Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Jawaharlal Nehru National College of Engineering: Laboratory Manual
Uploaded by
sandeepb8Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Jawaharlal Nehru National College of Engineering: Laboratory Manual
Uploaded by
sandeepb8Copyright:
Available Formats
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
Jawaharlal Nehru National College of Engineering
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING
VI SEMESTER B.E.
COMPUTER GRAPHICS AND VISUALIZATION LABORATORY
Subject Code: 06CSL67
LABORATORY MANUAL
Prepared By:
Mr.Ravindra.S Lecturer, CSE
1
Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga.
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
1.Program to recursively subdivide a tetrahedron to from 3D Sierpinski gasket. The number of recursive steps is to be specified by the user. /* Recursive subdivision of tetrahedron to form 3D Sierpinski gasket */ //tetra_vtu.cpp #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <GL/glut.h> typedef float point[3]; /* initial tetrahedron */ point v[]={{0.0, 0.0, 1.0}, {0.0, 0.942809, -0.33333}, {-0.816497, -0.471405, -0.333333}, {0.816497, -0.471405, -0.333333}}; static GLfloat theta[] = {0.0,0.0,0.0}; int n; void triangle( point a, point b, point c) /* display one triangle using a line loop for wire frame, a single normal for constant shading, or three normals for interpolative shading */ { glBegin(GL_POLYGON); glNormal3fv(a); glVertex3fv(a); glVertex3fv(b); glVertex3fv(c); glEnd(); } void divide_triangle(point a, point b, point c, int m) { /* triangle subdivision using vertex numbers righthand rule applied to create outward pointing faces */ point v1, v2, v3; int j; if(m>0) { for(j=0; j<3; j++) v1[j]=(a[j]+b[j])/2; for(j=0; j<3; j++) v2[j]=(a[j]+c[j])/2; for(j=0; j<3; j++) v3[j]=(b[j]+c[j])/2; divide_triangle(a, v1, v2, m-1); divide_triangle(c, v2, v3, m-1); divide_triangle(b, v3, v1, m-1); Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga.
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
} else(triangle(a,b,c)); /* draw triangle at end of recursion */ } void tetrahedron( int m) { /* Apply triangle subdivision to faces of tetrahedron */ glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); divide_triangle(v[0], v[1], v[2], m); glColor3f(0.0,1.0,0.0); divide_triangle(v[3], v[2], v[1], m); glColor3f(0.0,0.0,1.0); divide_triangle(v[0], v[3], v[1], m); glColor3f(0.0,0.0,0.0); divide_triangle(v[0], v[2], v[3], m); } void display(void) { glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); glLoadIdentity(); tetrahedron(n); glFlush(); } void myReshape(int w, int h) { glViewport(0, 0, w, h); glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION); glLoadIdentity(); if (w <= h) glOrtho(-2.0, 2.0, -2.0 * (GLfloat) h / (GLfloat) w, 2.0 * (GLfloat) h / (GLfloat) w, -10.0, 10.0); else glOrtho(-2.0 * (GLfloat) w / (GLfloat) h, 2.0 * (GLfloat) w / (GLfloat) h, -2.0, 2.0, -10.0, 10.0); glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW); glutPostRedisplay(); }
Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga.
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
void main(int argc, char **argv) { //n=atoi(argv[1]); printf(" No. of Divisions ? "); scanf("%d",&n); glutInit(&argc, argv); glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGB | GLUT_DEPTH); glutInitWindowSize(500, 500); glutCreateWindow("3D Gasket"); glutReshapeFunc(myReshape); glutDisplayFunc(display); glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST); glClearColor (1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0); glutMainLoop(); }
Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga.
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
2. Program to implement Liang-Barsky line clipping algorithm. // Liang-Barsky Line Clipping Algorithm with Window to viewport Mapping */ #include <stdio.h> #include <GL/glut.h> double xmin=50,ymin=50, xmax=100,ymax=100; // Window boundaries double xvmin=200,yvmin=200,xvmax=300,yvmax=300; // Viewport boundaries int cliptest(double p, double q, double *t1, double *t2) { double t=q/p; if(p < 0.0) // potentially enry point, update te { if( t > *t1) *t1=t; if( t > *t2) return(false); // line portion is outside } else if(p > 0.0) // Potentially leaving point, update tl { if( t < *t2) *t2=t; if( t < *t1) return(false); // line portion is outside } else if(p == 0.0) { if( q < 0.0) return(false); // line parallel to edge but outside } return(true); } void LiangBarskyLineClipAndDraw (double x0, double y0,double x1, double y1) { double dx=x1-x0, dy=y1-y0, te=0.0, tl=1.0; if(cliptest(-dx,x0-xmin,&te,&tl)) // inside test wrt left edge if(cliptest(dx,xmax-x0,&te,&tl)) // inside test wrt right edge if(cliptest(-dy,y0-ymin,&te,&tl)) // inside test wrt bottom edge if(cliptest(dy,ymax-y0,&te,&tl)) // inside test wrt top edge { if( tl < 1.0 ) { x1 = x0 + tl*dx; y1 = y0 + tl*dy; } if( te > 0.0 ) { x0 = x0 + te*dx; y0 = y0 + te*dy; } Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga. 5
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
// Window to viewport mappings double sx=(xvmax-xvmin)/(xmax-xmin); // Scale parameters double sy=(yvmax-yvmin)/(ymax-ymin); double vx0=xvmin+(x0-xmin)*sx; double vy0=yvmin+(y0-ymin)*sy; double vx1=xvmin+(x1-xmin)*sx; double vy1=yvmin+(y1-ymin)*sy; //draw a red colored viewport glColor3f(1.0, 0.0, 0.0); glBegin(GL_LINE_LOOP); glVertex2f(xvmin, yvmin); glVertex2f(xvmax, yvmin); glVertex2f(xvmax, yvmax); glVertex2f(xvmin, yvmax); glEnd(); glColor3f(0.0,0.0,1.0); // draw blue colored clipped line glBegin(GL_LINES); glVertex2d (vx0, vy0); glVertex2d (vx1, vy1); glEnd(); } }// end of line clipping void display() { double x0=60,y0=20,x1=80,y1=120; glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); //draw the line with red color glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); //bres(120,20,340,250); glBegin(GL_LINES); glVertex2d (x0, y0); glVertex2d (x1, y1); glEnd(); //draw a blue colored window glColor3f(0.0, 0.0, 1.0); glBegin(GL_LINE_LOOP); glVertex2f(xmin, ymin); glVertex2f(xmax, ymin); glVertex2f(xmax, ymax); glVertex2f(xmin, ymax); glEnd(); LiangBarskyLineClipAndDraw(x0,y0,x1,y1); glFlush(); } void myinit() { glClearColor(1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0); Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga. 6
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); glPointSize(1.0); glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION); glLoadIdentity(); gluOrtho2D(0.0,499.0,0.0,499.0); } void main(int argc, char** argv) { //int x1, x2, y1, y2; //printf("Enter End points:"); //scanf("%d%d%d%d", &x1,&x2,&y1,&y2); glutInit(&argc,argv); glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE|GLUT_RGB); glutInitWindowSize(500,500); glutInitWindowPosition(0,0); glutCreateWindow("Liang Barsky Line Clipping Algorithm"); glutDisplayFunc(display); myinit(); glutMainLoop(); }
Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga.
