928 - #23
LEGV0928 - #27 LEGV0928 - #30
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Introduction
Slides
LEGV0928 - #34 Vee engine cylinder block - Three oil manifolds. The one at the center supplies the main and camshaft bearings. The two outer manifolds supply the piston cooling spray jets. Piston cooling jet. Inlet valve lube metering pump - injects a small amount of oil into the inlet manifold where it is mixed with the intake air to lubricate the inlet valves and valve seats to reduce wear. Disassembled centrifugal oil filter. Show students the flow of the oil and the lub system components on the engine. Do lab exercises with students (page 9)
LEGV0928 - #36 LEGV0928 - #37
LEGV0928 - #44
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Lubrication system
Lab exercises
1) Removal of oil filter elements. Disassembly & Assembly (SENR3594-03) page 119.
2) Removal, disassembly & assembly of centrifugal filter. Disassembly & Assembly (SENR3594-03) page 127.
Page:
Service Training MALAGA
3600 Engines - Basic
III. AIR INTAKE & EXHAUST SYSTEM
Thorben MARCH 1998
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Intake & exhaust system
Instructor notes
Explain general air flow of the engine and show slides about engine aftercooler.
For optimum engine performance and low fuel consumption, two exhaust manifold designs are used on the 3600 family of engines. A divided or split exhaust manifold system is installed on the 3606 and 3612 diesel engines. The turbocharger(s) used with this manifold design has a double entry inlet. A single larger diameter exhaust manifold design with single inlet into the turbocharger is used with 3608, 3616 and all spark ignited (gas) engines.
LEGV0928 - #59
In-line aftercooler core - mounted on theleft side of the engine. In-line cylinder block - with cast-in inlet manifold. Vee engine aftercooler core - mounted above the center of the vee. Location of vee engine aftercooler & air shutoff. An air shutoff is available for installation at the aftercooler inlet. The air shutoff is closed only when an overspeed occurs or when an emergency shutdown is initiated.
LEGV0928 - #60 LEGV0928 - #62
LEGV0928 - #61
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Intake & exhaust system
Camshaft 3612 engine
Rear end
Install the camshaft journals with the annular groove toward the front of the engine for both standard (CCW) rotation and reverse (CW) rotation engines. Install the camshaft segments with the groove toward the front of the engine for standard (CCW) rotation engines. Install the camshaft segments with the groove toward the rear of the engine for reverse (CW) rotation engines.
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Intake & exhaust system
Instructor notes
Talk about camshaft segments and journals. Camshaft The camshaft is running half the speed of the crankshaft. The camshaft is with the help of push rods and rocker arms activating the air inlet and exhaust valves and the unit injector. The camshafts in all 3600 engines are segmented. Each cylinder has its own segment but all the segments are the same. On Vee engines the segments in the left side are different than those in the right side. The segments in the in-line engine will be the same as the segments in the left or rigth of the Vee engine, depending on whether it is a standard or reverse rotation engine. Therefor there are basically two camshaft part numbers to service both in-line and Vee distillate fuel engines. Heavy fuel engine camshafts may be different. Camshaft segments installed on diesel engines before mid-1990 have thinner flanges and spacers. The bolts are also smaller.
Camshaft segmented
In-line uses same part as Vee
Earlier cam segments
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Intake & exhaust system
Cam segment trim
Dowel
E C A B
Dowel hole locations
Annular groove
Dowel
Dowel hole locations
At present there are three different kinds of camshaft segments. The difference between them is the number and the location of the dowel holes.
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Intake & exhaust system
Instructor notes
Explain trimming of camshaft journals. Cam journals There are three different kinds of cam journals: one with 5 dowel holes, one with 3 dowel holes and one with 2 dowel holes. When you order a camshaft journal you will get a plain journal and two dowels. Show slides about camshaft segments, journals, their removal and about rocker arm assembly and valves. LEGV0928 - #65 Camshaft segment, two spacers and camshaft rear journal. Camshaft journal - with 5 dowel holes. Camshaft segment removal tool. Camshaft segment removal. Valve lifter group. Cylinder head - shows air intake and rocker arm assembly. Bottom side of cylinder head - shows intake & exhaust valves. Let students remove two cam segments, three cam journals and one cam bearing.
