Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PH - Chem2 - Assign.
Uploaded by
Sunshine_Bacla_4275Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PH - Chem2 - Assign.
Uploaded by
Sunshine_Bacla_4275Copyright:
Available Formats
PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY PARTNER: SUNSHINE A.
BACLAAN FATIMA JAY PARADERO TOPIC: PROTEINS, ENZYMES & PEPTIDE HORMONES
PROTEINS
Gelatin - Metabolism: Hydrolysis of Collagen - Occurs in sheets, shreds, flakes or coarse powder. White or yellowish, has slight characteristic odor & taste. Stable in dry air. - Used in the preparation of capsules, coating of tablets and with glycerin, as a vehicle for suppositories. - Used as a vehicle when slow absorption is desired for drugs - Used to replace loss in blood volume in cases of shock - Administered: IV (to increase clotting of blood) or locally (to treat wounds in hemorrhagic conditions). Gelatin Film - Sterile, non-antigenic, absorbable, water insoluble gelatin film - Available as light yellow transparent brittle sheets (0.076 0.0228 mm thick) Gelatin sponge [Gelfoam, Surgifoam] - Sterile, absorbable, water insoluble gelatinbased sponge - Stable to dry heat at 150 for 4 hours - Absorb in 4-6 weeks when used as surgical sponge - Admin: topically (control capillary bleeding) Venoms Cobra venom solution - Injected IM as a non-narcotic analgesic in doses of 1 mL per day Snake venom solution - Used subcutaneously in doses of 0.4 1 mL as a hemostatic in recurrent epistaxis and thrombocytopenic purpura & as a prophylactic before tooth extraction & minor surgical procedures Stypven - From Russell Viper - Topically as hemostatic & thromboplastic agent Vein-apis - From Bees
Topically in acute & chronic arthritis, myostitis & neuritis Caerulein From Frog/ red-eyed tree frog, Agalychnis callidryas Used in radiography procedures to contract the gall bladder Sanvagine From Agalychnis callidryas Used as anxiolytic Bombesin From European bellied frog Used as anxiolytic
ENZYMES (proteins that have catalytic property)
Pancreatin [Panteric] - Cream-colored amorphous powder with a faint characteristic odor. - Dissolved slowly but incompletely in water; insoluble in alcohol - Used largely for pre-digestion of food & for the preparation of hydrolysates - Are digested by pepsin and acid in the stomach - Adult Dose: 325mg to 1g Trypsin Crystallized - Proteolytic enzyme - Solubility in water and saline = 500, 000 units per 10mL Pancrelipase [Cotazym] - Digestive aid - Used to help control steatorrhea and in other conditions in which pancreatic insufficiency impairs the digestion of fats in the diet. Chymotrypsin [Chymar] - Proteolytic enzyme - Used in cataract surgery Dormase Alpha [Pulmozyme] - Used in cystic fibrosis because of its ability to liquefy secretions from the lung effectively Hyaluronidase for injection [Alidase, Wydase] - Prepared from mammalian testes - Used to increase the spread and consequent absorption of hypodermoclytic solutions; to diffuse local anesthetics; and increase diffusion & absorption of other injected materials. - Enhances local anesthesia in eye surgery - Practically nontoxic but may cause a local infection to spread - Should never be injected in an infected area - Sensitivity to the drug is rare Imiglucerase Injection [Cerezyme]
- Used to treat type 1 Gaucher disease Sutilains [Travase] - Proteolytic enzyme - Used to dissolve necrotic tissue occurring in 2nd & 3rd degree burns as well as bed sores & ulcerated wounds - Contraindications: detergents & antiinfectives - The antibiotic penicillin, streptomycin, & neomycin do not inactivate sutilains Streptokinase [Kabikinase, Streptase] - Activates plasminogen to plasmin - Allergic reactions occur because of antibody formation in individuals treated with it. - Antibodies inactivate streptokinase & reduce its ability to prolong thrombin time - Indicated for acute myocardial infaction (IV), for local perfusion of an occluded vessel (Intra-arterial), and before angiography (Intracoronary) Urokinase [Abbokinase] - Plasminogen the only known substrate of urokinase - A direct activator of plasminogen - A non-antigenic and maybe used when streptokinase use is impossible because of antibody formation - Administered: IV or Intracoronary routes Alteplase [Activase] - A tissue plasminogen activator - Indicated for the IV management of acute myocardial infarction. Papain [Papase] - A light-brownish gray to weekly reddishbrown granules - Incompletely soluble in water - Best at a pH between 4 and 7 - Used locally in conditions similar to those for which pepsin is used - Has been reported to cause allergies in persons who are exposed to it Bromelains [Ananase] - Used in the treatment of soft-tissue inflammation and edema associated with traumatic injury, localized inflammation and post-operative tissue reactions - Available in 50,000 units tablets orally Diastase [Taka-Diastase] - Yellow, hygroscopic, almost tasteless powder - Freely soluble in water - Used in doses of 0.3 1g in the same condition as malt diastase - Combined with alkalies as an antacid
