Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Development 7
Uploaded by
pravin2mOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Development 7
Uploaded by
pravin2mCopyright:
Available Formats
Sr.No Q.1) Q.
2)
Q.3)
Q.4)
Q.5)
Q.6)
Q.7)
Q.8)
Q.9)
Q.10)
Q.11) Q.12)
Q.13)
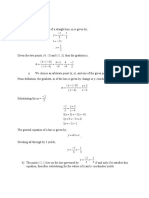
Questions Draw the development of lateral surface of the cone, the FV of which is shown in fig A Fig II (b) A cone of base 60 mm diameter axis 70 mm long is resting on its base on ground. It is cut by an auxiliary inclined plane inclined at 450 to HRP and interesting the axis 30 mm above the base. Draw the sectional top view, true shape of section and development of its lateral surface A right regular cone of 75 mm diameter and having an axis of 90 mm length, rests with its base in HP. A square hole of 30 mm sides is made in the truncated cone such that the axis of the square hole is perpendicular to the VP and passes through a point on the cone axis, 25 mm above the HP. The sides of the square hole are all inclined equally to the HP. Draw the development of the surface of the truncated cone. A hollow right circular cone made of paper is opened out and the development is a semicircle of 50 mm radius. A full circle of the largest possible size is drawn in ink inside this semicircle and the paper is folded back to its shape of cone. Draw the top view and front view of the cone keeping it in simple position and show the ink lines these views. A tetrahedron of 60 mm long edges is lying on the HP on one of its faces with an edge perpendicular to VP. It is cut by a section plane which is perpendicular to V.P. so that the true shape of the section is an isosceles triangle of base 45 mm long and altitude 35 mm. find the inclination of the cutting plane with the HP and draw elevation, sectional plan, true shape of section and develop the remained lateral surface of the tetrahedron A pentagonal pyramid of base 35 mm and height 70 mm is rests on its base in HP with one of its base side perpendicular to VP. It is to be cut by a section plane in such away that the true shape of section is equilateral triangle of maximum side. Locate the section plane, draw sectional top view, true shape of section and develop the remained lateral surface of pyramid A cone of base 60 mm and height of axis 70 mm resting on its base on HRP. It is cut by AIP in such a way that true shape of the section is isosceles triangle of base 50 mm. find the inclination of section plane with HRP. Draw FV sectional TV true shape of the section and develop its lateral surface Cube of 50 mm sides is resting on the ground having vertical faces equally inclined to F.R.P. It is cut by a section plane perpendicular to F.R.P. in such a way that true shape of the section is regular hexagon. Find the inclination of the section plane with H.P. Draw its F.V, sectional T.V, true shape of the section and develop its lateral surface. A pentagonal pyramid (Base 30 mm and axis height 75 mm) is resting on HRP on its base such that one of its base side is parallel to FRP. it is cut by an auxiliary plane perpendicular to FRP and inclined at 45 0 to HRP and bisects the axis. Draw the sectional top view, true shape of section and development of its lateral surface. A cone (Base diameter 80 mm and axis 90 mm) is resting on its base on HRP and it is cut by a plane parallel to FRP which is at a distance of 15 mm in front of the axis of cone. Draw its two views true shape of cut portion and development of lateral surface Fig shows elevation of a square pyramid with a rectangular slot cut through it. development the lateral surface of the remaining solid Fig (b) A pentagonal pyramid of base side 30 mm and axis 65 mm long rests on HP on its triangular face with its axis parallel to VP. It is cut by a horizontal section plane bisecting the axis. Draw the front view sectional top view and development of its lateral remained surface Fig (c) shows cylinder with cuts and central hole. Develop the lateral surface of the remaining solid