Journal trimming
LEGV0928 - #66 LEGV0928 - #67 LEGV0928 - #69 LEGV0928 - #71 SESV1535 - #49
LEGV0928 - #80
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Intake & exhaust system
Lab exercises
1) Removal of camshaft segment and journal. Disassembly & Assembly (SENR3594-03) page 213
2) Removal of camshaft bearing. Disassembly & Assembly (SENR3594-03) page 220.
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Intake & exhaust system
Cylinder head removal
Collar
Hydraulic cylinder
Pedestall
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Intake & exhaust system
Cylinder head removal
Collar
Cover Piston
Cylinder Stud Pedestall
Nut Washer
Cylinder head
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Intake & exhaust system
Instructor notes
Explain removal of cylinder head. Show following slides: LEGV0928 - #94 LEGV0928 - #96 LEGV0928 - #95 LEGV0928 - #97 LEGV0928 - #98 LEGV0928 - #101 LEGV0928 - #81 Cylinder head removal tool - hydraulic cylinder. Hydraulic hoses. Hydraulic cylinders installed on cylinder head. Hydraulic pump. Loosening procedure of cylinder head nut. Lifting device for cylinder head. Cylinder head - with Kiney valve. The Kiney valve is for manual relief of cylinder pressure. Explain removal of unit injector and valve springs and explain messure method of combustion ring and valve springs for reusebility. Show following slides: LEGV0928 - #85 8097 - #50 Unit injector removal. Combustion ring. Let students remove a cylinder head and disassemble / assemble it. Let them also check the combustion ring and the valve springs.
Page:
10
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Intake & exhaust system
Lab exercises
1) Removal of cylinder head. Disassembly & Assembly (SENR3594-03) page 183. Note before starting to remove the cylinder head : a) Drain the engine coolant to a level below the cylinder heads. b) Shut off the fuel supply and return, drain the fuel system and remove the fuel lines that connect the fuel manifolds to the cylinder head. c) Install plugs in the fuel lines and caps over the fittings on the cylinder head to keep dirt out of the fuel system.
2) Disassembling of the cylinder head. Disassembly & Assembly (SENR3594-03) page 191
3) Measurement of combustion gasket thickness. Disassembly & Assembly (SENR3594-03) page 187.
4) Measurement of valve springs. Spcifications (SENR3592-01) page 17.
Page:
11
Service Training MALAGA
3600 Engines - Basic
IV. COOLING SYSTEM
Thorben MARCH 1998
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Cooling system
Instructor notes
Two cooling systems System temeratures Basic operating parameters Caterpillar is providing two cooling systems: Combined circuit cooling & separate circuit cooling. Temperatures in the two systems are the same. 50 C (122 F) nominal water temperature to the AC and OC (DFE). 32 C (90 F) nominal water temperature to the AC and OC (HFE). 90 C (194 F) nominal jacket water temperature to the cylinder block circuit (DFE). 93 C (199 F) nominal jacket water temperature to the cylinder block circuit (HFE). 85 C (185 F) nominal oil to bearing temperature. Max. temperatures Over time, as the performance of the heat exchanger decreases due to fouling, the water temperature to the AC will increase. At higher ambient conditions, the water to the AC and OC is allowed to rise to 65 C (149 F) for DFE or 38 C (100 F) for HFE maximum before engine deration is required.
