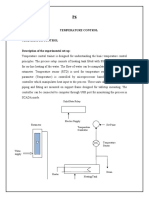
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Process Control Systems
Uploaded by
Hammad AnsariCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Process Control Systems
Uploaded by
Hammad AnsariCopyright:
Available Formats
Review of Last class class..
Industrial Electronics (3+0)
Week-02 23rd Sep 2012
Industrial Electronics Intro Course Intro Introduction to Process Control Systems Types of processes
Continous Batch Individual process Individual control Centralized control Distributed control
2
Process control configurations
Process Control Systems
Week-01
Instructor: Engr. Shiraz Latif
11
Structure of process control systems Introduction to PLC & Ladder logic
Open-loop v/s closed-loop systems
Open-loop p p control system y
Process is controlled by inputting to the controller the desired set point (command signal or reference f signal) i l) Accepting whatever the final results Only input is the desired set level hence blind control No information regarding current status Inexpensive and less complex Less accurate Poor process control
Open loop speed control Of DC motor
Closed-loop p control system y
Components p of closed-loop p control
Output of a process affects the input Current output is measured and compared to the desired output
Set point
Error signal = desired output actual output
Continuous adjustments until error becomes zero (ideally)
Input that determines the desired operating point for the process th Usually provided by the operator, or may be provided by some system Variable that is being measured and controlled Contains information about the process current status Feedback signal Ideally matches the set pint Ideally,
6
Process variable
. Components p
Error Amplifier
Container Filling Closed-loop process control
Determines whether the process operation matches th set the t point i t Differential amplifier Magnitude and polarity of error signaldetermines how the process be brought back under control Produces corrective output signal based on error signal Component C t that th t di directly tl affects ff t a process change h Eg. Motors, heaters, fans, solenoids
Controller
Output actuator
Container filling g process p control explanation.. p
Regulators:
How the process works?
Identify y inputs p and outputs.. p Identify
Set p point ? Process variable? Error amplifier? Controller? Output actuator?
9
A closed-loop system that maintains a steady level or value of some quantity Used in industrial processes to provide precise regulation p g of some parameter p like voltage, speed, current, tension, position, temperature
10
Process Control variables
Loop regulator L l t for f tension control of textile machines. Regulating prob: to synchronize the one side of loop to the other side side, to maintain the constant loop. How it works?
Process control systems applies to large section of industries Usually involves the manipulation of a variety of process variables in order to achieve automatic control. Number of variables depends p on the product p that is being g manufactured. Some of the variables can be
Pressure Temperature Flow Level Conductivity Weight
Variation in one variable can cause affect on other as well well.
12
11
Industrial Process Controllers
1 Two position control 1.
Industrial Process Control Modes; ;
Two Position Controller Proportional Controller Integral Controller Differential Controller PI Controller PD Controller PID Controller PID-Controller
oldest strategy gy for control use of a switch ON/Off control discontinuous form of control action also known as two position controller. primitive, cheap and effective method of control if a fairly f i l large l fluctuation fl t ti of f the th process variable i bl is i acceptable. A perfect ON/Off controller is
Purpose of control is to hold the measured variable output from a process within set limits
ON when the measurement is below the setpoint and the manipulated variable is at its maximum value, OFF when measurement is above the setpoint and the MV is a minimum.
14
13
Room heating system with on/off control
(74oF = 24oC) ( )
On/off controllers usually have inertia that introduces
What is control var? Set point ? What does the waveforms explain?
Overswings Delays or lag times before the variable attains the reference level again.
Why ?
15
16
2 Differential action 2.
Differential or delayed y ON/OFF action Simple ON/OFF action with additional hysteresis or a dead-band built in. set reference 75, switching points are delayed by 3 3F F. OFF @ 78F On @ 72 72F F hysteresis of 6F. There is, of course, still some inertia.
Hence, the room temperature will go from about 70F to about 80F.