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
3.Program to draw a color cube and spin it using OpenGL * Rotating cube with color interpolation */
transformation matrices.
/* Demonstration of use of homogeneous coordinate transformations and simple data structure for representing cube from Chapter 4 */ /*Both normals and colors are assigned to the vertices */ /*Cube is centered at origin so (unnormalized) normals are the same as the vertex values */ #include <stdlib.h> #include <GL/glut.h> GLfloat vertices[][3] = {{-1.0,-1.0,-1.0},{1.0,-1.0,-1.0}, {1.0,1.0,-1.0}, {-1.0,1.0,-1.0}, {-1.0,-1.0,1.0}, {1.0,-1.0,1.0}, {1.0,1.0,1.0}, {-1.0,1.0,1.0}}; GLfloat normals[][3] = {{-1.0,-1.0,-1.0},{1.0,-1.0,-1.0}, {1.0,1.0,-1.0}, {-1.0,1.0,-1.0}, {-1.0,-1.0,1.0}, {1.0,-1.0,1.0}, {1.0,1.0,1.0}, {-1.0,1.0,1.0}}; GLfloat colors[][3] = {{0.0,0.0,0.0},{1.0,0.0,0.0}, {1.0,1.0,0.0}, {0.0,1.0,0.0}, {0.0,0.0,1.0}, {1.0,0.0,1.0}, {1.0,1.0,1.0}, {0.0,1.0,1.0}}; void polygon(int a, int b, int c , int d) { /* draw a polygon via list of vertices */ glBegin(GL_POLYGON); glColor3fv(colors[a]); glNormal3fv(normals[a]); glVertex3fv(vertices[a]); glColor3fv(colors[b]); glNormal3fv(normals[b]); glVertex3fv(vertices[b]); glColor3fv(colors[c]); glNormal3fv(normals[c]); glVertex3fv(vertices[c]); glColor3fv(colors[d]); glNormal3fv(normals[d]); glVertex3fv(vertices[d]); glEnd(); } Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga. 8
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
void colorcube(void) { /* map vertices to faces */ polygon(0,3,2,1); polygon(2,3,7,6); polygon(0,4,7,3); polygon(1,2,6,5); polygon(4,5,6,7); polygon(0,1,5,4); } static GLfloat theta[] = {0.0,0.0,0.0}; static GLint axis = 2; void display(void) { /* display callback, clear frame buffer and z buffer, rotate cube and draw, swap buffers */ glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); glLoadIdentity(); glRotatef(theta[0], 1.0, 0.0, 0.0); glRotatef(theta[1], 0.0, 1.0, 0.0); glRotatef(theta[2], 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); colorcube(); glFlush(); glutSwapBuffers(); } void spinCube() { /* Idle callback, spin cube 2 degrees about selected axis */ theta[axis] += 1.0; if( theta[axis] > 360.0 ) theta[axis] -= 360.0; /* display(); */ glutPostRedisplay(); }
void mouse(int btn, int state, int x, int y) { /* mouse callback, selects an axis about which to rotate */ Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga. 9
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
if(btn==GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON && state == GLUT_DOWN) axis = 0; if(btn==GLUT_MIDDLE_BUTTON && state == GLUT_DOWN) axis = 1; if(btn==GLUT_RIGHT_BUTTON && state == GLUT_DOWN) axis = 2; } void myReshape(int w, int h) { glViewport(0, 0, w, h); glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION); glLoadIdentity(); if (w <= h) glOrtho(-2.0, 2.0, -2.0 * (GLfloat) h / (GLfloat) w, 2.0 * (GLfloat) h / (GLfloat) w, -10.0, 10.0); else glOrtho(-2.0 * (GLfloat) w / (GLfloat) h, 2.0 * (GLfloat) w / (GLfloat) h, -2.0, 2.0, -10.0, 10.0); glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW); } void main(int argc, char **argv) { glutInit(&argc, argv); /* need both double buffering and z buffer */ glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_DOUBLE | GLUT_RGB | GLUT_DEPTH); glutInitWindowSize(500, 500); glutCreateWindow("Rotating a Color Cube"); glutReshapeFunc(myReshape); glutDisplayFunc(display); glutIdleFunc(spinCube); glutMouseFunc(mouse); glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST); /* Enable hidden--surface--removal */ glutMainLoop(); }
Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga.
