Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Course Manual On Sourcing and Managing Funds
Uploaded by
ashisparida08Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Course Manual On Sourcing and Managing Funds
Uploaded by
ashisparida08Copyright:
Available Formats
Module Manual: Sourcing & Managing Funds (SMF) Academic Year: PGDM/FS/MM/IB 2012-2013
Introduction to the Module and Module Objective The past two decades have witnessed a dramatic transformation of the Indian business and financial scene, thanks to liberalization, privatization, globalization, automation, and the ascendance of the services sector. In the wake of these developments, investment and financing avenues have expanded considerably, competition has intensified in all sectors, institutional investors have become a major force, and corporate have grown in size and complexity. Sourcing & Managing Funds (SMF) is the core Module that describes the perspective of groups within the firm tasked to create firm value by a) deciding how much capital to raise and the best mix of different sources of capital, and b) managing those funds and generating relevant financial information, which includes describing future plans (budgets), evaluating new projects (capital budgeting), and evaluating the performance of divisions, managers and products. Some of these functions are housed within the office of the Chief Financial Officer (CFO), split between the Treasurer and the Controller. But many other functions are spread across the organisation, principally in the hands of strategy groups and product managers. Through this Module on SMF, students will get an insight into the issues involved in investment decision and financing of such decision. Therefore, the main focus will on understanding the techniques of capital budgeting and capital structure decision. INTRODUCTION TO THE TUTORS Name: Dr Anubha Gupta Phone Number: 0120-6670698 Email ID: anubha.gupta@iilmgsm.ac.in Cabin Location: 318 Name: Ms. Arpita Mehrotra Phone Number: Email ID: arpita.mehrotra@iilmgsm.ac.in Cabin Location: -
MODULE OVERVIEW Topic 1 Introduction & Develop Projections It describes how to develop free cash flow forecast by projecting future income statement and balance sheet with respect to capital expenditure decisions. Topic 2 Which Plans Should we Pursue? This includes an understanding of different financial techniques for evaluation and selection of long-term projects. Topic 3 Economic Income & Accounting Ratios It describes the difference between accounting and economic income while throwing some light on key profitability ratios. 2
Topic 4 Cost of Capital It includes the calculation of component and project cost of capital. Topic 5 Capital Structure It includes an understanding of optimum capital structure for financing capital investments. Topic 6 Control Issues It includes decentralisation, transfer pricing, and performance evaluation. Topic 7 Investor Relations & Communications It deals with managing expectations and grievances of the provider of capital.
MODULE LEARNING OUTCOMES Learning outcomes state what you should be able to do if you pass the module. By the end of this module you should be able to: forecast and develop financial projections understand method of evaluating long-term investment projects calculate cost of capital for financing projects understand the mix of debt and equity in financing decision understand decision making levels and their performance evaluation identify issues involved in managing relations with the provider of funds. understand management of short term assets and funds.
MODULE READINGS The students are expected to read the articles uploaded on Moodle, prescribed books which will provide a good theoretical construct to the subject. Besides this reading of journals and web resources will help understand this subject in practice.
