Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ion Exchange Regeneration Methods
Uploaded by
crespoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ion Exchange Regeneration Methods
Uploaded by
crespoCopyright:
Available Formats
4/16/13
Ion exchange regeneration methods
IX Home
Regeneration methods
for ion exchange units
Introduction
Most ion exchange resins are used in columns. Ion exchange operation is basically discontinuous: a loading phase, called service run, is followed by regeneration of the exhausted resins. There are two main methods for the regeneration process: Co-flow regeneration, where the fluids are flowing from the top to the bottom of the column both during the service run as well as during regeneration. Reverse flow regeneration, where the fluids are flowing alternatively upwards and downwards during service and regeneration. We will also give information about regenerant quantities (regeneration ratio), thoroughfare regeneration, and regenerant types and concentrations. See also the page about capacity.
Update 29 Nov 2012
Site map
Search page
Co-flow regeneration (CFR)
This regeneration technique has been used used at the beginning of ion exchange: the solution to treat flows from the top to the bottom of the column, and the regenerant uses the same path. The problem is that strongly acidic and strongly basic resins are not completely converted to the H or OH form at the end of the regeneration, because this would require too large an excess of chemical regenerant. As a result, the bottom layers of the resin bed are more contaminated than the top layers at the end of regeneration, so that when the next loading run begins the leakage is high due to the displacement of the contaminating ions by the H+ (or OH) ions produced in the exchange.
dardel.info/IX/processes/regeneration.html
1/10
4/16/13
Ion exchange regeneration methods
The dark zone in the picture above represents the proportion of exhausted resin, the yellow zone the proportion of regenerated resin. The small picture on the right explains what I mean: for instance, at level A, the resin is 50% exhausted and 50% regenerated. Above the exchange zone, the resin is fully exhausted, and below it is fullly regenerated. With co-flow regeneration, the only way to reduce this permanent leakage is to increase the quantity of regenerant so as to leave less contaminating ions at the outlet of the column.
Reverse flow regeneration (RFR)
This is also called "counterflow regeneraton". In the past, it was called counter-current regeneration, but the term is not strictly correct as the resin bed does not move. With reverse flow regeneration the regenerant is injected in the opposite direction of the service flow. There are two sub-cases: 1. Upflow loading and downflow regeneration, as in the floating bed and AmberpackTM processes. 2. Downflow loading and upflow regeneration, as in the UFDTM and UpcoreTM processes. In this case, the regenerant doesn't have to push the contaminating ions through the whole resin bed. The layers which are less exhausted will be regenerated first and will be the cleanest when the next loading run (exhaustion) starts.
dardel.info/IX/processes/regeneration.html 2/10
4/16/13
Ion exchange regeneration methods
Or with upflow loading:
Reverse flow regeneration offers two significant advantages: 1. The treated water has a much higher purity than with co-flow, due to a very low leakage. 2. Less regenerant is required, as the contaminating ions don't have to be pushed through the whole bed, and the leakage is almost independent of the regenerant dosage.
Treated water quality
dardel.info/IX/processes/regeneration.html 3/10
4/16/13
Ion exchange regeneration methods
At the end of regeneration, the exit layer of the column regenerated in CFR has the highest concentration of impurities, whereas in RFR the exit layer contains the most highly regenerated resin. This is why in CFR the contaminants at the bottom find their way into the treated water, more at the beginning than in the middle of the run, due to a "self regeneration" effect, whereas in RFR any displaced contaminant from the inlet layer gets immediately removed from a layer underneath. The graph shows the typical leakage profile during the loading phase (e.g. conductivity in S/cm but it can be any other leakage depending on the process). The ionic leakage obtained with reverse flow regeneration is usually so low, that it does not depend on the amount of regenerant used. With co-flow, low leakage values are obtained only with high regenerant dosage.