10
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
4. Program to create a house like figure and rotate it about a given fixed point using OpenGL functions. // Progam to draw a house and rotate about the pivot point #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> #include <GL/glut.h> GLfloat house[3][9]={{100.0,100.0,175.0,250.0,250.0,150.0,150.0,200.0,200.0}, {100.0,300.0,400.0,300.0,100.0,100.0,150.0,150.0,100.0}, {1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0}}; GLfloat rot_mat[3][3]={{0},{0},{0}}; GLfloat result[3][9]={{0}, {0}, {0}}; GLfloat h=100.0; // Pivot point GLfloat k=100.0; GLfloat theta; void multiply() { // Rotation MATRIX and Object Matrix => Resultant Transformed House int i,j,l; for(i=0;i<3;i++) for(j=0;j<9;j++) { result[i][j]=0; for(l=0;l<3;l++) result[i][j]=result[i][j]+rot_mat[i][l]*house[l][j]; } } void rotate() { GLfloat m,n; // Build the rotation matrix m=-h*(cos(theta)-1)+k*(sin(theta)); n=-k*(cos(theta)-1)-h*(sin(theta)); rot_mat[0][0]=cos(theta); rot_mat[0][1]=-sin(theta); rot_mat[0][2]=m; rot_mat[1][0]=sin(theta); rot_mat[1][1]=cos(theta); rot_mat[1][2]=n; rot_mat[2][0]=0; rot_mat[2][1]=0; rot_mat[2][2]=1; //multiply the two matrices: Rotation Matrix * Objet Matrix(house) multiply(); }
void drawhouse() { glColor3f(0.0, 0.0, 1.0); Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga. 11
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
glBegin(GL_LINE_LOOP); glVertex2f(house[0][0],house[1][0]); glVertex2f(house[0][1],house[1][1]); glVertex2f(house[0][3],house[1][3]); glVertex2f(house[0][4],house[1][4]); glEnd(); glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); glBegin(GL_LINE_LOOP); glVertex2f(house[0][5],house[1][5]); glVertex2f(house[0][6],house[1][6]); glVertex2f(house[0][7],house[1][7]); glVertex2f(house[0][8],house[1][8]); glEnd(); glColor3f(0.0, 0.0, 1.0); glBegin(GL_LINE_LOOP); glVertex2f(house[0][1],house[1][1]); glVertex2f(house[0][2],house[1][2]); glVertex2f(house[0][3],house[1][3]); glEnd(); }
void drawrotatedhouse() { glColor3f(0.0, 0.0, 1.0); glBegin(GL_LINE_LOOP); glVertex2f(result[0][0],result[1][0]); glVertex2f(result[0][1],result[1][1]); glVertex2f(result[0][3],result[1][3]); glVertex2f(result[0][4],result[1][4]); glEnd(); glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); glBegin(GL_LINE_LOOP); glVertex2f(result[0][5],result[1][5]); glVertex2f(result[0][6],result[1][6]); glVertex2f(result[0][7],result[1][7]); glVertex2f(result[0][8],result[1][8]); glEnd(); glColor3f(0.0, 0.0, 1.0); glBegin(GL_LINE_LOOP); glVertex2f(result[0][1],result[1][1]); glVertex2f(result[0][2],result[1][2]); glVertex2f(result[0][3],result[1][3]); glEnd(); } void display() { Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga. 12
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); drawhouse(); rotate(); drawrotatedhouse(); glFlush(); } void myinit() { glClearColor(1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0); glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); glPointSize(1.0); glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION); glLoadIdentity(); gluOrtho2D(0.0,499.0,0.0,499.0); } void main(int argc, char** argv) { printf("Enter the rotation angle\n"); scanf("%f", &theta); glutInit(&argc,argv); glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE|GLUT_RGB); glutInitWindowSize(500,500); glutInitWindowPosition(0,0); glutCreateWindow("house rotation"); glutDisplayFunc(display); myinit(); glutMainLoop(); }
Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga.
13
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
5.Program to implement the Cohen-Sutherland line-clipping algorithm.Make provision to specify the input line, window for clipping and viewport for displaying the clipped image. // Cohen-Suderland Line Clipping Algorithm with Window to viewport Mapping */ #include <stdio.h> #include <GL/glut.h> #define outcode int double xmin=50,ymin=50, xmax=100,ymax=100; // Window boundaries double xvmin=200,yvmin=200,xvmax=300,yvmax=300; // Viewport boundaries //bit codes for the right, left, top, & bottom const int RIGHT = 8; const int LEFT = 2; const int TOP = 4; const int BOTTOM = 1; //used to compute bit codes of a point outcode ComputeOutCode (double x, double y); //Cohen-Sutherland clipping algorithm clips a line from //P0 = (x0, y0) to P1 = (x1, y1) against a rectangle with //diagonal from (xmin, ymin) to (xmax, ymax). void CohenSutherlandLineClipAndDraw (double x0, double y0,double x1, double y1) { //Outcodes for P0, P1, and whatever point lies outside the clip rectangle outcode outcode0, outcode1, outcodeOut; bool accept = false, done = false; //compute outcodes outcode0 = ComputeOutCode (x0, y0); outcode1 = ComputeOutCode (x1, y1); do{ if (!(outcode0 | outcode1)) //logical or is 0 Trivially accept & exit { accept = true; done = true; } else if (outcode0 & outcode1) //logical and is not 0. Trivially reject and exit done = true; else { //failed both tests, so calculate the line segment to clip //from an outside point to an intersection with clip edge double x, y; //At least one endpoint is outside the clip rectangle; pick it. outcodeOut = outcode0? outcode0: outcode1; //Now find the intersection point; //use formulas y = y0 + slope * (x - x0), x = x0 + (1/slope)* (y - y0) Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga. 14
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
if (outcodeOut & TOP) //point is above the clip rectangle { x = x0 + (x1 - x0) * (ymax - y0)/(y1 - y0); y = ymax; } else if (outcodeOut & BOTTOM) //point is below the clip rectangle { x = x0 + (x1 - x0) * (ymin - y0)/(y1 - y0); y = ymin; } else if (outcodeOut & RIGHT) //point is to the right of clip rectangle { y = y0 + (y1 - y0) * (xmax - x0)/(x1 - x0); x = xmax; } else //point is to the left of clip rectangle { y = y0 + (y1 - y0) * (xmin - x0)/(x1 - x0); x = xmin; } //Now we move outside point to intersection point to clip //and get ready for next pass. if (outcodeOut == outcode0) { x0 = x; y0 = y; outcode0 = ComputeOutCode (x0, y0); } else { x1 = x; y1 = y; outcode1 = ComputeOutCode (x1, y1); } } }while (!done); if (accept) { // Window to viewport mappings double sx=(xvmax-xvmin)/(xmax-xmin); // Scale parameters double sy=(yvmax-yvmin)/(ymax-ymin); double vx0=xvmin+(x0-xmin)*sx; double vy0=yvmin+(y0-ymin)*sy; double vx1=xvmin+(x1-xmin)*sx; double vy1=yvmin+(y1-ymin)*sy; //draw a red colored viewport glColor3f(1.0, 0.0, 0.0); glBegin(GL_LINE_LOOP); glVertex2f(xvmin, yvmin); glVertex2f(xvmax, yvmin); glVertex2f(xvmax, yvmax); Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga. 15
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
glVertex2f(xvmin, yvmax); glEnd(); glColor3f(0.0,0.0,1.0); // draw blue colored clipped line glBegin(GL_LINES); glVertex2d (vx0, vy0); glVertex2d (vx1, vy1); glEnd(); } } //Compute the bit code for a point (x, y) using the clip rectangle //bounded diagonally by (xmin, ymin), and (xmax, ymax) outcode ComputeOutCode (double x, double y) { outcode code = 0; if (y > ymax) //above the clip window code |= TOP; else if (y < ymin) //below the clip window code |= BOTTOM; if (x > xmax) //to the right of clip window code |= RIGHT; else if (x < xmin) //to the left of clip window code |= LEFT; return code; } void display() { double x0=60,y0=20,x1=80,y1=120; glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); //draw the line with red color glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); //bres(120,20,340,250); glBegin(GL_LINES); glVertex2d (x0, y0); glVertex2d (x1, y1); glEnd(); //draw a blue colored window glColor3f(0.0, 0.0, 1.0); glBegin(GL_LINE_LOOP); glVertex2f(xmin, ymin); glVertex2f(xmax, ymin); glVertex2f(xmax, ymax); glVertex2f(xmin, ymax); glEnd(); CohenSutherlandLineClipAndDraw(x0,y0,x1,y1); glFlush(); } Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga. 16
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
void myinit() { glClearColor(1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0); glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); glPointSize(1.0); glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION); glLoadIdentity(); gluOrtho2D(0.0,499.0,0.0,499.0); } void main(int argc, char** argv) { //int x1, x2, y1, y2; //printf("Enter End points:"); //scanf("%d%d%d%d", &x1,&x2,&y1,&y2); glutInit(&argc,argv); glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE|GLUT_RGB); glutInitWindowSize(500,500); glutInitWindowPosition(0,0); glutCreateWindow("Cohen Suderland Line Clipping Algorithm"); glutDisplayFunc(display); myinit(); glutMainLoop(); }
Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga.
