Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TN Board Exam - Biology Zoology - Model Question Paper
Uploaded by
no1dubakoorOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TN Board Exam - Biology Zoology - Model Question Paper
Uploaded by
no1dubakoorCopyright:
Available Formats
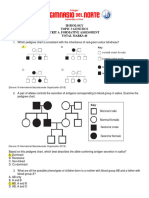
BIO ZOOLOGY CHATPER 4 MODERN GENETICS OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Colchicine stops mitosis at a. prophase b. metaphase c. anaphase d. telophase
2. For Karyotyping cells are subjected to ----------- solution a. isotonic b. hypertonic c. hypotonic d. concentrated
3. In karyotyping of human chromosome, many groups are classified based on the centromere position a. 5 b. 6 c. 7 d. 10
4. In karyotyping of human chromosome, which group exclusively contain metacentric a. Group A b. Group B c. Group C d. Group D
5. In karyotyping of human chromosome, which one of the following group is considered as largest group a. Group A b. Group B c. Group C d. Group D
6. In karyotyping of human chromosome, which group contain x chromosome a. Group A b. Group B c. Group C d. Group D
7. In karyotyping of human chromosome, x chromosome resemble ----- chromosome a. 5 b. 6 c. Y d. 3
8. In karyotyping of human chromosome, which group contain only 2 chromosome of submetacentric a. B b. C c. D d. E
9. In karyotyping of human chromosome, which group contain only 2 chromosome of shorter metacentric a. F b. E c. D d. C
10. In karyotyping of human chromosome, which group contain only short acrocentric chromosome a. Group E b. Group F c. Group G d. Group C
11. Y chromosome belongs to the group a. Group E b. Group F c. Group G d. Group C
12. The existence of mobile genetic elements were visualized by a. Waldeyer 13. Vehicle DNA is b. Johanson c. Barbara Meclintock d. Bridges
a. Vectors
b. endonucleases
c. foreign DNA
d. restriction endonucleases
14. Palindrome sequences recognized by a. ligase 15. EcoR1 is a a. ligase b. exo nucleases c. endo nucleases d. restriction endonucleases b. exo nucleases c. endo nucleases d. restriction endonucleases
16. The recombination of foreign DNA with plasmid DNA done by a. ligase b. exo nucleases c. endo nucleases d. restriction endonucleases
17. The first gene was cloned in a. 1980 b. 1973 c. 1999 d. 1978
18. The first gene was cloned by a. Watson and Crik b. Johanson c. Barbara Meclintock d. Hebert Bayer and Stanely cohen
19. In human beings, more than ----------- hereditary diseases have been indentified a. 200 b 300 c. 100 d. 400 20. Which one of the following genotype suffer from a fatal haemolytic anaemia a. Hba Hba b Hbs Hbs c. Hba Hbs d. Hbs Hba 21. Which one of the following hereditary disease cause damaged heart, kidney, spleen and brain.
a. Sickle
cell anaemia b. Thalassemia
c. Agammaglobulinemia
d. Albinism
22. In Sickle cell anaemia , genotype of carrier is a. Hba Hba b Hbs Hbs c. Hba Hbs 23. Erythroblastic anaemia is
a. Sickle
d. Hbx Hby
cell anaemia
b. Thalassemia
c. Agammaglobulinemia
d. Albinism
24. Peripheral haemolysis is the charateristic symptom of
a. Sickle
cell anaemia
b. Thalassemia
c. Agammaglobulinemia
d. Albinism
25. Splenomegaly and hepatomegaly is the charateristic symptom of
a. Sickle
cell anaemia
b. Thalassemia
c. Agammaglobulinemia
d. Albinism
26. Which one of the following is recessive gene disease
a. Sickle
cell anaemia
b. Thalassemia
c. Agammaglobulinemia
d. Albinism
27. Agammaglobulinemia mostly affects,
a. Boys
b. Womens
c. Elders
d. Babies
28. Failure in r-globulin synthesis resulting,
a. Sickle
cell anaemia
b. Thalassemia
c. Agammaglobulinemia
d. Albinism