No backwash with RFR
The whole effect of reverse flow regeneration relies on undisturbed resin layers. The resin with the highest degree of regeneration should always be at the column outlet. Therefore, the resin bed should not be backwashed before regeneration, and should not be allowed to fluidise at any time. So either the columns are completely filled with resin (packed beds) or the bed is held down during regeneration. See the "column design" page for the concepts of holddown and packed beds.
dardel.info/IX/processes/regeneration.html 4/10
4/16/13
Ion exchange regeneration methods
Regeneration steps
The general regeneration procedure for ion echange vessels is as follows: 1. Backwash resin bed (co-flow regeneration only) to remove suspended solids and decompact the bed. 2. Inject regenerant diluted in appropriate water quality. The injection is at a low flow rate, so that the contact time is 20 to 40 minutes. 3. Displace the regenerant with dilution water at the same flow rate. 4. Rinse the bed at service flow rate with feed water until the desired treated water quality is obtained. The above is valid for most ion exchange columns, e.g. softening, nitrate removal, de-alkalisation. For demineralisation, the cation column is regenerated first with acid, then the anion column with caustic soda; alternatively, both are regenerated at the same time. The regeneration of a mixed bed unit is more complicated. The steps are: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Backwash resin bed to separate the cation from the anion resin. Let the resins settle. Optionally: drain the water down to the resin bed surface. Inject caustic soda diluted in demineralised water. Displace the caustic with dilution water. Inject acid diluted in demineralised water. Displace the acid with dilution water. Drain the water down to the resin bed surface. Mix the resins with clean compressed air or nitrogen. Refill the unit slowly with water. Do the final rinse with feed water at service flow rate until the desired treated water quality is obtained.
Note: Cation and anion resin can be regenerated simultaneously to save time. Otherwise, always start with the anion resin.
Regeneration ratio
Definition:
dardel.info/IX/processes/regeneration.html 5/10
4/16/13
Ion exchange regeneration methods
Introduction The regeneration ratio or regenerant ratio is calculated as the total amount of regenerant (in equivalents) divided by the total ionic load (also in equivalents) during one cycle. It is is also equal to the number of eq/L regenerant per eq/L of resin operating capacity. A (theoretical) regenerant ratio of 1.00 (i.e. 100 %) would correspond to the stoichiometric quantity. All resins need a certain excess of regenerant above the stoichiometric quantity. Example Amberjet 1000 regenerated with 55 g HCl per litre operating capacity : 1.20 eq/L 55 g/L HCl = 55/36.5 = 1.507 eq/L Regenerant ratio = 1.507/1.20 = 1.26 = 126 % Excess The difference between ionic load and regenerant quantity is called excess regenerant. Excess [in eq]= regenerant [eq] - ionic load [eq] Excess [in %] = 100 x (regenerant ratio 1) Minimum values WAC resins require just above the stoichiometric quantity. A safe number is 105 to 110 %. WBA resins require 115 to 140 %, because most of them they have some strongly basic functional groups. When regenerated with ammonia or sodium carbonate, WBA resins require a regenerant ratio of 150 to 200 %. These regenerants can be used for WBA only, not for SBA resins. SAC and SBA resins require a larger excess than their weak counterparts. Co-flow regenerated SAC and SBA resins require more than those regenerated in reverse flow.
dardel.info/IX/processes/regeneration.html 6/10
4/16/13
Ion exchange regeneration methods
SAC resins regenerated in reverse flow with hydrochloric acid need an absolute minimum of 110 % regeneration, but a safer value is 120 %. If the water contains high hardness or low alkalinity, the minimum value must be increased. SAC resins regenerated with sulphuric acid require a larger excess than those regenerated with HCl. At least 40 % more. For SBA resins, there is no easy way to estimate a minimum, as it depends on the type of SBA resin (styrenic type 1 vs type 2 or acrylic resins). Important note: when calculating the regenerant ratio for SBA resins, one must take 2 equivalents of NaOH for each equivalent of CO2 or SiO2 . WAC/SAC couples can be regenerated with a global ratio of about 105 %. WBA/SBA couples can be regenerated with a global ratio of 110 to 120 %. More is required if the silica level is high in the feed water. The regenerant ratio for silica should be at least 800 %. This should be calculated separately as the quantity of NaOH (in eq) divided by the load of silica (in eq) during one cycle. One equivalent of silica is taken as 60 g as SiO2 .
Thoroughfare regeneration
When a weak and a strong resin are used in series, the following two rules must apply: 1. The feed water must pass first through the weak, then only through the strong resin. 2. The regenerant must pass first through the strong, then through the weak resin.