Required Readings Articles/Cases uploaded on Moodle Reference Books th Financial Management by Prasanna Chandra, TATA McGRAW HILL, 7 Edition. Principles of Corporate Finance by Richard A Breyley, Stewart C. Meyers, Franklin Allen, Pitbas Mohanty, Tata Mc Graw Hill, 8 ed. rd Corporate Finance by Aswath Damodaran, Wiley, 3 edition. th Corporate Finance by Ross, Westerfield, Jaffe and Kakni, Tata McGraw Hill, 8 edition th Financial Management by I.M.Pandey, Vikas Publishing House Pvt. Ltd, 9 Edition Cost Accounting - A Managerial Emphasis by Charles T Horngren, Srikant M. Datar and George Foster, Pearson Education, 13th Edition
Journals 3
Indian Journal of Finance Journal of Finance and Management Financial Management Journal of Accounting and Finance
Website = http://pages.stern.nyu.edu/~adamodar
Module Overview: Session 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Topic Introduction and Develop Projections Project Future Balance Sheet Develop and Project Cash Flows Discounting Cash Flows Which Plans should we pursue? Projecting terminal values, Links among NPV, share price & value creation. Terminal Values and Industry Multiples Economic Income Economic Income and Accounting Ratios Review of Phuket Beach Hotel: Valuing Mutually Exclusive Projects case and understanding cost Cost and Leverage - Estimating cost of capital with debt, project risk vs asset risk vs risk of debt & equity Cost of Capital - Estimating cost of debt, creating value by introducing debt, Impact of leverage on risk of debt & equity, Weighted average and marginal cost of capital. Cost of Capital - Estimating cost of preference, equity, Divisional and project cost of capital, Floatation cost, Applying the CAPM to estimate a project's cost of capital, Misconceptions surrounding cost of capital. Review of Marriott Corporation: Cost of Capital Divisional Cost of Capital Excel Based Assessment Optimal capital structure, NI & NOI approach. Capital Structure - Modigiliani-Miller position & exception Working Capital Management Working Capital Management - Continued Decentralisation & methods of transfer pricing and Performance evaluation Control Issues: Performance Evaluation Review of CUC International Case Investor Relations and Communication Overview of Main Issues raised in the Module
Lecture Lecture Seminar Seminar Lecture Lecture Lecture Lecture Seminar Seminar Lecture
12
Lecture
13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
Seminar Seminar Lecture Lecture Lecture Lecture Lecture Lecture Lecture Lecture Lecture
SESSION PLAN Session 1: Introduction & Develop Projections Overview of Module, and Prepare project future Income Statement. The Income Statement measures the performance over a specific period, calculation of Earnings Before Interest and Tax(EBIT), Which represents the earnings before taxes and financing costs. Required Reading: PC Chapter-5 (Page 107-116, Financial Planning & Forecasting) Illustration: Space age Electronics. Learning Outcome: To explain the method of financial planning and forecasting.
Session 2: Project future Balance Sheet Project future Balance sheet. The Balance Sheet is an Accountants snapshot of a firms accounting value on a particular date, as though the firm stood monetarily still. This session also includes projecting of and preparing future balance sheet for Space age Electronics. Required Reading: PC Chapter-5 (Page 107-116, Financial Planning & Forecasting) Illustration: Space age Electronics. Learning Outcome: To explain the method of financial planning and forecasting.
Session 3: Develop project cash flows Perhaps the most important item that can be extracted from financial statements is the actual cash flow of the firm. Thus this session covers a study of the various elements of cash flow stream, Principles of cash flow estimation, Cash flow illustrations, Projection of future cash flows for Space age Electronics. Required Readings: PC Chapter-12 (Page 304-314, Estimation of Project Cash Flows) Learning Outcome: The student should learn how to forecast cash flows of a project before applying project selection techniques.
