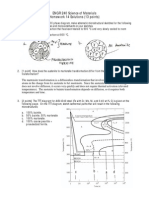
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gradient of A Scalar Field - Web Formulas
Uploaded by
Shiwam IsrieOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gradient of A Scalar Field - Web Formulas
Uploaded by
Shiwam IsrieCopyright:
Available Formats
Gradient of a Scalar Field - Web Formulas
http://www.web-formulas.com/Math_Formulas/Linear_Algebra_Gradie...
Search Sign up | Login Home | Math | Physics | Chemistry | Biology | Other | Tools Current Location > Math Formulas > Linear Algebra > Gradient of a Scalar Field
0
Like
Gradient of a Scalar Field
Distance Measuring DMI
DOT-Z1 DMI w/ GPS is very accurate, easy, & portable. No wiring or VSS!
www.micdynamics.com
Recently Added Math Formulas
Divergence of a Vector Field Stokes' Theorem Definition of the Determinant Definition of an Inverse of a Matrix Definition of Zero Matrix
The gradient of a scalar field is a vector field and whose magnitude is the rate of change and which points in the direction of the greatest rate of increase of the scalar field. If the vector is resolved, its components represent the rate of change of the scalar field with respect to each directional component. Hence for a two-dimensional scalar field (x,y).
And for a three-dimensional scalar field (x, y, z)
The gradient of a scalar field is the derivative of f in each direction. Note that the gradient of a scalar field is a vector field. An alternative notation is to use the del or nabla operator, f = grad f. For a three dimensional scalar, its gradient is given by:
Additional Formulas
Cartesian Coordinate Cylindrical Coordinate Spherical Coordinate Transform from Cartesian to Cylindrical Coordinate Transform from Cartesian to Spherical Coordinate Transform from Cylindrical to Cartesian Coordinate Transform from Spherical to Cartesian Coordinate Divergence Theorem/Gauss' Theorem Stokes' Theorem Definition of a Matrix
Gradient is a vector that represents both the magnitude and the direction of the maximum space rate of increase of a scalar. dV = (V) dl, where dl = ai dl In Cartesian
In Cylindrical
In Spherical
Properties of gradient We can change the vector field into a scalar field only if the given vector is differential. The given vector must be differential to apply the gradient phenomenon. The gradient of any scalar field shows its rate and direction of change in space. Example 1: For the scalar field (x,y) = 3x + 5y,calculate gradient of . Solution 1: Given scalar field (x,y) = 3x + 5y
Example 2: For the scalar field (x,y) = x4yz,calculate gradient of . Solution: Given scalar field (x,y) = x4yz
1 of 2
11/13/2012 10:16 PM
Gradient of a Scalar Field - Web Formulas
http://www.web-formulas.com/Math_Formulas/Linear_Algebra_Gradie...
Web-Formulas.com 2012 | Contact us | Terms of Use | Privacy Policy |
2 of 2
11/13/2012 10:16 PM
You might also like
- Grad Div CurlDocument3 pagesGrad Div CurlrodwellheadNo ratings yet
- Vector CalculusDocument52 pagesVector CalculusYeri KimNo ratings yet
- Del OperatorDocument39 pagesDel OperatorBryx William Garcia100% (1)
- Vector Analysis PDFDocument27 pagesVector Analysis PDFahmedNo ratings yet
- Motion in Two Dimensions: Onceptual UestionsDocument40 pagesMotion in Two Dimensions: Onceptual UestionsranahajNo ratings yet
- Vectors and Dirac Delta FunctionDocument39 pagesVectors and Dirac Delta FunctionSubrata RakshitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Motion2DDocument40 pagesChapter 3 Motion2Dredz00No ratings yet
- chpt2 Vector Analysis Part 2Document25 pageschpt2 Vector Analysis Part 2Ahmet imanlıNo ratings yet
- Gradient - Wikipedia PDFDocument10 pagesGradient - Wikipedia PDFOm Prakash SinghNo ratings yet
- Attenuating Diffracted Multiples with Apex-Shifted Radon TransformDocument14 pagesAttenuating Diffracted Multiples with Apex-Shifted Radon Transformmohamed_booksNo ratings yet
- Vector Derivatives Cylindrical Coordinates - RheaDocument8 pagesVector Derivatives Cylindrical Coordinates - RheaSubhashisGhoshNo ratings yet
