Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ECE Problem Set 1 Solutions
Uploaded by
icantdecideOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ECE Problem Set 1 Solutions
Uploaded by
icantdecideCopyright:
Available Formats
ECE 3710 Problem Set 1: Solution manual *P1.17.
* current : flow of charge, unit : amperes = coulombs/second Charge : (10 amperes ) (36,000 seconds) = 3.6 105 coulombs * energy : Integral (sum) of power between time intervals, unit : Joules * power : rate of energy transfer, P = V x I. unit : watts = joules/second Energy = 12.6 V 10 A 36,000 seconds = 4.536 106 Joules *P1.20. *Remember the Passive reference configuration Energy is being absorbed by the element. (a) P = -Vaia = 30 W (b) P = Vbib = 30 W Energy is being absorbed by the element. (c) P = - VDEiED = - 60 W Energy is being supplied by the element. *P1.36. *Remember the Kirchhoff Current Law At the node joining elements A and B, we have ia + ib = 0. Thus, ia = - 2 A. For the node at the top end of element C, we have ib + ic = 3. Thus, ic = 1 A. Finally, at the top right-hand corner node, we have 3 + ie = id. Thus, id = 4 A. Elements A and B are in series. Elements C, D, and E are in parallel. *P1.41. *Remember the Kirchhoff Voltage Law KVL on the lower left-hand loop, we have -5 + Va + 10 = 0. Thus, Va = -5 V. Then for the top-most loop, we have Vc 15 Va = 0. Thus, Vc = 10 V. Finally, on the lower right-hand loop, we have 15 + Vb 10 = 0. Thus, Vb = -5 V. *P1.42. *Both Kirchhoff Laws. KCL At the node joining elements A and B, we have ia + ib = 0. Thus, ib = - 2 A. For the node at the top end of element C, we have ib + ic + id = 0. Thus, ic = 1 A. KVL For the right-hand side loop, we have Vc = Vd. Thus, Vc = 4 V. For the left-hand side loop, we have Vc = Va + Vb. Thus, Vb = - 6 V. Power Element A : Pa = 10 V -2 A = -20 W Element B : Pb = -6 V -2 A = 12 W Element C : Pc = 4 V 1 A = 4 W Element D : Pd = 4 V 1 A = 4 W Pa + Pb + Pc + Pd = 0.
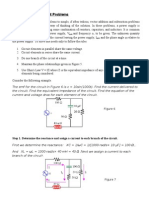
*P1.58. *Ohms Law. Power in a resistor Power = Voltage Current. 100 W = 100 V Current. Thus, current = 1 A. Ohms Law : V = I R. 100 V = 1 A R. Thus, R = 100 . Assuming that resistance remains constant, if voltage is reduced by 10 percent then the current is also reduced by 10 percent. Since power in a resistor is V I or I2R, the power will be 81% of the pervious power. Thus, there is a 19% reduction in power. *P1.62. A voltage source guarantees an absolute amount of voltage and polarity across 2 terminals. A current source guarantees an absolute amount of current in a direction defined through a series connected elements. a. Not contradictory. b. Contradictory. When 2 current sources are connected in series they contradict each other. Currents in series elements must be equal. c. Not contradictory. d. Contradictory. Current through an open circuit is zero by definition and current in series elements must be equal. Thus, this is contradictory to the definition of the 2 A current source. e. Contradictory. The voltage across a short circuit is zero by definition. However, voltages across parallel elements must be equal. Thus, the two elements connected in parallel is contradictory. *P1.63. KCL on the node connecting the 2 A current source and the 5 resistor. iR = 2 A. Power in resistor = I2R = 4 5 = 20 W. Absorbs power. Power in 10V voltage source = VI = 10 V 2 A = 20 W. Absorbs power. Power in 2 A current source = VI = 20 V -2 A = - 40 W. Supplies power. *P1.64. Start from the far right, where all the info needed is given, and move towards to the left. Far right 5 resistor, has 1 A flowing through. Thus, the voltage across is 5 V, positive polarity being the top terminal. Parallel elements will have equal voltage across them. We can calculate the current flowing through the other 5 and 10 resistor, 1A and 0.5 A. Perform KCL on the nodes starting from the far right. We can show that the current flowing through the 5 resistor on the far left is 2.5 A. Thus, the voltage across the 5 resistor on the far left is 12.5 V, positive polarity being the left terminal. KVL shows that Vx = 12.5 V + 5 V = 17.5 V
*P1.70. The 4 and 2 resistor are connected in series. Thus, the current through the 4 resistor is also 1 A. Vx = 1 A 4 = 4 V. The dependent current source will supply 0.5 A/V 4 V = 2 A current downwards and will have a Vx + 1 A 2 = 6 V voltage across itself, the top terminal having the positive polarity. KCL at the top middle node leads to the current flowing through the 3 resistor being 3 A, in the direction into the node. As a result Vs = 3 A 3 + 6 V = 15 V.