17
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
6.Program to create a cylinder and a parallelepiped by extruding a circle and quadrilateral respectively. Allow the user to specify the circle and the quadrilateral. //Cylinder and Parallelepiped by extruding Circle and Quadrilateral //cyl_pp_vtu.cpp #include <GL/glut.h> #include <math.h> #include <stdio.h> void draw_pixel(GLint cx, GLint cy) { glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); glBegin(GL_POINTS); glVertex2i(cx,cy); glEnd(); } void plotpixels(GLint h, GLint k, GLint x, GLint y) { draw_pixel(x+h,y+k); draw_pixel(-x+h,y+k); draw_pixel(x+h,-y+k); draw_pixel(-x+h,-y+k); draw_pixel(y+h,x+k); draw_pixel(-y+h,x+k); draw_pixel(y+h,-x+k); draw_pixel(-y+h,-x+k); } void Circle_draw(GLint h, GLint k, GLint r) // Midpoint Circle Drawing Algorithm { GLint d = 1-r, x=0, y=r; while(y > x) { plotpixels(h,k,x,y); if(d < 0) d+=2*x+3; else {d+=2*(x-y)+5; --y; } ++x; } plotpixels(h,k,x,y); } void Cylinder_draw() { GLint xc=100, yc=100, r=50; GLint i,n=50; for(i=0;i<n;i+=3) { Circle_draw(xc,yc+i,r); } } Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga. 18
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
void parallelepiped(int x1, int x2,int y1, int y2, int y3, int y4) { glColor3f(0.0, 0.0, 1.0); glPointSize(2.0); glBegin(GL_LINE_LOOP); glVertex2i(x1,y1); glVertex2i(x2,y3); glVertex2i(x2,y4); glVertex2i(x1,y2); glEnd(); } void parallelepiped_draw() { int x1=200,x2=300,y1=100,y2=175,y3=100,y4=175; GLint i,n=40; for(i=0;i<n;i+=2) { parallelepiped(x1+i,x2+i,y1+i,y2+i,y3+i,y4+i); } } void init(void) { glClearColor(1.0,1.0,1.0,0.0); // Set display window color to white glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION); // Set Projection parameters gluOrtho2D(0.0,400.0,0.0,300.0); } void display(void) { glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); // Clear Display Window glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); // Set circle color to red (R G B) glPointSize(2.0); Cylinder_draw(); // Call cylinder parallelepiped_draw();// call parallelepiped glFlush(); // Process all OpenGL routines as quickly as possible } void main(int argc, char **argv) { glutInit(&argc,argv); // Initialize GLUT glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGB); // Set Display mode glutInitWindowPosition(50,50); // Set top left window position glutInitWindowSize(400,300); // Set Display window width and height glutCreateWindow("Cylinder and parallelePiped Display by Extruding Circle and Quadrilaterl "); // Create Display Window init(); glutDisplayFunc(display); // Send the graphics to Display Window glutMainLoop(); }
Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga.
19
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
7.Program, using OpenGL functions, to draw a simple shaded scene consisting of a tea pot on a table. Define suitably the position and properties of the light source along with the properties of the propertiesof the surfaces of the solid object used in the scene. /* simple shaded scene consisting of a tea pot on a table */ #include <GL/glut.h> void wall (double thickness) { //draw thin wall with top = xz-plane, corner at origin glPushMatrix(); glTranslated (0.5, 0.5 * thickness, 0.5); glScaled (1.0, thickness, 1.0); glutSolidCube (1.0); glPopMatrix(); } //draw one table leg void tableLeg (double thick, double len) { glPushMatrix(); glTranslated (0, len/2, 0); glScaled (thick, len, thick); glutSolidCube (1.0); glPopMatrix(); } void table (double topWid, double topThick, double legThick, double legLen) { //draw the table - a top and four legs //draw the top first glPushMatrix(); glTranslated (0, legLen, 0); glScaled(topWid, topThick, topWid); glutSolidCube (1.0); glPopMatrix(); double dist = 0.95 * topWid/2.0 - legThick/2.0; glPushMatrix(); glTranslated (dist, 0, dist); tableLeg (legThick, legLen); glTranslated (0.0, 0.0, -2 * dist); tableLeg (legThick, legLen); glTranslated (-2*dist, 0, 2 *dist); tableLeg (legThick, legLen); glTranslated(0, 0, -2*dist); tableLeg (legThick, legLen); glPopMatrix(); Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga. 20
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
} void displaySolid (void) { //set properties of the surface material GLfloat mat_ambient[] = {0.7f, 0.7f, 0.7f, 1.0f}; // gray GLfloat mat_diffuse[] = {.5f, .5f, .5f, 1.0f}; GLfloat mat_specular[] = {1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f}; GLfloat mat_shininess[] = {50.0f}; glMaterialfv (GL_FRONT, GL_AMBIENT, mat_ambient); glMaterialfv (GL_FRONT, GL_DIFFUSE, mat_diffuse); glMaterialfv (GL_FRONT, GL_SPECULAR, mat_specular); glMaterialfv (GL_FRONT, GL_SHININESS, mat_shininess); //set the light source properties GLfloat lightIntensity[] = {0.7f, 0.7f, 0.7f, 1.0f}; GLfloat light_position[] = {2.0f, 6.0f, 3.0f, 0.0f}; glLightfv (GL_LIGHT0, GL_POSITION, light_position); glLightfv (GL_LIGHT0, GL_DIFFUSE, lightIntensity); //set the camera glMatrixMode (GL_PROJECTION); glLoadIdentity(); double winHt = 1.0; //half-height of window glOrtho (-winHt * 64/48.0, winHt*64/48.0, -winHt, winHt, 0.1, 100.0); glMatrixMode (GL_MODELVIEW); glLoadIdentity(); gluLookAt (2.3, 1.3, 2.0, 0.0, 0.25, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0); //start drawing glClear (GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); glPushMatrix(); glTranslated (0.4, 0.4, 0.6); glRotated (45, 0, 0, 1); glScaled (0.08, 0.08, 0.08); glPopMatrix(); glPushMatrix(); glTranslated (0.6, 0.38, 0.5); glRotated (30, 0, 1, 0); glutSolidTeapot (0.08); glPopMatrix (); glPushMatrix(); glTranslated (0.25, 0.42, 0.35); //glutSolidSphere (0.1, 15, 15); glPopMatrix(); glPushMatrix(); glTranslated (0.4, 0, 0.4); table (0.6, 0.02, 0.02, 0.3); glPopMatrix(); Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga. 21