HORMONES
PITUITARY HORMONES Corticotropin Injection [ACTH inj., Acthar] - Exerts a tropic influence at adrenal cortex - pH range = 3 7 - used for tis adrenocorticotropic activity Respiratory Corticotropin Injection - Used intramuscularly for a more uniform and prolonged maintenance of activity Sterile corticotrophin Zinc Hydroxide Suspension - Dose: 40 units (IM) followed by a maintenance dose of 20 untis 2 or 3 times a week Cosyntropin [Cortrosyn] - Used as diagnostic agent to test for adrenal cortical deficiency - Dose: (IM or IV) Adult = 250 mg Children (2 yrs below) = 0.125 mg GROWTH HORMONE Somatrem (Systemic) [Protropin] - Administered: IM or SC - Therapy is continued as long as the patient responds or until the patient reaches mature adult height or until the epiphyses closes - Dose range: 0.05 to 0.1 IU Somatropin (rDNA origin) [Humatrope] - Administered: IM or SC - Dose range: 0.05 to 0.1 IU NEUROHYPOPHYSEAL HORMONES Oxytocin Injection - Prepared by synthesis - pH = 2.5 to 4.5 - expiration date = 3 years - widely used with or without amniotomy to induce and stimulate labor - administered: Injection or Sublingual Vasopressin Injection [Pitressin] - Each mL possesses a pressor activity equal to 20 posterior pituitary units - Expiration date = 3 years Vasopressin Tannate [Pitressin Tannate] - Administered: IM (1.5 to 5.0 pressor units daily) - Useful for patients who have diabetes insipidus - Should never be used intravenously (IV) Felypressin - Relatively low anti-diuretic activity and little oxytocic activity
Causes increase renal blood flow in the cat 5 times more effective as a vasopressin blood flow, especially in obstetrics and gynecology Lypressin [Diapid] - Available as topical solution, sprays, 50 pressor units (185 micrograms / mL) in 5mL containers - Dosage (topical, intranasal): one or more sprays applied to one or both nostrils one or more times a day Desmopressin Acetate [Stimate] - Drug of choice: treatment of Central Diabetes Insipidus because of its efficacy, ease of administration (intranasal), long duration of action, and lack of side effects - Can be administered IM or IV also - Indicted in the management of temporary polydipsia & polyuria associated with trauma to, or surgery in, the pituitary region PANCRATIC HORMONES Glucagon - Factor in the pathology of human diabetes - Regulation of the liver mediated mobilization of stored glucose - Principal consequence of high concentrations of glucagon: Persistent Hyperglycemia - Exert hyperglycemic action; it affects the liver cells - Inhibits the incorporation of amino acids into liver proteins - Fatty acid synthesis is decreased by glucagon; cholesterol formation is also reduced - Activates liver lipases & stimulates ketogenesis - Recommended for the treatment of severe hypoglycemic reaction caused by administration of insulin to diabetic or psychiatric patients - ADR: Nausea & Vomiting - Usual Dose: Adult (paranteral) = 500 microgram to 1mg repeated in 20 minutes if necessary Pediatric = 25 microgram per kg of body weight repeated in 20 minutes, if necessary GASTROINTESTINAL HORMONES Pentagastrin [Peptavlon] - Functional group: AMIDE
Indicated as diagnostic agent to elevate gastric acid secretory function & is useful in testing for anacidity in patients with suspected pernicious anemia, atrophic gastritis, or gastric carcinoma, hypersecretion on suspected duodenal output Administered: SC Optimal Dose: 6 microgram / kg Onset of action: 10 minutes after admin. Peak response: 20-30 minutes Duration of action: 60 80 minutes Half-life (plasma): (<10 minutes) Inactivated by liver, kidney, tissues of upper infectives Contraindications: Hypersensitivity or idiosyncrasy or pentagastrin Used with caution in patients with pancreatic, hepatic or biliary disease.