M 13 13
Year Jan 2003 Jan 2003
13
May 2003
13
Dec 2004
13
May 2005
13
Dec 2005
13
May 2006 Dec 2006
13
13
May 2007 Dec 2007
13
10 13
Dec 2007 May 2008 May 2008
10
Q.14)
Q.15) Q.16) Q.17) Q.18)
Fig (d) shows a cylinder which has a square hole cut through as shown. Draw the development of lateral surfaces of the cylinder (Fig is printed to scale ) OR Fig (e) shows the FV of an elbow joint of two circular pipes. Draw the development of the lateral surface (Fig is printed to the scale) Fig (f) shows the FV of a hexagonal prism cut by two flat planes at bottom and circular plane at top. Draw the development of lateral surface Fig (g) shows FV of a regular hexagonal pyramid, with edge of base 42 mm two of its base edges are perpendicular to VP. It has two slots cue through. Draw the development of lateral surfaces (fig is printed to the scale) Fig (h) Shows the square prism having a trapezoidal hole in it. Develop its lateral surface . Fig (I) shows the cut cone. develop its lateral surface
10 10 10 10 10 10
Dec 2008 Dec 2008 May 2009 Dec 2009 May 2010 May 2010
You might also like
- All Lab Layout-ModelDocument1 pageAll Lab Layout-Modelpravin2mNo ratings yet
- MSD Bos CseDocument40 pagesMSD Bos Csepravin2mNo ratings yet
- Ganesh Pip UdeDocument2 pagesGanesh Pip Udepravin2mNo ratings yet
- Carthymcqs 2003Document12 pagesCarthymcqs 2003Piyush ChavanNo ratings yet
- MECSE Final - 25 7 13 PDFDocument40 pagesMECSE Final - 25 7 13 PDFpravin2mNo ratings yet
- S .E. Comp. Sci. & Engg.) June 2013Document28 pagesS .E. Comp. Sci. & Engg.) June 2013rajanNo ratings yet
- 07-05-2010 PDFDocument6 pages07-05-2010 PDFpravin2mNo ratings yet
- Wireless CommDocument67 pagesWireless Commpravin2mNo ratings yet
- Turbo C++ FILELISTDocument7 pagesTurbo C++ FILELISTJivtesh KhuranaNo ratings yet
- MSBTE Diploma ApprovalDocument1 pageMSBTE Diploma Approvalpravin2mNo ratings yet
- Basic Problems On LineDocument1 pageBasic Problems On Linepravin2mNo ratings yet
- Pune PDocument5 pagesPune Ppravin2mNo ratings yet
- PointerDocument26 pagesPointerpravin2mNo ratings yet
- MECSE Final - 25 7 13 PDFDocument40 pagesMECSE Final - 25 7 13 PDFpravin2mNo ratings yet
- A Study On Frame Aggregation in Wireless NetworksDocument14 pagesA Study On Frame Aggregation in Wireless Networkspravin2mNo ratings yet
- VivekanandaDocument16 pagesVivekanandaavirupeceNo ratings yet
- CamsDocument95 pagesCamsbeljithvargheseNo ratings yet
- DRAWINGDocument2 pagesDRAWINGpravin2mNo ratings yet
- DOE Mechanical Science Volume 2 of 2 DOE-HDBK-10182-93Document130 pagesDOE Mechanical Science Volume 2 of 2 DOE-HDBK-10182-93Titer100% (1)
- Entc Se SyllabusDocument28 pagesEntc Se SyllabusKamal Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- II Semester Schedule for Students at XYZ CollegeDocument1 pageII Semester Schedule for Students at XYZ Collegepravin2mNo ratings yet
- Assignment On IsometericsDocument2 pagesAssignment On Isometericspravin2mNo ratings yet
- Insert Node at Last / End Position in Singly Linked List Inserting Node at Start in The SLL (Steps)Document7 pagesInsert Node at Last / End Position in Singly Linked List Inserting Node at Start in The SLL (Steps)pravin2mNo ratings yet
- Data Structure Program To Implement Dijkstra's Shortest Path AlgorithmDocument3 pagesData Structure Program To Implement Dijkstra's Shortest Path Algorithmpravin2mNo ratings yet
- Micro P Roce S SOR: Computer LanguagesDocument3 pagesMicro P Roce S SOR: Computer Languagespravin2mNo ratings yet