Session 4: Discounting cash flows Creating value, NPV and other methods of selecting plan. Capital Budgeting Decisions are a way of investing capital in profitable projects. These are long term and once taken, it is difficult to reverse them as it may involve huge costs. Thus this session covers the various techniques of evaluation capital budgeting projects such as, Net Present Value, Accounting Rate of Return, Payback period Method, etc. Required Readings: PC Chapter-12 (Page 279-298, Techniques of Capital Budgeting) MIRR-A better measure, Herbert Kieruff, 9 pages, HBSP-BH-285 Learning Outcome: Net Present Value is the best and widely used method employed for the evaluation and selection of project. Students would learn NPV and other methods of capital budgeting besides understanding the role of NPV in value creation
Session 5: Which plan should we pursue? Projecting terminal values, Links among NPV, share price & value creation. This session covers projecting of terminal values of a project and linking Net Present Value with Share price and their contribution to a firms value creation. Required Readings: PC Chapter-12 (Page 279-298, Techniques of Capital Budgeting) NPV and IRR, Accounting for time Excerpted from Manager's Tool Kit. 18 pages, HBSP 5245 BC 6
Learning Outcome: Net Present Value is the best and widely used method employed for the evaluation and selection of project. Students would learn NPV and other methods of capital budgeting besides understanding the role of NPV in value creation
Session 6: Terminal values & Industry multiples Projecting terminal values, using terminal growth rate valuation using industry multiples. The terminal value calculation is used to determine the value of the firm for all years beyond which one can reliably project cash flow using the discounted cash flows and industry multiples such as Economic Value and EBITDA. Required Readings: PC Chapter-12 (Page 279-298, Techniques of Capital Budgeting) Learning Outcome: Net Present Value is the best and widely used method employed for the evaluation and selection of project. Students would learn NPV and other methods of capital budgeting besides understanding the role of NPV in value creation
Session 7: Economic Income Economic Income and way for companies to account for changes in the value of a given asset in the market. Economic income is the way for companies to account for changes in the value of a given asset in the market. Economic income generally recognises unrealised gains, in addition to recognising realised gains. Required Readings/Video: Video on Economic Profit V/S Accounting Profit ; Khan Academy Learning Outcome: The student will understand the concept of economic income
Session 8: Economic Income & Accounting Ratios Economic Income vs NPV & ROI vs IRR, Key ratios, Zero NPV growth, Spreadsheet mechanics (Phuket Beach Hotel: Valuing Mutually Exclusive Projects). Accounting income or loss recognizes realized gains and losses, and does not recognize unrealized gains and losses. Economic income or loss recognizes all gains and losses, whether realized or unrealized. Case: Phuket Beach Hotel: Valuing Mutually Exclusive Projects case and understanding cost Learning Outcome: The student will understand the difference between accounting and economic income while appreciating key profitability and growth ratio.
Session 9: Review of Phuket Beach Hotel: Valuing Mutually Exclusive Projects case and understanding cost Top level analysis of Mutually Exclusive Projects, Basis on which the projects are called as mutually exclusive, WACC and Incremental Costs. Case: Phuket Beach Hotel: Valuing Mutually Exclusive Projects case and understanding cost Learning Outcome: The student will understand the difference between two projects on the basis of their duration and capital required and provide their judgement on the most profitable project.
Session 10: Cost & Leverages Estimating cost of capital with debt, project risk vs asset risk vs risk of debt & equity. This session covers detailed study of how to choose the discount rate when a project is all equity financed and when a project is both equity and debt financed. Required Readings: PC Chapter-14 (Page 367-386, The Cost of Capital) 7
Learning Outcome: To explain the method of calculating cost of capital and its role in evaluating a project.
Session 11: Cost of Capital Estimating cost of debt, creating value by introducing debt, Impact of leverage on risk of debt & equity, weighted average and marginal cost of capital. Understanding the effect of financial leverage on cash flows and the cost of capital. Required Readings: PC Chapter-14 (Page 367-386, The Cost of Capital) Learning Outcome: To explain the method of calculating cost of capital and its role in evaluating a project.
Session 12: Cost of Capital - continued Estimating cost of preference, equity, Divisional and project cost of capital, Floatation cost, Applying the CAPM to estimate a project's cost of capital, Misconceptions surrounding cost of capital. Understanding the calculation of cost of debt., equity, preference share capital; the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) and its use to determine a theoretically appropriate required rate of return of an asset, if that asset is to be added to an already welldiversified portfolio, given that asset's non-diversifiable risk. Required Readings: PC Chapter-14 (Page 367-386, The Cost of Capital), Chapter 9 (Page 237) Business Evaluation and Cost of Capital (11pages), Timothy A Luchermaan, Hbsp 9-210-037. Learning Outcome: To explain the method of calculating cost of capital and its role in evaluating a project.
Session 13: Review of Marriott Corporation: Cost of Capital Top level analysis of Cost of Capital and implementation of the same at Divisional level. Also, the importance of cost of capital in evaluating a project. Required Readings/Case: Marriott Corporation: Cost of Capital, Learning Outcome: The student will understand the method of calculating cost of capital and its role in evaluating a project.
Session 14: Estimating divisional cost of capital Implementation of cost of capital calculation of the same at the divisional level. Also, understanding the importance of cost of capital in evaluating a project. Required Readings: PC Chapter-14 (Page 367-386, The Cost of Capital) Learning Outcome: To explain the method of calculating cost of capital and its role in evaluating a project.
Session 15 Excel based assessment
Session 16: Capital Structure Is there an optimal capital structure, NI & NOI approach? Capital structure refers to the way a corporation finances its assets through some combination of equity, debt, or hybrid securities. A firm's capital structure is then the composition or 'structure' of its liabilities. Required Readings: PC Chapter-19 (Page 476-499, Capital Structure and Firm Value), 8
Chapter 20 (Page 511-536, Capital Structure Decision) Note on theory of Capital Structure, 7 pages; HBSP-9-279-069 Learning Outcome: To explain whether capital structure decision has an impact on share holder value.
Session 17: Capital Structure - Continued Modigiliani-Miller position, Exception to the MM theory taxes, financial distress, information asymmetric, conflict of interest. The ModiglianiMiller theorem forms the basis for modern thinking on capital structure. The basic theorem states that, under a certain market price process, in the absence of taxes, bankruptcy costs, agency costs, and asymmetric information, and in an efficient market, the value of a firm is unaffected by how that firm is financed. Required Readings: PC Chapter-19 (Page 476-499, Capital Structure and Firm Value), Chapter 20 (Page 511-536, Capital Structure Decision) Learning Outcome: To explain whether capital structure decision has an impact on share holder value.
Session 18: Working Capital Management This session covers Objectives of Net working capital, factors affecting the net working capital, Constituents of current assets and current liabilities, level of Current Assets and Current Assets financing policy and Computation of Net working Capital. Learning Outcomes: At the end of this session the students will know that Investment in current assets represents a substantial portion of total investment Factors to be considered while planning optimal working capital or the firm
Session 19: Working Capital Management - Continued This session covers Computation of Operating Cycle and Cash Cycle, Estimating cash required for working capital and concept of zero working capital. Working Capital Management involves managing the relationship between a firm's short-term assets and its short-term liabilities. In the context of long term, capital investment decisions, firm value is enhanced through appropriately selecting and funding NPV positive investments. Required Readings: Magic of Managing Balance sheet Karen Berman, Joe Knight HBSP:4978 BC, 7 pages. Learning Outcomes: At the end of this session the students will know the following: Working capital is influenced by various events of operating cycle of a firm i.e. from purchase of raw materials to collection of cash for sales Shorter the operating cycle, lesser the working capital requirements of the firm Procedure for estimating the cash requirement for working capital
Session 20: Control Issues Decentralisation & Methods of Transfer Pricing and Performance Evaluation. Decentralisation ensures correct controls are in place, will be the bottom-to-top flow of information, allowing decisions by officials of the organization to be well informed about lower tier operations. 9
Required Readings: Course Pack Learning Outcome: The student should learn mechanism of pricing inter-departmental transfer of goods, where each department has separate entity and head and how to evaluate the performance of each departmental head.
Session 21: Control Issues Performance evaluation Performance evaluation. Understanding the Mechanism of pricing transfer of goods, where each department has separate entity and evaluate the performance of each departmental head. Required Readings: Course Pack Learning Outcome: The student should learn mechanism of pricing transfer of goods, where each department has separate entity and evaluate the performance of each departmental head.
inter-departmental head and how to
inter-departmental head and how to
Session 22: Review of CUC International Case Top level analysis of the role of financial reporting and corporate finance policies as vehicles for communication between managers and outside investors. Required Readings: Course Pack Case: Marriott Corporation: Cost of Capital Learning Outcome: The student will understand the management's concern that the company's stock is undervalued because analysts viewed the company's accounting as aggressive. Students are asked to advise CUC's management on ways to improve investor confidence.
Session 23: Investor Relations & Communications When investors can't see what management can see or disagree with management's expectations, Managing investor expectations, Different channels of communication with investors, regulatory aspects of public investor base. Required Readings: Course Pack Case: CUC International (The group will submit a write up on the day as told by the faculty and also make a presentation) Learning Outcome: To learn how to manage investor relations and their expectations.
Session 24: Overview of main issues raised in Module
ASSESSMENT PLAN
S. Assessment Method no. 1 2 3 Excel based assessment Case Analysis End- Term
Marks 5 5 20 10
DETAILS OF ASSESSMENT Component 1: Excel based assessment (5 marks) Concepts covered till session 14 will be assessed. Component 2: Case Analysis (5 marks) Each group of six students will prepare a write-up for the assigned case. This write-up should be in the form of a business report not exceed 3 pages. Any supporting analysis can be attached as appendices. Each group will make a presentation on the three assigned cases as mentioned above. Component 3: End-Term Exam (5marks) A three-hour, closed book end-term examination will be held at the conclusion of the Module. The examination will test students' theoretical understanding through questions and their ability to apply theory to practice through case-lets. Feedback on students' performance in the exam will be provided when answer scripts are shown to students after a month of the exam.
CURRICULUM MAP Programme Learning Outcomes This table shows in which modules the main learning outcomes are developed and/or assessed: Module Sourcing & Managing Funds L1 * L2 * L3 * L4 * L5 * L6 L7 L8 L9
L-1: An understanding of organizations, their external context and their management. L-2: An awareness of current issues in business and management which is informed about research and practice in the field. L-3: An understanding of appropriate techniques sufficient to allow investigation into relevant business and management issues. L-4: The ability to acquire and analyse data and information. L-5: The ability to apply relevant knowledge to practical situations. L-6: The ability to work and lead effectively in a team based environment. L-7: An improvement in both oral and written communication skills L-8: Be cognizant of the impact of their individual & corporate actions on society and recognize ethical business practices. L-9: Be sensitive to the social, economic and environmental responsibilities of business.
TEACHING MAP This table shows the main delivery methods which are used across modules and stages: Module T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 11
Sourcing & * Managing Funds Notes: Delivery Methods: T1: Lectures T2: Seminars/tutorials T3: Live Projects and Presentations T4: Case Study T5: Guest Lectures T6: Lab Sessions
ASSESSMENT MAP This table shows the main assessment methods which are used across modules and stages: Module A1 A2 A3 A4 * A5 *
Sourcing & Managing * Funds Notes: A1: Individual assignment/case study A2: Group assignment/project/business plan A3: Open book examination/case study A4: Closed book examination A5: Group presentation
12
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- QuestionsDocument9 pagesQuestionsashisparida08No ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Evalueserve Intern ProfileDocument1 pageEvalueserve Intern Profileashisparida08No ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Industrial Visit YakultDocument21 pagesIndustrial Visit YakultIibs Noida Noida100% (1)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Note On Three-Pane ModelDocument6 pagesNote On Three-Pane ModelTanay Pandey50% (4)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
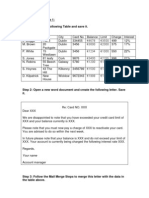