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
wall (0.02); glPushMatrix(); glRotated (90.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); wall (0.02); glPopMatrix(); glPushMatrix(); glRotated (-90.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0); wall (0.02); glPopMatrix(); glFlush(); } void main (int argc, char ** argv) { glutInit (&argc, argv); glutInitDisplayMode (GLUT_SINGLE|GLUT_RGB|GLUT_DEPTH); glutInitWindowSize (640, 480); glutInitWindowPosition (100, 100); glutCreateWindow ("simple shaded scene consisting of a tea pot on a table"); glutDisplayFunc (displaySolid); glEnable (GL_LIGHTING); glEnable (GL_LIGHT0); glShadeModel (GL_SMOOTH); glEnable (GL_DEPTH_TEST); glEnable (GL_NORMALIZE); glClearColor (0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.0); glViewport (0, 0, 640, 480); glutMainLoop(); }
Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga.
22
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
8. Program to draw a color cube and allow the user to move the camera suitably to experiment with perspective viewing. Use OpenGL functions. /* Rotating cube with viewer movement */ /* We use the Lookat function in the display callback to point the viewer, whose position can be altered by the x,X,y,Y,z, and Z keys. The perspective view is set in the reshape callback */ #include <stdlib.h> #include <GL/glut.h> GLfloat vertices[][3] = {{-1.0,-1.0,-1.0},{1.0,-1.0,-1.0}, {1.0,1.0,-1.0}, {-1.0,1.0,-1.0}, {-1.0,-1.0,1.0}, {1.0,-1.0,1.0}, {1.0,1.0,1.0}, {-1.0,1.0,1.0}}; GLfloat normals[][3] = {{-1.0,-1.0,-1.0},{1.0,-1.0,-1.0}, {1.0,1.0,-1.0}, {-1.0,1.0,-1.0}, {-1.0,-1.0,1.0}, {1.0,-1.0,1.0}, {1.0,1.0,1.0}, {-1.0,1.0,1.0}}; GLfloat colors[][3] = {{0.0,0.0,0.0},{1.0,0.0,0.0}, {1.0,1.0,0.0}, {0.0,1.0,0.0}, {0.0,0.0,1.0}, {1.0,0.0,1.0}, {1.0,1.0,1.0}, {0.0,1.0,1.0}}; void polygon(int a, int b, int c , int d) { glBegin(GL_POLYGON); glColor3fv(colors[a]); glNormal3fv(normals[a]); glVertex3fv(vertices[a]); glColor3fv(colors[b]); glNormal3fv(normals[b]); glVertex3fv(vertices[b]); glColor3fv(colors[c]); glNormal3fv(normals[c]); glVertex3fv(vertices[c]); glColor3fv(colors[d]); glNormal3fv(normals[d]); glVertex3fv(vertices[d]); glEnd(); }
void colorcube() { polygon(0,3,2,1); polygon(2,3,7,6); polygon(0,4,7,3); polygon(1,2,6,5); Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga. 23
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
polygon(4,5,6,7); polygon(0,1,5,4); } static GLfloat theta[] = {0.0,0.0,0.0}; static GLint axis = 2; static GLdouble viewer[]= {0.0, 0.0, 5.0}; /* initial viewer location */ void display(void) { glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); /* Update viewer position in modelview matrix */ glLoadIdentity(); gluLookAt(viewer[0],viewer[1],viewer[2], 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0); /* rotate cube */ glRotatef(theta[0], 1.0, 0.0, 0.0); glRotatef(theta[1], 0.0, 1.0, 0.0); glRotatef(theta[2], 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); colorcube(); glFlush(); glutSwapBuffers(); } void mouse(int btn, int state, int x, int y) { if(btn==GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON && state == GLUT_DOWN) axis = 0; if(btn==GLUT_MIDDLE_BUTTON && state == GLUT_DOWN) axis = 1; if(btn==GLUT_RIGHT_BUTTON && state == GLUT_DOWN) axis = 2; theta[axis] += 2.0; if( theta[axis] > 360.0 ) theta[axis] -= 360.0; display(); } void keys(unsigned char key, int x, int y) { /* Use x, X, y, Y, z, and Z keys to move viewer */ if(key == 'x') viewer[0]-= 1.0; if(key == 'X') viewer[0]+= 1.0; if(key == 'y') viewer[1]-= 1.0; if(key == 'Y') viewer[1]+= 1.0; if(key == 'z') viewer[2]-= 1.0; if(key == 'Z') viewer[2]+= 1.0; display(); Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga. 24
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
} void myReshape(int w, int h) { glViewport(0, 0, w, h); /* Use a perspective view */ glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION); glLoadIdentity(); if(w<=h) glFrustum(-2.0, 2.0, -2.0 * (GLfloat) h/ (GLfloat) w, 2.0* (GLfloat) h / (GLfloat) w, 2.0, 20.0); else glFrustum(-2.0, 2.0, -2.0 * (GLfloat) w/ (GLfloat) h, 2.0* (GLfloat) w / (GLfloat) h, 2.0, 20.0); /* Or we can use gluPerspective */ /* gluPerspective(45.0, w/h, -10.0, 10.0); */ glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW); } void main(int argc, char **argv) { glutInit(&argc, argv); glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_DOUBLE | GLUT_RGB | GLUT_DEPTH); glutInitWindowSize(500, 500); glutCreateWindow("Colorcube Viewer"); glutReshapeFunc(myReshape); glutDisplayFunc(display); glutMouseFunc(mouse); glutKeyboardFunc(keys); glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST); glutMainLoop(); }
Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga.
