Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Break Even Analysis
Uploaded by
Shiv MalhotraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Break Even Analysis
Uploaded by
Shiv MalhotraCopyright:
Available Formats
introduction to break-even analysis
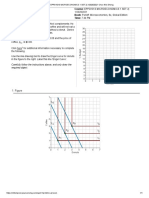
Introduction Break-even analysis is a technique widely used by production management and management accountants. It is based on categorising production costs between those which are "variable" (costs that change when the production output changes) and those that are "fixed" (costs not directly related to the volume of production). Total variable and fixed costs are compared with sales revenue in order to determine the level of sales volume, sales value or production at which the business makes neither a profit nor a loss (the "break-even point"). The Break-Even Chart In its simplest form, the break-even chart is a graphical representation of costs at various levels of activity shown on the same chart as the variation of income (or sales, revenue) with the same variation in activity. The point at which neither profit nor loss is made is known as the "break-even point" and is represented on the chart below by the intersection of the two lines:
In the diagram above, the line OA represents the variation of income at varying levels of production activity ("output"). OB represents the total fixed costs in the business. As output increases, variable costs are incurred, meaning that total costs (fixed + variable) also increase. At low levels of output, Costs are greater than Income. At the point of intersection, P, costs are exactly equal to income, and hence neither profit nor loss is made. Fixed Costs Fixed costs are those business costs that are not directly related to the level of production or output. In other words, even if the business has a zero output or high output, the level of fixed costs will remain broadly the same. In the long term fixed costs can alter - perhaps as a result of investment in production capacity (e.g. adding a new factory unit) or through the growth in overheads required to support a larger, more complex business. Examples of fixed costs: - Rent and rates
-Depreciation -Research and development -Marketing costs (non- revenue related) -Administration costs Variable Costs Variable costs are those costs which vary directly with the level of output. They represent payment output-related inputs such as raw materials, direct labour, fuel and revenue-related costs such as commission. A distinction is often made between "Direct" variable costs and "Indirect" variable costs. Direct variable costs are those which can be directly attributable to the production of a particular product or service and allocated to a particular cost centre. Raw materials and the wages those working on the production line are good examples. Indirect variable costs cannot be directly attributable to production but they do vary with output. These include depreciation (where it is calculated related to output - e.g. machine hours), maintenance and certain labour costs. Semi-Variable Costs Whilst the distinction between fixed and variable costs is a convenient way of categorising business costs, in reality there are some costs which are fixed in nature but which increase when output reaches certain levels. These are largely related to the overall "scale" and/or complexity of the business. For example, when a business has relatively low levels of output or sales, it may not require costs associated with functions such as human resource management or a fully-resourced finance department. However, as the scale of the business grows (e.g. output, number people employed, number and complexity of transactions) then more resources are required. If production rises suddenly then some short-term increase in warehousing and/or transport may be required. In these circumstances, we say that part of the cost is variable and part fixed.
Definition of 'Break-Even Analysis'
An analysis to determine the point at which revenue received equals the costs associated with receiving the revenue. Break-even analysis calculates what is known as a margin of safety, the amount that revenues exceed the break-even point. This is the amount that revenues can fall while still staying above the break-even point.
For example, if it costs $50 to produce a widget, and there are fixed costs of $1,000, the break-even point for selling the widgets would be: If selling for $100: 20 Widgets (Calculated as 1000/(100-50)=20) If selling for $200: 7 Widgets (Calculated as 1000/(200-50)=6.7) In this example, if someone sells the product for a higher price, the break-even point will come faster. What the analysis does not show is that it may be easier to sell 20 widgets at $100 each than 7 widgets at $200 each. A demand-side analysis would give the seller that information.
Limitations It is important to understand what the results of your breakeven analysis are telling you. If, for example, the calculation reports that you would break even when you sold your 500th unit, decide whether this seems feasible. If you don't think you can sell 500 units within a reasonable period of time (dictated by your financial situation, patience and personal expectations), then this may not be the right business for you to go into. If you think 500 units is possible but would take a while, try lowering your price and calculating and analyzing the new breakeven point. Alternatively, take a look at your costs - both fixed and variable - and identify areas where you might be able to make cuts. Lastly, understand that breakeven analysis is not a predictor of demand, so if you go into market with the wrong product or the wrong price, it may be tough to ever hit the breakeven point.