29. The incidence of albinism in human is a. 1:5000 to 1:2500 b. 1:500 to 1:25000 c. 1:1000 to 1: 5000 d. 1:2000 to 1:2500
30. Disease caused by an autosomal dominant gene is
a. SCID b. Thalassemia c. Huntingtons
chorea
d. Albinism
31. Onset of Huntingtons chorea is between ------------ years a. 35-40 b. 12-15 c. 18-25 d. above 60
32. In Huntingtons chorea the affected gene located in ----------- chromosome a. 5 b. 4 c. Y d. 3
33. Which one of the following disease characterized by uncontrolled jerking of the body
a. SCID b. Thalassemia c. Huntingtons
chorea
d. Albinism
34. ADA gene located in ----------- chromosome a. 7 b. 20 c. X d. Y
35. Which one of the following hereditary disease is called extremely rare
a. SCID b. Thalassemia c. Huntingtons
chorea d. Albinism
36. Bubble Boy Syndrome,
a. SCID b. Thalassemia c. Huntingtons
chorea d. Albinism
37. Huntingtons chorea is the a. Incurable disease b. cured by bone marrow transplant c. prevented by vaccine d.cured by WBC transplant 38. In HGP total number of genes identified by sequencing the genome are, a. 25000 b.30000 c.50000 d. 5000
39. Total number of different m-RNA identified so far is, a. 25000 b.60000 c.50000 d. 75000
40. Nuclear transplantation developed by, a. R.Briggs and T.King b. Dr. Ian Wilmut c.Bridges d.Anand Mohan chakrabarty
BIO ZOOLOGY CHATPER 4 MODERN GENETICS OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Colchicine stops mitosis at b. prophase b. metaphase c. anaphase d. telophase
2. For Karyotyping cells are subjected to ----------- solution b. isotonic b. hypertonic c. hypotonic d. concentrated
3. In karyotyping of human chromosome, many groups are classified based on the centromere position b. 5 b. 6 c. 7 d. 10
4. In karyotyping of human chromosome, which group exclusively contain metacentric b. Group A b. Group B c. Group C d. Group D
5. In karyotyping of human chromosome, which one of the following group is considered as largest group b. Group A b. Group B c. Group C d. Group D
6. In karyotyping of human chromosome, which group contain x chromosome a. Group A b. Group B c. Group C d. Group D
7. In karyotyping of human chromosome, x chromosome resemble ----- chromosome a. 5 b. 6 c. Y d. 3
8. In karyotyping of human chromosome, which group contain only 2 chromosome of submetacentric a. B b. C c. D d. E
9. In karyotyping of human chromosome, which group contain only 2 chromosome of shorter metacentric a. F b. E c. D d. C
10. In karyotyping of human chromosome, which group contain only short acrocentric chromosome a. Group E b. Group F c. Group G d. Group C
11. Y chromosome belongs to the group a. Group E b. Group F c. Group G d. Group C
12. The existence of mobile genetic elements were visualized by a. Waldeyer 13. Vehicle DNA is a. Vectors b. endonucleases c. foreign DNA d. restriction endonucleases b. Johanson c. Barbara Meclintock d. Bridges
14. Palindrome sequences recognized by a. ligase 15. EcoR1 is a a. ligase b. exo nucleases c. endo nucleases d. restriction endonucleases b. exo nucleases c. endo nucleases d. restriction endonucleases
16. The recombination of foreign DNA with plasmid DNA done by a. ligase b. exo nucleases c. endo nucleases d. restriction endonucleases
17. The first gene was cloned in a. 1980 b. 1973 c. 1999 d. 1978
18. The first gene was cloned by a. Watson and Crik b. Johanson c. Barbara Meclintock d. Hebert Bayer and Stanely cohen
19. In human beings, more than ----------- hereditary diseases have been indentified a. 200 b 300 c. 100 d. 400 20. Which one of the following genotype suffer from a fatal haemolytic anaemia a. Hba Hba b Hbs Hbs c. Hba Hbs d. Hbs Hba 21. Which one of the following hereditary disease cause damaged heart, kidney, spleen and brain.