25
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
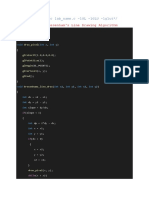
9. Program to fill any given polygon using scan-line area filling algorithm.(Use appropriate data structures.) // Scan-Line algorithm for filling a polygon #define BLACK 0 #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <GL/glut.h> float x1,x2,x3,x4,y1,y2,y3,y4; void edgedetect(float x1,float y1,float x2,float y2,int *le,int *re) { float mx,x,temp; int i; if((y2-y1)<0) { temp=y1;y1=y2;y2=temp; temp=x1;x1=x2;x2=temp; } if((y2-y1)!=0) mx=(x2-x1)/(y2-y1); else mx=x2-x1; x=x1; for(i=y1;i<=y2;i++) { if(x<(float)le[i]) le[i]=(int)x; if(x>(float)re[i]) re[i]=(int)x; x+=mx; } } void draw_pixel(int x,int y,int value) { glColor3f(1.0,1.0,0.0); glBegin(GL_POINTS); glVertex2i(x,y); glEnd(); } void scanfill(float x1,float y1,float x2,float y2,float x3,float y3,float x4,float y4) { int le[500],re[500]; int i,y; for(i=0;i<500;i++) { le[i]=500; re[i]=0; } edgedetect(x1,y1,x2,y2,le,re); edgedetect(x2,y2,x3,y3,le,re); edgedetect(x3,y3,x4,y4,le,re); edgedetect(x4,y4,x1,y1,le,re); Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga. 26
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
for(y=0;y<500;y++) { if(le[y]<=re[y]) for(i=(int)le[y];i<(int)re[y];i++) draw_pixel(i,y,BLACK); } } void display() { x1=200.0;y1=200.0;x2=100.0;y2=300.0;x3=200.0;y3=400.0;x4=300.0;y4=300.0; glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); glColor3f(0.0, 0.0, 1.0); glBegin(GL_LINE_LOOP); glVertex2f(x1,y1); glVertex2f(x2,y2); glVertex2f(x3,y3); glVertex2f(x4,y4); glEnd(); scanfill(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4); glFlush(); } void myinit() { glClearColor(1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0); glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); glPointSize(1.0); glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION); glLoadIdentity(); gluOrtho2D(0.0,499.0,0.0,499.0); }
void main(int argc, char** argv) { glutInit(&argc,argv); glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE|GLUT_RGB); glutInitWindowSize(500,500); glutInitWindowPosition(0,0); glutCreateWindow("Filling a Polygon using Scan-line Algorithm"); glutDisplayFunc(display); myinit(); glutMainLoop(); }
Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga.
27
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
10. Program to display a set of values { fij } as a rectangular mesh. // rect_mesh_vtu.cpp // Rectangular Mesh using set of points f(i,j)=f(xi,yi) where xi=x0+i*dx, yi=y0+j*dy #include <stdlib.h> // standard definitions #include <GL/glut.h> // GLUT #define maxx 20 #define maxy 25 #define dx 15 #define dy 10 GLfloat x[maxx]={0.0},y[maxy]={0.0}; GLfloat x0=50,y0=50; // initial values for x, y GLint i,j; void init() { glClearColor(1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0); glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); glPointSize(5.0); glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION); glLoadIdentity(); gluOrtho2D(0.0,499.0,0.0,499.0); glutPostRedisplay(); // request redisplay } void display(void) { /* clear window */ glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); glColor3f(0.0, 0.0, 1.0); // set color to blue /* draw rectangles */ for(i=0;i<maxx;i++) x[i]=x0+i*dx; // compute x[i] for(j=0;j<maxy;j++) y[j]=y0+j*dy; // compute y[i] glColor3f(0.0, 0.0, 1.0); for(i=0;i<maxx-1;i++) for(j=0;j<maxy-1;j++) { glColor3f(0.0, 0.0, 1.0); glBegin(GL_LINE_LOOP); glVertex2f(x[i],y[j]); glVertex2f(x[i],y[j+1]); glVertex2f(x[i+1],y[j+1]); glVertex2f(x[i+1],y[j]); glEnd(); glFlush(); } glFlush(); Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga. 28
COMPUTER GRAPHICS &VISULIZATION LAB
} void main(int argc, char** argv) { glutInit(&argc, argv); // OpenGL initializations glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGB);// single buffering and RGB glutInitWindowSize(500, 400); // create a 500x400 window glutInitWindowPosition(0, 0); // ...in the upper left glutCreateWindow("Rectangular Mesh"); // create the window glutDisplayFunc(display); // setup callbacks init(); glutMainLoop(); // start it running }
PART B Develop a suitable Graphics package to implement the skills learnt in the theory and the exercises indicated in Part A. Use the OpenGL.
Dept. of CSE., JNNCE, Shimoga.