You might also like
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Break Even Analysis in ProductionDocument17 pagesBreak Even Analysis in Productionyashwant4043994No ratings yet
- Initial Feasibel Solution Using Northwest Corner RulesDocument24 pagesInitial Feasibel Solution Using Northwest Corner RulesRoi MilyardiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 TP EndDocument43 pagesChapter 03 TP EndMesfin MekuriaNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming Graphical MethodDocument7 pagesLinear Programming Graphical MethodDevkaran LodhiNo ratings yet
- Given An Actual Demand of 60 For A Period When Forecast of 70Document17 pagesGiven An Actual Demand of 60 For A Period When Forecast of 70arjunNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting Chapter 5 by GarrisonDocument4 pagesManagerial Accounting Chapter 5 by GarrisonJoshua Hines100% (1)
- Modified Internal Rate of ReturnDocument4 pagesModified Internal Rate of ReturnDjoko Nugroho100% (1)
- Chapter 11 - Network Models - Operations ResearchDocument12 pagesChapter 11 - Network Models - Operations ResearchAnkit Saxena100% (5)
- Waiting Lines PDFDocument51 pagesWaiting Lines PDFAlen Thomas Kattakayam100% (1)
- Classification of Production SystemsDocument4 pagesClassification of Production SystemsBizuayehu TadesseNo ratings yet
- Facility Location & LayoutDocument27 pagesFacility Location & LayoutDnyaneshwar1986No ratings yet
- Transportation and Assignment ProblemDocument67 pagesTransportation and Assignment ProblemRovick TarifeNo ratings yet
- Cost of CapitalDocument30 pagesCost of CapitalDellendo Farquharson100% (1)
- Linear ProgrammingDocument15 pagesLinear Programmingjogindra singh100% (1)
- Nature and Scope of Managerial EconomicsDocument19 pagesNature and Scope of Managerial EconomicsBedria NariNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 Transportatiofor Night ClassDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 3 Transportatiofor Night ClassHACHALU FAYE100% (1)
- LKAS 19 2021 UploadDocument31 pagesLKAS 19 2021 Uploadpriyantha dasanayake100% (1)
- Tranportation and Transshipment ProblemDocument58 pagesTranportation and Transshipment ProblemSumit Jha50% (2)
- CH (7) Incremental Analysis (Decision Making)Document11 pagesCH (7) Incremental Analysis (Decision Making)Khaled Abo YousefNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Tools: Determinants and Matrices: Eaching Uggestions M5-7Document3 pagesMathematical Tools: Determinants and Matrices: Eaching Uggestions M5-7José Manuel Orduño VillaNo ratings yet
- Render 10Document28 pagesRender 10eliane вelénNo ratings yet
- Alpha University College Mba Program Worksheet (Practice Questions) For The Course Quantitative Analysis For Management DecisionDocument3 pagesAlpha University College Mba Program Worksheet (Practice Questions) For The Course Quantitative Analysis For Management DecisionAmanuel Mitiku100% (1)
- 5.2.1 Program Evaluation Review Technique PPT Only PDFDocument11 pages5.2.1 Program Evaluation Review Technique PPT Only PDFCecillia Yuliana HalimNo ratings yet
- Transportation ProblemDocument50 pagesTransportation ProblemSam HarithNo ratings yet
- Short Run Decision AnalysisDocument31 pagesShort Run Decision AnalysisMedhaSaha100% (1)
- Case Study For Inventroy Managmenet ImprovementsDocument6 pagesCase Study For Inventroy Managmenet ImprovementsAfaq KhanNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Fixed Cost and Variable CostDocument2 pagesDifference Between Fixed Cost and Variable CostGhalib HussainNo ratings yet
- Aggregate PlanningDocument20 pagesAggregate PlanningdhilipkumarNo ratings yet
- MODI Method Examples Transportation Problem PDFDocument4 pagesMODI Method Examples Transportation Problem PDFsukhdev thakurNo ratings yet
- Scheduling and Sequencing-IDocument71 pagesScheduling and Sequencing-IPrateek Konvicted100% (2)
- FORECASTINGDocument37 pagesFORECASTINGRegina Jazzmim QuezadaNo ratings yet
- Article Review On: Profitable Working Capital Management in Industrial Maintenance CompaniesDocument5 pagesArticle Review On: Profitable Working Capital Management in Industrial Maintenance CompaniesHabte DebeleNo ratings yet
- Stevenson Chapter 3 - ForecastingDocument50 pagesStevenson Chapter 3 - ForecastingSium Adnan Khan 1511153030No ratings yet