a. Sickle
cell anaemia
b. Thalassemia c. Agammaglobulinemia
d. Albinism
22. In Sickle cell anaemia , genotype of carrier is a. Hba Hba b Hbs Hbs c. Hba Hbs
d. Hbx Hby
23. Erythroblastic anaemia is
a. Sickle
cell anaemia
b. Thalassemia c. Agammaglobulinemia
d. Albinism
24. Peripheral haemolysis is the charateristic symptom of
a. Sickle
cell anaemia
b. Thalassemia c. Agammaglobulinemia
d. Albinism
25. Splenomegaly and hepatomegaly is the charateristic symptom of
a. Sickle
cell anaemia
b. Thalassemia c. Agammaglobulinemia
d. Albinism
26. Which one of the following is recessive gene disease
a. Sickle
cell anaemia
b. Thalassemia
c. Agammaglobulinemia
d. Albinism
27. Agammaglobulinemia mostly affects, a. Boys b. Womens c. Elders d. Babies
28. Failure in r-globulin synthesis resulting,
a. Sickle
cell anaemia
b. Thalassemia
c. Agammaglobulinemia
d. Albinism
29. The incidence of albinism in human is a. 1:5000 to 1:2500 b. 1:500 to 1:25000 c. 1:1000 to 1: 5000 d. 1:2000 to 1:2500
30. Disease caused by an autosomal dominant gene is
a. SCID b. Thalassemia c. Huntingtons
chorea d. Albinism
31. Onset of Huntingtons chorea is between ------------ years a. 35-40 b. 12-15 c. 18-25 d. above 60
32. In Huntingtons chorea the affected gene located in ----------- chromosome a. 5 b. 4 c. Y d. 3
33. Which one of the following disease characterized by uncontrolled jerking of the body
a. SCID b. Thalassemia c. Huntingtons
chorea d. Albinism
34. ADA gene located in ----------- chromosome a. 7 b. 20 c. X d. Y
35. Which one of the following hereditary disease is called extremely rare
a. SCID b. Thalassemia c. Huntingtons
chorea d. Albinism
36. Bubble Boy Syndrome,
a. SCID
b. Thalassemia
c. Huntingtons
chorea d. Albinism
37. Huntingtons chorea is the a. Incurable disease b. cured by bone marrow transplant c. prevented by vaccine d.cured by WBC transplant 38. In HGP total number of genes identified by sequencing the genome are, a. 25000 b.30000 c.50000 d. 5000
39. Total number of different m-RNA identified so far is, a. 25000 b.60000 c.50000 d. 75000
40. Nuclear transplantation developed by, a. R.Briggs and T.King b. Dr. Ian Wilmut c.Bridges d.Anand Mohan chakrabarty
You might also like
- Healthy Cooking Oil from RiceDocument7 pagesHealthy Cooking Oil from Ricehusainkabir63_113901No ratings yet
- Answers To Genetics Practice Exam 1Document15 pagesAnswers To Genetics Practice Exam 1cowboyNo ratings yet
- புதிய காற்று மாத இதழ் - ஜூன் 2008.Document64 pagesபுதிய காற்று மாத இதழ் - ஜூன் 2008.vrbalaNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy of Angiosperms - Full - Omnipage WorkDocument811 pagesTaxonomy of Angiosperms - Full - Omnipage Workno1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Plants of Jamaica GuideDocument86 pagesMedicinal Plants of Jamaica Guideno1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- SexDocument74 pagesSexbill jons0% (1)
- Organization of Genes and Chromosomes CompleteDocument13 pagesOrganization of Genes and Chromosomes Completebiotecnika_testNo ratings yet
- 15 Coned CCRN GastrointestinalDocument21 pages15 Coned CCRN GastrointestinalAkbar TaufikNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsNo ratings yet
- MCQSDocument10 pagesMCQSahmed100% (2)
- Genetics Entrance QuestionsDocument3 pagesGenetics Entrance Questionsjaleelkabdul75% (4)
- Physiology 2020 Evaluation 11: Gastrointestinal PhysiologyDocument5 pagesPhysiology 2020 Evaluation 11: Gastrointestinal PhysiologyCourtneyNo ratings yet
- A Concise Textbook of Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryDocument304 pagesA Concise Textbook of Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryRadu Breahna91% (22)
- Epoetin AlfaDocument2 pagesEpoetin AlfaKasandra Dawn Moquia BerisoNo ratings yet
- Karapitiya OSCE 2017 With AnswersDocument34 pagesKarapitiya OSCE 2017 With Answersweerawarna fernandoNo ratings yet
- Mcqs On GeneticsDocument10 pagesMcqs On Geneticspkm7929100% (2)
- Manual de Plante MedicinaleDocument115 pagesManual de Plante Medicinalevrajitorul100% (3)
- Genetics Practice Practice Exam 1Document14 pagesGenetics Practice Practice Exam 1cowboyNo ratings yet
- 12 Biology sp10Document14 pages12 Biology sp10Unknown PersonNo ratings yet
- 49868AK Set 1-2 General - Biology - Quiz - 2-Oct31-MergedDocument8 pages49868AK Set 1-2 General - Biology - Quiz - 2-Oct31-Mergedf20230821No ratings yet
- Mock Exam 1Document9 pagesMock Exam 1lujain100% (1)
- Practice Test in Biological Science 3Document14 pagesPractice Test in Biological Science 3Sha CalsesNo ratings yet
- bt301 Full Book McqsDocument31 pagesbt301 Full Book McqsAarish AliNo ratings yet
- Biology MQ XiiDocument67 pagesBiology MQ XiiAditya Mohan GuptaNo ratings yet
- K101PracticeExam3 SP19Document8 pagesK101PracticeExam3 SP19Braxton PhillipsNo ratings yet
- Paper Practice Test With KEY AttachedDocument8 pagesPaper Practice Test With KEY AttachedmspallardNo ratings yet
- 620biology QB Xii 23-24 Term 1Document23 pages620biology QB Xii 23-24 Term 1Jiya PandeyNo ratings yet
- Med 12th Feb (1med)Document39 pagesMed 12th Feb (1med)Naeem AminNo ratings yet
- 526063MDocument8 pages526063MSiva RajanNo ratings yet
- KAZIRANGA ENGLISH ACADEMY BIOLOGY TEST CLASS XIIDocument8 pagesKAZIRANGA ENGLISH ACADEMY BIOLOGY TEST CLASS XIIKaziranga English AcademyNo ratings yet
- 1st October - Term 1 - BiologyDocument4 pages1st October - Term 1 - Biologyaaravp2029No ratings yet
- Practice Test in Biological ScienceDocument6 pagesPractice Test in Biological Sciencenhoj eca yabujNo ratings yet
- 12 Principles of Inheritance and Variation MCQ PDFDocument6 pages12 Principles of Inheritance and Variation MCQ PDFMallikarjuna MuthyaluNo ratings yet
- Sci9 - Pre Test 5Document2 pagesSci9 - Pre Test 5Nancy AmaroNo ratings yet
- BS Part 6Document7 pagesBS Part 6Lea Fe Comilang ArcillaNo ratings yet
- Genetics qad soln- 1Document29 pagesGenetics qad soln- 1c4655qg67pNo ratings yet
- Pathology SWT 13.11. 2023Document19 pagesPathology SWT 13.11. 2023Teena VajiNo ratings yet
- Additional BIOLOGY 12th NM Pa 1Document8 pagesAdditional BIOLOGY 12th NM Pa 1JAGMOHAN SHARDANo ratings yet
- Theory QuestionsDocument121 pagesTheory Questionsjanakansenthil2010No ratings yet
- Sample Paper MPhil Zoology Newn 2Document20 pagesSample Paper MPhil Zoology Newn 2Amna TariqNo ratings yet
- Bio QuestionsDocument69 pagesBio Questionseman.1122505No ratings yet
- QP Bio Xii SPDocument5 pagesQP Bio Xii SPAachal GayreNo ratings yet
- 11th Bio - Botany One Mark Question Bank With Answer Key English Medium 2022-23Document8 pages11th Bio - Botany One Mark Question Bank With Answer Key English Medium 2022-23Cute Sweet100% (1)
- BSC Nursing Previous Year Question PaperDocument16 pagesBSC Nursing Previous Year Question PaperSadiya Pathan100% (1)
- Biology Module 1 QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesBiology Module 1 QuestionnairePhen MontalboNo ratings yet
- Unit C ExamDocument18 pagesUnit C Examapi-199149636No ratings yet
- DBT BET JRF 2019 Solved Question Paper With Answer KeyDocument36 pagesDBT BET JRF 2019 Solved Question Paper With Answer KeySHYAM KUMAR 155100590% (1)
- Previous Year QuestionDocument10 pagesPrevious Year QuestionsdayNo ratings yet
- Plant Science JRF 2009Document21 pagesPlant Science JRF 2009YASHPAL SINGHNo ratings yet
- Paper I-IV (Past Question)Document22 pagesPaper I-IV (Past Question)Shashanka PoudelNo ratings yet
- Biology Entry Test 2017 2018Document5 pagesBiology Entry Test 2017 2018Collen Tinashe MakoniNo ratings yet
- Chromosome and Genetics MCQsDocument18 pagesChromosome and Genetics MCQselanthamizhmaranNo ratings yet
- National Standard Examination in Biology 2009-2010: Indian Association of Teachers in Biological SciencesDocument21 pagesNational Standard Examination in Biology 2009-2010: Indian Association of Teachers in Biological SciencespreetsyadNo ratings yet
- AIIMS PG 2005 Question Paper PDFDocument26 pagesAIIMS PG 2005 Question Paper PDFramNo ratings yet
- TN Sinh 2Document23 pagesTN Sinh 2Lê Hoàng Kim KhánhNo ratings yet
- Genetics - PYQs and Concept Maps-AKDocument92 pagesGenetics - PYQs and Concept Maps-AKSaiNagaVignesh BandhamNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Biology Time: 90 Minutes General Instructions:: Sample Question Paper-1Document23 pagesClass Xii Biology Time: 90 Minutes General Instructions:: Sample Question Paper-1RitishnaNo ratings yet
- Pedia 102 Quiz 2 SemifinalsDocument19 pagesPedia 102 Quiz 2 Semifinalsquidditch07100% (1)
- Wbjee 2012 Biology Question PaperDocument8 pagesWbjee 2012 Biology Question Papersaurav guptaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing 102 Unit Test AnswersDocument11 pagesPediatric Nursing 102 Unit Test Answersquidditch07No ratings yet
- WS Bio T3 GeneticsDocument11 pagesWS Bio T3 GeneticsLAURA SOFIA MANJARRES ESPITIANo ratings yet
- MCQs on Biotechnology Topics for University ExamDocument8 pagesMCQs on Biotechnology Topics for University ExamaprilNo ratings yet
- NIMHANS 2007 DM/MCh Paper for MBBSDocument51 pagesNIMHANS 2007 DM/MCh Paper for MBBSravasoNo ratings yet
- HAEM2000 Block 2 Test 2014 MCQDocument10 pagesHAEM2000 Block 2 Test 2014 MCQMatsiri ImmanuelNo ratings yet
- KMS Biology Xii 2Document8 pagesKMS Biology Xii 2Sandeep KNo ratings yet
- Aiims PG 2005 (Based On Memory)Document197 pagesAiims PG 2005 (Based On Memory)Aadityarajsinh GohilNo ratings yet
- NUST Bio Sciences Past PaperDocument29 pagesNUST Bio Sciences Past PaperAsad KhanNo ratings yet
- 67-11th Bio-Botany EM - One Marks Questions With Keys - English Medium PDF DownloadDocument8 pages67-11th Bio-Botany EM - One Marks Questions With Keys - English Medium PDF Downloadsheikabdulpari.nNo ratings yet
- Quiz On Gene Expression, Mutation, Allele FrequencyDocument4 pagesQuiz On Gene Expression, Mutation, Allele Frequencyernesto_ayocNo ratings yet
- Centers of Origin of Crop Plants: The Eight Vavilovian Centers (Fig. 5-1, 5-2)Document9 pagesCenters of Origin of Crop Plants: The Eight Vavilovian Centers (Fig. 5-1, 5-2)Hrudaya BiharaNo ratings yet
- Lesson-02 COMMON STAINING TECHDocument13 pagesLesson-02 COMMON STAINING TECHno1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Chap 1 - Print RedyDocument8 pages9 Science Chap 1 - Print Redyno1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- Equivalence Degrees G.O.Document11 pagesEquivalence Degrees G.O.no1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Plants - Rural Resource Pack - NetherlandsDocument43 pagesMedicinal Plants - Rural Resource Pack - Netherlandsno1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- Medicinal PlantsDocument11 pagesMedicinal Plantsno1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- Sharma and Kumar - Ethano Botanical Studies of Medicinal Plants in RajhastanDocument6 pagesSharma and Kumar - Ethano Botanical Studies of Medicinal Plants in Rajhastanno1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- Adsl Modem SetupDocument1 pageAdsl Modem Setupno1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Plants of Khasi HillsDocument6 pagesMedicinal Plants of Khasi Hillsno1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- Medicnal Plants and Socio Economin in North IndiaDocument6 pagesMedicnal Plants and Socio Economin in North Indiano1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- Bank ChallanDocument1 pageBank Challanno1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- Public Question Chapterwise TM 11.11.10Document24 pagesPublic Question Chapterwise TM 11.11.10no1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- PG RegularisationDocument3 pagesPG Regularisationno1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- TN Board Exam - Biology Zoology - Model Question PaperDocument7 pagesTN Board Exam - Biology Zoology - Model Question Paperno1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- Wetland Guide - RamsarDocument60 pagesWetland Guide - Ramsarno1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- 9 TET Syllabus Paper 1 Environmental Studues & ScienceDocument18 pages9 TET Syllabus Paper 1 Environmental Studues & ScienceMohankumar P KNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Angiosperms SystematicsDocument3 pagesMCQ On Angiosperms Systematicsno1dubakoor100% (1)
- Incridable 3d Paper Model TemplateDocument1 pageIncridable 3d Paper Model Templateno1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- Paryavanmitra TAMILDocument38 pagesParyavanmitra TAMILno1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- Environmental Grant Application Forms - NGC Eco ClubDocument5 pagesEnvironmental Grant Application Forms - NGC Eco Clubno1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Angiosperms SystematicsDocument3 pagesMCQ On Angiosperms Systematicsno1dubakoor100% (1)
- KALAVATHIDocument183 pagesKALAVATHIno1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- Algae Economic ImportanceDocument9 pagesAlgae Economic Importanceno1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- Home SoE Report 2009Document194 pagesHome SoE Report 2009Alok KumarNo ratings yet
- Green School AwardDocument3 pagesGreen School Awardno1dubakoorNo ratings yet
- Expanded Dengue Syndrome: Gastrointestinal Manifestations.: March 2018Document7 pagesExpanded Dengue Syndrome: Gastrointestinal Manifestations.: March 2018NicholasNo ratings yet
- comments-NvoX wEtwDkDocument28 pagescomments-NvoX wEtwDkElina GeorgievaNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Củng Cố Tuần 4Document12 pagesBài Tập Củng Cố Tuần 4Phương ThùyNo ratings yet
- Oral Pre Cancerous LesionsDocument49 pagesOral Pre Cancerous LesionsAmit MishraNo ratings yet
- The Boston C StoryDocument3 pagesThe Boston C StoryVincent John RigorNo ratings yet
- Prolonged Survival in Stage III Melanoma With Ipilimumab Adjuvant TherapyDocument11 pagesProlonged Survival in Stage III Melanoma With Ipilimumab Adjuvant TherapyIvo AfianiNo ratings yet
- 10 11648 J Ijmi 20170505 12Document5 pages10 11648 J Ijmi 20170505 12Anchit AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Leuk OrrheaDocument6 pagesLeuk Orrheababon3No ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia in The Newborn: AIIMS-NICU Protocols 2010Document13 pagesHypoglycemia in The Newborn: AIIMS-NICU Protocols 2010abhivnairNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Discharge + PruritisDocument56 pagesVaginal Discharge + PruritisEkoApriandhiNo ratings yet
- Git NursingDocument245 pagesGit NursingWeng Maesa MontemayorNo ratings yet
- 3711 PORTFOLIO FinalDocument10 pages3711 PORTFOLIO Finalgivenl193No ratings yet
- Amazing Sanitary Napkin Relieves Infection, Stress with 6,070 Negative IonsDocument6 pagesAmazing Sanitary Napkin Relieves Infection, Stress with 6,070 Negative Ionsrostenec100% (1)
- Arab Board Exam Nov 2014Document5 pagesArab Board Exam Nov 2014Firyal Balushi100% (4)
- Mono79 10Document15 pagesMono79 10Constantin MirelaNo ratings yet
- Liver Cancer Imaging Role of CT, MRI, US and PETDocument5 pagesLiver Cancer Imaging Role of CT, MRI, US and PETflorinscribdNo ratings yet
- Cazuri Vindecare Paleo Medicina PDFDocument13 pagesCazuri Vindecare Paleo Medicina PDFRama KrisnaNo ratings yet
- The Platyhelminthes (Flatworms) : Flukes: - Trematodes Are Parasites of Vertebrates. They HaveDocument29 pagesThe Platyhelminthes (Flatworms) : Flukes: - Trematodes Are Parasites of Vertebrates. They HaveRiya KayarkarNo ratings yet
- MusculoskeletalDocument119 pagesMusculoskeletalsimplyrosalyn100% (5)
- Approach To A Patient With "Solitary Thyroid Nodule" (STN)Document6 pagesApproach To A Patient With "Solitary Thyroid Nodule" (STN)Jacob Alexander MarpaungNo ratings yet
- Seminar 2 QuestionsDocument10 pagesSeminar 2 QuestionsWafaa AdamNo ratings yet
- Intradural Spinal Cord Tumors: UpplementDocument1 pageIntradural Spinal Cord Tumors: Upplementlauzark gashbellNo ratings yet
- Analytical Exposition on Fast Food and HealthDocument6 pagesAnalytical Exposition on Fast Food and HealthAyin KatiliNo ratings yet