29
You might also like
- CG & V LabmanualDocument44 pagesCG & V Labmanualsri kbsNo ratings yet
- CG Lab Programs Using Opengl: #Include VoidDocument32 pagesCG Lab Programs Using Opengl: #Include Voidsundaravanan_rmNo ratings yet
- 01 3D GasketDocument3 pages01 3D Gasketprani123No ratings yet
- Implement Brenham's Line Drawing Algorithm For All Types of SlopeDocument24 pagesImplement Brenham's Line Drawing Algorithm For All Types of SlopeSuhas.RNo ratings yet
- Program1:Implement Brenham's Line Drawing Algorithm For All Types of SlopeDocument33 pagesProgram1:Implement Brenham's Line Drawing Algorithm For All Types of SlopeSwapnapriyaNo ratings yet
- Tinywow - Computer Graphics Experiments (2) - 41880454Document77 pagesTinywow - Computer Graphics Experiments (2) - 41880454xedewej976No ratings yet
- Lab04 - Nguyen Đuc Hoai Vu - 102220048Document9 pagesLab04 - Nguyen Đuc Hoai Vu - 102220048Vũ HoàiNo ratings yet
- CG Lab PDFDocument8 pagesCG Lab PDFhementh bvNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics ManualDocument54 pagesComputer Graphics ManualKarthik BhargavNo ratings yet
- Cgmannual2018 ContentDocument24 pagesCgmannual2018 ContentFunZoa LifeNo ratings yet
- CG Lab ManualDocument25 pagesCG Lab ManualMisba nausheenNo ratings yet
- Program To Recursively Subdivide A Tetrahedron To Form 3D Serpinsky Gasket - The Number of Recursive Steps Is To Be Specified by The UserDocument29 pagesProgram To Recursively Subdivide A Tetrahedron To Form 3D Serpinsky Gasket - The Number of Recursive Steps Is To Be Specified by The Userani2011No ratings yet
- CG Lab ProgramsDocument17 pagesCG Lab ProgramsNigarNo ratings yet
- CG Lab ProgramsDocument17 pagesCG Lab ProgramsNigarNo ratings yet
- Program 1: AIM:Implement Brenham's Line Drawing Algorithm For All Types of SlopeDocument26 pagesProgram 1: AIM:Implement Brenham's Line Drawing Algorithm For All Types of SlopeAasim InamdarNo ratings yet
- Cbcs CG Manual 15csl68-1Document25 pagesCbcs CG Manual 15csl68-1TECH WORLDNo ratings yet
- 7Document2 pages7Nithin SSNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document5 pagesDocument 1fyfyNo ratings yet
- Cube RotationDocument3 pagesCube RotationPramoda SNo ratings yet
- Cube RotationDocument3 pagesCube RotationHittu PrasadNo ratings yet
- Mimansa Pathania, CG Lab File, 500091628Document26 pagesMimansa Pathania, CG Lab File, 500091628Divyansh SinghNo ratings yet
- Prak Grafika Komputer Minggu 10Document12 pagesPrak Grafika Komputer Minggu 10Shabrinaa InaasNo ratings yet
- Mimansa Pathania, CG Lab File, 500091628-2Document25 pagesMimansa Pathania, CG Lab File, 500091628-2Divyansh SinghNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology Silchar Cachar, AssamDocument9 pagesNational Institute of Technology Silchar Cachar, AssamCSE-B-140 Deepak KumarNo ratings yet
- CG Manual PDFDocument33 pagesCG Manual PDFJaina H ShahNo ratings yet
- Fractal Tree ProjectDocument12 pagesFractal Tree ProjectJaid Mulla UTNo ratings yet
- All CG ProgramsDocument45 pagesAll CG Programsharipriya.888mNo ratings yet
- Gedung 3dimensi Visual StudioDocument13 pagesGedung 3dimensi Visual StudioshellaNo ratings yet
- CG RemovedDocument29 pagesCG RemovedabhishekNo ratings yet
- Program 1:-Implement Bresenham's Line Drawing Algorithm For All Types of SlopeDocument25 pagesProgram 1:-Implement Bresenham's Line Drawing Algorithm For All Types of SlopeRV YashvanthNo ratings yet
- Message 2Document4 pagesMessage 2RonaldinhoNo ratings yet
- CG Lab Report Must Edit The StyleDocument50 pagesCG Lab Report Must Edit The StyleHasanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- A) Program To Implement A FLYING KITEDocument36 pagesA) Program To Implement A FLYING KITEAnusha YenadkaNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument15 pagesNew Text DocumentTeja Sai Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- CarDocument3 pagesCarNitin TupsamudreNo ratings yet
- Coding Visual StudioDocument14 pagesCoding Visual Studiogilbert danielNo ratings yet
- CGV Lab ManualDocument28 pagesCGV Lab Manualrenuka_ec694456No ratings yet
- #Include #Include #Include #Include #IncludeDocument12 pages#Include #Include #Include #Include #IncludeJaina H ShahNo ratings yet
- LAB7Document2 pagesLAB7Kishonandan MvNo ratings yet
- Program NoDocument59 pagesProgram NoKp KayumNo ratings yet
- Prak Grafika Komputer Minggu 11Document17 pagesPrak Grafika Komputer Minggu 11Shabrinaa InaasNo ratings yet
- Note 75202235034 PMDocument13 pagesNote 75202235034 PMchowdri gowdaNo ratings yet
- Link ClickDocument36 pagesLink Clickxiso2507No ratings yet
- program 1 - Bresenham's Line Drawing Algorithm: / To Compile GCC Lab - Name.c - LGL - lGLU - LglutDocument30 pagesprogram 1 - Bresenham's Line Drawing Algorithm: / To Compile GCC Lab - Name.c - LGL - lGLU - LglutGlenvin Anil RosarioNo ratings yet
- Lab4 CDocument4 pagesLab4 CArif AhmedNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Course Code: 422 Course Title: Computer Graphics LabDocument6 pagesAssignment: Course Code: 422 Course Title: Computer Graphics LabTayaba RahamanNo ratings yet
- Olympics Logo Animation: Submitted By: Submitted ToDocument15 pagesOlympics Logo Animation: Submitted By: Submitted ToPraneet KumarNo ratings yet
- CG Lab P7Document3 pagesCG Lab P7Pavan KulkarniNo ratings yet
- CGV Lab ManualDocument30 pagesCGV Lab ManualJagath JNo ratings yet
- CG Lab ReportDocument167 pagesCG Lab ReportAyesha shirurNo ratings yet
- Lab Program - 1: Implement Bresenham's Line Drawing Algorithm For All Types of SlopeDocument25 pagesLab Program - 1: Implement Bresenham's Line Drawing Algorithm For All Types of SlopepavanNo ratings yet
- Program To Recursively Subdivide A Tetrahedron To From 3D Sierpinski Gasket - The Number of Recursive Steps Is To Be Specified by The UserDocument3 pagesProgram To Recursively Subdivide A Tetrahedron To From 3D Sierpinski Gasket - The Number of Recursive Steps Is To Be Specified by The UserDhyan MohanNo ratings yet