- Cost Accounting IIDocument62 pagesCost Accounting IIShakti S SarvadeNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Plant Location and Layout PDFDocument25 pagesLecture - Plant Location and Layout PDFrafesh100% (1)
- QueueDocument14 pagesQueueZharlene SasotNo ratings yet
- A Project On The Economic Order QuantityDocument26 pagesA Project On The Economic Order QuantityFortune Fmx MushongaNo ratings yet
- EDP Auditing Article ReviewDocument6 pagesEDP Auditing Article ReviewWedaje Alemayehu100% (2)
- Operations Management-CP PDFDocument4 pagesOperations Management-CP PDFrey cedricNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 LP-3Document68 pagesChapter 2 LP-3Ayalew Lake100% (1)
- Financial Control - 2 - Flexible Budgets and Variances - Webb Company With SolutionDocument5 pagesFinancial Control - 2 - Flexible Budgets and Variances - Webb Company With SolutionQuang NhựtNo ratings yet
- Hurwicz Criterion in Decision TheroryDocument11 pagesHurwicz Criterion in Decision TherorysubinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Network ModelsDocument22 pagesChapter 11 - Network ModelsAbo Fawaz100% (1)
- Solved Example Transportation Problem Help For Transportation Model, Management, Homework Help - TranstutorsDocument17 pagesSolved Example Transportation Problem Help For Transportation Model, Management, Homework Help - Transtutorssandipghosh1230% (1)
- Finance Assistant CV TemplateDocument2 pagesFinance Assistant CV TemplateRizky WidiyantoNo ratings yet
- COSTACC Lecture 2 Process CostingDocument80 pagesCOSTACC Lecture 2 Process Costingallforgod19No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Financial Estimates and ProjectionsDocument15 pagesChapter 6 Financial Estimates and ProjectionsKusum Bhandari33% (3)
- Chapter1 - Statistics For Managerial DecisionsDocument26 pagesChapter1 - Statistics For Managerial DecisionsRanjan Raj UrsNo ratings yet
- Mba 206Document240 pagesMba 206Operation ResearchNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document8 pagesChapter 10Ayoub BokhabrineNo ratings yet
- Productivity Problems 1 3 AnsDocument1 pageProductivity Problems 1 3 Anssami damtewNo ratings yet
- Exercises On Transportation ProblemDocument2 pagesExercises On Transportation Problemalish8100% (1)
- Final Case Study InstructionsDocument1 pageFinal Case Study InstructionsEmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Current Liability PayrollDocument39 pagesChapter 3 Current Liability PayrollAbdi Mucee Tube100% (1)
- 11 Solutions PDFDocument9 pages11 Solutions PDFKenneth KibataNo ratings yet
- 04 Marginal CostingDocument67 pages04 Marginal CostingAyushNo ratings yet
- What Is Breakeven PointDocument2 pagesWhat Is Breakeven PointRuchee ThakurNo ratings yet
- BreakEven Asgnmnt BSPA 3rd YearDocument5 pagesBreakEven Asgnmnt BSPA 3rd YearZuhair NaqviNo ratings yet
- Break-Even Point NotesDocument3 pagesBreak-Even Point NotesMinu Mary Jolly100% (1)
- The Nature of The Firm: Economica Vol. 4 (November 1937)Document10 pagesThe Nature of The Firm: Economica Vol. 4 (November 1937)Helbert Romero NavarroNo ratings yet
- Introduction and History of CadburyDocument10 pagesIntroduction and History of CadburyShahriar Azgar60% (5)
- Ichimoku Kinko Hyo StrategyDocument3 pagesIchimoku Kinko Hyo StrategyDaniel GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship and Enterprise Creation-1Document90 pagesEntrepreneurship and Enterprise Creation-1Nsemi NsemiNo ratings yet
- CRM Revel WhitepaperDocument12 pagesCRM Revel Whitepaperblahze100% (2)
- Test Bank For Principles of Macroeconomics 6th Edition by Taylor Sample ChapterDocument62 pagesTest Bank For Principles of Macroeconomics 6th Edition by Taylor Sample Chapterhailuhenok50No ratings yet
- 004 - 06 (Edna) Jarillo - 1988Document14 pages004 - 06 (Edna) Jarillo - 1988Edna PossebonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PPTs Hedging Strategies Using FuturesDocument19 pagesChapter 3 PPTs Hedging Strategies Using FuturesMrunaal NaseryNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Todaro, Economic Development - Ch.3 (Wiscana AP)Document4 pagesTopic 3 - Todaro, Economic Development - Ch.3 (Wiscana AP)Wiscana Chacha100% (1)