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Cooling system
D Cylinder Block, Head & Turbo A JW Pump C B
D (3606/3608) Oil Cooler
D (3612/3616) E D Aftercooler Heat Exchanger C Page: 3
AC/OC Pump
Expansion Tank
A - Mixed temp. from engine and coolers B - Mixing chamber from AC & OC C - Regulator D - Factory orifices E - Factory or customer orifices Coolant going to Expansion Tank - 50C for DO & 32C for HFO Coolant going to Cylindeer Block etc. - 90C for DO & 93 C for HFO
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Cooling system
Instructor notes
Combined system The combined circuit system is also known as the single circuit - two pump system. The main advantage of the combined circuit system is that it requires only one external cooling circuit with only one heat exchanger or radiator. There is less coolant and cooling system piping can be relatively simple.
Advantage combined system
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Cooling system
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Cooling system
D Cylinder Block, Head & Turbo E JW Pump Expansion Tank C
E Heat Exchanger (JW Circuit) F Heat Exchanger (AC/OC Circuit) F C Page: 6
Vent Line D Oil Cooler
Makeup Line
D Aftercooler
AC/OC Pump
A - Mixed temp. from engine and coolers B - Mixing chamber from AC & OC C - Regulator D - Factory orifices E - Factory or customer orifices F - Customer orifices Coolant going to AC/OC - 50C for DO & 32C for HFO Coolant going to Cylindeer Block etc. - 90C for DO & 93 C for HFO
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Cooling system
Instructor notes
Makeup line (separate circuit) The only connection between the AC / OC circuit and the engine jacket water circuit is a makeup line that goes from the expansion tank to the water pump supply line. This line keeps the AC / OC circuit filled when it shares the expansion tank with the jacket water circuit. There is no active flow between the circuits. The total radiator surface area may be 20 % less at 45 C (110 F) ambient and up to 30 % less at higher ambients, when compared to a combined circuit. Maintains nominal water temperature to the AC and OC while rejecting heat from the cylinder block and heads at higher temperatures. The total external flow is approximately twice the external flow of the single circuit system. Half of the flow (high temperature circuit) must be cooled to nominal jacket water temperature and the low temperature circuit cooled to nominal AC / OC water temperature.
Advantage separate system
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Cooling system
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Cooling system
Instructor notes
Explain combined and separate circuit cooling systems. Show slides about piston and liner removal and piston assembly disassembling. LEGV0928 - #109 LEGV0928 - #110 LEGV0928 - #111 LEGV0928 - #115 LEGV0928 - #117 LEGV0928 - #118 LEGV0928 - #119 LEGV0928 - #120 LEGV0928 - #121 LEGV0928 - #123 Connecting rod cap bolts. Lower the connecting rod cap. Install crank protectors. Piston $ connecting rod assembly. Removal of piston retaining rings. Piston pin guide. Piston ring removal. Measure piston and rings. Cylinder liner removal tool. Installation of liner removal tool. Remove piston and liner and disassemble piston assembly. Show and explain the three kinds of different liners.
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Cooling system
Lab exercises
1) Removal of piston & connecting rod assemblies. Disassembly & Assembly (SENR3594-03) page 203 2) Removal of cylinder liner. Disassembly & Assembly (SENR3594-03) page 210. 3) Measurement of piston rings. Guideline for reusable parts (SEBF8107). 4) Removal and installation of crankshaft main bearings. Disassembly & Assembly (SENR3594-03) page 222 5)Installation of cylinder liner. Disassembly & Assembly (SENR3594-03) page 211 6) Installation of piston & connecting rod assemblies. Disassembly & Assembly (SENR3594-03) page 205 7) Installation of cylinder head. Disassembly & Assembly (SENR3594-03) page 187
Page:
10
Service Training MALAGA
3600 Engines - Basic
DIESEL
V. FUEL SYSTEM
Thorben MARCH 1998
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Fuel system
Pressure relief valve
Check valve
Secondary fuel filter elements
Filter change valve
Check valve
Secondary fuel filter elements
Relief valve
Main fuel pump
Check valve Check valve
Check valve
Hand priming pump
Main fuel tank
Primary Fuel filters
Page: 2
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Fuel system
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Fuel system
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Fuel system
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Fuel system
Adjustment screw for rack zero setting inside Link to governor See detail below Spring loaded link Rack
Control bar
Bolted and doweled
To other injectors Storage for zero-ing pin
Power setting screw under this cover
Location for dial gage
Install zero-ing pin here
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Fuel system
Injector synchronization
B A
A) Rack B) Rack synchronization distance C) Trim bolt
For injector synchronization slide the rack synchronization gauge (6V9057) between shoulder on rack and head of trim bolt. During the injector synchronization the synchronization gauge is touching the trim bolt. As a result the gauge might not be completely straight between the rack and the injector body. There have been some cases where the service man has grinded a piece out of the gauge to make it fit perfectly. DONT DO THIS !!