- Program To Generate A Line Using DDA AlgorithmDocument56 pagesProgram To Generate A Line Using DDA Algorithmpoonam64No ratings yet
- B Spline C ImplementationDocument24 pagesB Spline C ImplementationSnehalNo ratings yet
- Gerin Bagaslino - 52417512Document13 pagesGerin Bagaslino - 52417512Gerin BagaslinoNo ratings yet
- Code To Animate A 2D Helicopter GameDocument6 pagesCode To Animate A 2D Helicopter GameAmisha KhirariNo ratings yet
- Prak Grafika Komputer Minggu 4Document6 pagesPrak Grafika Komputer Minggu 4Shabrinaa InaasNo ratings yet
- CG Lab P2Document4 pagesCG Lab P2MartinNo ratings yet
- Mod4 SBDocument81 pagesMod4 SBsandeepb8No ratings yet
- 2nd IADocument1 page2nd IAsandeepb8No ratings yet
- Deep Learning With Pytorch: Neural Style TransferDocument1 pageDeep Learning With Pytorch: Neural Style Transfersandeepb8No ratings yet
- Mod3 SBDocument124 pagesMod3 SBsandeepb8No ratings yet
- 82c55 NewDocument27 pages82c55 Newsandeepb8No ratings yet
- Lor Abhay K PDocument1 pageLor Abhay K Psandeepb8No ratings yet
- Single Image Super Resolution in Spatial and Wavelet DomainDocument10 pagesSingle Image Super Resolution in Spatial and Wavelet DomainIJMAJournalNo ratings yet
- Matlab TutorialDocument173 pagesMatlab TutorialSaurabh Tiwari100% (8)
- Automation Test FrameworksDocument22 pagesAutomation Test Frameworkssandeepb8No ratings yet
- Instructions Option EntryDocument1 pageInstructions Option Entrysandeepb8No ratings yet
- CodeBlocks SimpleCPP ManualDocument59 pagesCodeBlocks SimpleCPP Manualsandeepb8No ratings yet
- RESUME Software Testing ResumeDocument2 pagesRESUME Software Testing ResumeIpsita Panda100% (1)
- The Master of Science in Engineering by ResearchDocument4 pagesThe Master of Science in Engineering by Researchsandeepb8No ratings yet
- Gate 2012 BrochureDocument16 pagesGate 2012 BrochureShantanu ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- 6th Sem CG ManualDocument74 pages6th Sem CG Manualfathima parveenNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.-3 Aim: To Draw A Line, Triangle and Circle Using Functions of Graphics.h Header File. DescriptionDocument51 pagesExperiment No.-3 Aim: To Draw A Line, Triangle and Circle Using Functions of Graphics.h Header File. DescriptionCSENo ratings yet
- Lab Manual CGMT - 5CS4 - 21 - 1 - 11 - 2022Document75 pagesLab Manual CGMT - 5CS4 - 21 - 1 - 11 - 2022VEDANT KALIANo ratings yet
- Raj Kumar Goel Institute of Technology, Ghaziabad: Topics To Be CoveredDocument6 pagesRaj Kumar Goel Institute of Technology, Ghaziabad: Topics To Be CoveredSubhash GuptaNo ratings yet
- VB CG Pue2 2021 (Aka)Document2 pagesVB CG Pue2 2021 (Aka)Atul PanwarNo ratings yet
- A New, Fast Method For 2D Polygon Clipping: Analysis and Software ImplementationDocument14 pagesA New, Fast Method For 2D Polygon Clipping: Analysis and Software ImplementationSpeed Resolve TCGNo ratings yet
- Name: Pranav G Dasgaonkar Roll No: 70 CLASS: 8 (CMPN-2) CG Experiment No: 10Document16 pagesName: Pranav G Dasgaonkar Roll No: 70 CLASS: 8 (CMPN-2) CG Experiment No: 10shubham chutkeNo ratings yet
- NewSyllabus 2246202071054981Document6 pagesNewSyllabus 2246202071054981Gavi AhujaNo ratings yet
- CG Lab Manual 2022-2023Document33 pagesCG Lab Manual 2022-2023Shubham AudattapureNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics Question BankDocument9 pagesComputer Graphics Question BankNagunuri SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Liang Barsky Line Clipping AlgorithmDocument2 pagesLiang Barsky Line Clipping AlgorithmPoojaRRaneNo ratings yet
- Point Clipping Algorithm in Computer Graphics: Week 15Document6 pagesPoint Clipping Algorithm in Computer Graphics: Week 15Sarah FarooqiNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics & MultimediaDocument9 pagesComputer Graphics & MultimediaMathan NaganNo ratings yet
- Cohen Sutherland Line ClippingDocument4 pagesCohen Sutherland Line ClippingAditya SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2D Viewing and ClippingDocument79 pages2D Viewing and Clippingkjindal1221No ratings yet
- Computer Graphics Lab ManualDocument11 pagesComputer Graphics Lab ManualMisbah ArshadNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics (CSE 4103)Document34 pagesComputer Graphics (CSE 4103)Atik Israk LemonNo ratings yet
- Home Computer Fundamentals Computer Graphics Biometrics Computer Network Java HTML CSSDocument16 pagesHome Computer Fundamentals Computer Graphics Biometrics Computer Network Java HTML CSSARUN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Problem Cohen Sutherland Line ClippingDocument1 pageProblem Cohen Sutherland Line ClippinganyrhingNo ratings yet
- CG (Line Clipping: Cohen Sutherland Line Clipping) : BITS PilaniDocument14 pagesCG (Line Clipping: Cohen Sutherland Line Clipping) : BITS PilaniYash GuptaNo ratings yet
- CG Second Sessional PaperDocument2 pagesCG Second Sessional PaperNaresh BadveNo ratings yet
- Computer GraphicsDocument2 pagesComputer Graphicsliza50% (2)
- Sample - CG - MCQ - Unit 2Document56 pagesSample - CG - MCQ - Unit 2Animan XanderNo ratings yet
- Cohen Sutherland AlgorithmDocument28 pagesCohen Sutherland AlgorithmshubhangiNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics All MCQDocument58 pagesComputer Graphics All MCQMatiko DesalegnNo ratings yet
- 08 Clipping Cad CamDocument59 pages08 Clipping Cad CamAmit YadavNo ratings yet
- Practical-1: Aim:-Write A Program To Implement DDA Line Drawing Algorithm. AlgorithmDocument37 pagesPractical-1: Aim:-Write A Program To Implement DDA Line Drawing Algorithm. AlgorithmDrishti GuptaNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics and Multimedia: Presentation On: Cohen-Sutherland Line Clipping AlgorithmDocument17 pagesComputer Graphics and Multimedia: Presentation On: Cohen-Sutherland Line Clipping AlgorithmDeepansh DuggalNo ratings yet
- Segment and Window ClippingDocument51 pagesSegment and Window ClippingYogita GhumareNo ratings yet
- Liang-Barsky Line Clipping AlgorithmDocument10 pagesLiang-Barsky Line Clipping Algorithmpankaj manglaNo ratings yet