Separate columns in service Why is it so?
dardel.info/IX/processes/regeneration.html
Separate columns in regeneration
7/10
4/16/13
Ion exchange regeneration methods
1. The weak resin has a high capacity and good regeneration efficiency, but does not remove all ions. Therefore it must be placed first, and the strong resin will be used to remove whatever the weak resin has not removed, albeit with a lower efficiency. 2. The strong resin requires a high excess of regenerant. The weak resin requires almost no excess. Therefore the regenerant passes through the strong resin first, and the weak resin is regenerated with the excess regenerant coming out of the strong resin. The above pictures are for old-fashioned, separate columns with co-flow regeneration. Below the same for an Amberpack double compartment column.
Amberpack in service
Amberpack in regeneration
All the above applies equally to a couple of weak acid and strong acid cation exchange resins.
Regenerant types and concentrations
Types of regenerant
Sodium chloride (NaCl) is normally used to regenerate SAC resins in the softening process, and SBA resins used for nitrate removal. For softening, potassium chloride (KCl) can also be used when the presence of sodium in the treated solution is undesirable. In some hot condensate softening processes, ammonium chloride (NH4 Cl) can be used. For nitrate removal, the SBA resin can be regenerated with other compounds providing chloride ions, such as hydrochloric acid (HCl). For decationisation the first step of a demineralisation process SAC resins must be regenerated with a strong acid. The most common acids are hydrochloric and sulphuric acids.
dardel.info/IX/processes/regeneration.html 8/10
4/16/13
Ion exchange regeneration methods
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is very efficient and does not cause precipitations in the resin bed. Sulphuric acid (H2 SO4 ) is sometimes cheaper and easier to store and to handle in general, but less efficient than hydrochloric acid: the operating capacity of the SAC resin is lower. Additionally, its concentration must be carefully adjusted to prevent calcium sulphate precipitation (see below). Once a CaSO4 precipitate is formed, it is very difficult to remove from the resin bed. Nitric acid (HNO3 ) can also be used in principle, but is not recommended as it can cause exothermic reactions; explosions have been observed in some cases, so that the use of nitric acid is considered dangerous. For dealkalisation, the WAC resin is best regenerated with hydrochloric acid (HCl). When using sulphuric acid, the concentration must be kept under 0.8 % to avoid calcium sulphate precipitation. Other, weaker acids can also regenerate WAC resins, such as acetic acid (CH3 COOH) or citric acid, a molecule containing three COOH groups: (CH2 COOH-C(OH)COOH-CH2 COOH = C6 H8 O7 ). Have a look at the 3-dimensional formula. SBA resins are always regenerated with caustic soda (NaOH) in the demineralisation process. Caustic potash (potassium hydroxide KOH) is in principle also applicable, but usually more expensive. WBA resins are usually also regenerated with caustic soda, but other regenerants weaker alkalis can also be used, such as: Ammonia (NH3 ) Sodium carbonate (soda ash, Na2 CO3 )
Concentrations
The most usual concentrations are: NaCl (softening and nitrate removal): 10 % HCl (decationisation, de-alkalisation and demineralisation): 5 % NaOH (demineralisation): 4 % H 2 SO4 : for SAC resins, the acid concentration must be carefully selected between 0.7 and 6 % as a function of the proportion of calcium in the feed water (which is the same in the SAC resin). For WAC resins, the concentration is usually 0.7 %. Too high a concentration may cause calcium sulphate precipitation. For SAC resins, stepwise concentrations are often used: after a first step at a low concentration, a second step is carried out at a higher concentration once a great part of the calcium on the resin has been eluted. In rare cases, three steps are used. The steps at higher concentrations reduce the quantity of dilution water and increase the sulphuric acid efficiency.
dardel.info/IX/processes/regeneration.html
9/10
4/16/13
Ion exchange regeneration methods
There are cases where different concentrations (often lower, rarely higher) must be selected.