PARATHYROID HORMONES Parathyroid injection - Used therapeutically as an antihypocalcemic agent for the temporary control of tetany in acute hypoparathyroidism Teriparatide [Forteo] - Used for the treatment of osteoporosis in men & post-manopausal in women ANGIOTENSINS Angiotensin Amide - Administered: Continuous Infusion - Used as an adjunct to various hypotension states; and in administration of general anesthetics to control acute hypotension BLOOD PROTEINS Thrombin - Used as a topical hemostatic because it can clot blood, plasma - May initiate clotting when combined with gelatin sponge or fibrin foam - External use: Topically to the wound as a solution containing 100 2,000 units/mL in NaCl irrigation or sterile water for injection or as dry powder BIOTECHNOLOGY-DERIVED PHARMACEUTICAL PRODUCTS Dornase Alpha - Used in the treatment of cystic fibrosis - Dose (Adult): 2.5 mg inhaled once daily - Administered by nebulizer - ADR: sore throat, hoarseness, facial edema
Imiglucerase [Cerezyme] - Deficiency of imiglucerase causes gaucher disease - Indicated for the long-term replacement therapy of Gaucher disease - Admin: IV - Initial dose: 2.5 to 60 units/kg - Infused over 1-2 hours - The dose is usually repeated every 2 weeks - ADR: dizziness, headache, abdominal discomfort, nausea, rash Interferons - Exhibit antiviral & antiproliferative activity, enhance phagocytic activity & augment specific cytotoxicity of lymphocyte for certain cells - ADR: flu-like symptoms, bone marrow suppression, neurotioxic effects, hypocalcemia, anorexia, & other GI symptoms & weight loss Interferon Alfa-2a Recombinant [Roferon] - Used in the treatment of hairy cell leukemia & acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) related kaposic Sorzoma - Absorbed well after IM or IV admin. - Half-life: 5- 7 hours (IM route) - Solution store in refrigeration 36 to 46 degrees Fahrenheit Peginterferon Alfa-2a Recombinant - Treatment of hepatitis C Interferon Alfa-2a Recombinant [Intron A] - Treatment of hairy cell leukemia, condyloma accuminata (genital warts), AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma, Hepatitis C and Hepatitis B - Administered: IM or SC - Half-life: 2-3 hours (IM or SC) and 8 hours (IV) Interferon Alfa-n3 (inj.) [Alferon N] - Indicated by intralesional injection for treatment of genital warts Interferon Beta-1a [Rebif, Avonex] - Slow progression of multiple sclerosis as well as the rate of relapse of this disease Interferon Beta-1b, Recombinant [Betaseron] - Administered: IV, IM, SC, Intrathecal, Intralesional - Prevention of exacerbations in patients suffering from relapsing / remitting multiple sclerosis - Dose: 8 million units (SC) every other day - Treatment of malignant glioma & malignant melanoma Aldesleukin [Proleukin]
Treatment of adult metastatic renal carcinoma - Administered: IV infusion, - Dose: 10, 000 to 50, 000 Units / kg every 8 hours per 12 days - Metabolized in kidney - No active form found in urine - Side effects: fever, hypotension, pulmonary congestion, & dyspnea, GI bleeding, respiratory failure, & renal failure, seizures, and death. Erythropoietin - Produce primarily by the peritubular cells in the cortex of the kidney and up to 15% is produced in the liver - Erythropoietin levels decrease in patines with renal fialure Epoetin Alfa [Epogen, Procrit] - Indicated to patients with chronic renal failure & anemia associated with aids - Admin: IV Colony stimulating Fators (Natural glycoproteins produced in lymphocytes and monocytes) Filgrastim [Neupogen] - Decrease incidence of fibril neutropenea in patients with nonmyeloid malignancies - Used within 24 hours Sargamostim [Leukine] - Is a lineage-nonspecific hematopoietic factor because it promotes the proliferation and maturation of granulocytes and monocytes - Primary indication: myeloid engraftment following autologous bone marrow transplantation and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Antihemophili factor [Humate-P, hemophil M, Koate HP, Monoclate P] - A glycoprotein found in human plasma and a necessary co factor in the blood-clotting mechanism Antihemophilic Factor (Recombinant) [Kogenate, Helixate] - Indicted for the treatment of hemophilia A - Administered: IV route - Temporarily prevents bleeding episodes in hemophiliacs and may be used to prevent excessive bleeding during surgical procedures in these patients. -