- Mail Merge Excercie 1Document2 pagesMail Merge Excercie 1ashisparida0871% (7)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- HCL Technologies Project Report on Products and SolutionsDocument7 pagesHCL Technologies Project Report on Products and Solutionsashisparida08No ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Industrial Visit YakultDocument21 pagesIndustrial Visit YakultIibs Noida Noida100% (1)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Kartikey Vasaniya: Academic BackgroundDocument1 pageKartikey Vasaniya: Academic Backgroundashisparida08No ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Industrial Visit YakultDocument21 pagesIndustrial Visit YakultIibs Noida Noida100% (1)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Bussiness Communication (Term 1)Document20 pagesBussiness Communication (Term 1)ashisparida08No ratings yet
- Graph Logarithmic FunctionsDocument3 pagesGraph Logarithmic FunctionsDerren Nierras Gaylo100% (1)
- IASG Thematic Paper - Education - Rev1Document17 pagesIASG Thematic Paper - Education - Rev1Black BullsNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Final Portfolio EssayDocument7 pagesFinal Portfolio Essayapi-340129196No ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- 9 Signs You'Re An Old SoulDocument3 pages9 Signs You'Re An Old SoulJorge Ramírez VelazcoNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Londie T. Martin - Dissertation AbstractDocument2 pagesLondie T. Martin - Dissertation AbstractLondie T. MartinNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Postgraduate Seeks Disarmament InternshipDocument2 pagesPostgraduate Seeks Disarmament Internshipfmurray128934No ratings yet
- Annotated Bibiliography ResearchDocument6 pagesAnnotated Bibiliography Researchpem100% (1)
- Career Decisions 3 02 WorksheetDocument7 pagesCareer Decisions 3 02 Worksheetapi-359030415No ratings yet
- Nikbakht H. EFL Pronunciation Teaching - A Theoretical Review.Document30 pagesNikbakht H. EFL Pronunciation Teaching - A Theoretical Review.researchdomain100% (1)
- Nasa PresentationDocument16 pagesNasa PresentationVishal NimbrayanNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Automotive Battery Servicing (CBLM)Document3 pagesAutomotive Battery Servicing (CBLM)MARY JOY AGMIT100% (8)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Dharma Talk Given by Jordan KramerDocument3 pagesDharma Talk Given by Jordan KramerjordanmettaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Name E-Mail ID MobileDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Name E-Mail ID MobileAvik KunduNo ratings yet
- Cled Grade 7 Las05 Q4Document2 pagesCled Grade 7 Las05 Q4Val RenonNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Lesson Plan English 9 MayDocument2 pagesLesson Plan English 9 MayPerakash KartykesonNo ratings yet
- Belief StatementDocument7 pagesBelief Statementapi-366576866No ratings yet
- Listening SkillsDocument9 pagesListening SkillsMohd Shabir100% (1)
- Genki English Top 50 Games eBookDocument52 pagesGenki English Top 50 Games eBookManu Mtnz Rabadán100% (2)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- At WellDocument9 pagesAt Wellamsi2009No ratings yet
- Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering & Technology: Application Form For Faculty PositionsDocument4 pagesGokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering & Technology: Application Form For Faculty PositionsMohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Ecd 201 Professional Career PlanDocument8 pagesEcd 201 Professional Career Planapi-457148195No ratings yet
- Vote of ThanksDocument4 pagesVote of Thanksrosanth5713100% (1)
- Verbal Abuse-Irony RaftDocument8 pagesVerbal Abuse-Irony Raftapi-282043501No ratings yet
- Syllabus - Hoa Iii - Sy 2017-2018Document6 pagesSyllabus - Hoa Iii - Sy 2017-2018smmNo ratings yet
- India - State Education Report - TamilnaduDocument24 pagesIndia - State Education Report - TamilnaduMonica DhanasekarNo ratings yet
- System: Priscila Leal, Graham V. CrookesDocument11 pagesSystem: Priscila Leal, Graham V. CrookesShaimoz Ithe WatuirituNo ratings yet
- School & SocietyDocument142 pagesSchool & Societykedir aymelloNo ratings yet
- Dll-Tle-He 6 Q1 - W1Document4 pagesDll-Tle-He 6 Q1 - W1John Patrick D. Enoya100% (2)
- The Use of Moocs As A Potential Avenue To Modernize Learning in The PhilippinesDocument19 pagesThe Use of Moocs As A Potential Avenue To Modernize Learning in The PhilippinesJohn LloydNo ratings yet
- Lean OutlineDocument2 pagesLean OutlineTee Hor ChangNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)