Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology Revision Worksheet
Uploaded by
skeltenboiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology Revision Worksheet
Uploaded by
skeltenboiCopyright:
Available Formats
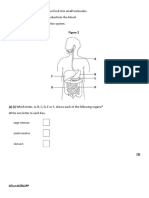
Biology Revision 1. The diagram shows some of the structures in the thorax.
Exhaled air
16%
3.0%
(i) Explain why exhaled air contains less oxygen than inhaled air. [2] (ii) Why does exhaled air contain more carbon dioxide than inhaled air? [2] 2. Yeast is a microscopic fungus which is able to respire without oxygen. A student set up the following apparatus to investigate respiration in yeast.
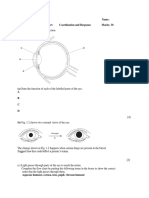
(a) Name the structures labelled A, B, C, D and E. [5] (b) Match the correct letter from the diagram with the following: (i) a structure which contains alveoli. [1] (ii) a structure which carries air into the lungs. [1] (iii) a structure which contracts and moves downwards when we breathe in. [1] (c) Name the structure found at the position marked X. [1] (d) The table shows some of the differences between inhaled and exhaled air. Oxygen Inhaled air 21% Carbon dioxide 0.03% 1 (a) Explain why the yeast and sugar solution was made up in boiled and cooled water. [2] (b) After some time bubbles of a gas were seen in the test tube. What was this gas? [1] (c) The limewater was clear at the start of the investigation. What colour would it be after 20 minutes? [1] (d) A student set up two sets of apparatus, one at 10oC and one at 30oC. The student timed how long it took for the limewater to change colour.
(i) Name three things you would do to make sure this was a fair test? [3] (ii) At which temperature would the limewater change colour most quickly? [1] (iii) Give a reason for your answer. [2] 3. The graph shows the level of lactic acid in the blood before, during and after a period of exercise.
(e) After exercise the amount of oxygen taken in is approximately double the normal intake. Account for this difference. [2] 4. The diagram shows a section through an alveolus and a surrounding blood vessel
(a) Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D. [4] (b) What type of blood vessel is E? [1] (c) Name the gas moving in the direction shown by (i) arrow X. [1] (ii) arrow Y. [1] (d) Name the process by which gases pass across the alveolar walls. [1] (a) What was the normal level of lactic acid in the blood? [1] (b) By how much did the level of lactic acid increase during exercise? [1] (c) How long after the period of exercise did it take for the lactic acid concentration to return to normal? [1] (d) Name the process which produces lactic acid. [1] 2 (e) What do the arrows Z represent? [1] (f) What happens to oxygen once it has entered the blood? [2] (g) The air breathed into the body often contains dust and bacteria. How are these prevented from entering the alveoli? [3]
You might also like
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Transport In HumansFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Transport In HumansNo ratings yet
- S 495160Document4 pagesS 495160Khondokar Tarakky0% (1)
- Asset QuestionsDocument4 pagesAsset QuestionsReshma SharmaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Coordination and Response WsDocument2 pagesIGCSE Coordination and Response WsAnand Kumar ShuklaNo ratings yet
- 1 How Plants Grow and Chapt1 of Book3 PhotosynDocument15 pages1 How Plants Grow and Chapt1 of Book3 Photosynrashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Answers Chapters 01 05Document7 pagesIGCSE Answers Chapters 01 05María Eugenia MolteniNo ratings yet
- KS3 Science 2005 Paper 1 Level 3-6Document36 pagesKS3 Science 2005 Paper 1 Level 3-6Qiana Hayward100% (2)
- CH 7 Respiration StudentDocument25 pagesCH 7 Respiration StudentHamirah Abd HamidNo ratings yet
- (42 Marks) Answer All Question: Section ADocument15 pages(42 Marks) Answer All Question: Section AGie KieNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Biology RevisionDocument13 pagesYear 8 Biology RevisionKHAUSALYA A/P VERAKUMARNo ratings yet
- 01 Biology Exploring LifeDocument63 pages01 Biology Exploring LifeEphraim BonasoNo ratings yet