You might also like
- PositionJob DescriptionTop SpecificationDocument2 pagesPositionJob DescriptionTop SpecificationSunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- You Are Invtited To Our Bday PartyDocument1 pageYou Are Invtited To Our Bday PartySunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- Tree Planting Activity: "Let's Give Back To Mother Nature!"Document1 pageTree Planting Activity: "Let's Give Back To Mother Nature!"Sunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- Vinori Pharmacy Vinori Pharmacy: Jay A. Baclaan Manager Jay A. Baclaan ManagerDocument1 pageVinori Pharmacy Vinori Pharmacy: Jay A. Baclaan Manager Jay A. Baclaan ManagerSunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- IDDocument1 pageIDSunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- Behavioral Cognitive TheoryDocument3 pagesBehavioral Cognitive TheorySunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- TurkeyDocument24 pagesTurkeySunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- Answer SheetDocument1 pageAnswer SheetSunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- Gaisano Metro ColonDocument1 pageGaisano Metro ColonSunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- Juris - Ra 9165 Part 2 of ExamDocument6 pagesJuris - Ra 9165 Part 2 of ExamSunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- Answer Sheet 1 - 300Document1 pageAnswer Sheet 1 - 300Sunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- Report ThursdayDocument8 pagesReport ThursdaySunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- Gaisano Metro ColonDocument1 pageGaisano Metro ColonSunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- The Famous Whale Shark ReportDocument15 pagesThe Famous Whale Shark ReportSunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- Baclaan ADocument8 pagesBaclaan ASunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- DispensingDocument13 pagesDispensingSunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- 04.0 Drug Dispensing Procedure 2007Document16 pages04.0 Drug Dispensing Procedure 2007Sunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- Street FoodsDocument2 pagesStreet FoodsSunshine_Bacla_4275100% (1)
- Technical StudyDocument4 pagesTechnical StudySunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- PositionJob DescriptionTop SpecificationDocument2 pagesPositionJob DescriptionTop SpecificationSunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- Mel A. Baclaan: Bachelor of Science in Hotel and Restaurant ManagementDocument1 pageMel A. Baclaan: Bachelor of Science in Hotel and Restaurant ManagementSunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- Jay A. Baclaan: Bachelor of Science in Hotel and Restaurant ManagementDocument1 pageJay A. Baclaan: Bachelor of Science in Hotel and Restaurant ManagementSunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- The Famous Whale Shark ReportDocument15 pagesThe Famous Whale Shark ReportSunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- 4th Yr (1st Sem) Schedule ReprintsDocument1 page4th Yr (1st Sem) Schedule ReprintsSunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- Street FoodsDocument2 pagesStreet FoodsSunshine_Bacla_4275100% (1)
- Portrait FormDocument10 pagesPortrait FormSunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- EgyptDocument3 pagesEgyptSunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- Organized Part 1Document8 pagesOrganized Part 1Sunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