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : Fuel system
LAB EXERCISES
1) Installation of camshaft bearing. Disassembly & Assembly (SENR3594-3) page 220 2) Installation of camshaft segment and journal. Disassembly & Assembly (SENR3594-3) page 213 3) Timing the camshaft(s) to the crankshaft. Disassembly & Assembly (SENR3594-03) page 148. System Operation Testing & Adjustment (SENR3593-01) page 48 4) Timing of unit injector. Systems Operation Testing & Adjusting (SENR3593-01) page 53. 5) Fuel setting. Systems Operation Testing & Adjusting (SENR3593-01) page 68. 6) Injector synchronization. Systems Operation Testing & Adjusting (SENR3593-01) page 55. 7) Check valve clearance. System Operation Testing & Adjustment (SENR3593-01) page 73
Page:
Service Training MALAGA
3600 Engines - Basic
PRE-/POSTTEST
Thorben MARCH 1998
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : PRE-TEST
1. When is the Caterpillar Dinner this week ?
2. When the engine is at top center #1 cylinder compression stroke, how many injectors can be timed without turning the crankshaft ? ___ALL ___1/2 ___NONE ___NONE OF THE ABOVE
3. The fuel linkage has to be set in the reference position for ALL limkage adjustments. (T or F)
4. The valve bridges need to be adjusted every time the valve lash is adjusted. (T or F)
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : PRE-TEST
5. Why must the linkage be adjusted between the governor and the control house ? ___To reduce linkage deadband in the governor shutoff position ___To synchronize the air-fuel ratio control to the engine ___To prevent engine overspeed on startup ___To improve governor stability at low idle ___All of above
6. All the valve bridges can be adjusted without rotating the crankshaft. (T or F)
7. Holes have to be drilled and tapped in the top of a piston before it can be removed. (T or F)
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : PRE-TEST
8. When installing a piston, a V(or X) mark on the piston must be aligned with a V (or X) mark stamped on the engine block to: ___Prevent piston interference with the crankshaft ___Prevent piston interference with the piston cooling jet ___Make installation easier ___Permit installation of the piston and liner as a kit
9. The unit injector must be removed with a pry bar. (T or F)
10. The proper tensioning pressure for all cylinder heads is: ___30,000 kPa (4350 psi) ___35,000 kPa (5075 psi) ___40,000 kPa (5800 psi)
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : PRE-TEST
11. The priority valve controls engine oil pressure by: ___Bypassing lube oil to the pump inlet ___Bypassing filtered oil into the sump ___Bypassing unfiltered oil into the sump ___Bypassing both filtered & unfiltered oil to the sump
12. When changing oil filter elements with the engine running, which statement is true: ___The filter change valve can be rotated directly from the service position to the run position ___ The oil filters will drain completely if given enough time with the drain valve open ___The filter change valve must be rotated to the fill position and the pressure in both filters equalized before it can be rotated to the run position
Page:
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : PRE-TEST
13. The inlet valve faces are lubricated: ___By natural oil flow past the valve stems guide ___By spray nozzles in the manifold connected directly to the lube oil supply ___By a low volume metering pump and lines that inject a small amount of oil into the inlet manifold ___All of the above
14. A pressure relief valve in the lube system priority valve gives the priority valve additional bypass capability if oil pressure exceeds 150 psi (1035 kPa). (T or F)
15. The oil pump is driven at approximately 1.5 times engine speed. (T or F)
16. The engine oil pump from a reverse rotation engine can not be made to work on a standard rotation engine. (T or F)
Page: 6
3600 Engines - Basic
CHAPTER : PRE-TEST
17. The gauges in the oil filter covers measure oil filter differential pressure. (T or F)
18. The centrifugal oil filters are bypass type filters and can only be serviced with the engine stopped. (T or F)
19. On Vee engines the camshaft segments in the left side are different than those in the right side. (T or F)
20. The camshaft segments in the in-line engine will be the same as the segments in the left or right side of the Vee engine, depending on whether it is a standard or reverse rotation engine. (T or F)