- GEP Worksheets - Diffusion and Osmosis RevisedDocument10 pagesGEP Worksheets - Diffusion and Osmosis RevisedprameetaNo ratings yet
- Breathing AnswersDocument9 pagesBreathing AnswersTamicka Bonnick100% (1)
- Revision Practice Questions - Cells & TransportDocument11 pagesRevision Practice Questions - Cells & TransportMarina BrazendaleNo ratings yet
- Unit Test-I, First Term 2018: Maavashu School L.Maavah/ Rep - of MaldivesDocument7 pagesUnit Test-I, First Term 2018: Maavashu School L.Maavah/ Rep - of MaldivesBalakrishnan MarappanNo ratings yet
- Biology Drawing Skills Handbook PDFDocument20 pagesBiology Drawing Skills Handbook PDFAna SantosNo ratings yet
- 4 Microorganisms QueDocument6 pages4 Microorganisms Querashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- 9Bb-6 Leaves and RootsDocument1 page9Bb-6 Leaves and RootsHAMAD NoorNo ratings yet
- Year 8 - Food and Digestion and RespirationDocument11 pagesYear 8 - Food and Digestion and RespirationAngeline Ngou100% (1)
- IGCSE Biology Revision Notes - Kingdoms, ClassificationDocument4 pagesIGCSE Biology Revision Notes - Kingdoms, ClassificationClara ToNo ratings yet
- Characteristics-and-classification-of-living-organisms-Paper 2 Classified Solved Question CIE IGCSE GCSE OLevel BiologyDocument32 pagesCharacteristics-and-classification-of-living-organisms-Paper 2 Classified Solved Question CIE IGCSE GCSE OLevel BiologyIGCSE Physics & ChemistryNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument5 pagesRespiratoryKrisdiansah PurnawidjajaNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Pranav BISUMBHER - G8 Assignment 2 Gas PressureDocument2 pagesKami Export - Pranav BISUMBHER - G8 Assignment 2 Gas PressurePranav BISUMBHER100% (2)
- Cells, Diffusion & Osmosis QuestionsDocument11 pagesCells, Diffusion & Osmosis QuestionsGozde Ozan BayraktarNo ratings yet
- Biology: PAPER 1 Multiple ChoiceDocument20 pagesBiology: PAPER 1 Multiple ChoiceAdnan AshrafNo ratings yet
- Characteristics & Classification of Living Organisms (Multiple Choice) 2 QPDocument8 pagesCharacteristics & Classification of Living Organisms (Multiple Choice) 2 QPAdetohunNo ratings yet
- Biology CH 7 Practice TestDocument6 pagesBiology CH 7 Practice Testvaleria100% (2)
- Worksheet Grade 8 Gas ExchangeDocument4 pagesWorksheet Grade 8 Gas ExchangeListya RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument9 pagesTransport in PlantsNithoo NishNo ratings yet
- G8 Enzymes & Body Systems Progress Test SY 2017 - 18Document5 pagesG8 Enzymes & Body Systems Progress Test SY 2017 - 18pixelhoboNo ratings yet
- Exercises Bio f4 c3Document7 pagesExercises Bio f4 c3Azlin ShahNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Science Paper Inset Days PDFDocument56 pagesYear 8 Science Paper Inset Days PDFA.K MonNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheets: The Plant KingdomDocument8 pagesSummary Sheets: The Plant KingdomEngy AlasutyNo ratings yet
- Biology Revision GuideDocument22 pagesBiology Revision GuidePoornima AthikariNo ratings yet
- Respiration QuestionsDocument2 pagesRespiration QuestionsAnonymous Azxx3Kp9100% (1)
- Revision-Forces and Motion-Grade 9Document12 pagesRevision-Forces and Motion-Grade 9Nour A100% (1)
- Quiz 1Document4 pagesQuiz 1Sylva SagitaNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Practice TestDocument7 pagesStates of Matter Practice TestMuhammad AhmadNo ratings yet
- 7a QPDocument7 pages7a QPsureshthevanNo ratings yet
- G8 Preparation of Salts Lab ExperimentDocument4 pagesG8 Preparation of Salts Lab Experimentaswin100% (1)
- Ks3 Chem 7g Eq 64marks Solids Liquids and Gases Only 14pgsDocument14 pagesKs3 Chem 7g Eq 64marks Solids Liquids and Gases Only 14pgsRumeysaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Test IgcseDocument9 pagesCambridge Test IgcseMeily ZoelNo ratings yet
- Work Out Biology For First Examinations (PDFDrive)Document268 pagesWork Out Biology For First Examinations (PDFDrive)Rico ChanNo ratings yet
- 7a End of Unit Test StandardDocument6 pages7a End of Unit Test StandardMajdoline Sadeddine100% (1)
- Grade 7 ChemDocument19 pagesGrade 7 ChemAnand Kumar ShuklaNo ratings yet