- 1staticfields SN WB Part1Document7 pages1staticfields SN WB Part1sameer ghawanaNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus 2Document21 pagesVector Calculus 2Hergene FanerNo ratings yet
- Vector and Tensor Analysis 3Document5 pagesVector and Tensor Analysis 3Meetu KaurNo ratings yet
- Lec 6-13 Plane Curvilinear MotionDocument76 pagesLec 6-13 Plane Curvilinear MotionSaqib SherNo ratings yet
- Vector Analysis and Coordinate SystemsDocument127 pagesVector Analysis and Coordinate SystemsPriyanka KumariNo ratings yet
- AP Math - 154-1Document42 pagesAP Math - 154-1laurenemetcalfNo ratings yet
- An1 Derivat - Ro BE 2 71 Mathematical AspectsDocument8 pagesAn1 Derivat - Ro BE 2 71 Mathematical Aspectsvlad_ch93No ratings yet
- Understanding Vector Calculus: Practical Development and Solved ProblemsFrom EverandUnderstanding Vector Calculus: Practical Development and Solved ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Vector calculus from wiki PDFDocument52 pagesVector calculus from wiki PDFLynn Hollenbeck BreindelNo ratings yet
- Scalar MultiplicationDocument13 pagesScalar MultiplicationBalayya BNo ratings yet
- Motion in Plane NotesDocument9 pagesMotion in Plane NotesK S SayyedNo ratings yet
- NSSCAS Physics Mathematical Requirements - 30 September 2020Document54 pagesNSSCAS Physics Mathematical Requirements - 30 September 2020Peter KudumoNo ratings yet
- Shear transformation of vector 3i^+2jDocument23 pagesShear transformation of vector 3i^+2jIgorJales100% (1)
- EMF Theory by Sangeen PanezaiDocument100 pagesEMF Theory by Sangeen PanezaiSangeen Panezai0% (1)
- Unit-Iii Electromagnetic Waves - NotesDocument13 pagesUnit-Iii Electromagnetic Waves - NotesAnusha KovuruNo ratings yet
- Mathematics For Physics 2023. Chapter 1Document61 pagesMathematics For Physics 2023. Chapter 1Tuyết VânNo ratings yet
- Coordinate TransformationDocument9 pagesCoordinate TransformationJagdeep SekhonNo ratings yet
- Gradient of A Scalar Field Curl of A Vector FieldDocument22 pagesGradient of A Scalar Field Curl of A Vector FieldULtraSwoRDFiSHNo ratings yet
- Calculations With Magnitude and Direction: R Vector From LA To Las Vegas Has X 290 KMDocument50 pagesCalculations With Magnitude and Direction: R Vector From LA To Las Vegas Has X 290 KMemailymNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10. Equations of Motion - Introduction - W - AudioDocument25 pagesLecture 10. Equations of Motion - Introduction - W - AudioLeah Marie MahomocNo ratings yet
- Chap3 S11Document36 pagesChap3 S11Kasi FilsNo ratings yet
- CSS Physics 1 Notes Sample PaperDocument30 pagesCSS Physics 1 Notes Sample PaperM Faadi Malik100% (1)
- Emt (Ee) PDFDocument55 pagesEmt (Ee) PDFckvirtualize100% (4)
- Vector Calculus ConceptsDocument10 pagesVector Calculus ConceptsShubha VSNo ratings yet
- Peter's Index Lecture 2b Course Index: Physics HomeDocument6 pagesPeter's Index Lecture 2b Course Index: Physics Homereza mohammadianNo ratings yet
- VectorsDocument24 pagesVectorsdiane hoylesNo ratings yet
- Bwu Bta 22 187 MathDocument13 pagesBwu Bta 22 187 MathSayan SarkarNo ratings yet
- Kriging InterpolationDocument49 pagesKriging InterpolationJimmy MaharadjaNo ratings yet
- EC5302 ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS AND VECTOR ANALYSISDocument77 pagesEC5302 ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS AND VECTOR ANALYSISmumamaduraiNo ratings yet
- Curvilinear Motion AnalysisDocument51 pagesCurvilinear Motion AnalysisronieNo ratings yet
- EE340 Week4 Ch3 AhmedDocument46 pagesEE340 Week4 Ch3 AhmedMo7RahiNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus IdentitiesDocument6 pagesVector Calculus IdentitiesLorenzo CyprusNo ratings yet
- Physics - 05Document33 pagesPhysics - 05Raiyan IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Divergence and CurlDocument8 pagesDivergence and CurlaliNo ratings yet