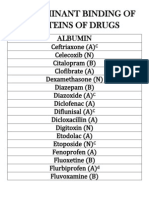
- Predominant Binding of Proteins of DrugsDocument14 pagesPredominant Binding of Proteins of DrugsSunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- Organized Part 1Document8 pagesOrganized Part 1Sunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- DocxDocument20 pagesDocxHarrington_773951393100% (1)
- A 1 CDocument8 pagesA 1 CRajiv RanjanNo ratings yet
- Project Seminar ReportDocument18 pagesProject Seminar Reportchava varshithaNo ratings yet
- Sindrome Metabolico y RESET PDFDocument2 pagesSindrome Metabolico y RESET PDFizrafkNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Hipoglikemia Pada Pasien Diabetes Melitus Tipe 2 Terhadap Kepatuhan Terapi Dan Kualitas HidupDocument7 pagesPengaruh Hipoglikemia Pada Pasien Diabetes Melitus Tipe 2 Terhadap Kepatuhan Terapi Dan Kualitas HidupAhmad RivaiNo ratings yet
- Special Topics in Pediatric NursingDocument60 pagesSpecial Topics in Pediatric NursingRichard S. RoxasNo ratings yet
- The Complete Weight Loss Guide: Brought To You byDocument6 pagesThe Complete Weight Loss Guide: Brought To You bySam YoussefNo ratings yet
- Nursing Thesis Proposal FormatDocument24 pagesNursing Thesis Proposal FormatCharlie Cotoner Falguera100% (1)
- Pharmacotherapy of Diabetes Mellitus: Dr. Ave Olivia Rahman, Msc. Bagian Farmakologi Fkik UnjaDocument42 pagesPharmacotherapy of Diabetes Mellitus: Dr. Ave Olivia Rahman, Msc. Bagian Farmakologi Fkik UnjaGita Tanbao SuselinNo ratings yet
- Capillary Blood Glucose Monitoring or CBG MonitoringDocument5 pagesCapillary Blood Glucose Monitoring or CBG MonitoringRonilyn Mae Alvarez100% (1)
- U. S. DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE - America S Eating Habits - Changes and ConsequencesDocument494 pagesU. S. DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE - America S Eating Habits - Changes and ConsequencesSandra MianNo ratings yet
- OJUS and DM - OdtDocument14 pagesOJUS and DM - OdtArpit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Potential of Antidiabetic NutraceuticalsDocument26 pagesTherapeutic Potential of Antidiabetic Nutraceuticalsdajaslen1811No ratings yet
- Antidiabetic, Antihyperlipidemic and Antioxidant Properties of Roots of Ventilago Maderaspatana Gaertn. On StreptozotocinInduced Diabetic RatsDocument10 pagesAntidiabetic, Antihyperlipidemic and Antioxidant Properties of Roots of Ventilago Maderaspatana Gaertn. On StreptozotocinInduced Diabetic RatsIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug Studyjoaqiun100% (1)
- Nursing Acn-IiDocument80 pagesNursing Acn-IiMunawar100% (6)
- Weaknes S/ Fatigue Polyphag IaDocument5 pagesWeaknes S/ Fatigue Polyphag IaEwert Hesketh Nillama PaquinganNo ratings yet
- Blood GlucoseDocument3 pagesBlood GlucoseChamCham AquinoNo ratings yet
- 49 91 1 SMDocument3 pages49 91 1 SMFirjin LowingNo ratings yet
- Hand Mudras For DiabetesDocument5 pagesHand Mudras For DiabetesRITESH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Diabetes and Diabetic DietDocument4 pagesDiabetes and Diabetic DietSereneOne50% (2)
- Medicinal Plants and Diabetes PDFDocument8 pagesMedicinal Plants and Diabetes PDFTowhid HasanNo ratings yet
- (Diabetes No More) Diabetes DestroyerDocument30 pages(Diabetes No More) Diabetes Destroyerzigzag7842611100% (1)
- Sps. Flores v. Sps. PinedaDocument7 pagesSps. Flores v. Sps. PinedaRachel CayangaoNo ratings yet
- 715 PrometricDocument61 pages715 PrometricNosheen HaqNo ratings yet
- Quality of Life in Diabetes - Tutorial 4Document10 pagesQuality of Life in Diabetes - Tutorial 4Axiu Xabi'alonsoNyNo ratings yet
- Issue 29 - Volume 2Document32 pagesIssue 29 - Volume 2Indian WeekenderNo ratings yet
- Endocrine EmergenciesDocument25 pagesEndocrine EmergenciesayaNo ratings yet
- Biodata Kumud KsDocument7 pagesBiodata Kumud KsGhouse MohammedNo ratings yet
- Balducci2006 PDFDocument8 pagesBalducci2006 PDFDimasBanyakRejekiNo ratings yet