- 4.8 Sexual Reproductive System of Flowering PlantsDocument2 pages4.8 Sexual Reproductive System of Flowering PlantsdeviliceNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants (Vascular Bundle)Document6 pagesTransport in Plants (Vascular Bundle)Ahmed Kaleem Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis AnswersDocument9 pagesHomeostasis AnswersNur AmalinaNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgD13y6nWhFyA0ttCoBgCto3PkxIXkalLGmOKI2bAzX8L5UjynI-07Mkcbtfktx9YGVwOJ2iMyy kYQs4kPekkmeFVccUKI9RG19EriRDFPXptY PlUgLFGCHQ PDFDocument36 pagesACFrOgD13y6nWhFyA0ttCoBgCto3PkxIXkalLGmOKI2bAzX8L5UjynI-07Mkcbtfktx9YGVwOJ2iMyy kYQs4kPekkmeFVccUKI9RG19EriRDFPXptY PlUgLFGCHQ PDFN3P FrostNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions For KS3 - WorksheetDocument3 pagesChemical Reactions For KS3 - Worksheetmadam100% (1)
- Topic 1 Test - Cells & Organisms 2019.pdf AnsDocument9 pagesTopic 1 Test - Cells & Organisms 2019.pdf AnsHal OgleNo ratings yet
- Key Stage 3 ks3 Science 36P2 2009Document32 pagesKey Stage 3 ks3 Science 36P2 2009rusniza abdul razakNo ratings yet
- 7E7F SATs Question BookletDocument28 pages7E7F SATs Question BookletangeltwinkleNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 U4Document3 pagesTopic 1 U4api-263323894No ratings yet
- Topic 8 Revision Notes 2btdx6pDocument4 pagesTopic 8 Revision Notes 2btdx6psalmasomaNo ratings yet
- G7 Respiration Revision 1Document7 pagesG7 Respiration Revision 1PRIYA100% (1)
- Topic 1 Quantitative SLHL Test ADocument9 pagesTopic 1 Quantitative SLHL Test APak Hei Marcus CHOWNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: HistopathologyDocument2 pagesAssignment 1: Histopathologyskeltenboi100% (2)
- Chapter 6 - Movement of Molecules Across MembranesDocument47 pagesChapter 6 - Movement of Molecules Across MembranesskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- Practical 4 To Observe The Property of Acids and Base: Segi College Kuala LumpurDocument2 pagesPractical 4 To Observe The Property of Acids and Base: Segi College Kuala LumpurskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Practical ManualDocument10 pagesParasitology Practical Manualskeltenboi100% (1)
- Acid - Base Titration: PracticalDocument2 pagesAcid - Base Titration: PracticalskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- Transition Elements IntroductionDocument11 pagesTransition Elements IntroductionskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- Liver Enzyme LabDocument2 pagesLiver Enzyme LabskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- Biologi Tingkatan 5 Bab 3 Rangsangan Gerakbalas - Ms.enDocument19 pagesBiologi Tingkatan 5 Bab 3 Rangsangan Gerakbalas - Ms.enskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- J-Tube Experiment Sample AnsDocument3 pagesJ-Tube Experiment Sample Ansskeltenboi100% (3)
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 6Document37 pagesBiology Form 4 Chapter 6skeltenboiNo ratings yet
- Bio Form 4 Chapter 6: NutritionDocument9 pagesBio Form 4 Chapter 6: NutritionskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: HistopathologyDocument2 pagesAssignment 1: Histopathologyskeltenboi100% (2)
- Form 4 Biology Chapter 5 Cell DivisionDocument15 pagesForm 4 Biology Chapter 5 Cell DivisionskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- Parasitology AssignmentDocument4 pagesParasitology AssignmentskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- Medical Parasitology QuestionsDocument5 pagesMedical Parasitology Questionsskeltenboi74% (19)
- Practical Session Lab Demonstrator Jan Aprl 2015 UpdatedDocument3 pagesPractical Session Lab Demonstrator Jan Aprl 2015 UpdatedskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument14 pagesChemical BondingskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- Liver Enzyme LabDocument2 pagesLiver Enzyme LabskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and Osmosis WorksheetDocument5 pagesDiffusion and Osmosis Worksheetskeltenboi100% (1)
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2Document7 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 2skeltenboiNo ratings yet
- Medical Parasitology QuestionsDocument5 pagesMedical Parasitology Questionsskeltenboi74% (19)
- Lab Safety ScenariosDocument2 pagesLab Safety Scenariosskeltenboi50% (2)