- Vector Analysis FundamentalsDocument48 pagesVector Analysis FundamentalsMujeeb AbdullahNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document26 pagesCH 5Narendran KumaravelNo ratings yet
- Geostatistics KrigingDocument62 pagesGeostatistics Krigingskywalk189100% (1)
- Motion in a Plane ExplainedDocument32 pagesMotion in a Plane ExplainedaasifNo ratings yet
- Scalar and Vector FieldsDocument23 pagesScalar and Vector Fieldsaqib qayyumNo ratings yet
- AET MG UniversityDocument243 pagesAET MG UniversityJobins GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Microsoft PowerPoint - 4. ELMAG - 1 - Vector CalculusDocument86 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - 4. ELMAG - 1 - Vector CalculusDeni RistiantoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Field and Waves: EE 221 Spring 2004Document34 pagesElectromagnetic Field and Waves: EE 221 Spring 2004Ali Ahmad100% (1)
- AM Final SlidesDocument58 pagesAM Final Slideskrishna50bloggingNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Gauss Nodes Revolution: Numerical Integration Theory Radically Simplified And GeneralisedFrom EverandGauss Nodes Revolution: Numerical Integration Theory Radically Simplified And GeneralisedNo ratings yet
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- Introduction to LATEX BasicsDocument35 pagesIntroduction to LATEX BasicsShiwam IsrieNo ratings yet
- Formularium PDFDocument3 pagesFormularium PDFShiwam IsrieNo ratings yet
- Manual For Siemens S300 & S400Document238 pagesManual For Siemens S300 & S400Shiwam IsrieNo ratings yet
- Hmi MP177 Operating Instructions en US en-USDocument256 pagesHmi MP177 Operating Instructions en US en-USSuthep LairusameeNo ratings yet
- S7200SH 2Document546 pagesS7200SH 2Shiwam IsrieNo ratings yet
- E20001 A2200 p272 X 7600 - 2Document8 pagesE20001 A2200 p272 X 7600 - 2Shiwam IsrieNo ratings yet
- S7200SH 2Document546 pagesS7200SH 2Shiwam IsrieNo ratings yet
- Siemens S7-300 CPUDocument7 pagesSiemens S7-300 CPUTio_louis32No ratings yet
- s71200 System Manual en-US en-USDocument864 pagess71200 System Manual en-US en-USTO HaioceankNo ratings yet
- S7 1200 Getting Started en-US en-USDocument60 pagesS7 1200 Getting Started en-US en-USShiwam IsrieNo ratings yet
- Hmi Mp377 Mp377pro Operating Instructions en-US en-USDocument340 pagesHmi Mp377 Mp377pro Operating Instructions en-US en-USroypearsonNo ratings yet
- Ipc427c enDocument5 pagesIpc427c enShiwam IsrieNo ratings yet
- Brochure Simatic-Et200 en 2Document60 pagesBrochure Simatic-Et200 en 2Shiwam IsrieNo ratings yet
- Fix32 Scada-3Document50 pagesFix32 Scada-3Shiwam Isrie100% (1)
- 18 Analog and Digital Electronics U A BakshiDocument547 pages18 Analog and Digital Electronics U A BakshiBiswanath Patro100% (3)
- Radiowave PropagationDocument94 pagesRadiowave Propagationala_a_silawi100% (8)
- Tempmeasurement 120713052607 Phpapp01Document88 pagesTempmeasurement 120713052607 Phpapp01Shiwam IsrieNo ratings yet
- 1785 sg001 - en P - 10Document60 pages1785 sg001 - en P - 10Shiwam IsrieNo ratings yet
- Programming ExplanationDocument10 pagesProgramming ExplanationShiwam IsrieNo ratings yet
- Help Within Labview: Detailed Explanation: Ni Example FinderDocument4 pagesHelp Within Labview: Detailed Explanation: Ni Example FinderasutoshpatNo ratings yet
- Debugging ExplanationDocument6 pagesDebugging ExplanationasutoshpatNo ratings yet
- Graphical Programming: Detailed Explanation: Data FlowDocument3 pagesGraphical Programming: Detailed Explanation: Data FlowasutoshpatNo ratings yet
- LabVIEW ExercisesDocument31 pagesLabVIEW ExercisesShiwam IsrieNo ratings yet
- Execution Structures: Detailed Explanation: While LoopsDocument8 pagesExecution Structures: Detailed Explanation: While LoopsasutoshpatNo ratings yet
- Datatypes ExplanationDocument12 pagesDatatypes ExplanationasutoshpatNo ratings yet
- Fluke 39.41b Use'r ManualDocument74 pagesFluke 39.41b Use'r ManualShiwam IsrieNo ratings yet
- NI LabVIEW Environment - Detailed ExplanationDocument9 pagesNI LabVIEW Environment - Detailed ExplanationsastrakusumawijayaNo ratings yet