You might also like
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 69874 - Ch1. 解答Document10 pages69874 - Ch1. 解答郭禧約No ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document7 pagesChapter 01Fernando AndradeNo ratings yet
- Circuit LawsDocument44 pagesCircuit LawsBrian Mactavish MohammedNo ratings yet
- Electricity - Class Notes 2024-25Document9 pagesElectricity - Class Notes 2024-25samasama.gldNo ratings yet
- EE5251 Unit 1Document129 pagesEE5251 Unit 1SathyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Solution SheetDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Solution Sheetam_andremarinoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial de ElectricidadDocument78 pagesTutorial de ElectricidadfrederypsNo ratings yet
- BEE Electricity Basic PrinciplesDocument20 pagesBEE Electricity Basic PrinciplesMondaya, Jake Armond D.No ratings yet
- Review PSC KCL and KVLDocument40 pagesReview PSC KCL and KVLmmnldzNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING 1 (Final Term)Document20 pagesINTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING 1 (Final Term)Abdul Halil AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Handouts For Module 1.2 - EE211Document4 pagesHandouts For Module 1.2 - EE211Chrisser Van BaetNo ratings yet
- Unit I Basic Circuits AnalysisDocument36 pagesUnit I Basic Circuits AnalysisHarvey PingcasNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument20 pagesCurrent ElectricityblueegofxNo ratings yet
- EE454 HW 6Document12 pagesEE454 HW 6vivianl0102100% (3)
- Electronics Study Material For MSCDocument23 pagesElectronics Study Material For MSCiswaleha100% (1)
- Superposition TheoremDocument18 pagesSuperposition Theoremsouvikmondal8144No ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering: Principles and Applications, Fifth EditionDocument45 pagesElectrical Engineering: Principles and Applications, Fifth EditionHammad A. Irshad33% (9)
- Circuit Variables: Potential V Elevation HDocument12 pagesCircuit Variables: Potential V Elevation HIshank Singh ThandiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document14 pagesChapter 1Lucas EtienneNo ratings yet
- M31 Knig9404 Ism C31 PDFDocument33 pagesM31 Knig9404 Ism C31 PDFnorma_jeannNo ratings yet
- Basic Circuit Analysis LawsDocument50 pagesBasic Circuit Analysis LawsMuhd RzwanNo ratings yet
- 1645586126latihan Try OutDocument3 pages1645586126latihan Try Outyehuda pramanaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory 1 MidtermDocument101 pagesCircuit Theory 1 MidtermMcHaley HalNo ratings yet
- Electricity MagnestismDocument51 pagesElectricity MagnestismMiranti UrbaningrumNo ratings yet
- Electricity Notes-XDocument40 pagesElectricity Notes-XArchitaNo ratings yet
- Physics Cl10 Assign16Document2 pagesPhysics Cl10 Assign16Tapas Banerjee100% (1)
- Circuit Theory Part - 1 Tutorial - 7 (2) - 1 - 13Document13 pagesCircuit Theory Part - 1 Tutorial - 7 (2) - 1 - 13dcsekharNo ratings yet
- EEEB113 Chap 1 NotesDocument28 pagesEEEB113 Chap 1 NotesNabilahJasmiNo ratings yet
- Electricity PDFDocument9 pagesElectricity PDFAsa KaNo ratings yet
- HW1 ProblemDocument5 pagesHW1 Problem劉德信No ratings yet
- Nelson Thornes Electrcity and Thermal Physics Prac2Document26 pagesNelson Thornes Electrcity and Thermal Physics Prac2Mitul KaziNo ratings yet
- Superposition TheoremDocument18 pagesSuperposition TheoremDarshan A BhyrataeNo ratings yet
- Physics Class X For Sa I 2016 17Document94 pagesPhysics Class X For Sa I 2016 17Praveen MaramNo ratings yet
- REVIEWDocument203 pagesREVIEWERMIAS AmanuelNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Circuits 2 1Document6 pagesExperiment 3 Circuits 2 1justine ugayNo ratings yet
- Note 1 - Fundamental of Electric CircuitsDocument93 pagesNote 1 - Fundamental of Electric Circuitssyedfadlan91100% (1)
- BEE Soft Copy Notes 2015-16 (6-7-15)Document84 pagesBEE Soft Copy Notes 2015-16 (6-7-15)Sujit KumarNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism: DC Circuits ElectromagnetismDocument27 pagesElectricity and Magnetism: DC Circuits ElectromagnetismDhruv JainNo ratings yet
- EE320 - DC/AC Circuits (Part 1) : Electric ChargeDocument11 pagesEE320 - DC/AC Circuits (Part 1) : Electric ChargeIamellahollic KathportsNo ratings yet
- ElectricDocument40 pagesElectricnishant kumarNo ratings yet
- CurrentDocument40 pagesCurrentNurul Nabilah AzraNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ramesh Vaddi: (Lec-2:Basic Circuit Concepts)Document26 pagesDr. Ramesh Vaddi: (Lec-2:Basic Circuit Concepts)McLican EkkaNo ratings yet
- Electric C. Lec 1Document40 pagesElectric C. Lec 1adelehab89No ratings yet
- Electrical CircuitsDocument24 pagesElectrical CircuitsJoseph Kinley V. LumosadNo ratings yet
- Worked Solutions Chapter 4 Electronics: 4.1 Analysing Electronic CircuitsDocument9 pagesWorked Solutions Chapter 4 Electronics: 4.1 Analysing Electronic Circuits123HopperNo ratings yet
- 3 Circuit Analysis Using SubcircuitsDocument21 pages3 Circuit Analysis Using SubcircuitsAlejandro Salas VásquezNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument93 pagesElectricity and MagnetismKingPhysics100% (2)
- All Modules Notes-SoftDocument150 pagesAll Modules Notes-SoftVenkat saiNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 IsDocument23 pagesQuiz 1 IsNathan KingNo ratings yet
- Capacitors 1Document19 pagesCapacitors 1pNo ratings yet
- Parallel RLC Circuits and Resonance: Learning ObjectiveDocument26 pagesParallel RLC Circuits and Resonance: Learning Objectiveandrew smithNo ratings yet
- Nareshiare Beee PPT 2018 2019 7mb - 0Document204 pagesNareshiare Beee PPT 2018 2019 7mb - 0jainarayanNo ratings yet
- Phasors and AC Circuit ProblemsDocument6 pagesPhasors and AC Circuit ProblemsSurangaGNo ratings yet
- Where Do You Need This?: 1.maintenance Engineer 2.energy Management System 3.energy ManagerDocument31 pagesWhere Do You Need This?: 1.maintenance Engineer 2.energy Management System 3.energy Managerconference RequirementsNo ratings yet
- Lab 8Document13 pagesLab 8Richard LangNo ratings yet
- 4 ElectricityDocument49 pages4 ElectricityKaguya74No ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument16 pagesPhysics ProjectAbishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Key Terms: Chapter 3: The Lengths of The Unit-Cell EdgesDocument2 pagesKey Terms: Chapter 3: The Lengths of The Unit-Cell EdgesAndy DaNo ratings yet
- Material Science Terms Chapter 9Document2 pagesMaterial Science Terms Chapter 9icantdecideNo ratings yet
- Sailor Whale Amigurumi PatternDocument1 pageSailor Whale Amigurumi Patternicantdecide100% (2)
- GallifreyanDocument6 pagesGallifreyanDaniel NiculceaNo ratings yet
- Key Terms: Chapter 2: T, WhichDocument2 pagesKey Terms: Chapter 2: T, WhichicantdecideNo ratings yet
- Basic System Dynamics ConceptsDocument17 pagesBasic System Dynamics ConceptsicantdecideNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14. Op Amp Example Problems 10Document3 pagesChapter 14. Op Amp Example Problems 10icantdecideNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship - PPTX Version 1 - Copy (Autosaved) (Autosaved) (Autosaved) (Autosaved)Document211 pagesEntrepreneurship - PPTX Version 1 - Copy (Autosaved) (Autosaved) (Autosaved) (Autosaved)Leona Alicpala67% (3)
- 4039-Texto Del Artículo-12948-3-10-20211123Document14 pages4039-Texto Del Artículo-12948-3-10-20211123Ricardo ApazaNo ratings yet
- CBSE 10th ResultsDocument1 pageCBSE 10th ResultsAkshit SinghNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa Inggris TranslateDocument14 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggris TranslatevikaseptideyaniNo ratings yet
- Role of Communication at Mahabharatha WarDocument19 pagesRole of Communication at Mahabharatha WarAmit Kalita50% (2)
- HangersSupportsReferenceDataGuide PDFDocument57 pagesHangersSupportsReferenceDataGuide PDFIndra RosadiNo ratings yet
- Employee of The Month.Document2 pagesEmployee of The Month.munyekiNo ratings yet
- Kootenay Lake Pennywise April 26, 2016Document48 pagesKootenay Lake Pennywise April 26, 2016Pennywise PublishingNo ratings yet
- Music Production EngineeringDocument1 pageMusic Production EngineeringSteffano RebolledoNo ratings yet
- UAP Grading Policy Numeric Grade Letter Grade Grade PointDocument2 pagesUAP Grading Policy Numeric Grade Letter Grade Grade Pointshahnewaz.eeeNo ratings yet
- Level of Organisation of Protein StructureDocument18 pagesLevel of Organisation of Protein Structureyinghui94No ratings yet
- Ferobide Applications Brochure English v1 22Document8 pagesFerobide Applications Brochure English v1 22Thiago FurtadoNo ratings yet
- TechBridge TCP ServiceNow Business Case - Group 6Document9 pagesTechBridge TCP ServiceNow Business Case - Group 6Takiyah Shealy100% (1)
- Norman, K. R., Pali Philology & The Study of BuddhismDocument13 pagesNorman, K. R., Pali Philology & The Study of BuddhismkhrinizNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics WorksheetDocument5 pagesThermodynamics WorksheetMalcolmJustMalcolmNo ratings yet
- Pogon Lifta MRL PDFDocument128 pagesPogon Lifta MRL PDFMašinsko ProjektovanjeNo ratings yet
- Punches and Kicks Are Tools To Kill The Ego.Document1 pagePunches and Kicks Are Tools To Kill The Ego.arunpandey1686No ratings yet
- BSNL BillDocument3 pagesBSNL BillKaushik GurunathanNo ratings yet
- EC 2012 With SolutionsDocument50 pagesEC 2012 With Solutionsprabhjot singh1No ratings yet
- Blackbook 2Document94 pagesBlackbook 2yogesh kumbharNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1 AcousticsDocument14 pagesAssignment - 1 AcousticsSyeda SumayyaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Raiseplus Weekly Plan For Blended LearningDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Raiseplus Weekly Plan For Blended LearningMARILYN CONSIGNANo ratings yet
- Asus x453Document5 pagesAsus x453Rhiry Ntuh AthryNo ratings yet
- 2022 AMR Dashboard Funding Opportunity Announcement 11.18.2022Document16 pages2022 AMR Dashboard Funding Opportunity Announcement 11.18.2022Tuhin DeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Principle of Marketing UpdateDocument58 pagesChapter 5 - Principle of Marketing UpdateKhaing HtooNo ratings yet
- Journal of Molecular LiquidsDocument11 pagesJournal of Molecular LiquidsDennys MacasNo ratings yet
- How To Change Front Suspension Strut On Citroen Xsara Coupe n0 Replacement GuideDocument25 pagesHow To Change Front Suspension Strut On Citroen Xsara Coupe n0 Replacement Guidematej89No ratings yet
- UG ENGLISH Honours PDFDocument59 pagesUG ENGLISH Honours PDFMR.Shantanu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Learning English Through The Educational Games of Wordwall Website For Elementary Students by Group 1 (R4E)Document6 pagesLearning English Through The Educational Games of Wordwall Website For Elementary Students by Group 1 (R4E)NurulNo ratings yet
- Vq40de Service ManualDocument257 pagesVq40de Service Manualjaumegus100% (4)