21. How many cooling systems does Caterpillar provide ?
Page:
You might also like
- D399 Operation SystemDocument64 pagesD399 Operation SystemNOUR ZAINNo ratings yet
- Cooling System OperationDocument2 pagesCooling System OperationimekazNo ratings yet
- 3512B SD Engines Maintenance IntervalsDocument4 pages3512B SD Engines Maintenance Intervalsharikrishnanpd3327No ratings yet
- SEBF8357 11 CleaningDocument6 pagesSEBF8357 11 CleaningMohamed HamdallahNo ratings yet
- 3512C Marine Auxiliary SLM00001-UP (SEBP4539 - 43) - Documentation Overhaul 1Document5 pages3512C Marine Auxiliary SLM00001-UP (SEBP4539 - 43) - Documentation Overhaul 1Ademir JuniorNo ratings yet
- TA Steering 777DDocument4 pagesTA Steering 777DBroCactus100% (1)
- Turbo ChargerDocument93 pagesTurbo ChargerradytamaNo ratings yet
- Reutilizacion CaterpillarDocument50 pagesReutilizacion CaterpillarJorge EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Remove & Install Cylinder Head AssemblyDocument2 pagesRemove & Install Cylinder Head AssemblyJuan LopezNo ratings yet
- P086ti 1Document2 pagesP086ti 1Serhan AysanNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Schedule 3608Document4 pagesMaintenance Schedule 3608Nguyễn Văn SơnNo ratings yet
- Test Tools For The Cooling SystemDocument4 pagesTest Tools For The Cooling SystemNimNo ratings yet
- Pressure Test D16F Cylinder HeadDocument4 pagesPressure Test D16F Cylinder HeadbabyNo ratings yet
- C2.2 Sebu8137-04 MDocument36 pagesC2.2 Sebu8137-04 MMd Sh100% (1)
- CaterpillarG3300 RPDocument11 pagesCaterpillarG3300 RPEdinson Ariel Chavarro QuinteroNo ratings yet
- 385C Cat Vs 385B CatDocument69 pages385C Cat Vs 385B CatKolo BenduNo ratings yet
- Overhaul (Top End) : Manual de Operación y MantenimientoDocument3 pagesOverhaul (Top End) : Manual de Operación y MantenimientomanuelNo ratings yet
- General Fuel InformationDocument5 pagesGeneral Fuel InformationElmer Tintaya MamaniNo ratings yet
- 3500 Series Engines Hydramechanical Protective SystemDocument18 pages3500 Series Engines Hydramechanical Protective SystemEbied Yousif AlyNo ratings yet
- D399 Industrial Engine Troubleshooting GuideDocument49 pagesD399 Industrial Engine Troubleshooting GuideMohamed SaiedNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Line Projection - SMCS - 1216 - 040Document5 pagesCylinder Line Projection - SMCS - 1216 - 040ToispuoliNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Interval Schedule - Prime: Operation and Maintenance ManualDocument3 pagesMaintenance Interval Schedule - Prime: Operation and Maintenance ManualaliNo ratings yet
- Reuse & Salvage Guidelines (Valve & Valve Spring Spec)Document25 pagesReuse & Salvage Guidelines (Valve & Valve Spring Spec)carlos angelNo ratings yet
- SEBF8043 Crankshaft Visual InspectionDocument49 pagesSEBF8043 Crankshaft Visual InspectionpramNo ratings yet
- Engine Misfires, Runs Rough or Is UnstableDocument4 pagesEngine Misfires, Runs Rough or Is UnstableFaresNo ratings yet
- C15 Acert Spec SheetDocument4 pagesC15 Acert Spec SheetMalasquez Leon XavierNo ratings yet
- C11 Troubleshooting High Coolant Temperature PDFDocument3 pagesC11 Troubleshooting High Coolant Temperature PDFmanu luvungaNo ratings yet
- C6.6 Engine Fuel System Guide for 938H Wheel LoaderDocument15 pagesC6.6 Engine Fuel System Guide for 938H Wheel LoaderAlex HSNo ratings yet
- ZPS - CAT 3516C HD Caterpillar CAT 3516 C HD PDFDocument3 pagesZPS - CAT 3516C HD Caterpillar CAT 3516 C HD PDFVu TongNo ratings yet
- Crankshaft Position For Fuel Injector Adjustment and Valve Lash SettingDocument2 pagesCrankshaft Position For Fuel Injector Adjustment and Valve Lash SettingEva AprianaNo ratings yet
- Cat engine cutout test resultsDocument3 pagesCat engine cutout test resultsPILAR MARTINEZ100% (1)
- Engine specifications and maintenance proceduresDocument7 pagesEngine specifications and maintenance proceduresAbel Alejandro Vera TriviñosNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar C15 P1Z00331Document3 pagesCaterpillar C15 P1Z00331Hendra MechanicNo ratings yet
- 3406 Engine TroubleshootingDocument3 pages3406 Engine TroubleshootingB E BalaramenterpriseNo ratings yet
- Manual: SafetyDocument94 pagesManual: SafetyRichard ChuaNo ratings yet
- C13, C15, and C18 Engines Alternator Problem - Charging Problem Andor Noisy OperationDocument3 pagesC13, C15, and C18 Engines Alternator Problem - Charging Problem Andor Noisy OperationRaphael ThornerNo ratings yet
- Visual Inspection of The PistonDocument53 pagesVisual Inspection of The Pistondonsallus100% (3)
- CustomerGas Engine Training Catalogue 2007Document18 pagesCustomerGas Engine Training Catalogue 2007docrafi50% (2)
- Piston Ring Liner RodDocument4 pagesPiston Ring Liner Rodmuhammad arif100% (1)
- GRPTS TurbochargersDocument65 pagesGRPTS TurbochargersFaur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar MachinesDocument514 pagesCaterpillar Machinesjosmel2100% (1)
- Failures of Cylinder Head Valves On G3500C and G3500E Generator Set Engines (1100, 1105, 1121)Document5 pagesFailures of Cylinder Head Valves On G3500C and G3500E Generator Set Engines (1100, 1105, 1121)Ahmed Nahrawy100% (1)
- Major Overhaul Procedure Chart (Using Remanufactured Components)Document2 pagesMajor Overhaul Procedure Chart (Using Remanufactured Components)carlos gallego100% (1)
- Arbol de Levas EspecificacionesDocument73 pagesArbol de Levas Especificacionesariel avalosNo ratings yet
- G3600 PKG Tips - Air Intake & ExhaustDocument49 pagesG3600 PKG Tips - Air Intake & ExhaustshivNo ratings yet
- 3600 Tolls STDDocument8 pages3600 Tolls STDDanilo Craveiro DiettrichNo ratings yet
- 3512 Land Electric - LEHW0066-00 P2Document4 pages3512 Land Electric - LEHW0066-00 P2AustinNo ratings yet
- Manual de Mantenimiento Cat 3500Document46 pagesManual de Mantenimiento Cat 3500Kikemol Lv ONo ratings yet
- 3500 SW Project PDFDocument31 pages3500 SW Project PDFDjebali Mourad100% (2)
- C15 Acert - 18396631-004Document5 pagesC15 Acert - 18396631-004Hadj AbdelwahaBNo ratings yet
- Swing Motor - Test - Measurement of Case Drain OilDocument4 pagesSwing Motor - Test - Measurement of Case Drain Oilmekanicobucaro100% (1)
- Fixture For 3500 Cylinder Head MachiningDocument7 pagesFixture For 3500 Cylinder Head MachiningAndrés BlancoNo ratings yet
- G3306 Gas Petroleum EnginepdfDocument4 pagesG3306 Gas Petroleum EnginepdfGustavo López CarriónNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Interval Schedule: Operation and Maintenance ManualDocument4 pagesMaintenance Interval Schedule: Operation and Maintenance ManualDeividas B100% (1)
- Get Maximum Return On Your Investment: CAT Certified Power Train RebuildDocument4 pagesGet Maximum Return On Your Investment: CAT Certified Power Train RebuildJean Claude EidNo ratings yet
- Repair Options: Cat 777D Off-Highway TruckDocument4 pagesRepair Options: Cat 777D Off-Highway TruckmkNo ratings yet
- 3600 Engines - BasicDocument57 pages3600 Engines - Basicmizahur100% (1)
- 1999 SR125 Suppl Serv ManualDocument25 pages1999 SR125 Suppl Serv ManualBobby HawkNo ratings yet
- 2001 2002 SRX Supplemental ManualDocument59 pages2001 2002 SRX Supplemental ManualplacecanadaNo ratings yet
- 994 Cargador ArticuladoDocument112 pages994 Cargador Articuladokom376376100% (1)
- 3500bepg MotorDocument46 pages3500bepg Motorkom376376100% (2)
- 300BAUX (Excavadora Hidraulica 300B)Document17 pages300BAUX (Excavadora Hidraulica 300B)kom376376No ratings yet
- 23 11 13-Fuel Oil Piping SystemsDocument14 pages23 11 13-Fuel Oil Piping Systemskom376376No ratings yet
- Motor de 16 Litros Descripcion de TrabajoDocument165 pagesMotor de 16 Litros Descripcion de TrabajoSHEGUITONo ratings yet
- Pump Size: 1-1/2 X 2 X 9L Model: B1-1/2Z - L: Type CCMD FM CPLG FM Belt Sae Hydraulic Ac EngineDocument2 pagesPump Size: 1-1/2 X 2 X 9L Model: B1-1/2Z - L: Type CCMD FM CPLG FM Belt Sae Hydraulic Ac EngineWilmer CaceresNo ratings yet
- Kawasaki ZG1200 Voyager XII Service Manual SupplementDocument78 pagesKawasaki ZG1200 Voyager XII Service Manual SupplementJeffrey Warneking100% (4)
- Massey Ferguson MF 383 LX TRACTOR Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 3540037)Document15 pagesMassey Ferguson MF 383 LX TRACTOR Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 3540037)qlb898316No ratings yet
- NUMBER: 3 1-10 S.M. REF.: Listed in Table ENGINE: EPA04 Series 60 DATE: March 2010Document14 pagesNUMBER: 3 1-10 S.M. REF.: Listed in Table ENGINE: EPA04 Series 60 DATE: March 2010Hamilton MirandaNo ratings yet
- Iwl Sr59 ManualDocument80 pagesIwl Sr59 ManualSimsonCZ1961100% (2)