- Using Labview To Measure Temperature With A ThermistorDocument18 pagesUsing Labview To Measure Temperature With A ThermistorjdaudpotoNo ratings yet
- Peer To PeerDocument15 pagesPeer To PeerAdopted BrillianceNo ratings yet
- 07 Maxwell's EquationsDocument28 pages07 Maxwell's EquationsShiwam IsrieNo ratings yet
- SF6 Circuit Breakers AdvantagesDocument4 pagesSF6 Circuit Breakers Advantagessekhar_ntpcNo ratings yet
- Entalglement - Amir D Aczel PDFDocument4 pagesEntalglement - Amir D Aczel PDFAlejandro LimaNo ratings yet
- Physics STPM Chapter 4Document2 pagesPhysics STPM Chapter 4nurulahmad37No ratings yet
- Precalculus Unit 6 Vectors NotesDocument30 pagesPrecalculus Unit 6 Vectors Notesapi-287816312100% (1)
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region XiDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region XiArgie Joy Marie AmpolNo ratings yet
- Remainder TheoremDocument2 pagesRemainder TheoremKurarin Jan MaikeruNo ratings yet
- Curvature Radiation From A Quantum-Electrodynamics Point of ViewDocument22 pagesCurvature Radiation From A Quantum-Electrodynamics Point of ViewMohammed NourNo ratings yet
- Tribologija TribologyDocument156 pagesTribologija Tribologypajoslav83100% (1)
- MATE464 W4 Tribology v2Document87 pagesMATE464 W4 Tribology v2Tuna CanNo ratings yet
- 08 Contour IntegrationvhdhdDocument14 pages08 Contour IntegrationvhdhdxhfakqaawuorgxbwneNo ratings yet
- TriodeDocument7 pagesTriodeAnonymous E4Rbo2sNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange Chromatography Separates ProteinsDocument3 pagesIon Exchange Chromatography Separates ProteinsAdeliza MortallaNo ratings yet
- Vacuum, General Relativity: PHY100 The Nature of The Physical WorldDocument21 pagesVacuum, General Relativity: PHY100 The Nature of The Physical WorldJacecosmozNo ratings yet
- ADV-1 Phase-2 ITR B-Lot T-171473Document15 pagesADV-1 Phase-2 ITR B-Lot T-171473Ashish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Bonding IPADDocument4 pagesStructure and Bonding IPADLarissa RubarajNo ratings yet
- Symmetry and Group TheoryDocument24 pagesSymmetry and Group Theorywicki0007100% (1)
- Chemistry Code No. 1/2 Set: 3 Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 100 General InstructionsDocument5 pagesChemistry Code No. 1/2 Set: 3 Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 100 General InstructionsShalini KumariNo ratings yet
- Homework 14 Solutions Spring 2001Document2 pagesHomework 14 Solutions Spring 2001Ikhwan Wf Miscellaneous AveroesNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument82 pagesMicrobiologyAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Bab 1 Ee201Document29 pagesBab 1 Ee201Noor Hanisah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- The Special Theory of RelativityDocument16 pagesThe Special Theory of Relativityyohanse mehabawNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Reactor InstrumentationDocument12 pagesNuclear Reactor InstrumentationRachit KanchanNo ratings yet
- Generator Van de GraaffDocument6 pagesGenerator Van de GraaffDinar PinandhitaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Engineering Question BankDocument5 pagesNuclear Engineering Question Bankaerochandru.87No ratings yet
- Maharashtra HSC Physics Paper 2 - TargetDocument17 pagesMaharashtra HSC Physics Paper 2 - Targetanujtheterrible100% (2)
- Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Hyderabad M.Tech II Semester Examinations Structural Dynamics QuestionsDocument3 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Technological University Hyderabad M.Tech II Semester Examinations Structural Dynamics QuestionsFrank JohnNo ratings yet
- Shear Building - SeismicDocument13 pagesShear Building - SeismicArut MV100% (1)
- CH04 - Heat Exchanger - AmanDocument104 pagesCH04 - Heat Exchanger - AmanNabilah MustafaNo ratings yet
- Geodesic MathDocument21 pagesGeodesic Matherbercam0% (1)
- Viscous ForceDocument20 pagesViscous ForceMostafaNo ratings yet