Neutralisation of the regenerants
See a separate page on the way to neutralise regenerants and increase ion exchange capacity. Franois de Dardel
dardel.info/IX/processes/regeneration.html
10/10
You might also like
- Incineration SolidWaste ManagementDocument16 pagesIncineration SolidWaste Managementsai ramanaNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Pressure Vessel Using PV Elite SoftwareDocument8 pagesDesign and Analysis of Pressure Vessel Using PV Elite SoftwareVitor OlivettiNo ratings yet
- 6.C.b Industrial Waste Incineration GB2009Document21 pages6.C.b Industrial Waste Incineration GB2009AgungGhaniKramawijayaNo ratings yet
- (Polish Maritime Research) Development of New Technologies For Shipping Natural Gas by SeaDocument9 pages(Polish Maritime Research) Development of New Technologies For Shipping Natural Gas by SeafarshidianNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Oxy Reactor CatalystDocument9 pagesComparative Analysis of Oxy Reactor CatalystSaad ArifNo ratings yet
- PD - 8010 4 2015Document52 pagesPD - 8010 4 2015jasonNo ratings yet
- Strength Calcul SheetDocument379 pagesStrength Calcul Sheetmustufa akolawalaNo ratings yet
- Waste Incineration Insert v2Document2 pagesWaste Incineration Insert v2Namik HadziibrahimovicNo ratings yet
- PD - 8010 5 2015Document78 pagesPD - 8010 5 2015jasonNo ratings yet
- Power Generation From Combustion NEWDocument49 pagesPower Generation From Combustion NEWhridita purbaNo ratings yet
- Eor PDFDocument20 pagesEor PDFLawrenceLopezNo ratings yet
- 03 NitrationDocument50 pages03 NitrationShary Rafaqat100% (1)
- Vibration Analysis 2Document6 pagesVibration Analysis 2Loxman ZahariNo ratings yet
- Advances in Catalysis Volume 1 - Walter G. Frankenburg (Academic Press, 1948)Document337 pagesAdvances in Catalysis Volume 1 - Walter G. Frankenburg (Academic Press, 1948)MHavoc100% (1)
- Platfroming of Naphtha ProjectDocument150 pagesPlatfroming of Naphtha ProjectNoman Aslam100% (1)
- Advances in Catalysis, Volume 57 Chapter 1Document97 pagesAdvances in Catalysis, Volume 57 Chapter 1Abhishek AbhiNo ratings yet
- Spoor-M. 1992 Modeling and Stochastic Simulation of The Reactions and Absorption of NOx in Water MSC PDFDocument124 pagesSpoor-M. 1992 Modeling and Stochastic Simulation of The Reactions and Absorption of NOx in Water MSC PDFDongO Jung100% (1)
- Separator ComponentsDocument16 pagesSeparator ComponentsvsroilgasNo ratings yet
- Carbon Capture and Sequestration-A Review: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental ScienceDocument11 pagesCarbon Capture and Sequestration-A Review: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental ScienceVika XieNo ratings yet
- Cooling Towers Information PackageDocument25 pagesCooling Towers Information Packagemdawg467No ratings yet
- 2003 Cochran RP Hydrate Control Remediation PDFDocument8 pages2003 Cochran RP Hydrate Control Remediation PDFArsénioNo ratings yet
- Integrated Training Program / Phase B - Flare Protection Systems Page 1 of 33Document33 pagesIntegrated Training Program / Phase B - Flare Protection Systems Page 1 of 33metasoniko2014No ratings yet
- Cooling Tower Lewis FactorDocument6 pagesCooling Tower Lewis Factorshivajireturns100% (1)
- Solubility of Calcium Carbonate in WaterDocument2 pagesSolubility of Calcium Carbonate in WaterKEHALI AbdelheqNo ratings yet
- Thermal Conductivity of GasesDocument2 pagesThermal Conductivity of GasesFlorian_AngererNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1Sehrish ZaidiNo ratings yet
- OverviewDocument21 pagesOverviewgreenhen15No ratings yet
- Oxy Enrich Process For Capacity Enhancement of Claus Based Sulfur Recovery UnitDocument22 pagesOxy Enrich Process For Capacity Enhancement of Claus Based Sulfur Recovery Unitsara25dec689288No ratings yet
- Analysis of Temperature Control of CSTR Using S FunctionDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Temperature Control of CSTR Using S FunctionSolecito FuentesNo ratings yet