- Beda Pajak Dan RetribusiDocument6 pagesBeda Pajak Dan RetribusiimantaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 - Alternative Measures of National Income - pptx-1Document20 pagesCH 2 - Alternative Measures of National Income - pptx-1renatyas14No ratings yet
- The Management of Innovation and Technology - The Shaping of Technology and Institutions of The Market Economy - J Howells (Sage Publications LTD)Document301 pagesThe Management of Innovation and Technology - The Shaping of Technology and Institutions of The Market Economy - J Howells (Sage Publications LTD)Edward100% (2)
- IE54500 - Exam 3: 1. Static Game of Complete InformationDocument5 pagesIE54500 - Exam 3: 1. Static Game of Complete InformationM100% (1)
- Microeconomics: Asynchronous AssignmentDocument3 pagesMicroeconomics: Asynchronous AssignmentKhushi naharNo ratings yet
- PWC Divestment Services eDocument3 pagesPWC Divestment Services ep10souravnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 30 Impairment of AssetDocument15 pagesChapter 30 Impairment of AssetCrizel Dario0% (1)
- Unit 6 TestDocument4 pagesUnit 6 TestmecribbsNo ratings yet
- Unit 12 Capitalist Industrialization: StructureDocument20 pagesUnit 12 Capitalist Industrialization: StructureAbhijeet JhaNo ratings yet
- Ishraq IA2 Checklist - Sheet1Document6 pagesIshraq IA2 Checklist - Sheet1Dan KurutoNo ratings yet
- Product, Services, and ExperiencesDocument11 pagesProduct, Services, and ExperiencesAubrey Joy PlantoNo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument26 pagesManagerial EconomicsMr BhanushaliNo ratings yet
- Use The Line Drawing Tool To Draw The Engel Curve For DonutsDocument1 pageUse The Line Drawing Tool To Draw The Engel Curve For DonutsChoo Wei shengNo ratings yet
- Labour Market Trends and DynamicsDocument7 pagesLabour Market Trends and DynamicsppriyasonuNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Principles of Economics 7th EditionDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Principles of Economics 7th EditionKevinHarrisonnkrqm100% (38)
- Market Failure in SingaporeDocument5 pagesMarket Failure in SingaporeMichael Loh100% (2)
- Module 2 - InflationDocument36 pagesModule 2 - Inflationnmkanjoo2743No ratings yet
- The Philippine Society: Class StructureDocument4 pagesThe Philippine Society: Class StructureJaymar Sardz VillarminoNo ratings yet
- Software Project ManagementDocument252 pagesSoftware Project ManagementVijay Anand67% (3)
- CV Tarun Das For Monitoring and Evaluation Expert July 2016Document9 pagesCV Tarun Das For Monitoring and Evaluation Expert July 2016Professor Tarun DasNo ratings yet
- Itl 528 Assignment 2b 5day ExtendedDocument14 pagesItl 528 Assignment 2b 5day Extendedapi-470484168No ratings yet
- Getting to Yes: How to Negotiate Agreement Without Giving InFrom EverandGetting to Yes: How to Negotiate Agreement Without Giving InRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (652)
- I Will Teach You to Be Rich: No Guilt. No Excuses. No B.S. Just a 6-Week Program That Works (Second Edition)From EverandI Will Teach You to Be Rich: No Guilt. No Excuses. No B.S. Just a 6-Week Program That Works (Second Edition)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Purchasing, Inventory, and Cash Disbursements: Common Frauds and Internal ControlsFrom EverandPurchasing, Inventory, and Cash Disbursements: Common Frauds and Internal ControlsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The ZERO Percent: Secrets of the United States, the Power of Trust, Nationality, Banking and ZERO TAXES!From EverandThe ZERO Percent: Secrets of the United States, the Power of Trust, Nationality, Banking and ZERO TAXES!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- The Science of Prosperity: How to Attract Wealth, Health, and Happiness Through the Power of Your MindFrom EverandThe Science of Prosperity: How to Attract Wealth, Health, and Happiness Through the Power of Your MindRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (231)
- How to Measure Anything: Finding the Value of "Intangibles" in BusinessFrom EverandHow to Measure Anything: Finding the Value of "Intangibles" in BusinessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (28)