17
You might also like
- Control EngineeringDocument110 pagesControl EngineeringCasey Long67% (3)
- Design of Nonlinear Control Systems With The Highest Derivative in FeedbackDocument374 pagesDesign of Nonlinear Control Systems With The Highest Derivative in Feedbackingcivil01No ratings yet
- P&ID NotesDocument17 pagesP&ID Notesnokaraju100% (1)
- Building Management System - BMS 1Document31 pagesBuilding Management System - BMS 1jaffna100% (1)
- Practical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsFrom EverandPractical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- LNG Dynamic HysysDocument52 pagesLNG Dynamic HysysSrihari Kodimela75% (4)
- Control Lab Project ReportDocument28 pagesControl Lab Project ReportDanyal QamarNo ratings yet
- Braking ResistorDocument10 pagesBraking ResistorJoa QuispeNo ratings yet
- 4528.R380.02 Slide Handout For StudentsDocument62 pages4528.R380.02 Slide Handout For StudentsCiputra 'Boy' TampubolonNo ratings yet
- Technical Article Temperature ControlDocument2 pagesTechnical Article Temperature ControlCarlos PérezNo ratings yet
- Industrial Process Control Basic ConceptsDocument39 pagesIndustrial Process Control Basic Conceptskaezzar10100% (1)
- Characterization and Modeling of A Dynamixel ServoDocument38 pagesCharacterization and Modeling of A Dynamixel Servogimmegmailemail100% (1)
- Automatic Controllers & Control ModesDocument74 pagesAutomatic Controllers & Control ModesVishal IyerNo ratings yet
- The Working Principle of A PID Controller For BeginnersDocument15 pagesThe Working Principle of A PID Controller For BeginnersSaber AbdelaalNo ratings yet
- Process Control and Common TermsDocument210 pagesProcess Control and Common TermsGeorge Markas100% (1)
- PID Controller Working Principle Explained For BeginnersDocument6 pagesPID Controller Working Principle Explained For BeginnersPramillaNo ratings yet
- 1-Introduction To Process ControlDocument30 pages1-Introduction To Process ControlRazif Metta100% (4)
- PIDControlDocument2 pagesPIDControlchatty8567% (3)
- Pid Tuning OperatorDocument18 pagesPid Tuning OperatorkarmoweldingNo ratings yet
- Practical Process Control Textbook 20060612Document296 pagesPractical Process Control Textbook 20060612karopa904082No ratings yet
- Design and Tuning of Fuzzy Logic PID ControllerDocument19 pagesDesign and Tuning of Fuzzy Logic PID ControllerPriya BhardwajNo ratings yet
- PID ControllerDocument18 pagesPID ControllerCheng Khie Chieh100% (1)
- Theory and Applications of HVAC Control Systems A Review of Model Predictive Control MPCDocument13 pagesTheory and Applications of HVAC Control Systems A Review of Model Predictive Control MPCKhuleedShaikhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Optimum Controller Chapter 2: Optimum Controller Settings Settings GGDocument5 pagesChapter 2: Optimum Controller Chapter 2: Optimum Controller Settings Settings GGLakshmiNo ratings yet
- P, I, D, PI, PD, and PID ControlDocument14 pagesP, I, D, PI, PD, and PID ControlArnav KothiyalNo ratings yet
- The PROCON PH Process Control System Is Based Around The PH Rig and Is A SelfDocument10 pagesThe PROCON PH Process Control System Is Based Around The PH Rig and Is A Selfmiantahir89No ratings yet
- Incubator Project (UMP)Document24 pagesIncubator Project (UMP)adiamiru100% (3)
- Instruction Manual: Pid Based Pressure Loop TrainerDocument28 pagesInstruction Manual: Pid Based Pressure Loop TrainerKiran BennyNo ratings yet
- Control SystemsDocument18 pagesControl Systemsgayatri jaltareNo ratings yet
- Mesb333 Pid ControlDocument13 pagesMesb333 Pid ControlMohd KhairiNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems and Control Systems': An Open-Loop ControllerDocument5 pagesEmbedded Systems and Control Systems': An Open-Loop Controllermohed_kamalNo ratings yet
- Summary For Chapter 8Document3 pagesSummary For Chapter 8Zeny NaranjoNo ratings yet
- PID ControllersDocument9 pagesPID Controllerszs94qjqcx7No ratings yet