- NGE Lectures OHT-1Document79 pagesNGE Lectures OHT-1SamNo ratings yet
- IND 202 U2a Gas and Liquid Separation FCivan XXDocument61 pagesIND 202 U2a Gas and Liquid Separation FCivan XXrenatoNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Tools and Control Parameters For Refinery HeatersDocument7 pagesDiagnostic Tools and Control Parameters For Refinery HeaterskrishnaNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Design Lecture - 07Document24 pagesHeat Exchanger Design Lecture - 07Mohmmad ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer in Packed BedDocument10 pagesHeat Transfer in Packed BedNidhi JainNo ratings yet
- Adsorption FundamentalsDocument16 pagesAdsorption FundamentalstoxictazNo ratings yet
- Carbon Nanotubes PresentationDocument11 pagesCarbon Nanotubes PresentationrajualagNo ratings yet
- BoilerDocument35 pagesBoilerKamran ShakeelNo ratings yet
- Topsoe Sec Ref Cat RKS 2Document5 pagesTopsoe Sec Ref Cat RKS 2Vo Duc Minh MinhNo ratings yet
- Ethylene PipesDocument8 pagesEthylene Pipesingbarragan87No ratings yet
- Heater Treater SeparatorDocument2 pagesHeater Treater SeparatorMurat KalfaNo ratings yet
- Improve Flaring OperationsDocument4 pagesImprove Flaring Operationsaa dd qqNo ratings yet
- FDP01 MDM3 Asyyy 14 343015 0001 01Document77 pagesFDP01 MDM3 Asyyy 14 343015 0001 01Khánh TrầnNo ratings yet
- Financial Feasibility Study Between Purchasing and Hiring LNG Carrier in IRANIAN LNG IndustryDocument11 pagesFinancial Feasibility Study Between Purchasing and Hiring LNG Carrier in IRANIAN LNG IndustryMohamed SONo ratings yet
- Converting Mass Flow RateDocument3 pagesConverting Mass Flow RateAgung PriambodhoNo ratings yet
- Design and In-Service Inspections: Guy Baylac Technical Advisor To EPERCDocument27 pagesDesign and In-Service Inspections: Guy Baylac Technical Advisor To EPERCmngNo ratings yet
- Uncovering The Realities of Simulation, Part 2 (Of 2)Document9 pagesUncovering The Realities of Simulation, Part 2 (Of 2)bjsatolaNo ratings yet
- Liquid Monopropellant CombustionDocument4 pagesLiquid Monopropellant Combustionherdi sutanto adigunaNo ratings yet
- Initial and Boundary Value Problems Involving Ordinary DifferentialDocument24 pagesInitial and Boundary Value Problems Involving Ordinary DifferentialMr. ONo ratings yet
- 1998 Irving Refinery Hydrocracker Furnace Accident ReportDocument18 pages1998 Irving Refinery Hydrocracker Furnace Accident Reportbazil17No ratings yet
- Room Temperature Synthesis of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Morphological Evaluation and Their Catalytic Applications For Degradation of Dyes and C-N Bond Formation Reaction PDFDocument11 pagesRoom Temperature Synthesis of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Morphological Evaluation and Their Catalytic Applications For Degradation of Dyes and C-N Bond Formation Reaction PDFAshpavi ArunNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of The Synthesis of Higher Aliphatic Alcohols From SyngasDocument8 pagesKinetics of The Synthesis of Higher Aliphatic Alcohols From SyngasLina ArevaloNo ratings yet
- 00 Ca e 10150 - 02 PDFDocument103 pages00 Ca e 10150 - 02 PDFMauro MLRNo ratings yet
- Erosion Due To FlowDocument3 pagesErosion Due To FlownguyenNo ratings yet
- Cryogenic TurboexpandersDocument9 pagesCryogenic TurboexpandersDwinaRahmayaniNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Basic Concepts: MAE 320-Chapter 1Document10 pagesIntroduction and Basic Concepts: MAE 320-Chapter 1Abdu AbdoulayeNo ratings yet
- (TP0A004) Accuracy of Metering Versus Tank Gauging of Vessel Delivered Petroleum LiquidsDocument4 pages(TP0A004) Accuracy of Metering Versus Tank Gauging of Vessel Delivered Petroleum LiquidsRoberto Carlos TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Proceedings of the Twelfth International Cryogenic Engineering Conference Southampton, UK, 12–15 July 1988From EverandProceedings of the Twelfth International Cryogenic Engineering Conference Southampton, UK, 12–15 July 1988R. G. ScurlockNo ratings yet