- The Accounting Game: Learn the Basics of Financial Accounting - As Easy as Running a Lemonade Stand (Basics for Entrepreneurs and Small Business Owners)From EverandThe Accounting Game: Learn the Basics of Financial Accounting - As Easy as Running a Lemonade Stand (Basics for Entrepreneurs and Small Business Owners)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Accounting 101: From Calculating Revenues and Profits to Determining Assets and Liabilities, an Essential Guide to Accounting BasicsFrom EverandAccounting 101: From Calculating Revenues and Profits to Determining Assets and Liabilities, an Essential Guide to Accounting BasicsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- A Beginners Guide to QuickBooks Online 2023: A Step-by-Step Guide and Quick Reference for Small Business Owners, Churches, & Nonprofits to Track their Finances and Master QuickBooks OnlineFrom EverandA Beginners Guide to QuickBooks Online 2023: A Step-by-Step Guide and Quick Reference for Small Business Owners, Churches, & Nonprofits to Track their Finances and Master QuickBooks OnlineNo ratings yet
- The E-Myth Chief Financial Officer: Why Most Small Businesses Run Out of Money and What to Do About ItFrom EverandThe E-Myth Chief Financial Officer: Why Most Small Businesses Run Out of Money and What to Do About ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Ratio Analysis Fundamentals: How 17 Financial Ratios Can Allow You to Analyse Any Business on the PlanetFrom EverandRatio Analysis Fundamentals: How 17 Financial Ratios Can Allow You to Analyse Any Business on the PlanetRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Accounting For Small Businesses QuickStart Guide: Understanding Accounting For Your Sole Proprietorship, Startup, & LLCFrom EverandAccounting For Small Businesses QuickStart Guide: Understanding Accounting For Your Sole Proprietorship, Startup, & LLCRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How to Start a Business: Mastering Small Business, What You Need to Know to Build and Grow It, from Scratch to Launch and How to Deal With LLC Taxes and Accounting (2 in 1)From EverandHow to Start a Business: Mastering Small Business, What You Need to Know to Build and Grow It, from Scratch to Launch and How to Deal With LLC Taxes and Accounting (2 in 1)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Overcoming Underearning(TM): A Simple Guide to a Richer LifeFrom EverandOvercoming Underearning(TM): A Simple Guide to a Richer LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (21)
- The Intelligent Investor, Rev. Ed: The Definitive Book on Value InvestingFrom EverandThe Intelligent Investor, Rev. Ed: The Definitive Book on Value InvestingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (760)
- Financial Accounting For Dummies: 2nd EditionFrom EverandFinancial Accounting For Dummies: 2nd EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (10)
- Finance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)From EverandFinance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (32)
- Start, Study and Pass The CPA Exam FAST - Proven 8 Step CPA Exam Study PlaybookFrom EverandStart, Study and Pass The CPA Exam FAST - Proven 8 Step CPA Exam Study PlaybookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Attention Pays: How to Drive Profitability, Productivity, and AccountabilityFrom EverandAttention Pays: How to Drive Profitability, Productivity, and AccountabilityNo ratings yet
- Tax-Free Wealth: How to Build Massive Wealth by Permanently Lowering Your TaxesFrom EverandTax-Free Wealth: How to Build Massive Wealth by Permanently Lowering Your TaxesNo ratings yet
- Your Amazing Itty Bitty(R) Personal Bookkeeping BookFrom EverandYour Amazing Itty Bitty(R) Personal Bookkeeping BookNo ratings yet
- Accounting Principles: Learn The Simple and Effective Methods of Basic Accounting And Bookkeeping Using This comprehensive Guide for Beginners(quick-books,made simple,easy,managerial,finance)From EverandAccounting Principles: Learn The Simple and Effective Methods of Basic Accounting And Bookkeeping Using This comprehensive Guide for Beginners(quick-books,made simple,easy,managerial,finance)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- The Credit Formula: The Guide To Building and Rebuilding Lendable CreditFrom EverandThe Credit Formula: The Guide To Building and Rebuilding Lendable CreditRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)