- Topological Sorting: "Dependency Resolution" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocument4 pagesTopological Sorting: "Dependency Resolution" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, Seepravin2mNo ratings yet
- WWW - Cse.ust - HK Faculty Golin COMP271Sp03 Notes MyL09Document28 pagesWWW - Cse.ust - HK Faculty Golin COMP271Sp03 Notes MyL09Kumar AmitNo ratings yet
- Multiway TreeDocument51 pagesMultiway Treepravin2mNo ratings yet
- What Are Threaded Binary Trees and AdavantagesDocument1 pageWhat Are Threaded Binary Trees and Adavantagespravin2mNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Section 3 Independent PracticeDocument25 pagesSection 3 Independent PracticejazzyNo ratings yet
- Section 8.4 and 8.5Document24 pagesSection 8.4 and 8.5Dishelle Anne Tinaza HufanaNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 - Q3 Math LessonDocument42 pagesGrade 4 - Q3 Math LessonHF ManigbasNo ratings yet
- SRDP Am Ma Formelsammlung ENDocument24 pagesSRDP Am Ma Formelsammlung ENOmar AliNo ratings yet
- Mensuration Assignment 11 PDFDocument9 pagesMensuration Assignment 11 PDFRitesh SethiaNo ratings yet
- Important Questions 1b by FitjeeDocument19 pagesImportant Questions 1b by FitjeeMovie LoversNo ratings yet
- An Overview On Conic SectionDocument14 pagesAn Overview On Conic SectionAzeNo ratings yet
- Maths 13.2 PDFDocument7 pagesMaths 13.2 PDFBrian LiNo ratings yet
- Geometry and Trigonometry EssentialsDocument6 pagesGeometry and Trigonometry EssentialsAbhay SoniNo ratings yet
- 2015 ANA GR 7 Mathematics Test - 2015Document20 pages2015 ANA GR 7 Mathematics Test - 2015wadeNo ratings yet
- DOE Fundamentals Handbook Module on GeometryDocument112 pagesDOE Fundamentals Handbook Module on Geometryaji jayaNo ratings yet
- MCQ Class ViiiDocument29 pagesMCQ Class Viiish867783% (6)
- 07a10191 Engineering GraphicsDocument11 pages07a10191 Engineering GraphicsSRINIVASA RAO GANTA100% (1)
- Surveying II - Week 2 Intersections: 1.1. Intersection Using Inner AnglesDocument9 pagesSurveying II - Week 2 Intersections: 1.1. Intersection Using Inner Anglesbest essaysNo ratings yet
- Question 1Document9 pagesQuestion 1mwidaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document25 pagesChapter 1Noor Faizah ZohardinNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanChelsy PlaysNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 8 Maths Activity 1Document2 pagesCBSE Class 8 Maths Activity 1angel shopNo ratings yet
- MAA SL 3.1-3.3 3D GEOMETRY – TRIANGLESDocument14 pagesMAA SL 3.1-3.3 3D GEOMETRY – TRIANGLESHaluk BulutNo ratings yet
- 4MA0 4H Que 20170117Document28 pages4MA0 4H Que 20170117abhayNo ratings yet
- Maths VIII PDFDocument3 pagesMaths VIII PDFneomatrix70No ratings yet
- Plane and Solid Geometry Module Bsed Math1Document50 pagesPlane and Solid Geometry Module Bsed Math1Ces Sy100% (3)
- Grand Test: Maths: Class: 7 Max. Marks: 50 Name: DateDocument3 pagesGrand Test: Maths: Class: 7 Max. Marks: 50 Name: Datebilal sheikhNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry 1Document21 pagesAnalytic Geometry 1Carlo GaliciaNo ratings yet
- 2023 Ms SolutionsDocument9 pages2023 Ms SolutionsThumuluri SrijithNo ratings yet
- 10 Mathematics SA 1 Ebook NewDocument394 pages10 Mathematics SA 1 Ebook Newselva.uae8207100% (1)
- Chapter 4 GeometryDocument30 pagesChapter 4 Geometrydarlene bianzonNo ratings yet
- Circles Equations and PropertiesDocument25 pagesCircles Equations and PropertiesAmol ChavanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank in MathDocument127 pagesQuestion Bank in MathLalit100% (1)
- Annalice R. Quinay DLL Math 6 q3 Week 9Document9 pagesAnnalice R. Quinay DLL Math 6 q3 Week 9Ronald GalangNo ratings yet