- Chemical Formulae and EquationsDocument19 pagesChemical Formulae and EquationsskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- Practical Session Lab Demonstrator Jan Aprl 2015 UpdatedDocument3 pagesPractical Session Lab Demonstrator Jan Aprl 2015 UpdatedskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- Reflective Writing Guide - Brodie PDFDocument20 pagesReflective Writing Guide - Brodie PDFjparanotiNo ratings yet
- PAR 2314 Course OutlineDocument5 pagesPAR 2314 Course OutlineskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- MEL 1232 Course OutlineDocument6 pagesMEL 1232 Course OutlineskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Exercise 1 - Dot-Cross DiagramsDocument1 page1.3 Exercise 1 - Dot-Cross DiagramsskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- Water Samples Results Tables 1 - MICHAELDocument3 pagesWater Samples Results Tables 1 - MICHAELskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- Exam Detail ChemistryDocument1 pageExam Detail ChemistryskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- Kill Team List - Eldar v2.1Document6 pagesKill Team List - Eldar v2.1Rogal DornNo ratings yet
- 1.. Resume Untad Respirasi Dr. ZAENAL MUTTAQINDocument26 pages1.. Resume Untad Respirasi Dr. ZAENAL MUTTAQINNi Made Dwiki AndriyaniNo ratings yet
- Extended Cold Weather Clothing System: ComponentsDocument3 pagesExtended Cold Weather Clothing System: ComponentsSokolov ShermenNo ratings yet
- Ppe and First AidDocument5 pagesPpe and First Aidjela rose camilonNo ratings yet
- Punch PowerDocument2 pagesPunch PowerguidocesanoNo ratings yet
- S-Works Camber 29 S-Works Camber 29 Frame: Specs Key Features Specs Key FeaturesDocument4 pagesS-Works Camber 29 S-Works Camber 29 Frame: Specs Key Features Specs Key FeaturesSickLinesNo ratings yet
- Anti-Skid Braking System (ABS)Document24 pagesAnti-Skid Braking System (ABS)Rajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- TF22 - DCYF Meet Program (Morning)Document12 pagesTF22 - DCYF Meet Program (Morning)Ryan RaposoNo ratings yet
- GTA San Andreas CheatDocument2 pagesGTA San Andreas CheatcapthawkNo ratings yet
- Leg ExercisesDocument7 pagesLeg ExercisesChoirun Nisa Nur AiniNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Test 1Document6 pagesAdd Maths Test 1velavanNo ratings yet
- SBN Product CatalogDocument50 pagesSBN Product CatalogChien Nguyen100% (1)
- Grammar 2esoDocument5 pagesGrammar 2esoSonia GamezNo ratings yet
- Arthur Jones Nautilus Bulletin #1 - ConclusionsDocument3 pagesArthur Jones Nautilus Bulletin #1 - ConclusionsJuan Pablo100% (1)
- Cross-Country Olympic 3: Start List Men EliteDocument3 pagesCross-Country Olympic 3: Start List Men EliteClub de Ciclismo de Montaña PichinchaNo ratings yet
- Cool Yellow DudeDocument7 pagesCool Yellow Dudemelany323No ratings yet
- Soulbound - Dark Industrial FantasyDocument458 pagesSoulbound - Dark Industrial FantasythhpitiNo ratings yet
- BW TMDocument28 pagesBW TMCarlos CastilloNo ratings yet
- Activity in Excel Santos, Kristel JoyDocument24 pagesActivity in Excel Santos, Kristel JoyKristel Joy SantosNo ratings yet
- China Team Selection Test 1998 47Document2 pagesChina Team Selection Test 1998 47Biswarup BurmanNo ratings yet
- T900 Pre Test Inspection BookletDocument51 pagesT900 Pre Test Inspection Bookletdeming9120100% (1)
- Hocking Hills GuideDocument3 pagesHocking Hills GuideChuck LNo ratings yet
- Strength Training / Muscle Building: The Fitness WikiDocument5 pagesStrength Training / Muscle Building: The Fitness WikiRajulapati VinodkumarNo ratings yet
- Catalog Lenso 2016 PDFDocument37 pagesCatalog Lenso 2016 PDFRagea GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Tendonitis of The Long Head of The Biceps-Orthoinfo - AaosDocument5 pagesTendonitis of The Long Head of The Biceps-Orthoinfo - Aaosapi-228773845100% (1)
- ProbabilityDocument17 pagesProbabilityLochi LiyanageNo ratings yet
- Laro NG LahiDocument6 pagesLaro NG LahiSol Kizziah MeiNo ratings yet
- Baby Song Lyrics-Justin Bieber With PDF File DownloadDocument4 pagesBaby Song Lyrics-Justin Bieber With PDF File DownloadPramod RanaNo ratings yet
- HOPE-3-Quarter 2Document48 pagesHOPE-3-Quarter 2reymart100% (1)
- World of Warcraft - (2007) Tides of Darkness - Aaron RosenbergDocument125 pagesWorld of Warcraft - (2007) Tides of Darkness - Aaron RosenbergCătălina Vulpița100% (4)