- Pid Control TheoryDocument8 pagesPid Control TheorySonu SinghNo ratings yet
- Pci Lab Manual (2) StudentDocument67 pagesPci Lab Manual (2) StudentTewodros AsfawNo ratings yet
- Various Types of ControllerDocument59 pagesVarious Types of ControllerZakariyaNo ratings yet
- ExercisesDocument18 pagesExercisescetec1234No ratings yet
- W7ADocument15 pagesW7AShujah RashidNo ratings yet
- Special Nonlinear Pid ControllersDocument25 pagesSpecial Nonlinear Pid ControllersawalmeidaNo ratings yet
- Exp - P6 - Temperature ControlDocument10 pagesExp - P6 - Temperature ControlSiddesh PatilNo ratings yet
- DR20Document136 pagesDR20Daryl Asto MercadoNo ratings yet
- PID CONTRILLER J (1) )Document18 pagesPID CONTRILLER J (1) )Loretta CardozoNo ratings yet
- 2023 PCI360S Introductory ConceptsDocument19 pages2023 PCI360S Introductory ConceptsSifanele PotwanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Controller PrinciplesDocument34 pagesChapter Two: Controller PrinciplesBekaluNo ratings yet
- Process ControlDocument2 pagesProcess ControlFakharAbbasNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 Control Configuration 4.1 Pid ControllerDocument8 pagesChapter - 4 Control Configuration 4.1 Pid ControllerMoorthy ManikandanNo ratings yet
- CHP 1Document18 pagesCHP 1BRIAN CLIFFNo ratings yet
- Working or Operation of PID ControllerDocument7 pagesWorking or Operation of PID Controllerjohn glenn magnoNo ratings yet
- PROCON Student ManualDocument48 pagesPROCON Student ManualPaul100% (1)
- Report ControlDocument33 pagesReport Controlajwadalfatani100% (5)
- PID - Scanner 2000Document12 pagesPID - Scanner 2000hectorivantovarjaimesNo ratings yet
- Se201 (A4)Document4 pagesSe201 (A4)Mehran Rasheed GorayaNo ratings yet
- Closed-Loop Control Toolbox APP-RTT-E-GBDocument11 pagesClosed-Loop Control Toolbox APP-RTT-E-GBLuis Enrique PariapazaNo ratings yet
- What Is A PID ControllerDocument11 pagesWhat Is A PID ControllerANRG Batch 11No ratings yet
- Pid EeeeDocument28 pagesPid Eeeecyprian obotaNo ratings yet
- PID ControllersDocument6 pagesPID ControllersNguyễn HảiNo ratings yet
- 21 THDocument32 pages21 THujjwal kumarNo ratings yet
- Tarea2 Investigacion-Mcca-190090Document13 pagesTarea2 Investigacion-Mcca-190090Christian MendezNo ratings yet
- Department of Petrochemical Engineering College of Technical Engineering University of Polytechnic-DuhokDocument11 pagesDepartment of Petrochemical Engineering College of Technical Engineering University of Polytechnic-DuhokWalid AdnanNo ratings yet
- Module 10 - Loop TuningDocument41 pagesModule 10 - Loop TuningHtet LwinNo ratings yet
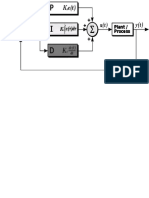
- Kfetrkt: Plant T) Process KeDocument4 pagesKfetrkt: Plant T) Process KeAmogh RNo ratings yet
- Name: Roll: Year: Department: Subject: Subject CodeDocument11 pagesName: Roll: Year: Department: Subject: Subject CodeMayukh BiswasNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 PLC PDFDocument15 pagesUnit 3 PLC PDFMahesh ShendeNo ratings yet
- IPCDocument15 pagesIPCu can't see meNo ratings yet
- Temp Control Che LabDocument10 pagesTemp Control Che LabStephanie SomongcadNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.1: Now Manually Move The AVS-1 Bar To Control The Flow Through The Valve in To The ContainerDocument16 pagesExperiment No.1: Now Manually Move The AVS-1 Bar To Control The Flow Through The Valve in To The ContainerfahadfiazNo ratings yet
- ECNG3004 Control System ApplicationsDocument7 pagesECNG3004 Control System ApplicationsMarlon BoucaudNo ratings yet
- PPC 2 CemeDocument39 pagesPPC 2 CemeHammad AnsariNo ratings yet
- Greater Karachi Regional Plan - 2047 (CRC Decision)Document4 pagesGreater Karachi Regional Plan - 2047 (CRC Decision)Hammad AnsariNo ratings yet
- Population Growth and Economic Development of PakistanDocument24 pagesPopulation Growth and Economic Development of PakistanHammad Ansari100% (1)
- Right-Sizing in Public Sector OrganizationsDocument24 pagesRight-Sizing in Public Sector OrganizationsHammad AnsariNo ratings yet