- Engine Fuel System Troubleshooting GuideDocument19 pagesEngine Fuel System Troubleshooting GuidePablo Rojas Valenzuela100% (1)
- Sm-Perkins 4000 Series 4006-23 Tag1a, Tag2a and Tag3a Inline Diesel Engine PDFDocument34 pagesSm-Perkins 4000 Series 4006-23 Tag1a, Tag2a and Tag3a Inline Diesel Engine PDFelnido dpp100% (1)
- Assignment 2: Name: Levitaran A/L Sager MATRICS: A0000623 Lecture: Sir. Azni Bin MonDocument12 pagesAssignment 2: Name: Levitaran A/L Sager MATRICS: A0000623 Lecture: Sir. Azni Bin MonlevitranNo ratings yet
- Engine LubeDocument43 pagesEngine LubeBruce LyndeNo ratings yet
- 2022.10.26 Presentación DFSE HHPDocument36 pages2022.10.26 Presentación DFSE HHPjorgejimenez1985No ratings yet
- Workshop Manual. VW Polo Estate 1998 4-Cyl. Injection Engine (4 Valve), Mechanics (APE, AUA) - Edition 11.1999, 00056407620Document162 pagesWorkshop Manual. VW Polo Estate 1998 4-Cyl. Injection Engine (4 Valve), Mechanics (APE, AUA) - Edition 11.1999, 00056407620Аргос GNo ratings yet
- Catalog - SolenoidDocument37 pagesCatalog - SolenoidMIHAINo ratings yet
- Flow Control Valve Metal GRDocument1 pageFlow Control Valve Metal GRBiswanath LenkaNo ratings yet
- MPMC Offer For Light Tower 2011-01Document1 pageMPMC Offer For Light Tower 2011-01NAHOUI ABDELOUAHABNo ratings yet
- Carburador Toyota 1991Document23 pagesCarburador Toyota 1991William Martínez B.No ratings yet
- Engine: QSB3.3-C99 Machine: AP240 Tier 3 Specification: Z07-620-2Document60 pagesEngine: QSB3.3-C99 Machine: AP240 Tier 3 Specification: Z07-620-2abelmonte_geotecnia67% (3)
- FINI Belt Compressor Spare - Parts BK-114 and BK-119Document17 pagesFINI Belt Compressor Spare - Parts BK-114 and BK-119Ingar SlangNo ratings yet
- Schulz Piston Machine CatalogDocument6 pagesSchulz Piston Machine CatalogjerrNo ratings yet
- Lebw4957 05Document50 pagesLebw4957 05PhamLeDanNo ratings yet
- SCK Products Catalogue 220219 - PRINT FILEDocument147 pagesSCK Products Catalogue 220219 - PRINT FILEΔημήτρης Φιλ.No ratings yet
- WSI-Catalog of Valve Stem Seal PDFDocument5 pagesWSI-Catalog of Valve Stem Seal PDFyearetgNo ratings yet
- XL CodesDocument3 pagesXL CodesAntonioPalloneNo ratings yet
- KDS 90-92-2008 EngDocument221 pagesKDS 90-92-2008 EnghottytumNo ratings yet
- 3512 Land Drilling Spec SheetDocument4 pages3512 Land Drilling Spec Sheetavinash_12290% (1)
- How To Adjust The Idle Mixture On Holley CarbsDocument4 pagesHow To Adjust The Idle Mixture On Holley CarbsIsaias PrestesNo ratings yet
- Tuning Weber DCOE CarburetorsDocument14 pagesTuning Weber DCOE CarburetorsSlevinooo100% (5)
- Yanmar 4TNV84T (Himoinsa 28kVA)Document40 pagesYanmar 4TNV84T (Himoinsa 28kVA)omarpat100% (7)
- FaultDocument4 pagesFaultmarcelgarrigaNo ratings yet
- Motor boxer Vocho: características e historia del icónico motor del Volkswagen SedánDocument16 pagesMotor boxer Vocho: características e historia del icónico motor del Volkswagen SedánLuisNo ratings yet