- Desanding CycloneDocument4 pagesDesanding CyclonecrespoNo ratings yet
- The Benefits of BCAAs - Poliquin ArticleDocument8 pagesThe Benefits of BCAAs - Poliquin Articlecrespo100% (2)
- Forklift OperationDocument5 pagesForklift OperationcrespoNo ratings yet
- Numerology - Best Dates To MarryDocument10 pagesNumerology - Best Dates To MarrycrespoNo ratings yet
- GT2 Inlet Pressure DropDocument1 pageGT2 Inlet Pressure DropcrespoNo ratings yet
- Generator ProductsDocument16 pagesGenerator Productspatro242No ratings yet
- One - Touch Fittings: Series: WP2Document12 pagesOne - Touch Fittings: Series: WP2PrashantNo ratings yet
- Sunfix Blue SPRDocument7 pagesSunfix Blue SPRDyeing 2 Wintex100% (2)
- Grand Vitara 2005Document35 pagesGrand Vitara 2005PattyaaNo ratings yet
- Module II Activated Sludge Math ProblemsDocument5 pagesModule II Activated Sludge Math ProblemsArashNo ratings yet
- The Coffee Shop Easy Reading - 152542Document1 pageThe Coffee Shop Easy Reading - 152542Fc MakmurNo ratings yet
- Barium Chloride 2h2o LRG MsdsDocument3 pagesBarium Chloride 2h2o LRG MsdsAnas GiselNo ratings yet
- Jetline: Theoretical Working Point Performance ChartDocument1 pageJetline: Theoretical Working Point Performance ChartMohamed GamalNo ratings yet
- The Church of Kapnikarea in Athens - N. GkiolesDocument13 pagesThe Church of Kapnikarea in Athens - N. GkiolesMaronasNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Ionic EquilibriumDocument2 pagesQuiz - Ionic EquilibriumSiddNo ratings yet
- Stahl - PUDSDocument29 pagesStahl - PUDSsusanasusana_No ratings yet
- The Russian Review - 2020 - ROTH EY - Listening Out Listening For Listening in Cold War Radio Broadcasting and The LateDocument22 pagesThe Russian Review - 2020 - ROTH EY - Listening Out Listening For Listening in Cold War Radio Broadcasting and The LateOkawa TakeshiNo ratings yet
- Content For Essay and Paragraph Writing On Maritime HistoryDocument15 pagesContent For Essay and Paragraph Writing On Maritime HistoryRaju KumarNo ratings yet
- Latest Research Papers On Manet SecurityDocument7 pagesLatest Research Papers On Manet Securitygz9g97haNo ratings yet
- RestrictedDocument51 pagesRestrictedsridharpalledaNo ratings yet
- RA No. 9514 Revised Fire CodeDocument11 pagesRA No. 9514 Revised Fire Coderaegab100% (32)
- Eurolite Led TMH 7 PDFDocument2 pagesEurolite Led TMH 7 PDFSarahNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Phonetics PDFDocument82 pagesAcoustic Phonetics PDFAnonymous mOSDA2100% (2)
- 5 Kingdoms of OrganismsDocument13 pages5 Kingdoms of OrganismsChoirul Anam100% (2)
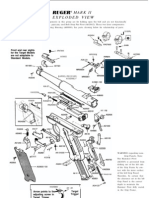
- Ruger MKIIDocument1 pageRuger MKIIMike Pape100% (1)
- The Seventh House in AstrologyDocument6 pagesThe Seventh House in Astrologytratak100% (1)
- Load ScheduleDocument8 pagesLoad SchedulemerebookNo ratings yet
- Ingles y Español Unidad 7Document9 pagesIngles y Español Unidad 7Pier Jhoani Ñañez LlanosNo ratings yet
- Manual Elspec SPG 4420Document303 pagesManual Elspec SPG 4420Bairon Alvira ManiosNo ratings yet
- CSA Pre-Test QuestionnaireDocument16 pagesCSA Pre-Test Questionnairedaniella balaquitNo ratings yet
- AVEVA E3D Tutorial Equipment Modeling With Practical ExampleDocument8 pagesAVEVA E3D Tutorial Equipment Modeling With Practical ExampleRamon Alejandro Porras Hernandez100% (1)
- Academic Program Required Recommended Academic Program Required RecommendedDocument1 pageAcademic Program Required Recommended Academic Program Required Recommendedonur scribdNo ratings yet
- Website Catalog MOTORS v2 PDFDocument8 pagesWebsite Catalog MOTORS v2 PDFИгорь КернякевичNo ratings yet
- Igc 3 Practical NeboshDocument20 pagesIgc 3 Practical NeboshAbdelkader FattoucheNo ratings yet
- 9 Daftar Pustaka VaricelaDocument2 pages9 Daftar Pustaka VaricelaAfrina FaziraNo ratings yet
- Jerms B 2109 - 0BDocument10 pagesJerms B 2109 - 0BNothing is ImpossibleNo ratings yet