- Facility Planning & Layouts Basic CriteriaDocument15 pagesFacility Planning & Layouts Basic CriteriaHammad AnsariNo ratings yet
- Inventory ManagementDocument83 pagesInventory ManagementHammad AnsariNo ratings yet
- IEEE Certificate 2012Document1 pageIEEE Certificate 2012Hammad AnsariNo ratings yet
- Internship Weekly Report: Third Week, 11th July 2011 To 16th July 2011Document5 pagesInternship Weekly Report: Third Week, 11th July 2011 To 16th July 2011Hammad AnsariNo ratings yet
- Applications and Advantages For Protection Schemes Using IEC 61850 StandardDocument11 pagesApplications and Advantages For Protection Schemes Using IEC 61850 StandardHammad AnsariNo ratings yet
- Sustainable WirelessDocument7 pagesSustainable WirelessHammad AnsariNo ratings yet
- Na-254 Karachi East-XviDocument1 pageNa-254 Karachi East-XviHammad AnsariNo ratings yet
- Fuikura 60S ManualDocument119 pagesFuikura 60S ManualArturo Sierra100% (1)
- Introduction To GSMDocument86 pagesIntroduction To GSMHammad AnsariNo ratings yet
- GSM Planning & OptimizationDocument13 pagesGSM Planning & OptimizationHammad Ansari100% (1)
- ChannelsDocument51 pagesChannelsHammad AnsariNo ratings yet
- 65 NM CMOS Devices For Low Power ApplicationsDocument1 page65 NM CMOS Devices For Low Power ApplicationsHammad AnsariNo ratings yet
- Identification of Energy Theft and Tampered Meters Using A Central Observer Meter: A Mathematical ApproachDocument6 pagesIdentification of Energy Theft and Tampered Meters Using A Central Observer Meter: A Mathematical ApproachHammad AnsariNo ratings yet
- TRPTraining GuidelinesDocument27 pagesTRPTraining GuidelinesHammad AnsariNo ratings yet
- Multiple Moving Target Detection, Tracking, and Recognition From A Moving ObserverDocument6 pagesMultiple Moving Target Detection, Tracking, and Recognition From A Moving ObserverHammad AnsariNo ratings yet
- Control System QBDocument29 pagesControl System QBPrabhavathi AadhiNo ratings yet
- EMCS Technology Solutions V2Document78 pagesEMCS Technology Solutions V2alexosi7No ratings yet
- DLC3010 Digital LevelDocument16 pagesDLC3010 Digital LevelAnonymous zTUWsMNo ratings yet
- Ejsr 57 1 14Document19 pagesEjsr 57 1 14Manikandaprabu NallasivamNo ratings yet
- Chen4570 Sp00 FinalDocument11 pagesChen4570 Sp00 FinalmazinNo ratings yet
- Tebis KNX - Home and Building Control SystemDocument62 pagesTebis KNX - Home and Building Control SystemFathan MubinaNo ratings yet
- Water Flow Control System V2 PDFDocument12 pagesWater Flow Control System V2 PDFAayushSrivastava100% (1)
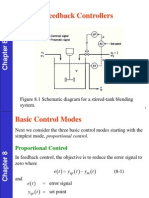
- Feedback Controllers: Figure 8.1 Schematic Diagram For A Stirred-Tank Blending SystemDocument18 pagesFeedback Controllers: Figure 8.1 Schematic Diagram For A Stirred-Tank Blending Systeml7aniNo ratings yet
- CNC CimDocument16 pagesCNC CimAbdulhmeed MutalatNo ratings yet
- FC102 - Control Pi EjemploDocument2 pagesFC102 - Control Pi Ejemplojose_balcazar89No ratings yet
- Control - Systems. TWO MARKSDocument32 pagesControl - Systems. TWO MARKSdivya vaidhyanathanNo ratings yet
- Control Lab 2Document7 pagesControl Lab 2Kelvin Ting S BNo ratings yet
- Control System 2Document36 pagesControl System 2RajeevSangamNo ratings yet
- Distributed Control SystemDocument5 pagesDistributed Control Systemjital1994No ratings yet
- Introduction About Amtek: 1.amtek LTD.: An OverviewDocument47 pagesIntroduction About Amtek: 1.amtek LTD.: An OverviewSahil SethiNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy Logic ControllerDocument4 pagesFuzzy Logic ControllerSalma KhanNo ratings yet
- Controls Exit OTDocument13 pagesControls Exit OTJeffrey Wenzen AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- 05 MathematicalReference PDFDocument484 pages05 MathematicalReference PDFmirofeloNo ratings yet
- Section 9 - 4150 and 4160 Pressure Controllers PDFDocument43 pagesSection 9 - 4150 and 4160 Pressure Controllers PDFMahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet