Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomical Landmarks of The Crown
Uploaded by
Hayley WelshOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomical Landmarks of The Crown
Uploaded by
Hayley WelshCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomical Landmarks of the Crown
Crown Elevations
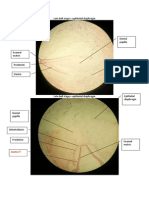
Lobes One of the primary centres of calcification and growth formed during the crown development. Each tooth begins to develop from 4 lobes or more. The pulp chamber has pulp horns corresponding to these lobes).
Types of Lobes Mamelones o They three small round projections of enamel present in the incisal 1/3 of newly erupted incisors o o Ideal age to see = 6-7 years Mamelones eventually wears down into a flat edge
Cingulum(cingula) o Enlargement or bulge on the cervical 1/3 of lingual surface of the crown in anterior teeth.
Cusps o Pyramidal projections on the incisal portion of the canine and occlusal surfaces of the posterior teeth(premolars and molars)
Tubercles Small elevation due to excessive formation of enamel Tubercle of carabelli found on the palatal surface of Upper E and 6 and sometimes lingual surfaces of incisors over the cingulum Tubercles are not cusps as it is formed of enamel only while cusp is formed of pulp horn covered by dentin and enamel therefore tubercles are not primary centres of calcification
Ridges It is a linear elevation on different surfaces of the crown
Facial surfaces o Labial ridge o found on the labial surface of canines result of the overdevelopment of the middle labial lobe
Buccal ridge Found on the buccal surfaces of premolars Result of the overdevelopment of the middle buccal lobe
Cervical ridge Found on the cervical 1/3 of the facial surfaces of all teeth
Lingual surfaces o o o o Incisal ridges found on the incisal 1/3 of lingual surfaces of all incisors Cusp ridges found on the incisal 1/3 of lingual surfaces of canines and premolars Lingual ridges found on middle 1/3 of lingual surface of upper and lower canines. Marginal ridges found on the mesial and distal margins on the lingual surfaces of all anterior teeth
Occlusal surfaces o Marginal ridges o Found on the occlusal surfaces of all posterior teeth mesial and distal to the triangular fossae
Triangular ridges Found on the occlusal surfaces of all posterior teeth forming cusps.
Transverse Ridge Formed from the extension of the triangular ridges of the buccal and lingual cusp
Oblique ridge Formed from the extension of the triangular ridges obliquely. Usually found on maxillary molars, connecting between ML and DB cusps.
Crown Depressions
Linear Depressions Developmental Grooves linear depression denoting complete union/fusion of primary lobes Supplemental grooves small irregularly placed auxiliary grooves that branches from developmental grooves. They do not represent the complete union/fusion of the lobes. They are found on the occlusal surfaces of 7s, 8s and lower 5s Fissures found on the bottom of developmental grooves result from incomplete union of the primary lobes. It is a fault in enamel. These can not be seen but can feel it. Sulcus broad depression or valley on the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth
Circumscribed Depressions Fossa small depression or concavity found on both anterior and posterior teeth o o Lingual Fossa found on the lingual surfaces of anterior teeth Mesial and Distal Triangular Fossa found on the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth, mesial and distal to the marginal ridges o Central Fossa found on the occlusal surfaces of molars. They are formed by the converging of ridges, terminating at a central point where there is the junction of grooves Pits o True small pinpoint depression present at the bottom of a fossa o Central pit found at the bottom of a central fossa Mesial and distal pits found at the bottom of the mesial and distal triangular pits
Faulty usually found at the end of the developmental groove and its the result of incomplete formation of enamel Buccal Pit located at the end of the buccal developmental grooves or lower molars
Socket the bony space in the alveolar bone containing the roots of erupted tooth Crypt bony space in the alveolar bone containing the developing unerupted tooth
You might also like
- Teeth and Supporting TissueDocument15 pagesTeeth and Supporting TissuehamidjigarNo ratings yet
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)From EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No ratings yet
- Tooth Landmarks 1Document45 pagesTooth Landmarks 1Lavanya Kalapala67% (3)
- Permanent Anterior Teeth06Document5 pagesPermanent Anterior Teeth06Tram BuiNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 C Anatomical LandmarksDocument6 pagesLec 2 C Anatomical LandmarksRohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Structures of TeethDocument13 pagesAnatomical Structures of TeethPrashantP.GandhiNo ratings yet
- Pengantar Anatomi Gigi, Teriminologi, & NomenklaturDocument19 pagesPengantar Anatomi Gigi, Teriminologi, & NomenklaturniputusellyowNo ratings yet
- Dental Landmarks GuideDocument12 pagesDental Landmarks GuideRagaveeNo ratings yet
- Teeth and Supporting StructuresDocument8 pagesTeeth and Supporting StructuresRosette GoNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy LectureDocument37 pagesDental Anatomy LectureHitesh Chopra100% (2)
- Mandibular Permanent Lateral IncisorDocument4 pagesMandibular Permanent Lateral IncisorHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Dental AnatomyDocument14 pagesDental Anatomyheenagoswami158No ratings yet
- Self Study Dental AnatomyDocument60 pagesSelf Study Dental Anatomynathansolai100% (1)
- Crown and Root Landmark GuideDocument62 pagesCrown and Root Landmark GuideSara Al-Fuqaha'No ratings yet
- 2016-Pengantar Anatomi Gigi, Teriminologi, & NomenklaturDocument24 pages2016-Pengantar Anatomi Gigi, Teriminologi, & NomenklaturniputusellyowNo ratings yet
- Occlusion WorksheetDocument6 pagesOcclusion WorksheetMya MacmillanNo ratings yet
- Tooth Morphology Basics: Howard Chi, D.M.DDocument79 pagesTooth Morphology Basics: Howard Chi, D.M.DMihaela Vasiliu0% (1)
- Terminoligies of Tooth MorphologyDocument33 pagesTerminoligies of Tooth MorphologyAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Maxillary MolarsDocument46 pagesMaxillary MolarsraminismahelNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Structures of TeethDocument13 pagesAnatomical Structures of TeethBob Permana SimanungkalitNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Centeral IncisorDocument22 pagesMaxillary Centeral IncisordrnaglaaNo ratings yet
- Dental OsteologyDocument154 pagesDental OsteologyfabrizioaryanNo ratings yet
- Developing ToothDocument3 pagesDeveloping ToothZHIARA MAE FACUNNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy Lec.3Document14 pagesDental Anatomy Lec.3Sinan A. ShwailiyaNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy & Occlusion NOTESDocument7 pagesDental Anatomy & Occlusion NOTESyosman1000100% (1)
- All Dental AnatomyDocument114 pagesAll Dental AnatomyKhanh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 8 CaninesDocument51 pages8 CaninesDidar Sadiq KwekhaNo ratings yet
- Permanent Upper Canine NotesDocument5 pagesPermanent Upper Canine NotesHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Cfe 2Document10 pagesCfe 2Said SaidNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of the Oral Cavity and its StructuresDocument5 pagesAnatomy of the Oral Cavity and its StructuresSimina TanaseNo ratings yet
- Lec1 2019 Converted 2Document10 pagesLec1 2019 Converted 2Said SaidNo ratings yet
- Human Dentition Handouts Semester II 2021/2022Document92 pagesHuman Dentition Handouts Semester II 2021/2022Siddharth SinghNo ratings yet
- Dental Morphology 1Document108 pagesDental Morphology 1Goutham SunilNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy: The Permanent Canines .Document7 pagesDental Anatomy: The Permanent Canines .S:M:ENo ratings yet
- Lect 1 4th GradeDocument8 pagesLect 1 4th Gradesinem yıldırımNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec 4 PDFDocument6 pagesAnatomy Lec 4 PDFHaedr KhaleelNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy Final ReviewDocument10 pagesDental Anatomy Final ReviewSalma AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mandibular PremolarsDocument28 pagesMandibular PremolarsraminismahelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Elevations and DepressionsDocument23 pagesLecture 3 Elevations and Depressionsnoha.arch00No ratings yet
- Lower CentralDocument1 pageLower CentralHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- 2 ND PDFDocument22 pages2 ND PDFBan jassamNo ratings yet
- The Biting Surface of Molar Is Called OCCLUSAL SurfaceDocument5 pagesThe Biting Surface of Molar Is Called OCCLUSAL SurfaceCroitort53No ratings yet
- The Permanent Mandibular PremolarsDocument67 pagesThe Permanent Mandibular PremolarsSushmitKoju100% (1)
- Maxillary and Mandibular Anterior Tooth Anatomy NotesDocument6 pagesMaxillary and Mandibular Anterior Tooth Anatomy NotesDrSumaiya SayyedNo ratings yet
- Tooth IdentificationDocument19 pagesTooth Identificationardy420No ratings yet
- Page 4251072Document16 pagesPage 4251072YuAyu Permata SariNo ratings yet
- DevelopmentofocclusionDocument33 pagesDevelopmentofocclusionDeepak NarayanNo ratings yet
- Intraoral Soft Tissue Anatomy: Morphology 115Document57 pagesIntraoral Soft Tissue Anatomy: Morphology 115Asrar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Maxillary 2nd MolarDocument11 pagesMaxillary 2nd MolarAli Al-Qudsi100% (1)
- All Dental AnatomyDocument114 pagesAll Dental AnatomyKhanh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- permanent incisorDocument2 pagespermanent incisorTemmuz AkyolNo ratings yet
- 8 Maxillary MolarsDocument20 pages8 Maxillary MolarsS:M:ENo ratings yet
- Anatomical Landmark: Dr. Simaa AbdulameerDocument9 pagesAnatomical Landmark: Dr. Simaa AbdulameerSimaa AlsalamyNo ratings yet
- 7 Upper 1st PremolarDocument28 pages7 Upper 1st Premolarmoh.ahm3040No ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document30 pagesPresentation 1ahmedrashed00No ratings yet
- Maxillary 2nd Premolar: Smaller Less Seldom SeenDocument16 pagesMaxillary 2nd Premolar: Smaller Less Seldom SeenAbdallah Essam Al-ZireeniNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy Final ReviewDocument11 pagesDental Anatomy Final Reviewvitro4No ratings yet
- Maxillary Permanent Central IncisorsDocument68 pagesMaxillary Permanent Central IncisorsAmit Singh100% (1)
- Permanent Maxillary Molars: Form and FunctionDocument35 pagesPermanent Maxillary Molars: Form and FunctionpadmineekrishnanNo ratings yet
- Headache History TakingDocument1 pageHeadache History TakingHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum ExamDocument2 pagesCerebellum ExamHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- General Medicine ScenarioDocument8 pagesGeneral Medicine ScenarioHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Year 1 OsceDocument1 pageYear 1 OsceHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine NotesDocument54 pagesInternal Medicine NotesHayley Welsh75% (4)
- Oral Medicine Exam Guide covering Ulcerations, Blisters, White Patches, Erythema, Swelling, Pigmentations, Pain & Salivary Gland conditionsDocument2 pagesOral Medicine Exam Guide covering Ulcerations, Blisters, White Patches, Erythema, Swelling, Pigmentations, Pain & Salivary Gland conditionsHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- You Are A Paediatric Registrar at GCUH and Judy, Has Brought Her Son Dylan, Age 3, To See You With Concerns of Delayed DevelopmentDocument2 pagesYou Are A Paediatric Registrar at GCUH and Judy, Has Brought Her Son Dylan, Age 3, To See You With Concerns of Delayed DevelopmentHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Basic Life SupportDocument2 pagesBasic Life SupportHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Ankle & Foot ExamDocument2 pagesAnkle & Foot ExamHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Scenario - Colicky PainDocument6 pagesPaediatric Scenario - Colicky PainHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- O&G StationDocument4 pagesO&G StationHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- General Medical ScenarioDocument5 pagesGeneral Medical ScenarioHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- PBL Case 3 - Felipe and GarciaDocument25 pagesPBL Case 3 - Felipe and GarciaHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- New Questions Oral Med in 2014Document3 pagesNew Questions Oral Med in 2014Hayley WelshNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument48 pagesPharmacologyHayley Welsh90% (10)
- Perio Notes CombinedDocument71 pagesPerio Notes CombinedHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Local Anaesthetic CourseDocument123 pagesLocal Anaesthetic CourseHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Questions PerioDocument9 pagesQuestions PerioHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Prepoll TimesDocument68 pagesPrepoll TimesHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- GAMSAT PRACTICE TEST: Complete 5.5-Hour Exam with Sections on Reasoning, Writing, ScienceDocument11 pagesGAMSAT PRACTICE TEST: Complete 5.5-Hour Exam with Sections on Reasoning, Writing, ScienceHayley Welsh100% (1)
- Geometric Outlines of Permanent TeethDocument1 pageGeometric Outlines of Permanent TeethHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- List of DentinDocument1 pageList of DentinHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- MFPM Surface Anatomy & MorphologyDocument5 pagesMFPM Surface Anatomy & MorphologyHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Maturational Changes in The Jaw and TeethDocument4 pagesMaturational Changes in The Jaw and TeethHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Permanent Lateral IncisorDocument4 pagesMandibular Permanent Lateral IncisorHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology Practice QuestionsDocument4 pagesCardiovascular Physiology Practice QuestionsHayley Welsh100% (1)
- Lab 2 SummaryDocument6 pagesLab 2 SummaryHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Late Bell Stage Tooth Development Epithelial Diaphragm RoleDocument3 pagesLate Bell Stage Tooth Development Epithelial Diaphragm RoleHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Direct Factors Affecting The PeriodontiumDocument4 pagesDirect Factors Affecting The PeriodontiumHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Neural Crest Cell: As The Groove Gets Deeper, Neural Crest. After The Neural Fold Meet andDocument4 pagesNeural Crest Cell: As The Groove Gets Deeper, Neural Crest. After The Neural Fold Meet andHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- What's The Line Between Middle Class, Upper Middle Class, and Upper Class in Britain - QuoraDocument11 pagesWhat's The Line Between Middle Class, Upper Middle Class, and Upper Class in Britain - QuoraFaizan ButtNo ratings yet
- ASBMR 14 Onsite Program Book FINALDocument362 pagesASBMR 14 Onsite Program Book FINALm419703No ratings yet
- Role of TaxationDocument5 pagesRole of TaxationCarlo Francis Palma100% (1)
- Benchmarking The Formation Damage of Drilling FluidsDocument11 pagesBenchmarking The Formation Damage of Drilling Fluidsmohamadi42No ratings yet
- Fractional GradingDocument7 pagesFractional Gradingapi-355619062No ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Introduction To TCPIP NetworkingDocument15 pagesChapter 1. Introduction To TCPIP NetworkingPoojitha NagarajaNo ratings yet
- Functional Appliances 2018Document45 pagesFunctional Appliances 2018tonhanrhmNo ratings yet
- Lung BiopsyDocument8 pagesLung BiopsySiya PatilNo ratings yet
- Vadiyanatha AstakamDocument4 pagesVadiyanatha AstakamRaga MalikaNo ratings yet
- ArenavirusDocument29 pagesArenavirusRamirez GiovarNo ratings yet
- Dreams and Destiny Adventure HookDocument5 pagesDreams and Destiny Adventure HookgravediggeresNo ratings yet
- Mr. Honey's Large Business DictionaryEnglish-German by Honig, WinfriedDocument538 pagesMr. Honey's Large Business DictionaryEnglish-German by Honig, WinfriedGutenberg.orgNo ratings yet
- Readingdev 7Document2 pagesReadingdev 7api-190328610No ratings yet
- Origin and Development of Law of Sea PDFDocument135 pagesOrigin and Development of Law of Sea PDFkimmiahujaNo ratings yet
- 1022-Article Text-2961-1-10-20200120Document10 pages1022-Article Text-2961-1-10-20200120Zuber RokhmanNo ratings yet
- Richard CuretonDocument24 pagesRichard CuretonHayk HambardzumyanNo ratings yet
- 7 Years - Lukas Graham SBJDocument2 pages7 Years - Lukas Graham SBJScowshNo ratings yet
- Why Narcissists Need You To Feel Bad About Yourself - Psychology TodayDocument51 pagesWhy Narcissists Need You To Feel Bad About Yourself - Psychology Todaytigerlo75No ratings yet
- Femap-58 Volume2 508Document357 pagesFemap-58 Volume2 508vicvic ortegaNo ratings yet
- The BrigadeDocument517 pagesThe Brigadele_chiffre4860100% (3)
- Comprehension Used ToDocument2 pagesComprehension Used TomarialecortezNo ratings yet
- Communicative Strategy Powerpoint CO With VideoDocument20 pagesCommunicative Strategy Powerpoint CO With VideoGlydel Octaviano-GapoNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Transformer Model For TransientsDocument10 pagesThree Phase Transformer Model For TransientsYeissonSanabriaNo ratings yet
- Pragmatic Marketing FrameworkDocument2 pagesPragmatic Marketing FrameworkohgenryNo ratings yet
- Materi 2 Academic WritingDocument7 pagesMateri 2 Academic Writingna03friezaNo ratings yet
- The Army Crew Team Case AnalysisDocument3 pagesThe Army Crew Team Case Analysisarshdeep199075% (4)
- Discuss in Details With Appropriate Examples What Factors Could Lead To Sympatric and Allopatric SpeciationDocument5 pagesDiscuss in Details With Appropriate Examples What Factors Could Lead To Sympatric and Allopatric SpeciationKhairul ShahmiNo ratings yet
- The Republic of LOMAR Sovereignty and International LawDocument13 pagesThe Republic of LOMAR Sovereignty and International LawRoyalHouseofRA UruguayNo ratings yet
- Progress Test 5 (Units 13-15) : Complete All Seven Sections. There Are Seventy Marks in TotalDocument7 pagesProgress Test 5 (Units 13-15) : Complete All Seven Sections. There Are Seventy Marks in TotalIlia GviniashviliNo ratings yet
- Scientech 2502ADocument2 pagesScientech 2502Aashutosh kumarNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- The Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossFrom EverandThe Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)